biochem final (multiple choice)
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
weak forces create constantly forming and breaking interactions at physiological temperatures, but cumulatively impart stability to biological structures generated by their collective activity include all except
a. hydrogen bonds
b. van der Waals forces
c. covalent bonds
d. ionic interactions
e. hydrophobic interactions
covalent bonds
which of the following fibrous proteins is composed exclusively of a-helices (alpha-helices)?
a. collagen
b. fibroin
c. a-keratin (alpha-keratin)
d. B-keratin (beta-keratin)
e. hemoglobin
a-keratin (alpha-keratin)
a two-domain protein composed of a single polypeptide (a/alpha) may have formed (during evolution) by _____, but a large protein composed of seven identical subunits (a7) may be an example of _____.
a. post-translational modification, cooperativity
b. gene fusion, genetic economy
c. stabilization, collective motion
gene fusion, genetic economy
in micelles,
a. polar ends form hydrophobic interactions with water
b. nonpolar ends form hydrophilic interactions with water
c. hydrocarbon tails form hydrophobic interactions with water
d. polar ends are hydrophobic and nonpolar ends are hydrophilic
e. hydrocarbon tails are excluded from the water into hydrophobic domains
hydrocarbon tails are excluded from the water into hydrophobic domains
in order to _____ the osmotic pressure created by the contents of the cytosol, cells tend to store substances such as amino acids and sugars in ____ form.
a. increase, monomeric
b. minimize, polymeric
c. minimize, monomeric
d. maximize, polymeric
e. increase, polymeric
minimize, polymeric
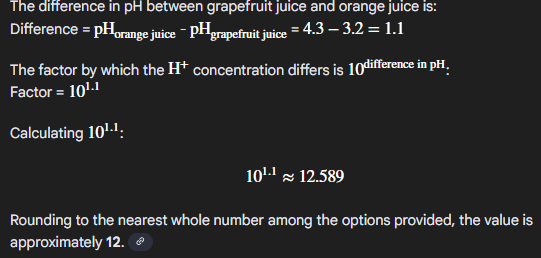
grapefruit juice at pH 3.2 contains about ___ times as much H+ as orange juice at pH 4.3
a. 0.9
b. 10-7.5
c. 12
e 101
12
in a four-helix-bundle protein, the amino acid residues on the interior faces of the a-helices (alpha-helices) are typically
a. arranged to form salt bridges
b. negatively charged
c. hydrophobic
d. positively charged
hydrophobic
Enthalpy change is
a. the sum of heat absorbed and work
b. not a thermodynamic state function
c. a measure of disorder in a system
d. equal to the heat transferred at constant pressure
e. determined by pressure change at a constant temperature
equal to the heat transferred at constant pressure
“high-energy” compounds that exhibit a large negative free energy of hydrolysis (delta G knot prime < -25 kJ/mol) include all except
a. phosphate esters
b. enol phosphates
c. phosphate anhydrides
d. acyl phosphates
e. guanidino phosphates
f. thioesters
phosphate esters
when ATP hydrolysis (to ADP + Pi, (ΔG°’= -35.7 kJ/mol) is coupled to an unfavorable reaction, the equilibrium position of that reaction is shifted by a factor of
a. 10
b. 100
c. 104
d. 106
e. 108
106

which of the following amino acids has more than one chiral carbon?
a. serine
b. lysine
c. threonine
d. cysteine
e. aspartic acid
threonine
glutamic acid has pKa’s of 2.2, 4.3, and 9.7. what is the isoelectric point of glutamic acid?
a. 3.25
b. 4.3
c. 5.4
d. 7.0
e. 8.65
3.25
which of these peptides would absorb light at 280nm?
a. ala-lys-his
b. ser-gly-asn
c. ala-ala-trp
d. val-pro-leu
ala-ala-trp
glyphosate (the old “Roundup”) is ____ and an effective herbicide at a level of ____ per acre, but imazapyr and imazapic (“Arsenal” and “Chopper”) are ____ and effective at a level of ___ per acre.
a. persistent, pounds, biodegradable, grams
b. biodegradable, pounds, persistent, grams
c. persistent, grams, biodegradable, pounds
d. biodegradable, grams, persistent, pounds
biodegradable, pounds, persistent, grams
a common reaction of two cysteine residues in protein results in the formation of ____.
a. thioester bonds
b. disulfide bonds
c. dithiol bonds
d. thioester bonds
e. none of the above
disulfide bonds
protein isolation and purification techniques include all the following methods except
a. gas-liquid chromatography
b. affinity chromatography
c. electrophoresis
d. solubility (“salting in” and “salting out”)
e. ion exchange chromatography
gas-liquid chromatography
α-Helices and β-sheets are components of ____ structures.
a. primary
b. secondary
c. tertiary
d. quaternary
e. all are true
secondary
reaction of peptide, ala-met-ser, which phenylisothiocyanate at pH 8.0 followed by mild acidification (the first cycle of the Edman method) would release (“PTH” stands for phenylthiohydantoin)
a. the labeled peptide ala-met-lys-ser-PTH
b. PTH-ser and the peptide ala-met-lys
c. PTH-ala, PTH-ser, PTH-lys and PTH-met
d. PTH-ala and the peptide met-lys-ser
PTH-ala and the peptide met-lys-ser
the C-terminal residue of a polypeptide can be found by first cleaving the polypeptide with
a. chymotrypsin
b. carboxypeptidase
c. trypsin
d. CNBr
e. none of the above
carboxypeptidase
all of the information necessary for folding the peptide chain into its “native” structure is contained in the _____ of the peptide.
a. amino acid sequence
b. amino acid composition
c. configuration
d. amino acid side chain charges
e. post-translational modifications
amino acid sequence
which are the four most common elements in the human body?
a. H, Ca, O, Na
b. H, O, Fe, C
c. H, O, C, N
d. O, C, Fe, N
H, O, C, N
by limiting the orientation that neighboring water molecules can assume, solutes give _____ to the solvent and _____ the dynamic interplay among H2O molecules that occurs in pure water.
a. pressure, disrupt
b. disorder, increase
c. disorder, decrease
d. order, diminish
e. order, increase
order, diminish
the “Good” buffers have all the following characteristics except:
a. they are relatively expensive
b. they are strong nucleophiles
c. they show small changes of pKa with temperature
d. they contain nitrogen heterocycles and sulfonic acid groups
they are relatively expensive
an interaction between two subunits of a protein was determined to have a delta G degree’ = -57.05 kJ/mol. what is the Keq for the reaction at 25 degrees C?
a. 1.02
b. 1.32
c. 10-10
d. 1010
1010
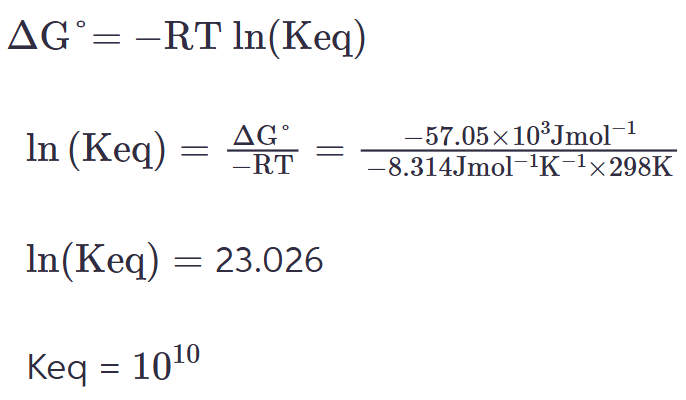
an “antiparallel hairpin” is composed of
a. an alpha-helix, a beta-turn, and a second alpha- helix
b. a strand of beta-sheet, a beta-turn, and a second strand of beta-sheet
c. a strand of beta-sheet, an alpha-helix, and a second strand of beta-sheet
d. an alpha-helix, a strand of random coil, and a second alpha-helix
a strand of beta-sheet, a beta-turn, and a second strand of beta-sheet
all the statements about the classification of these amino acids are correct except:
a. aspartic and asparagine are acidic
b. alanine and valine are neutral, nonpolar
c. serine and glutamine are polar, uncharged
d. lysine and arginine are basic
e. tyrosine and phenylalanine are aromatic
aspartic and asparagine are acidic amino acids
which equation defines a system at equilibrium?
a. ΔG > 0
b. ΔG° = delta G
c ΔG = 0
d. ΔG° = 0
e. ΔG = RT ln ([products]/[reactants])
ΔG = 0
rank the following compounds in the order of increasing (i.e., more negative) free energy of hydrolysis
A: acetyle phosphate
B: 1,3-diphosphoglycerate
C: pyrophosphate
D: AMP
a. A, B, C, D
b. D, C, B, A
c. B, C, A, D
d. C, D, B, A
e. D, C, A, B
D, C, B, A (-14.2, -19.2, -43.1, -49.4 kJ/mol)
using a cation exchange resin (such as Dowex-50), a mixture of four amino acids is separated using an eluting gradient of increasing NaCl concentration. what would be the likely elution sequence?
a. asp, arg, ser, lys
b. arg, asp, lys, ser
c. lys, arg, asp, ser
d. asp, ser, lys, arg
e. ser, asp, lys, arg
asp, ser, lys, arg
which of the following is NOT a common post-translational modification of a protein?
a. prenylation
b. arylation
c. phosphorylation
d. methylation
e. ADP-ribosylation
arylation
quaternary structures may be used to
a. increase protein stability
b. provide genetic economy
c. bring catalytic sites together
d. provide a, b, and c
provide a, b, and c
ninhydrin has all these properties except
a. it can be used to detect amino acids following chromatography
b. it produces a purple-colored product reaction with alanine
c. it provides a yellow product upon reaction with histidine
d. it can be used to quantify most amino acids
it provides a yellow product upon reaction with histidine
which of the following sugar alcohols yield a cold, sweet tase and is used in many candy bars?
xylitol
glycerol
ribitol
ethylene
xylitol
gram-positive bacteria possess which of the following?
lipopolysaccharide layer
inner and outer membranes
peptidoglycan
all the above
peptidoglycan
the most abundant lipid in red blood cell membranes is
phosphatidylcholine
cholesterol
phosphatidylinositol
phosphatidylserine
cholesterol
A-DNA and A-RNA double helices are ___-handed, B-DNA double helices are ___-handed, and Z-DNA double helices are ___- handed.
right, right, left
which of the following properties of sucrose is responsible for the fact that it does not undergo mutarotation when dissolved in water?
sucrose is composed entirely of D-sugars
sucrose is more than 10 carbons
sucrose is not a reducing sugar
sucrose has both furanose and pyranose substructures
sucrose is not a reducing sugar
which of the following class of enzymes does not require ATP?
flippases
floppases
type II restriction endonucleases
type II restriction endonucleases
which of the following polysaccharides is not synthesized by any mammal?
glycogen
chitin
heparin
chondroitin sulfate
chitin
to judge from the illustrations in your textbook (and in class), the outer branches of the oligosaccharides of glycoproteins are particularly rich in
ribose
mannose
galactose
arabinose
mannose
which of the following proteins does not catalyze active transport?
bacteriorhodopsin
KcsA
gastric H+,K+ ATPase
KcsA
the reason that the blood of humans is a saturated solution of uric acid, which may crystallize in the extremities to cause gout, is thought to be:
humans lack the enzyme urate oxidase
uric acid is an excellent antioxidant and may help to prevent cancer
gout usually occurs late in life, and thus has little effect on procreation
all three reasons are true
all three reasons are true
which class of lipids would be found on the skin of an apple or the feathers of a duck?
glycerophospholipids
triacylglycerols
sphingolipids
waxes
terpenes
steroids
waxes
which class of lipids is the main target for hydrolysis by enzymes in rattlesnake venom?
glycerophospholipids
triacylglycerols
sphingolipids
waxes
terpenes
steroids
glycerophospholipids
which of the following polynucleotides does not (usually) have a well-defined secondary or tertiary structure?
mRNA
rRNA
tRNA
DNA
mRNA
the thickness of a typical phospholipid membrane bilayer is:
4 Å
15 Å
26 Å
37 Å
48 Å
37Å
a bacterial protein toxin that creates an open channel in the victim’s cell membrane is using what form of membrane transport to kill the cell?
passive diffusion
facilitated diffusion
active transport
facilitated diffusion
assuming a random distribution of the four DNA bases, a restriction endonuclease that recognizes a 6-base sequence will encounter that sequence once in every how many bases?
128
2401
4096
16,384
65,536
4096
the most important factor governing the high selectivity of the KcsA protein’s potassium channel is:
the pH-gating of the channel
the construction of the channel from 12 alpha-helices
the presence of four K+ binding sites
the channel’s mimic of normal K+ hydration
the hydrolysis of ATP to drive K+ transport
the channel’s mimic of normal K+ hydration
the “Central Dogma of Molecular Biology” (as well more tangible evidence) suggests that which type of molecule held the central role in primordial life?
DNA
RNA
protein
polysaccharide
complex lipid
RNA
β-D-Galactose and β-D-mannose are
enantiomers
diastereomers
anomers
epimers
all the above
diastereomers
the presence of thymine, rather than uracil, as a base in DNA is thought to facilitate what process?
detection of errors caused by chemical degradation of DNA
more rapid uncoiling of DNA for replication
removal of the 2’-hydroxy group in ribonucleotides during DNA synthesis
steric inhibition of incorrect base pairing
detection of errors caused by chemical degradation of DNA
which of the following sugars is an aldopentose?
ribitol
ribulose
xylose
xylulose
mannose
ribose
xylose, ribose
if carbon 1 is the carbonyl group of galactose, which carbon determines if the sugar is a D- or L-stereoisomer?
C-1
C-2
C-3
C-4
C-5
C-6
C-5
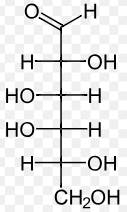
all of the statements about the following pairs of sugars are correct EXCEPT:
galactose and mannose are epimers
L-galactose and D-galactose are enantiomers
glucose and mannose are epimers
glucose has fewer chiral centers than sucrose and fructose
Galactose and mannose are diastereomers.
Glyceraldehyde and dihydroxyacetone are stereoisomers
glucose and galactose are epimers
glucose has fewer chiral centers than sucrose and fructose
which of the following disaccharides contains an α(1—>4) glycosidic bond?
sucrose
lactose
maltose
cellobiose
cellulose
maltose
glucaric acid is formed by oxidation of which carbon of glucuronic acid?
C-1
C-2
C-5
C-6
both C-1 and C-6
both C-1 and C-6
in the Gram stain procedure, a brief treatment with ethanol or acetone washes away the outer membrane of Gram ___ bacteria, exposing their ___ layer of peptidoglycan (as compared to Gram ___ bacteria), from which the crystal violet is easily extracted.
negative; thicker; positive
positive; thicker; negative
negative; thinner; positive
positive; thinner; negative
negative; thinner; positive
cellulose is extremely resistant to hydrolysis, but cellulase catalyzes the hydrolysis and comes from:
the pancreas
bacteria that live in the rumen
the liver
protons secreted into the rumen
the intestinal wall.
bacteria that live in the rumen
dietary essential fatty acids for humans include
linolenic and oleic acids
palmitic and oleic acids
oleic and linoleic acids
linoleic and linolenic acids
linoleic acid (an omega-6) and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) (an omega-3)
glycosphingolipids consist of a ___ with one or more ___ residues in a ___ linkage at the 1-hydroxy moiety.
sugar; fatty acids; esters
ceramide; sugar; β-glycosidic
ceramide; fatty acids; amide
glycerol; fatty acids; ester
ceramide; sugar; β-glycosidic
a triterpene that is both the biosynthetic precursors of all steroids and a lubricant for delicate machinery where a free-flowing lipid with very low vapor pressure is required is
lanosterol
cortisone
β-carotene
squalene
squalene
membranes with unsaturated fatty acids in their components are more flexible and fluid because:
unsaturated fatty acids pack closely together to from ordered arrays
unsaturated fatty acids bend at the double bond preventing close packing
saturated fatty acids have a “kink” that produces more fluid aggregates
unsaturated fatty acids have cis double bonds that block “kink” formation
all are correct
unsaturated fatty acids bend at the double bond preventing close packing
in most cases, glycerophospholipids have ___ fatty acid at position 1 and ___ fatty acid at position 2 of the glycerol.
a saturated; a saturated
a saturated; an unsaturated
an unsaturated; a saturated
an unsaturated; an unsaturated
a saturated; an unsaturated
cholesterol is a component of all the following except:
lipoproteins
plant cell plasma membranes
animal cell membranes
membranes of intracellular organelles
all are true
plant cell plasma membranes
steroid hormones include all the following except:
stigmasterol
progesterone
cortisone
estradiol
testosterone
stigmasterol
which of the following would be the most likely interaction between a peripheral membrane protein that contained a high lysine content and a membrane?
ionic interaction
hydrophobic interaction
lipid insertion
covalent bonding
amide hydrolysis
ionic interaction
in passive diffusion, the transported species moves across the membrane in the _____ favored direction _____.
kinetically; using a transport protein
kinetically; without a specific transport system/molecule
thermodynamically; using a transport protein
thermodynamically; without a specific transport system/molecule
thermodynamically; without a specific transport system/molecule
β-Fluoroalanine, an excellent drug that was never approved for human use by the FDA, is
a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug that selectively inhibits COX-2
an anti-hypercholesteremic drug that inhibits HMG-CoA reductase
an anti-bacterial agent that inhibits cell wall biosynthesis
a form of vitamin A that was shown to cause cancer in humans
a masking agent for performance-enhancing drugs, chiefly testosterone.
an anti-bacterial agent that inhibits cell wall biosynthesis
flippases are enzymes that flip:
fatty acids from one position on glycerol to another position
glucose form α- to β-glucose
amino acids from one position to another in a protein
cholesterol from one organelle to another
phospholipids across to the other side of a membrane
phospholipids across to the other side of a membrane
Lipids that spontaneously form micelles, monolayers and bilayers have what property?
waxy
polar
amphipathic
bipolar
polyisoprenoid
amphipathic
In eukaryotic cells phospholipids, glycolipids and cholesterol are synthesized by enzymes located in the ____ and ____, and flow of these components to other membranes in the cell is mediated by ____.
plasma membrane; mitochondria; osmosis
endoplasmic reticulum; Golgi; osmosis
plasma membrane, Golgi; lipid transfer proteins
endoplasmic reticulum; Golgi; lipid transfer proteins
endoplasmic reticulum; plasma membrane; flippases
endoplasmic reticulum; Golgi; lipid transfer proteins
the effect of the KscA potassium channel is an example of
passive diffusion
facilitated diffusion
active transport
membrane skeleton fencing
facilitated diffusion
the most highly oxidized purine is ____, but it is ___ found in nucleic acids.
guanine; always
adenine; always
hypoxanthine; never
xanthine; always
uric acid; never
caffeine; never
uric acid; never
cAMP and cGMP are ___ with phosphate esterified as cyclic ___ and are important as ___ of cellular metabolism.
nucleotides; phosphodiesters; inhibitors
nucleotides; phosphomonoesters, regulators
nucleotides; phosphodiesters, regulators
nucelosides; phosphomonoesters, stimulators
nucleotides; phosphodiesters, regulators
The net charge on nucleotide monophosphates is:
a. +1
b. 0
c. -1
d. -2
e. -3
-2
in double-stranded DNA containing 32%, cytosine, the percentage of adenine would be:
32%
68%
18%
0%
insufficient information to answer question
18%
Which molecule contains an acid anhydride bond?
a. DNA
b. ATP
c. UMP
d. RNA
e. cAMP
ATP
The methyl group of thymine is ultimately an evolutionary response to
the ease of hydrolysis of RNA
the need for extra solubility in membranes
photochemical dimerization in DNA
the nonenzymatic deamination of cytosine
the nonenzymatic deamination of cytosine
In eukaryotic cells, a class of ____- and ____-rich proteins called ____ interact ionically with the anionic phosphate groups in the DNA backbone to form ____.
a. lysine; leucine; prions; ribosomes
b. arginine; lysine; histones; nucleosomes
c. arginine; alanine; histones; nucleosomes
d. arginine; lysine; prions; ribosomes
e. none are true
arginine; lysine; histones; nucleosomes
RNA is ____ stable to alkaline hydrolysis than DNA because RNA’s vicinal ____ group makes the 3’-phosphodiester bond susceptible to ____ cleavage.
less; 3’-OH; nucleophilic
less; 2’-OH; nucleophilic
more; 2’-OH; electrophilic
more; 2’-OH; nucleophilic
less; 2’-OH; nucleophilic
which of the following statements correctly identifies a type II restriction endonuclease?
they work on both DNA and RNA
they recognize a palindromic sequence and cut just before the palindromic sequence
the result of this endonuclease is blunt ends
they degrade DNA by removing bases from each end
they cut DNA at sites in specific nucleotide sequences with a 2-fold axis symmetry
they cut DNA at sites in specific nucleotide sequences with a 2-fold axis symmetry
the chief fatty acid of olive oil (and clearly “empty calories”) is
palmitic acid
palmitoleic acid
oleic acid
linoleic acid
oleic acid
which of the following isoprenoid vitamins is derived from a steroid?
vitamin A
vitamin D
vitamin E
vitamin K
vitamin D
which of the following molecules would be an unlikely lipid anchor for a peripheral membrane protein?
an amide-linked myristoyl group
a thioester-linked stearoyl group
a thioether-linked farnesyl group
an ester-linked cholesteryl group
an ester-linked cholesteryl group
which of the following is not a selectivity filter for a protein involved in facilitated diffusion?
a narrow constriction in the pore formed by the protein
a requirement that several ions be transported together
a requirement for hydrolysis of ATP along with transport
a pH-switchable gate over the pore formed by the protein
a requirement for hydrolysis of ATP along with transport
The Na+, K+-ATPase of animal cells transports ___ sodium ions and hydrolyzes ___ molecules of ATP for each potassium ion transported
3;1
2; 1
1.5; 0.5
1; 1
3; 1
the DNA-directed synthesis of RNA is known as
replication
transcription
translation
termination
transcription
the long term stability of DNA is enhanced by
steric hindrance from the thymine methyl groups
easy protonation of the nucleotide bases
lack of 2’-hydroxyl groups of he deoxyriboses
small cross section of the minor groove
lack of 2’-hydroxyl groups of he deoxyriboses
which mechanism of enzyme catalysis is illustrated by the role of the serine hydroxyl group in reactions catalyzed by chymotrypsin?
approximation
tight binding of transition states
covalent intermediates
use of general acids and bases
covalent intermediates
benzene, a hydrocarbon, has a poor solubility in water chiefly because of
the hydrophobic effect
the amphiphiliity of water
the high polarity of benzene
poor solvation of benzene molecules
the hydrophobic effect (benzenes nonpolar)
HEPES is superior to phosphate or Tris as a buffer for biological experiments chiefly because of
its low cost
its pka of 7.55
its low MW
its low Δpka/degrees C
its low Δpka/degrees C
the presence of magnesium ions typically makes the hydrolysis of ATP ____ due to ____
more favorable; reduced charge-charge repulsion among the phosphates
less favorable; reduced charge-charge repulsion among the phosphates
more favorable; increased charge-charge repulsion among the phosphates
less favorable; increased charge-charge repulsion among the phosphates
more favorable; reduced charge-charge repulsion among the phosphates
which of the following amino acids has a side chain group that is less acidic than a typical α-ammonium group (the protonated α-amino group of an amino acid)?
asp
cys
glu
tyr
cys
the genetic defect that makes an individual unable to convert phenylalanine to tyrosine leads to the very serious disease ___, but a genetic defect that causes urine to turn black in air is the hallmark of the much less serious disease ____.
acromegaly; hypercholesteremia
hyperthyroidism; Marfan’s syndrome
phenylketonuria; alkaptonuria
Marfan’s syndrome; phenylketonuria
phenylketonuria; alkaptonuria
the arrangement of the subunits in a protein is an element of ____ structure.
primary
secondary
tertiary
quaternary
quaternary
disulfide bonds are most frequently stabilized ___ structure in proteins
primary
secondary
tertiary
quaternary
tertiary
in order to cleave a polypeptide “to the right” of methionine residues, one should treat the peptide with..
trypsin
chymotrypsin
cyanogen bromide
carboxypeptidase
cyanogen bromide
which of the following secondary structures has a strong dipole that is used by some proteins for charge neutralization?
α-helices
parallel β-sheet
antiparallel β-sheet
β-turn
α-helices
in a four-helix-bundle protein, the amino acid residues on the interior faces of the α-helices are typically
arranged to form salt bridges
negatively charged
hydrophobic
positively charged
hydrophobic