C790 WGU FOUNDATIONS IN NURSING INFORMATICS
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
HIS implementation benefits to healthcare
can improve cost control, increase the timeliness and accuracy of patient care and administration information, increase service capacity, reduce personnel costs and inventory levels, and improve the quality of patient care.
Nurse informaticist role in health information system
Looks for information, verifies ownership of information and connects other parties within the healthcare organization.
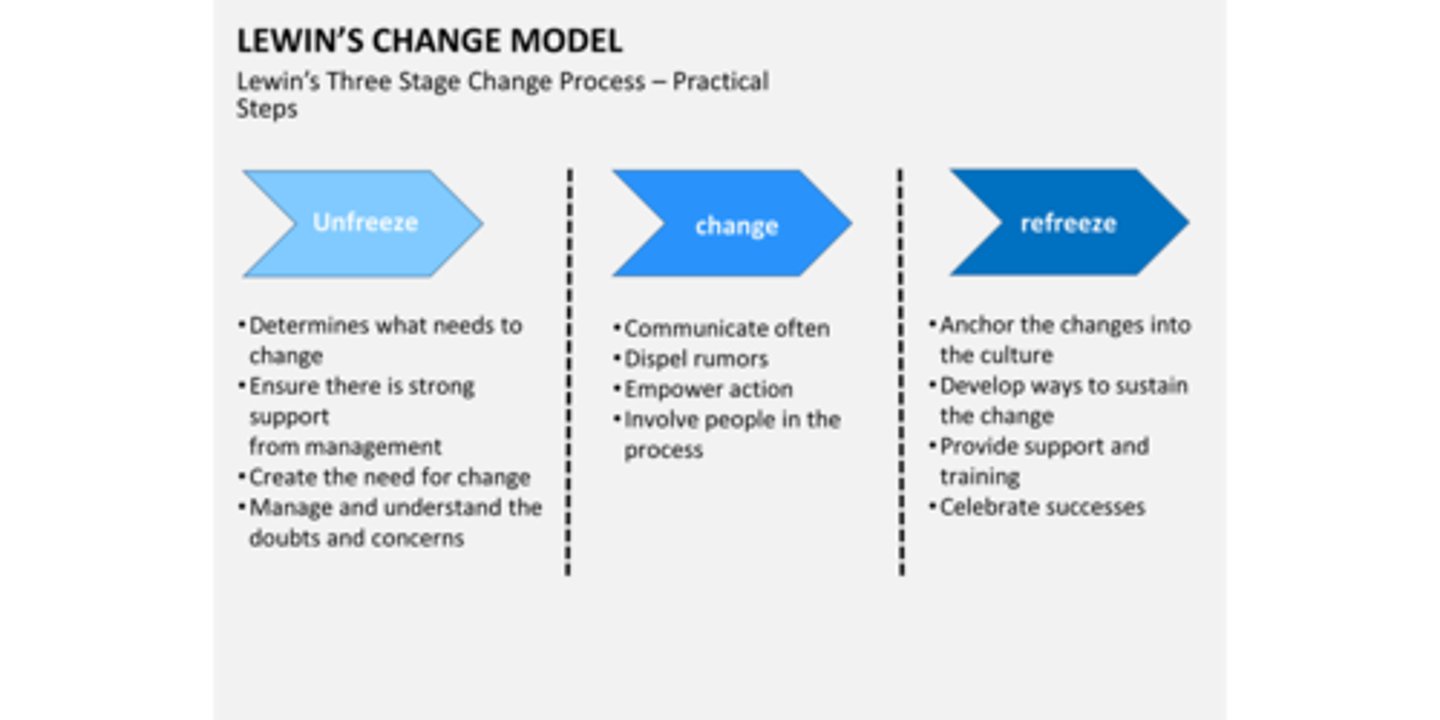
Lewin's Change Model
unfreezing, changing, refreezing
(planning, action, results).
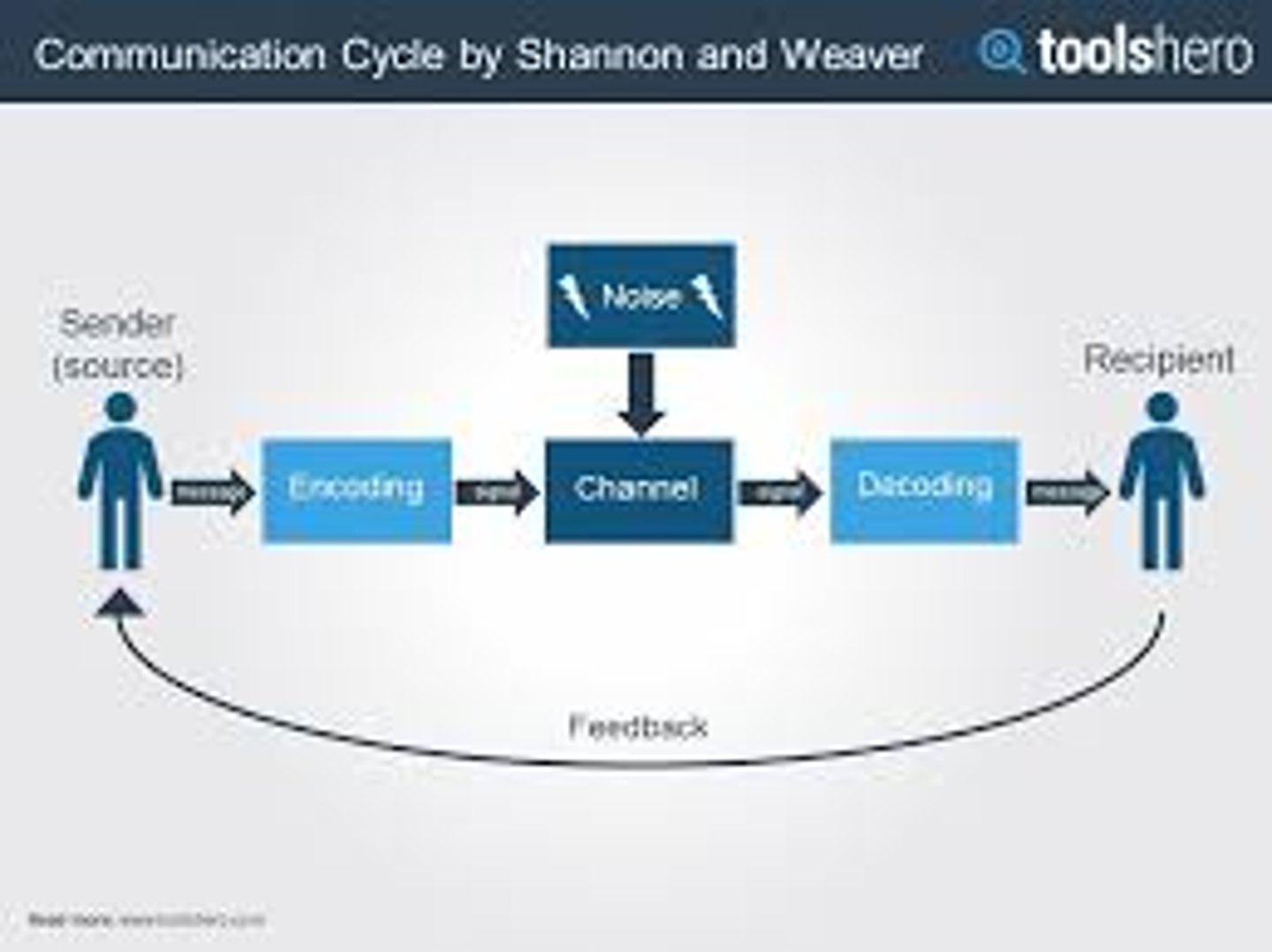
Shannon & Weaver's mathematical model
Encoder (Transmitter): Encoder is the sender who uses machine, which converts message into signals or binary data. It might also directly refer to the machine.
Channel: Channel is the medium used to send message.
Decoder (Receiver): Decoder is the machine used to convert signals or binary data into message or the receiver who translates the message from signals.
Receiver (Destination): Receiver is the person who gets the message or the place where the message must reach. The receiver provides feedback according to the message.
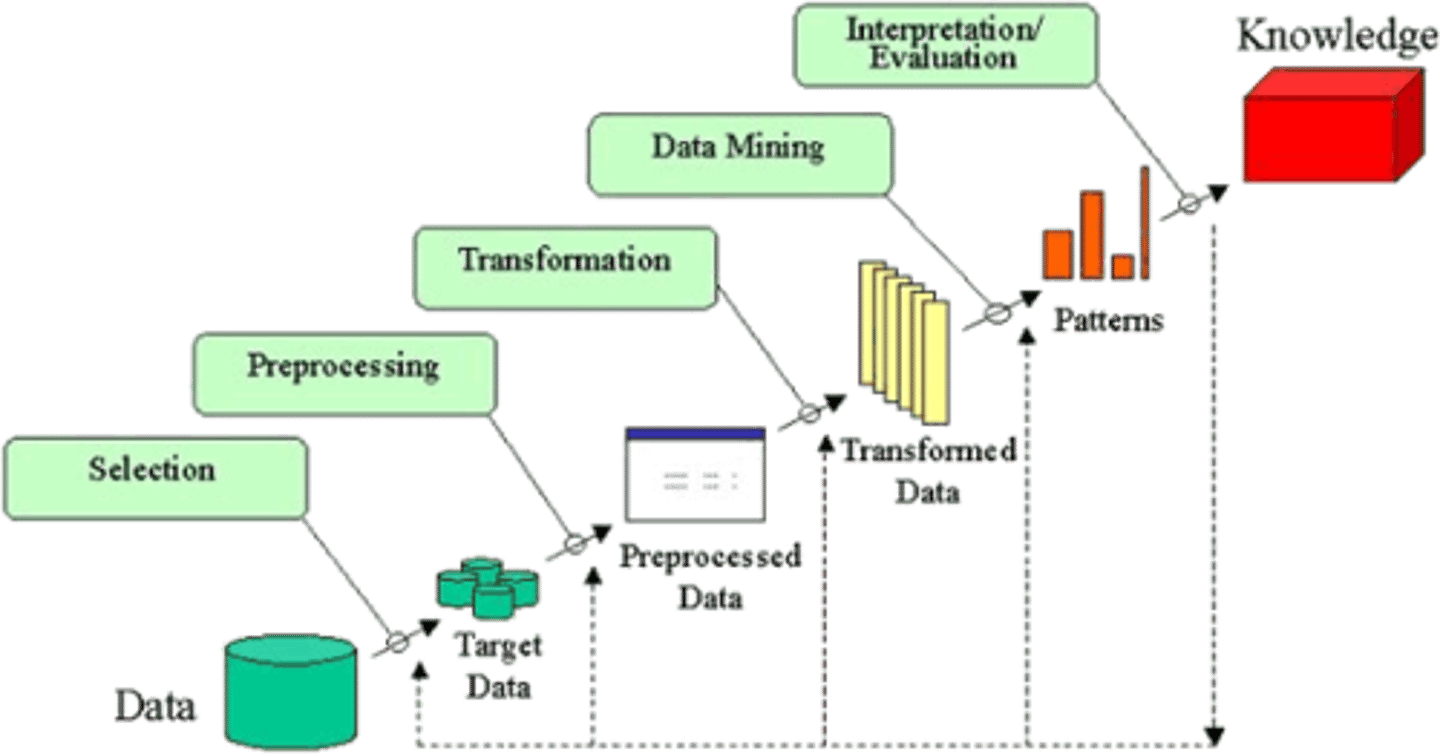
Bloom's knowledge discovery from databases (DDD)/data mining steps
Selection
Preprocessing
Transformation
Data Mining
Interpretation
Transformation
CIO role in HIS implementation
oversees the operation of the information technology department and consults with other C-level personnel on technology-related needs and purchasing decisions.
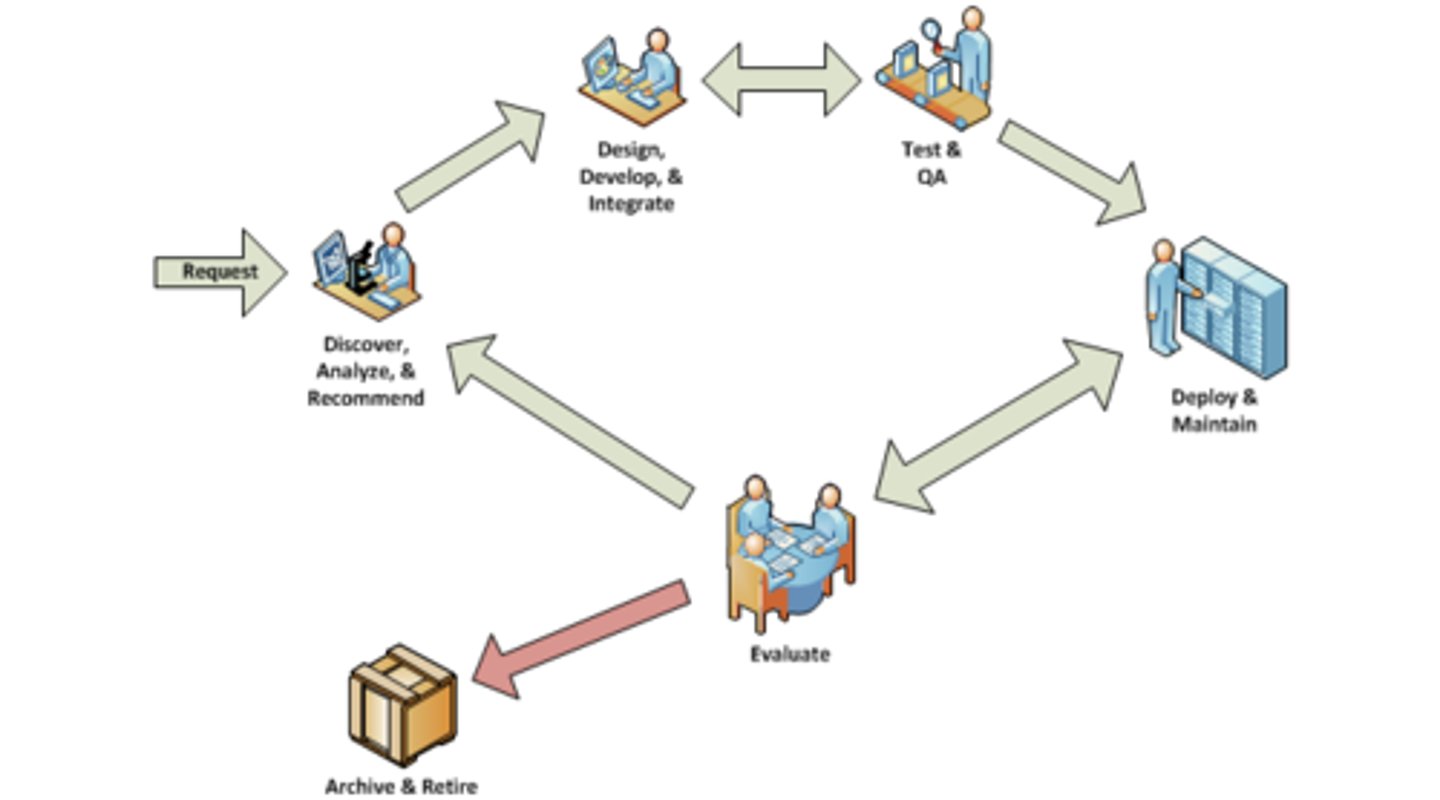
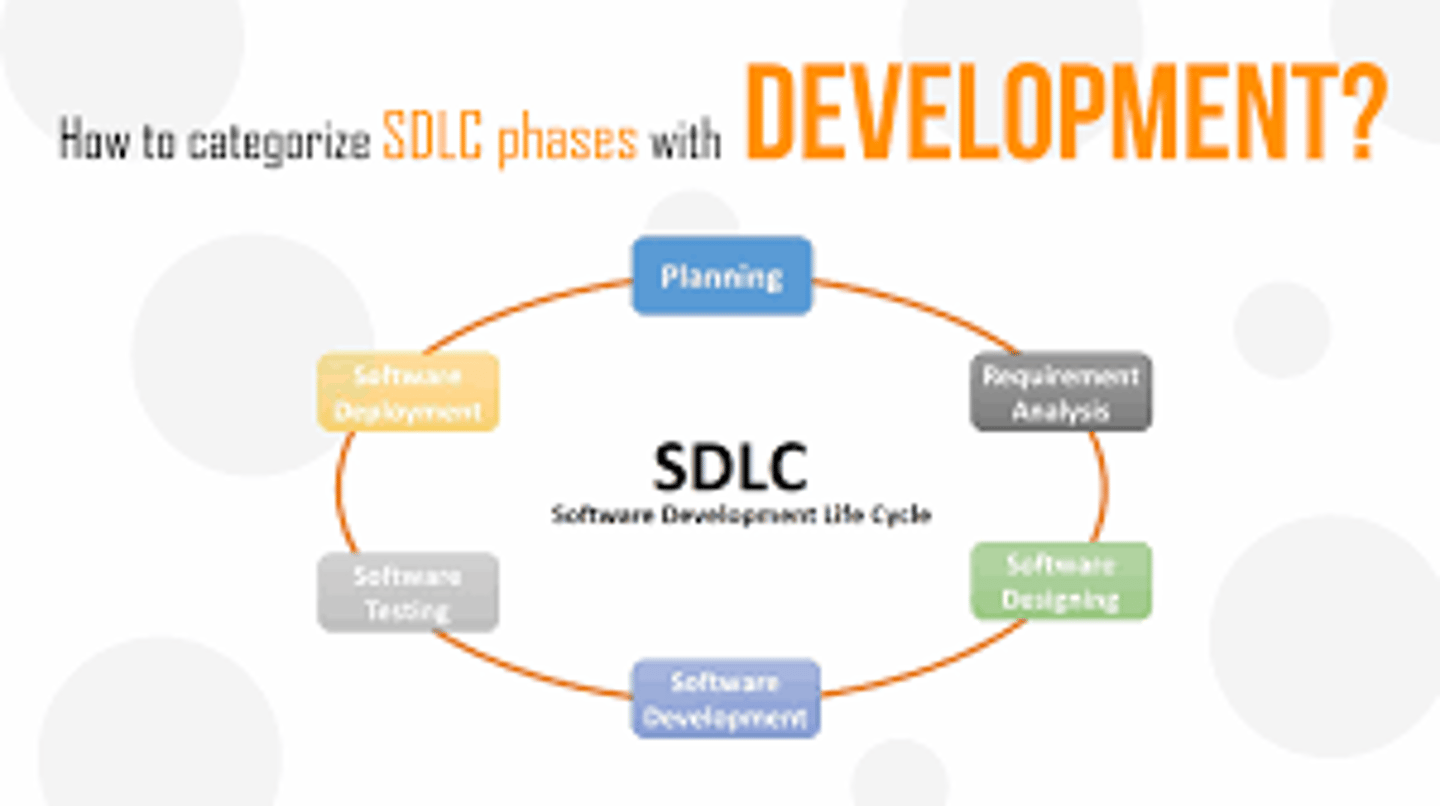
SLC Phases
Solution Life Cycle
* Discover, Analyze, & Recommend.
* Design, Develop, & Integrate.
* Test & Quality Assurance.
* Deploy & Maintain.
* Evaluate.
* Archive & Retire.
SDLC
#1) Requirement Gathering and Analysis.
#2) Design.
#3) Implementation or Coding.
#4) Testing.
#5) Deployment.
#6) Maintenance.
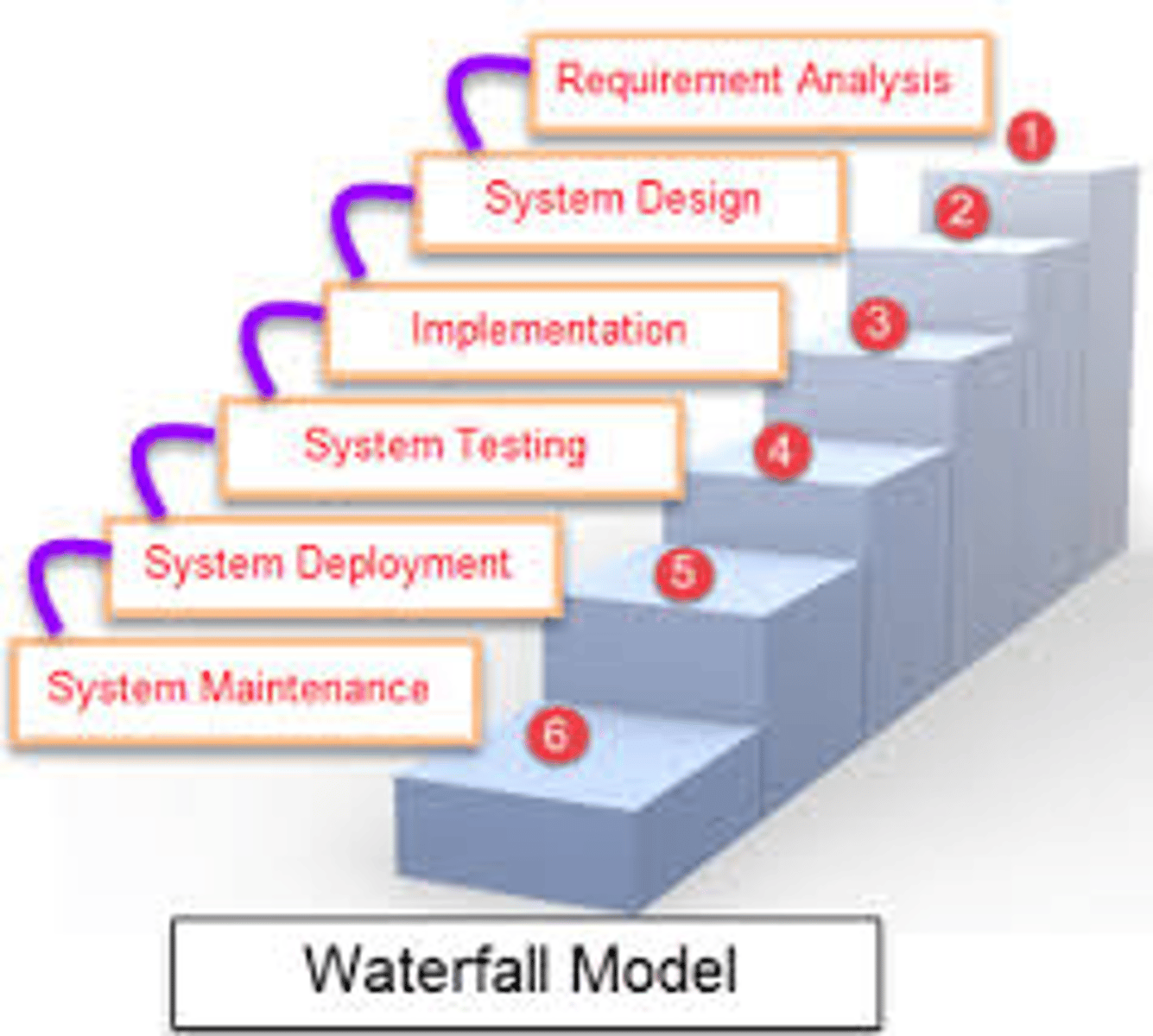
Waterfall Model Phases
Requirements analysis and definition
System and software design
Implementation and unit testing
Integration and system testing
Operation and maintenance
NO OVERLAP
Agile Model
A development model that emphasizes continuous feedback and cross-functional teamwork.

adaptive approach to the SDLC
approach that assumes the project must be more flexible and adapt to changing needs as the project progresses
Predictive approach to the SDLC
an approach that assumes the project can be planned in advance and that the new information system can be developed according to the plan
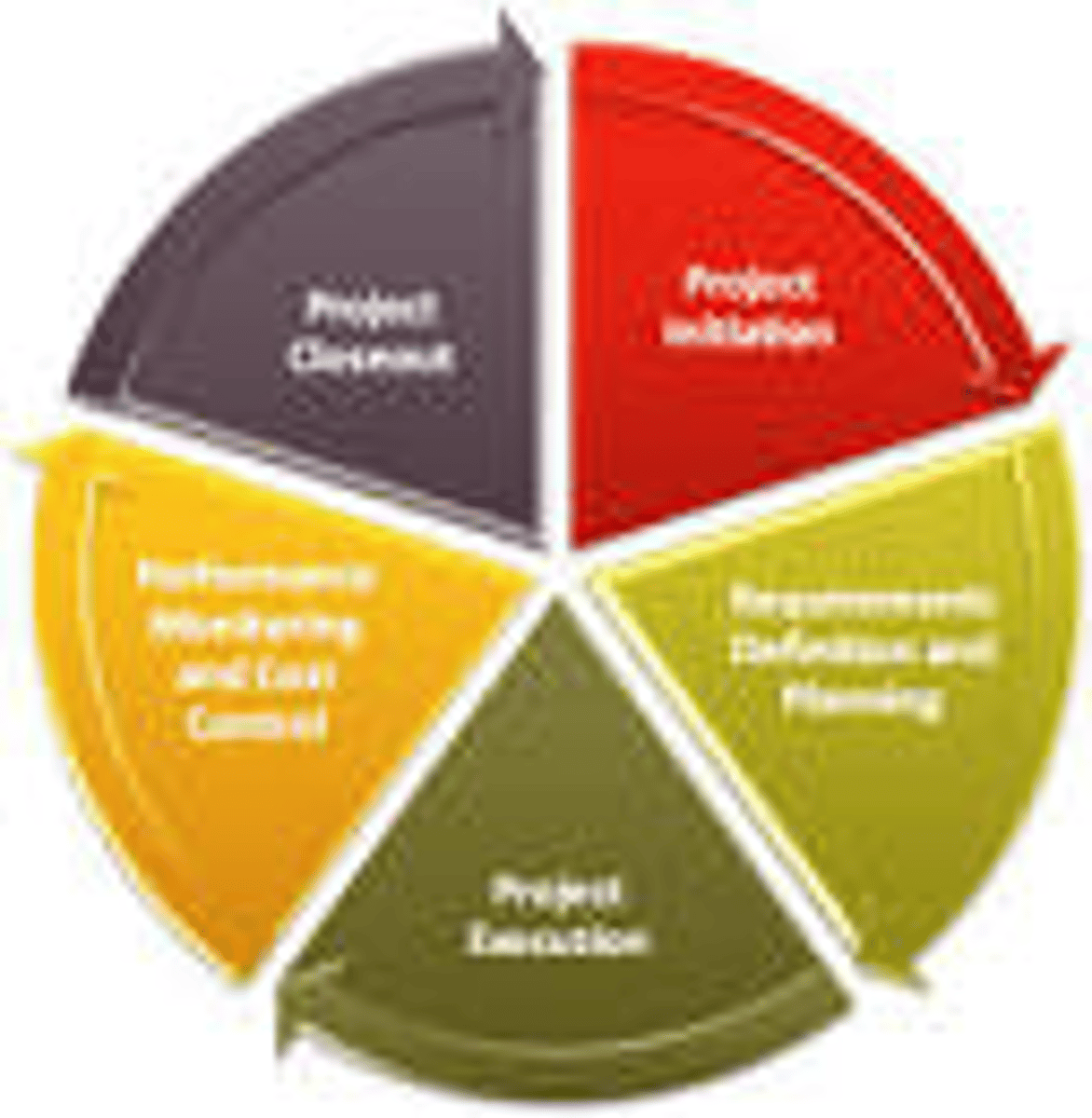
Project Management Phases
Project management consists of a number of required activities that are grouped into four major stages of activity referred to as phases
Definition Phase
Planning Phase
Execution Phase
Analysis Phase
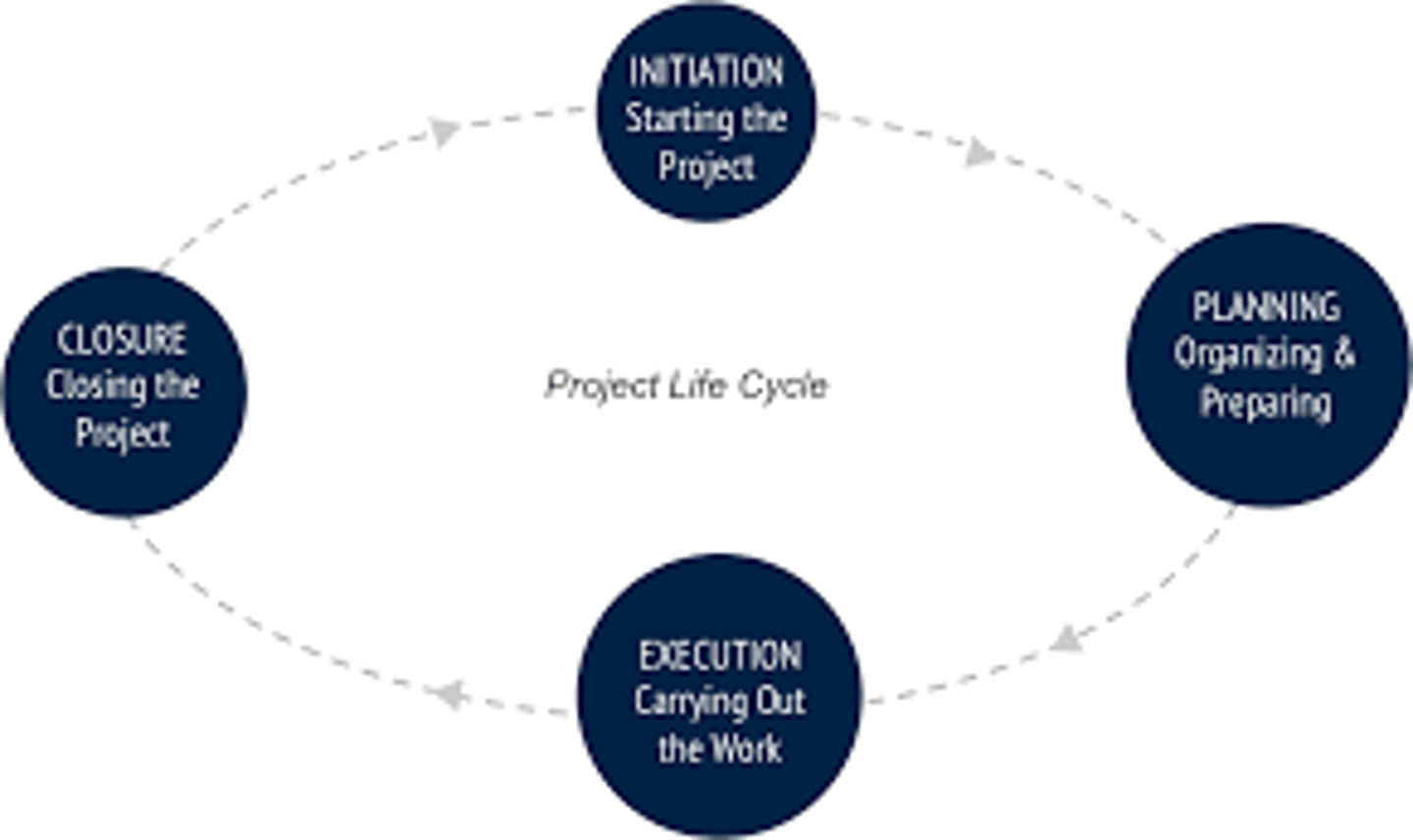
Project Life Cycle
initiation, planning, execution, closure
Usability and user experience
"effectiveness, efficiency and satisfaction with which specified users achieve specified goals in particular environments"
Standardized Clinical Terminology
required directly or indirectly to describe health conditions (e.g. symptoms, complaints, illness, diseases, disorders, etc.), and healthcare activities
Decision Support Tools
Screen for illness and disease.
Identify at risk patients
Aid w/ disease management
NIC (Nursing Interventions Classification)
Defines, and assists in choosing the appropriate nursing interventions for nurses, student nurses, administrators, and faculty
NOC (Nursing Outcomes Classification)
Standardizes the terminology and criteria for measurable or desirable outcomes as a result of nursing interventions.
SNOMED
Systemized Nomenclature of Medicine
LOINC
Terms and codes used for electronic exchange of lab results and clinical observations.
AHRQ
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
PNDS
Preoperative Nursing Data Set
Common language for preoperative nurses
DBMS
a software suite designed to organize and search data.
HL7
standards development organization accredited by the American National Standards Institute that addresses issues at the 7th, or application, level of healthcare system interconnections
ANSI
A private, non-profit organization that coordinates the development and use of voluntary consensus standards in the United States.
WEDI (Workgroup for Electronic Data Interchange)
supports standards with the goal of enhancing the quality of care, improving efficiency, and reducing costs of healthcare in the U.S.
DIKW framework
describes a hierarchical relationship between data, information, knowledge and wisdom
Mind Mapping
is a visual way to capture ideas and how they relate to one another.
system thinking
a way of monitoring the entire system by viewing multiple inputs being processed or transformed to produce outputs while continuously gathering feedback on each part
Six Sigma
A business process for improving quality, reducing costs, and increasing customer satisfaction
HCIS
health care information system
interoperability
the capability of two or more computer systems to share data and resources, even though they are made by different manufacturers
technical interoperability
is the ability to exchange the data from one point to another. Syntactic and functional interoperability are additional terms that refer to the movement of data that does not necessarily ensure the meaning of the data.
semantic interoperability
guarantees that the meaning of the exchanged data remains the same on both ends of the transaction
process interoperability
coordinates business processes at the organizational level; allowing the systems to work together.
system check
a mechanism provided by the computer system to assist users by prompting them to complete a task, verify information, or prevent entry of inappropriate information
Data Mining
is a knowledge management tool that engages software to uncover inter-relationships within large data sets.
CER (Comparative Effectiveness Research)
conduct and synthesis of research comparing interventions and strategies to prevent, diagnose and treat health conditions
ABC (Alternative Billing Codes) Codes
capture non-physician and alternative medicine health services provided by health professionals.
CCC (Clinical Care Classification)
document Nursing Care in EHR
CDA (Clinical Document Architecture)
Used to share documents across systems, an HL7 standard.
CPT
Current Procedural Terminology used to code procedures.
DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine)
standard protocol used for blending a picture archiving and communications system and various imaging modalities
FHIR
Fast Health Interoperability Resources
NCPDP (National Council for Prescription Drug Programs)
Standards supporting drug prescribing, dispensing, monitoring, managing and paying for meds and pharm services.
X12N
A subcommittee of X12 that defines EDI standards for the insurance industry, including healthcare insurance
ASTM
American Society of Testing and Materials
Develops international standards for materials, products, systems, and services
ICD
International Classification of Diseases. ICD-10
ICNP
International Classification for Nursing Practice
IEEE
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
A professional organization that develops communications and network standards, among other activities.
ISO
International Organization for Standardization/Industry
Standards Organization
Over 155+ standards
NANDA
North American Nursing Diagnosis Association
Purpose is to define, refine, and promote a taxonomy of nursing diagnostic terminology of general use to professional nurses.
NMMDS
Nursing Management Minimum Data Set
It contains 19 data elements related to staffing, patient populations, model of care delivery and type of nursing unit.
NMDS
Nursing Minimum Data Set
Contains 16 elements of nursing data, definitions, demographics and service
Omaha
Practice and documentation standardized taxonomy designed to describe client care
Consisting of an assessment component (Problem Classification Scheme)
A care plan/services component (Intervention Scheme)
An evaluation component (Problem Rating Scale for Outcomes)
UMLS (Unified Medical Language System)
Projects to link various biomedical vocabularies nomenclatures together.
It’s goal is to enable computers to understand medical meaning.
Project initiation
-Identify the problem
-Quantify approval factors
-Perform risk and feasibility study
-Review with client & obtain approval.
project planning
planning, organizing and scheduling the project
analysis
focuses on discovering and understanding the details of the problem or need
design
configuring and structuring the new system components
implementation
programming and testing the system
deployment
installing and putting the system into operation