Empirical Communication Research (4)
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
COMM111
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Why do we use empirical approaches?
We live in a deeply mediatised world — the media we use, and platforms we connect with other on have real world consequences (Couldry & Hepp, 2017)
Journalists often take empirical approaches to understand what's going on with the world (like stats, percentages)
Charities, governments etc. Base their research on social sciences
Science
A systematic and organised body of knowledge in any area of inquiry that is acquired using “the scientific method”
Natural Science
The science of naturally occurring objects of phenomena
physics, astronomy, geology, biology
Social Science:
The science of people, of collections of people such as:
Groups, firms, societies, or economies, and their individual or collective behaviours
ex: sociology, history, economics, linguistics, political science
Scientific Knowledge
A generalised body of laws and theories which explain a phenomenon or behaviour of interest that are acquired using the scientific method
We arrive at the scientific laws or theories through a process of logic (theory) and evidence (observation)
Laws - Scientific Knowledge
The observed patterns of phenomenon or behaviours
ex: thermodynamics / law of supply and demand
Theories - Scientific Knowledge
Systemic explanation of the underlying phenomenon or behaviour
ex. quantum mechanics / theory of cognitive dissonance
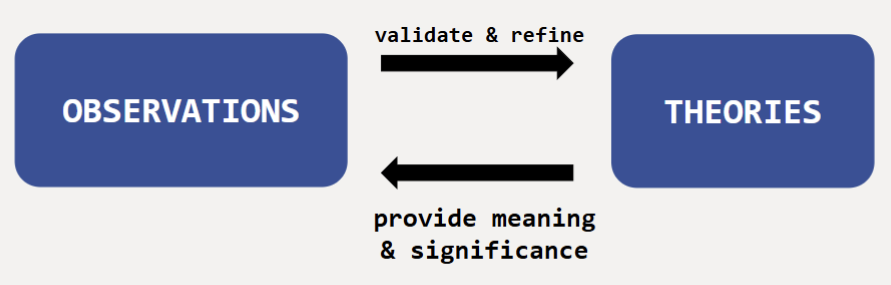
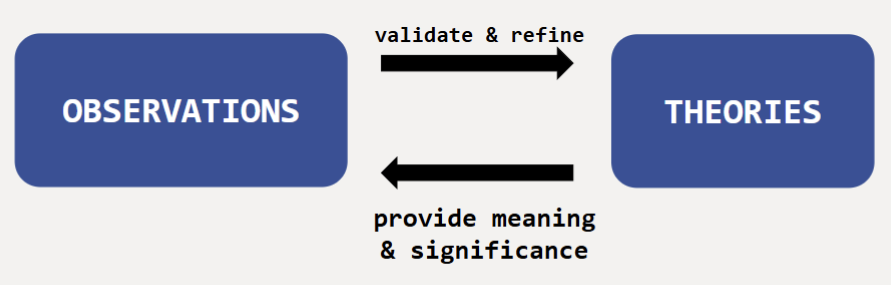
Observations and Theories
They have a cyclical relationship. Observations validate and refine theories. Theories provide meaning and significance to observation
Theories - Scientifical Research
Developing abstract concepts about a natural or social phenomenon and relationships between those concepts (ex. building theories)
Empirical - Scientific Research
Testing the theoretical concepts and relationships to see how well they reflect our observations of reality, with the goal of ultimately building better theory(s)
Inductive Research
The goal is to infer theoretical concepts and patterns from observed data (theory building)
Begin with a research question and the collection of empirical data, which are used to generate hypothesis and theory
Qualitative approach, interviews
Deductive Research
Goal is to test concepts and patterns known from theory using empirical data (theory testing)
Approaches usually begin with a theory-driven hypothesis, which guide data collection and analysis
Types of Scientific Research
Exploratory
Descriptive
Explanatory
Exploratory Scientific Research
To scope magnitude and extent of phenomenon, generate initial ideas, test feasibility of more extensive study
Descriptive Scientific Research
Examines the what, where, and when of a phenomenon
Explanatory Scientific Research
Tries to identify causal factors and outcomes of the target phenomenon
Scientific Method
A standardized set of techniques for building scientific knowledge, such as how to make valid observations, how to interpret results, and how to generalise those results
Must satisfy 4 key characteristics
Logical
Scientific inferences must be based on logical principles of reasoning
Confirmable
Inferences derived must match with observed evidence
Repeatable
Other scientists should be able to independently replicate, or repeat a scientific study and obtain similar, if not identical, results
Scrutinizable
The procedures used and the inferences derived must withstand critical scrutiny (peer review) by other scientists
Qualitative Research
Analysis of smaller number of cases
For richer data sets
Emphasis on “sense-making” or understanding a phenomenon in depth
Usually inductive ie. categories are generated from a “close reading” of raw data
Quantitative Research
Analysis of larger number of cases and observations
Statistics driven
Usually deductive (ie. Categories are pre-defined and looked for (and quantified) in raw data
Units of Analysis
The person, collective, or object that is the target of the investigation
Individuals – political attitudes of voters
Groups – comparing media literacy across age groups
Organizations – campaign communication strategies of political parties
Countries – comparing journalism cultures between the UK and China
Technologies – communicative affordances of Facebook vs. Whatsapp
Objects – layout and functionality of an online interface
Shapes what type of data you should collect for your study and who/what you collect it from
Mental Abstractions
Concepts
Generalizable properties or characteristics associated with objects, events, or people
Representation, ideology, audience, censorship
Construct
An abstract concept that is specifically chosen (or theoretically “created”) to explain a given phenomenon
Media frames, self-efficacy, uncertainty, cognitive dissonance
Variable
A measurable representation of an abstract construct
Operational Definition of Framing
“To frame is to select some aspects of a perceived reality and make them more salient in a communicating text, in such a way as to promote a particular problem definition, causal interpretation, moral evaluation, and/or treatment recommendation” (Entman, 1993, p.52)
Framing
Defined as a four-dimensional construct → we need to measure four variables to capture the construct
Types of variables
Independent variable
Moderating variable
Mediating variable
Dependent variable
Independent variable
The ones which a researcher can manipulate or control to see it’s effects on the dependent variable
Moderating variable
Variable that affects the strength and relationship
Mediating variable
Those that come between the independent and dependent variable by identifying the mechanisms
Dependent variable
The outcome responses that researchers are interested in
Proposition
A tentative and conjectural relationship between constructs that is stated in a declarative form ((e.g., “negative portrayals of
immigrants lead to more negative attitudes towards them”)
Hypothesis
An empirical formulation of propositions, stated as relationships between variables (e.g. “Exposure to stereotypical right-ring populist political posters activates negative stereotypes toward immigrants”
Theory
A set of systemically interrelated constructs and propositions intended to explain and predict a phenomenon or behaviour of interest, within certain boundary conditions and assumptions
e.g., Media Agenda-Setting Theory
The press and the media do not reflect reality; they filter and shape it;
Media concentration on a few issues and subjects leads the public to perceive those issues as more important than other issues;
Through the cognitive process “accessibility” i.e., the more frequently and prominently the news media cover an issue, the more instances of that issue become accessible in audience’s memories. When respondents are asked what the most important problem facing the country is, they answer with the most accessible news issue in memory, which is typically the issue the news media focused on the most