Cosmology
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What is the doppler effect?
The apparent change in the frequency and wavelength of waves received from an object moving relative to an observer compared to what would be observed without relative motion
What is pitch?
The frequency of sound waves
Explain red shift
If the galaxy is moving away from the Earth ('receding') the absorption lines will be red-shifted - they all move towards the red end of the spectrum, because the wavelength appears stretched.
Explain blue shift
If the galaxy is moving towards the Earth the absorption lines will be blue-shifted - they move towards the blue end of the spectrum, because the wavelength appears shorter.
State the Doppler equation and the meaning of each symbol and their units
λ is the source wavelength (measured in a lab on earth) and Δλ is the change in wavelength recorded by the observer. Units of both are m (metres)
f is the source frequency (measured in lab on earth) and Δf is the change in frequency recorded by the observer. Unit of both is Hz (Hertz)
v is the magnitude of the relative velocity between the source and observer, and c is the speed of light through a vacuum (3.00 x 108 ms-1). Unit of both is ms-1 (metres per second)
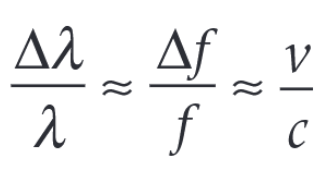
The Doppler equation can only be used in which situations?
The Doppler equation can only be used for objects with speeds far less than the speed of light.
What is the Astronomical Unit (definition, symbol, conversion, when the unit is used)?
The mean distance from the Earth to the Sun
Symbol AU
1 au = 150 million km = 1.50 x 1011m
Most often used to express the average distance between the Sun and other planets in the Solar System.
What is the light year (definition, symbol, conversion, when the unit is used)?
The light-year is the distance travelled by light in a vacuum in a time of one year.
Symbol ly
1 ly = 9.46×1015m
The light-year is often used when expressing distances to stars or other galaxies.
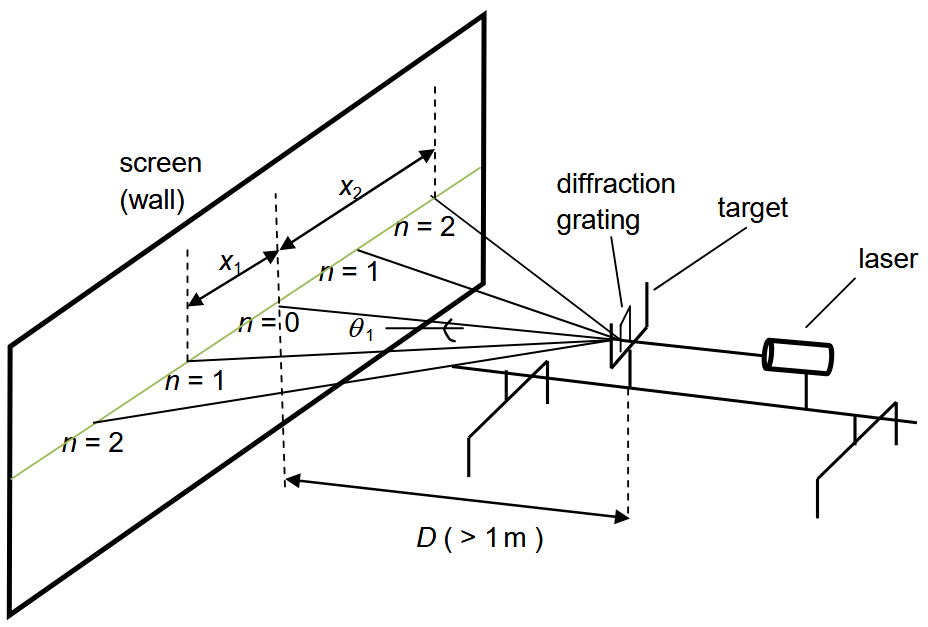
Describe a practical to determine the wavelength of light with a diffraction grating (diagram with labelled equipment, method, analysis, uncertainties, safety)
Method:
Record the number of lines per mm on your diffraction grating.
Set up the apparatus as shown in the diagram so that you can see two bright spots on either side of the central bright spot.
Measure the distance D from the grating to the screen using a metre rule
Measure the distance x1 from the central bright spot to the first bright spot on the left, n = 1, using a metre rule
Measure the distance x2 from the central bright spot to the second bright spot on the left, n = 2, using a metre rule
Analysis:
number of lines per m = number of lines per mm × 10-3
Calculate slit seperation using d = 1 / number of lines per m
Angle θn = arctan( xn / D ). Use this equation to calculate θ1 and θ2 from the recorded data
nλ = d × sin θ. Rearranging this gives λ = ( d × sin θ ) / n. Use this to calculate the values of wavelength for θ1 and θ2
Uncertainties:
The percentage uncertainty of λ can be reduced by increasing D and/or by measuring the distance between the central bright spot and a higher order bright spot
Safety:
Never look directly into the laser
Switch lasers off when not in use
Ensure the screen is a matt surface with no potential for reflection
Describe how the recession speed v of a distant galaxy can be determined using a diffraction grating to analyse the light from the galaxy
Pass light from receding galaxy through a diffraction grating. Determine wavelength of one of the spectral lines from the first order maximum using λ = d sin θ
Determine the wavelength of an identical line in a laboratory on earth, λ
∆λ = wavelegth of spectral line of light from galaxy - wavelength of idedentical spectral line on earth
∆λ / λ = v / c so recessional speed v = c ∆λ / λ
Explain the name ‘Annual parallax method’
Is called ‘annual’ as measurements are taken at 2 times over a year.
Is called ‘parallax’ as nearby stars appear at different positions depending on where you view them from
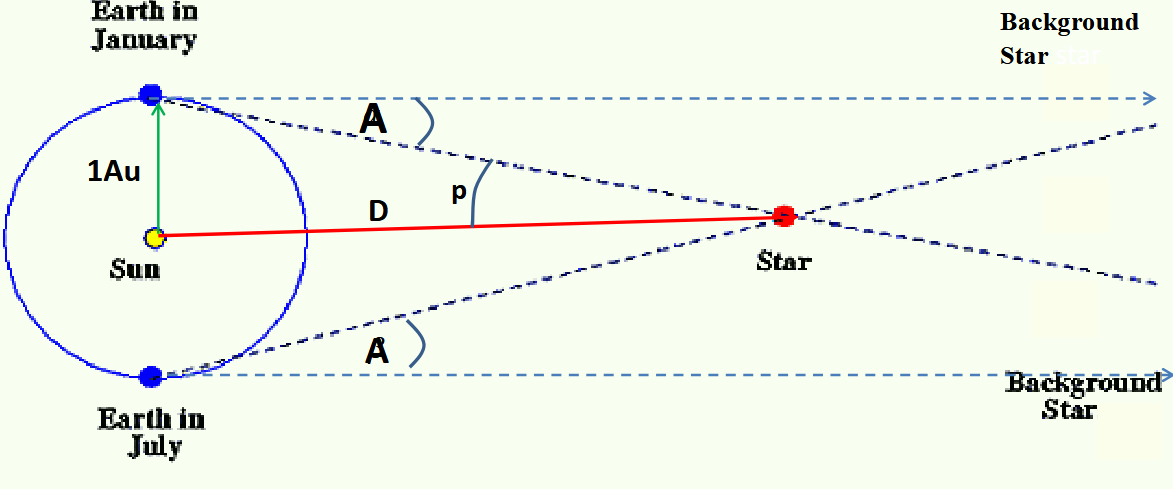
Explain the annual parallax method
The distance to nearby stars can be found using the annual parallax method
To do this angular displacements ‘A’ between a star and a distant star are measured, when the Earth is at opposite extremities of its orbit around the sun (eg. January and July)
The parallax angle ‘p’ is the average of A.
The angles are small so often stated in arc seconds. 1 arc sec = 1/3600 degrees
Distance D in m = 1.5 x 10¹¹ / tan(p°)
to be finished
What is the relationship between the degree, arcminute and arcsecond?
There are 60 arcminutes in 1°, and 60 arcseconds in each arcminute.
Define the arcminute
(1/60)°, a minute of arc
Define the arcsecond
(1/3600)° = 1/60 arcminutes, a second of arc
Define the parsec and draw a diagram to aid this definition
Distance at which 1AU subtends an angle of 1/3600th degree (=1 parsec)
1 pc = 1 AU / tan(1/3600°) ≈ 3.1 × 10¹⁶ m
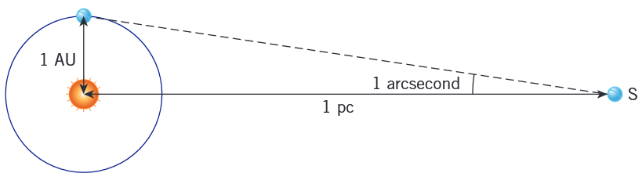
What is the parallax equation and the meaning and unit of each term?
p = 1/d
p is the parallax angle in arcsec
d is the distance to a nearby star (< 100 pc away) in parsec (pc)
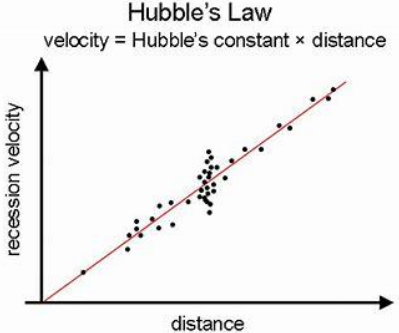
State Hubble’s Law
The recessional speed v of a galaxy is almost directly proportional to its distance d from the Earth
What is the equation relating the recessional speed of distant galaxies to their distance from us, and the meaning and unit of each term?
v = H0d
v is the recessional speed
H0 is the hubble constant
d is the ditant of the galaxy from us
What is the Cosmological Principle?
The assumption that, when viewed on a large enough scale, the Universe is homogeneous and isotropic, and the laws of physics are universal
What is meant by homogeneous (in the context of cosmology)?
Matter is distributed uniformly across the universe. Same type of structures are seen everywhere.
What is meant by isotropic?
The universe looks the same in all directions to every observer (no centre or edges)
What is meant by ‘the laws of physics is universal’?
The laws of Physics on Earth apply throughout the universe
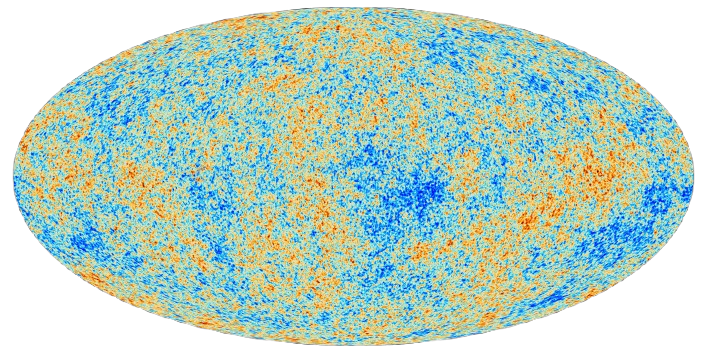
What is cosmic background radiation (CMBR)?
The microwave signal of uniform intensity detected from all directions of the sky, which fits the profile for a black body at a temperature of 2.7K
Which objects did Edwin Hubble take pictures of? What measurements did he take?
He photographed nebuli, and measure the variation in birghtness of the stars within them.
List Hubble’s findings
The distance to the Andromeda galaxy was ∼2 million ly, much farther than anyone expected. This showed the universe was much larger than we had innitialy thought.
Showed the universe was expanding
What does Hubble’s Law indicate about the size of the universe?
The universe is expanding
What does Hubble’s Law indicate about origin of the universe?
It suggests that all matter originated from a single point in the past, commonly referred to as the Big Bang
If everything is moving away from us are we the centre of the universe?
No, as there is no centre from which everything expands.
Describe the big bang
A moment in the past when all the matter in the Universe was contained in a singularity (a single point), the beginning of space and time, that expanded rapidly outwards
What experimental evidence supports the Big Bang?
Hubble's law shows that the Universe is expanding. It follows that, if we could run time backwards, the Universe would be much smaller, denser, and hotter, and would eventually reach a single point.
Physicist have detected a uniform microwave signal they could not account for. They had accidentally discovered the microwave background radiation that could only be explained by the Big Bang and the expansion of space.
Where does the uncertainty in the Hubble Constant arise from?
There is a large uncertainty in the value of H0 due to:
the large uncertainty in measuring the distance to the galaxies
some uncertainty in measuring the change in wavelength.
How can we use the Hubble constant to find the age of the universe?
At the beginning of the universe all matter is thought to have been concentrated in a single point.
A galaxy presently at distance D from us, would have taken time t = D/v to get to where it is today, assuming a constant rate of expansion
As v = H0/D, time 𝑡 = D / v = D / H0D = 1/ H0
As time t is the age of the universe, Age of universe = 1 / H0
How can we use the Hubble constant to estimate the Radius of the observable universe?
When we view a galaxy, we are seeing it in the past, as the light has taken a certain amount of time to reach us.
The further away a galaxy the more time it takes the light to reach us and the younger it will appear. So, the very furthest galaxies appear as the earliest galaxies.
Light from the most distant galaxies we can see, have taken a time equal to the age of the universe to travel to us; this is about 13 billion years (the first galaxies are thought to have formed about 200 million years after the big bang, so this is negligible compared to the age of the universe and does not need to be subtracted from the time).
Radius of observable universe = Distance earliest light has travelled = speed x time = speed of light x age of universe = c × 1 / H0 = c / H0
What is the Big Bang model?
It suggests that all matter in the universe was once concentrated at a single point (singularity). Basic principles:
Universe was initially exceedingly very small, very dense and very hot and expanded violently.
Since then, it has been continually expanding and cooling
How does Hubble’s Law support the big bang model?
The further away a galaxy, the greater its recessional speed.
Universe must be expanding and the galaxies spreading out with time.
Running back time implies the universe was closer together in the past.
At the beginning of time, all matter and energy would have been concentrated into one point (singularity). (So, the beginning of time is also the beginning of space)
What evidence, other than Hubble’s Law, is there to support the Big Bang Model?
Experimental Evidence:
Detection of a uniform Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation CMBR with blackbody temp. of 2.7K everywhere.
Explanation:
This is Predicted by the Big Bang Model
Early universe was saturated with high energy gamma photons of very short wavelength.
As the universe expanded, they would have stretched to a much longer wavelength, as the space-time continuum expanded. This is called Galactic Red Shift.
Reaching microwave wavelengths today with a blackbody temperature of 2.7K
Experimental Evidence:
Primordial Hydrogen and Helium account for nearly all the nuclear matter in the universe today. About 74% hydrogen and 24% helium.
Explanation:
The ratio of Hydrogen to Helium is consistent with the Big Bang Model
The temperature post Big Bang was only suitable for fusion to form helium for a short period, before being too cool
What is luminosity?
The total radiant power (of a star)