Topic 4 - Earth's Atmosphere - Composition and Structure
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Atmosphere?
The envelope of gases that surrounds Earth
Meteorology?
Studies the atmosphere and everything in it
Weather?
Short term conditions of the atmosphere
Climate?
The long term conditions of the atmosphere
What is the atmosphere’s purpose?
the atmosphere insulates earth from extreme temperatures, provides oxygen for lifeforms, protects earth from sun’s radiation
What are the three criteria for studying the atmosphere?
function, composition, structure
What defines earth’s atmosphere?
a mixture of gases and water in three phases - liquid, solid, gas
What are permanent gases?
these gases have not changed since the atmosphere that we breathe formed
What is the composition of the atmosphere?
nitrogen, oxygen, argon and carbon dioxide
Which variable gases are important for our health and well being ?
water vapor, carbon dioxide, ozone and methane
Why is water vapor important ?
its the source of precipitation and its a good source of greenhouse gas
What does water vapor do ?
it traps heat energy in the atmosphere and keeps Earth’s air warm
How is carbon dioxide added to the atmosphere by natural causes?
forest fires, exhalation, volcanoes
How is carbon dioxide added to the atmosphere human caused?
mining, factories, burning of fossil fuels
How is carbon dioxide removed in only two natural ways?
photosynthesis and from the oceans absorbing carbon dioxide
What is photosynthesis?
plants absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen
Why is carbon dioxide a problem?
traps outgoing thermal heat and blocks incoming thermal energy
What happens when there is too much carbon dioxide in the ocean?
can harm coral, seashells, fish scales and more
Why is ozone’s presence in the upper atmosphere essential to life on Earth?
It absorbs some solar radiation/uv radiation
Ozone is made up of ?
three Oxygen atoms bonded to form 1 molecule
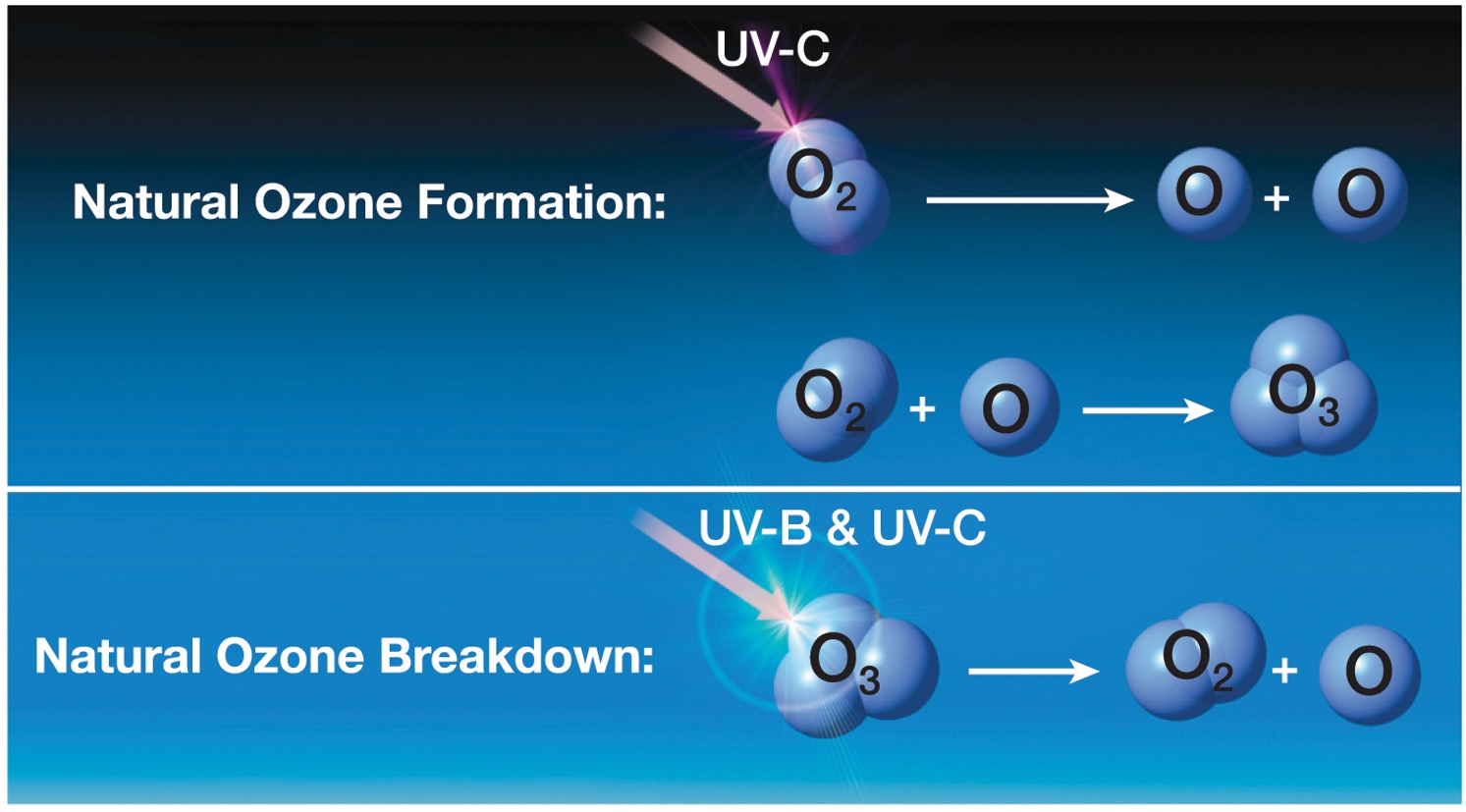
Why is ozone dangerous on earths surface?
ozone has chemical and its irritant to lungs, eyes, nose
Where does methane come from?
comes from digestive gases - produced from decomposition of organic material
Why is methane more harmful?
it stays in the atmosphere for 10 years and is more harmful than CO2
What are aerosols?
tiny droplets or particles suspended in the air
What are some natural sources of aerosols?
salt spray, dust, fine sand, water
protons have what type of charge?
positive charge (+1)
neutrons have what type of charge?
neutral charge (0)
electrons have what type of charge?
negative charge (-1)
What is air pressure?
the weight of all of the air molecules pushing down on earths surface
As you rise in altitude or elevation …
air pressure decreases because there are fewer air molecules
What is altitude?
how high in the air (ex: plane, hot air balloon)
What is elevation?
feet are in the ground (ex: mountain)
How many layers are on earth’s atmosphere?
5 layers
What are the 5 layers in order from bottom to top?
troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, exosphere
What is the ozonosphere ?
its the ozone layer
Where is the Exosphere located and what is the temperature like?
last layer and the temperature is really cold
Where is the thermosphere located and what is the temperature like?
4th layer and temperature increases with altitude
Where is the mesosphere located and what is the temperature like?
middle layer, meteors burn in this layer and the temperature decreases with altitude
Where is the stratosphere located and what is the temperature like?
2nd layer, heating is caused by the ozone absorbing the uv radiation
In which layer of earth’s atmosphere is the ozone layer located?
stratosphere
Where is the troposphere located and what is the temperature like?
first layer, all of our weather occurs in this layer and the temperature decreases with altitude
What is the ionosphere?
it extends from the upper mesosphere into the thermosphere, it contains abundant positively charged ions and free electrons
what are the aurora borealis and aurora australis?
aka northern lights or southern lights
How do the aurora borealis form?
plasma from the sun gets caught in earths magnetic field, the gases of the air become energized and as the energy lessens the gases glow which causes the auroras
What is air pollution?
Anything that makes the air bad smelling, difficult to breathe and potentially unhealthy
What are some examples of natural pollution sources?
sulfur springs, decomposing vegetation, volcanic eruptions, aerosols etc
Why is Mt Pinatubo well known?
tons of ash into the air caused the air temperature to decrease a small amount
How does air pollution move about?
wind
What is anthropogenic pollution?
pollution caused by human activity
What are primary pollutants?
pollutants released directly into the air
What are secondary pollutants?
form when primary pollutants react with other chemicals in the atmosphere to form pollutants
What is photochemical smog ?
A type of air pollution that occurs when sunlight reacts with pollutants from auto exhaust creating a brown haze
What are the consequences of anthropogenic pollutants?
lung disease, acid rain, forest damage etc
What is the Clean Air Act?
It was enacted in 1970 and it limited the use of and emission of materials that cause air pollution
What were CFC’s doing to the ozone layer?
the CFS’s were eating the ozone layer, it was deteriorating
What is the Montreal Protocol?
in 1987 a major international treaty was set in motion to discontinue the use of CFC’s
In what year did the industrialized countries ban the use of CFC’s?
1996