Theories of personality: exam 2- Hans Eysenck
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Hans Eysenck personal info
1916- 1997
born in Berlin then moved to England
personality dimensions- E, N, P
Personality dimension E
Extraversion vs. introversion
Personality dimension N
Neuroticism vs. emotional stability
personality dimension P
Psychoticism vs. impulse control
extraversion - traits/ biological
traits- sociable, lively, active, assertive, sensation seeking, carefree, dominant, and adventurous
biological- lower base level of cortical arousal
intraversion - traits/ biological
traits- shy away from excitement, react strongly to stimulation
biological- cortical arousal levels are already high
Neuroticism- traits of high scorers
anxious, depressed, guilt feelings, low self- esteem, tense, irrational, shy, and moody
results in chronic hypersensitivity
psychoticism- traits of high scorers
aggressive, cold, egocentric, impersonal, impulsive, antisocial, creative, and tough- minded
have problems with alcohol, drug abuse, and violent criminal behavior
(have authoritarian and controlling parents)
Primary role of hereditary
Eysenck believed that traits and dimensions were determined by hereditary
compared identical to fraternal twins
McCrae and Costa’s big 5 personality factors (OCEAN)*

Big- 5 research
Neuroticism, extraversion, openness, and conscientiousness have a strong hereditary components
all five factors have been found in diverse cultures
most of the factors remain stable to some degree over the life span
women report higher levels of neuroticism, extraversion, agreeableness, and conscientiousness than men
emotional correlates— well- being
high extraversion
low neuroticism
high agreeableness and conscientiousness
emotional correlates— extraversion
social support
likeable
positive emotions
emotional correlates— neuroticism
negative outcomes
behavioral correlates— conscientiousness
better grades and responsible at work
increased health
low score leads to use of alcohol and illegal drugs
behavioral correlates— agreeableness
fewer behavior problems
behavioral correlates— openness
various intellectual interests
seeks challenges
behavioral correlates— neuroticism
greater longevity
behavioral correlates— extraversion
more social relationships
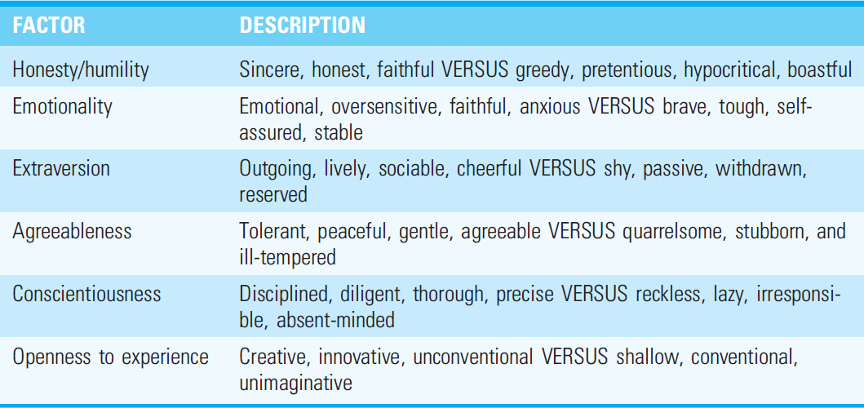
6 personality factors of the HEXACO model
Dark triad of personality
narcissism - obsessed with self
machiavellanism- need to manipulate others
psychopathy - insensitive to others
assess by self- rating tests like dirty dozen scale —- these don’t work well
Dark triad research
slight differences in appearance in people with high/ low levels of nuroticissm and psychopathy
people tend to associate more with people with low levels
in crowded scenarios, people are less averse to psychopathy to non- crowded scenarios.
in both crowds and non- crowds, people are averse towards narcissistic individuals.