Organic Chemistry Exam 3
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
I am a weak base
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What are examples of STRONG nucleophiles
High electron density, great at donating electrons

What are examples of GOOD nucleophiles
Good electron density , good at donating protons
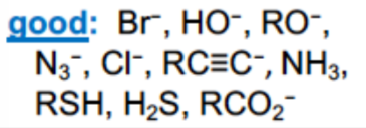
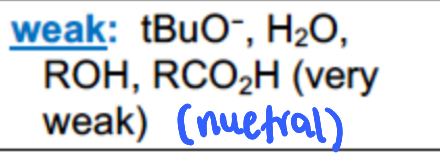
What are examples of WEAK nucleophiles
Low electron density, bad at donating protons
What are examples of STRONG bases
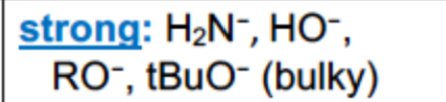
What are examples of WEAK bases
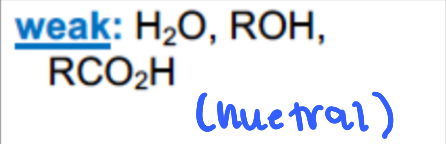
What are examples of GREAT leaving groups
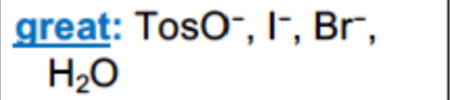
What are examples of GOOD leaving groups
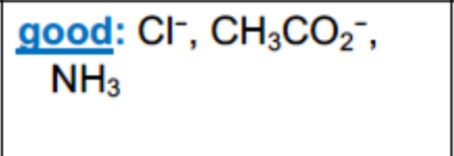
What are examples of POOR leaving groups

What are examples of polar protic solvents
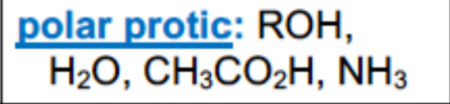
What are examples of polar aprotic solvents

What are examples of non-polar solvents

Sn2 reaction properties
Nucleophile: Must be strong
Leaving Group: Good/great
Solvent: Polar aprotic
Alkyl Halides: 1>2>3 (almost no reaction)
Reaction mechanism: 1 step (concerted)
Sterochemistry: Proceeds through inversion only
Rearrangements aren’t possible

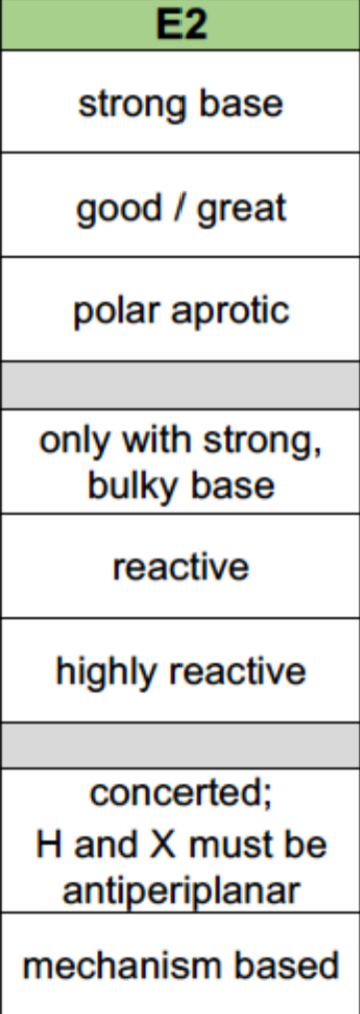
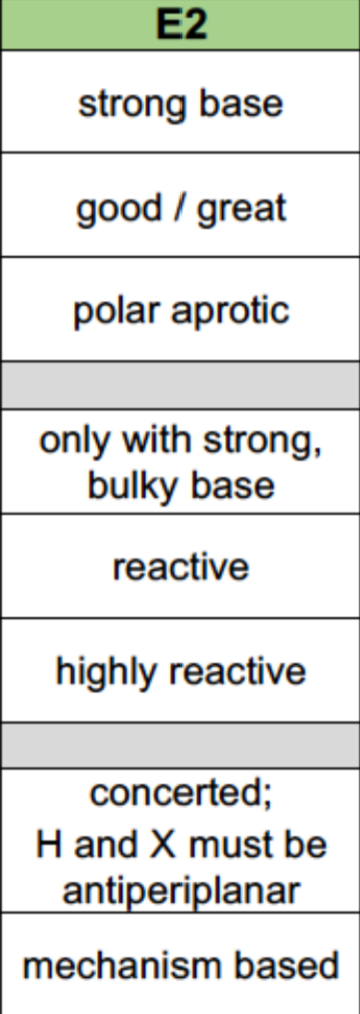
E2 Reaction Properties
Nucleophile: Strong base needed
Leaving Group: Good/great
Solvent: Polar aprotic
Alkyl Halides: 3>2>1(only with strong bulky bases)
Reaction mechanism: 1 step with H and RX being antiperiplanar (concerted)
Sterochemistry: Based on mechanisms
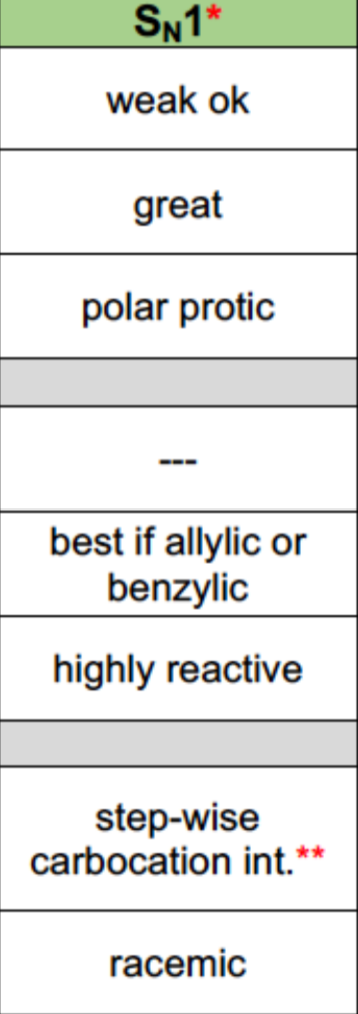
SN1 Properties
Nucleophile: Usually weak
Leaving Group: Great
Solvent: Polar protic
Alkyl Halides: 3>2>1 (almost no reaction)
Reaction mechanism: 2 steps (1. Removal of the leaving group, 2. Addition of nucleophile)
Stereochemistry: Proceeds through inversion and retention
Rearrangements are possible with Carbocation intermediates
Can form Hydrogen Bonds
E1 Reaction Properties
Nucleophile: Weak or strong (usually weak)
Leaving Group: Great
Solvent: Polar protic
Alkyl Halides: 3>2>1
Reaction mechanism: Stepwise Carbocation intermediate
Sterochemistry: Products must be trans due to cis steric strain
RX and H dont need to be antiperiplanar
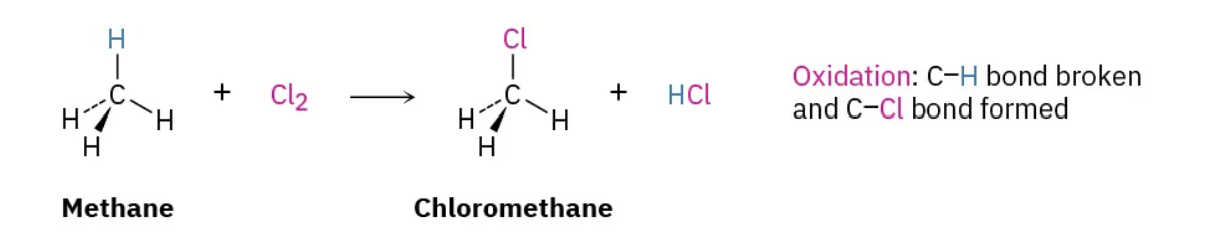
Oxidation
Decrease in C-H bonds, increase in C-O bonds (or equivalent)
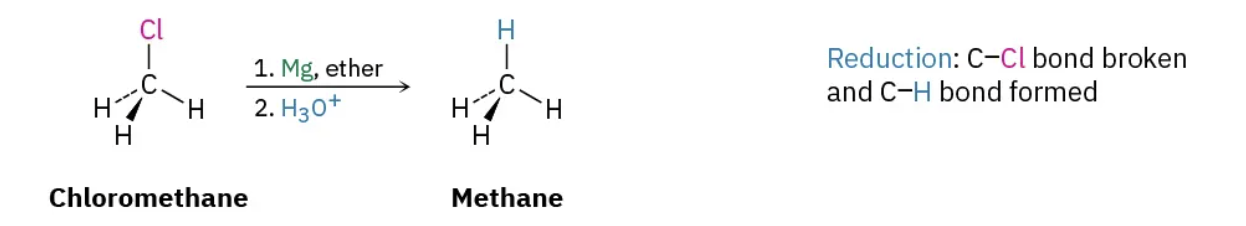
Reduction
Increase in C-H bonds, decrease in C-O bonds (or equivalent C-Cl, C-Br, etc).
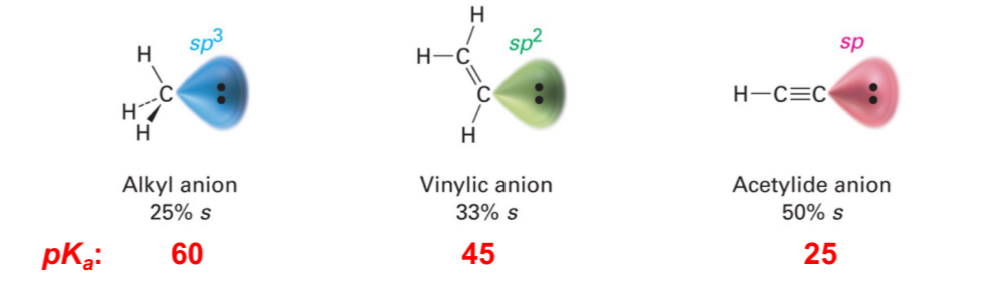
Acidity of Alkynes
Sp3 is weakest acid
Sp2 is middling acid
Sp is strongest acid
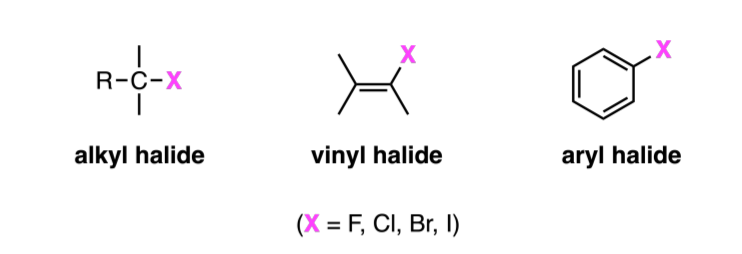
alkyl halide vs vinyl halide vs aryl halide
Alkyl halide: one or more halogen atoms bonded to Sp3 hybridized carbon
Vinyl Halide: halogen attached to a double bond
Aryl Halide: Halogen attached to an aromatic ring
How do Alkyl Halides change going down on periodic table
-they increase in size
-their carbon-halogen bonds increase in size
-their bond strength decreases
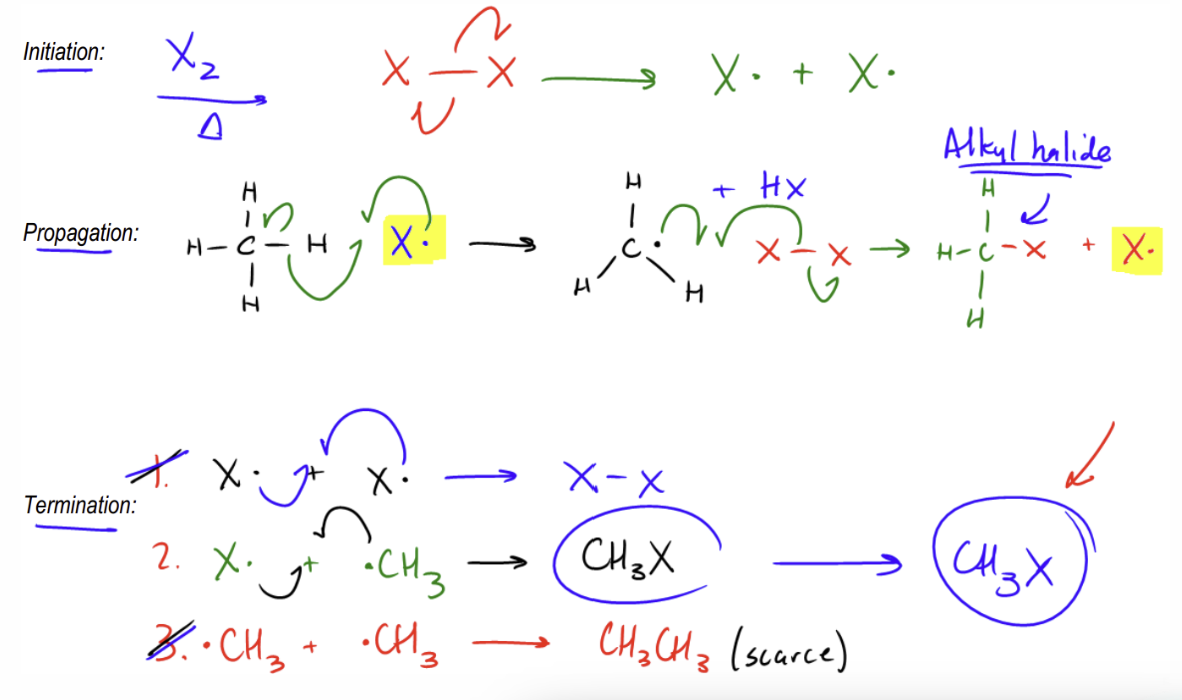
Steps of Radical Mechanisms
Initiation: breaking a stable molecule into two radicals (initiated by light hv)
Propagation: radical species bonds to a stable making one stable molecule and another radical
Termination: two radicals combine to form more stable molecules with no other products
Radical Chlorination (reactivity) and Radical Stability Patterns
Both reactivity and stability increase as you increase the amount of substituents on the carbon that aren’t Hydrogen
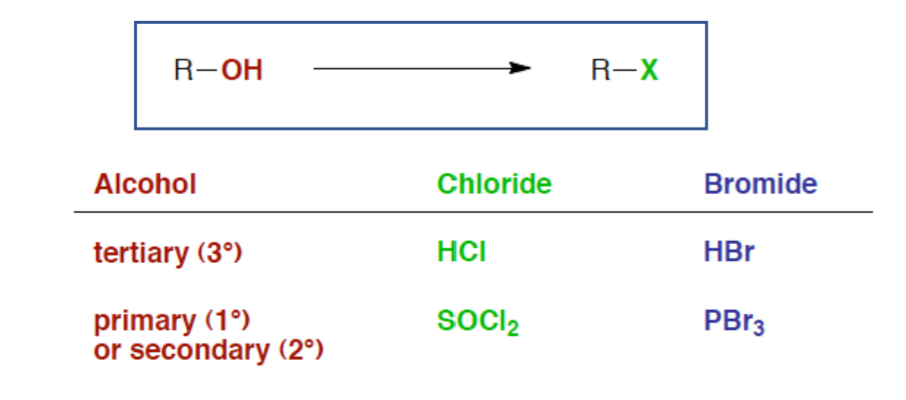
Alkyl Halides from Alcohols
Tertiary alcohol reacts with HCl or HBr
Primary and Secondary Alcohols react with SOCl2 and PBr3
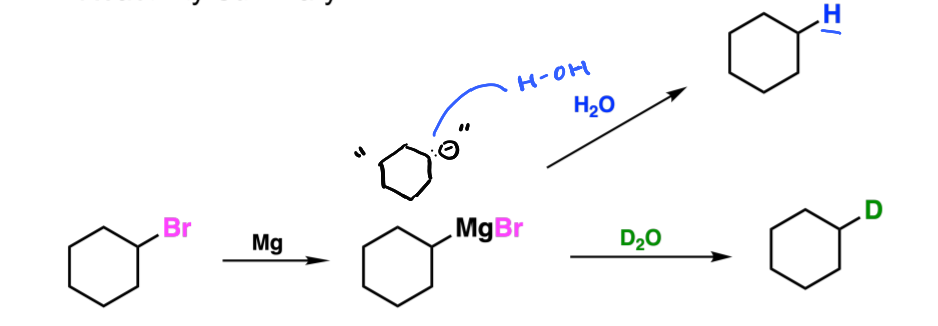
What is a Grignard reagent
When an alkyl halide reacts with Mg and a solvent, usually followed by some kind of weak base to substitute these alkyl halides
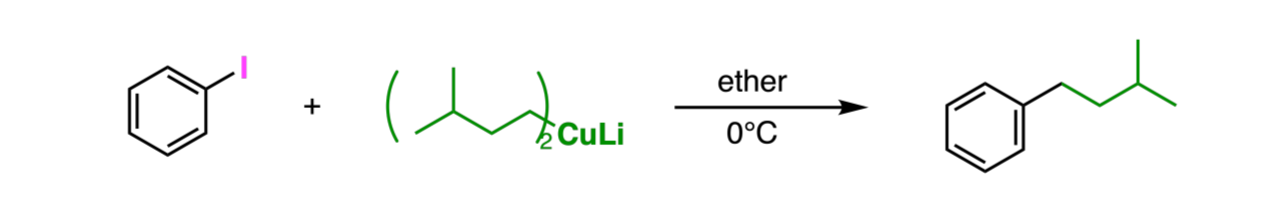
Gilman Reagents
-Makes a C-C bond into an sp2 or sp3 hybridized carbon atom
-Removes RX from molecule
-Usually used for Sn2 reactions
-(R)2CuLi
Suzuki-Miyarua Reaction
-used to couple two sp2 hybridized carbons
-Pd(PPh3)4 [pd catalysts]& KOH [strong base]
![<p>-used to couple two sp2 hybridized carbons</p><p>-Pd(PPh3)4 [pd catalysts]& KOH [strong base] </p><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8c8c9e68-5971-4d53-b903-24d23ff03394.png)
Difference of reaction graph for Sn1 and Sn2 when using polar protic vs polar aprotic for both
Sn1: Lowers reaction energy
Sn2: Speeds up reaction
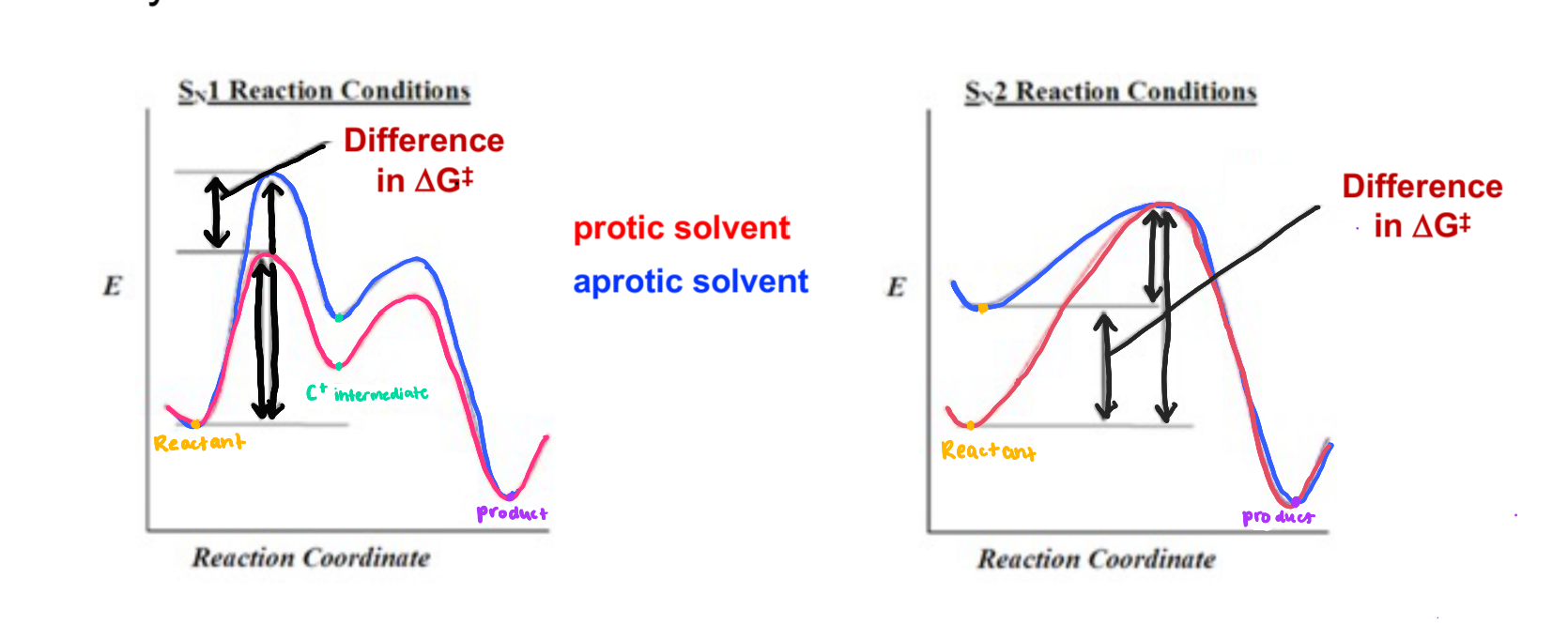
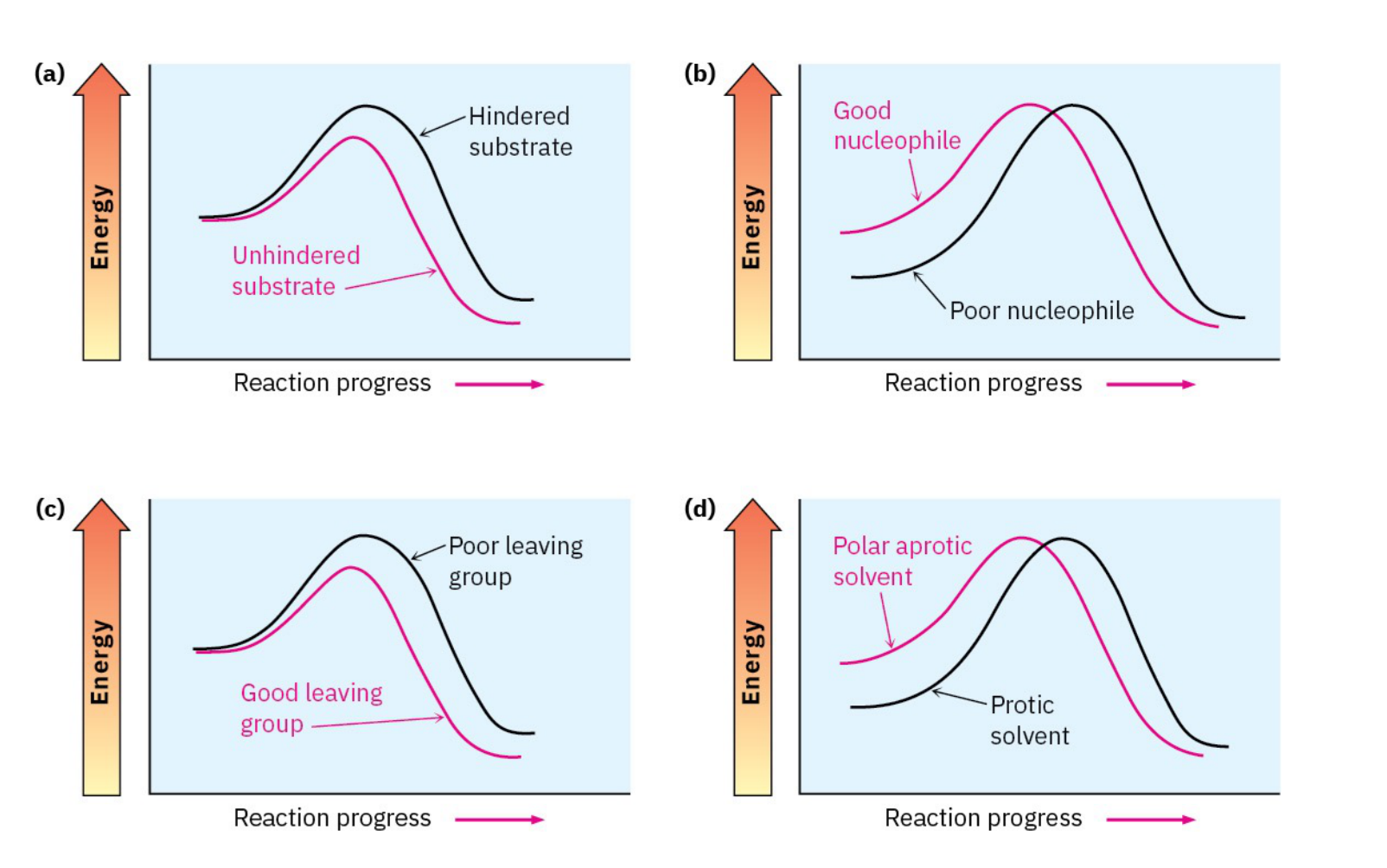
Sn2 reaction graph effects
-protic v aprotic
-good v poor nucleophile
-hindered vs unhindered substrate
-good leaving group v poor leaving group
-aprotic makes the reaction reach the product faster
-good nucleophile makes the reaction reach the product faster
-unhindered substrate decreases energy for first step
-good leaving group decreases energy for first step