5 - somatic nervous system
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What is the motor cortex responsible for and what is it driven by?
planning, initiating, and directing voluntary movements
basal ganglia
What are brainstem centers responsible for and what is it driven by?
basic movement and postural control
cerebellum
Where are upper motor neurons located?
just the CNS
Where are lower motor neurons located
extend out to skeletal muscles
What do upper motor neurons do?
control the muscles and the interneurons that affect them
Outline the 5 divisions of the somatic reflex arc
sensor (receptor)
afferent pathway - to the spinal cord or the brainstem
intergrating centre - grey matter of the spinal cord or brainstem synapse
efferent pathway - to the muscles
effector muscle gives response
Outline the 4 steps of the patellar reflex
striking patellar ligament stretches tendon and quadriceps femoris muscle
spindle is stretched, activating sensory neuron
sensory neuron activates α motorneuron
α motorneuron stimulates extrafusal muscles to contract
List 2 reasons as to why the patellar reflex is so fast
doesn’t require conscious thought
there is only 1 synapse between afferent and efferent neurons
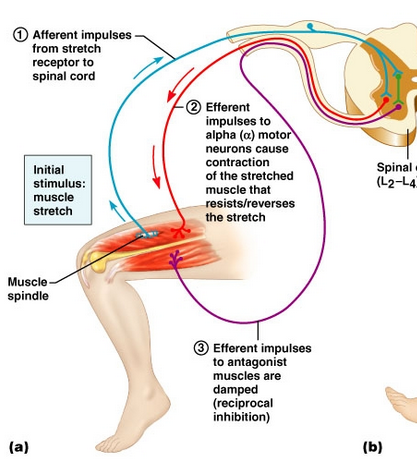
What does the afferent neuron extend to within the integrating centre (2 points)
efferent neuron (leads to muscle contraction)
interneuron that’s inhibitory to the hamstring muscle, creating a negative-feedback reflex arc
What maneuver is used to relax someone?
Jendrassik maneuver
Outline the Jendrassik maneuver (2 points)
patient clenches their teeth and tries to pull apart their interlocked fingers
occupies enough of the CNS that it doesn’t interfere with the patellar reflex
Define proprioception
how you know where your body is at any given time
State 2 ways that proprioception is detected
muscle spindles
golgi tendon organs
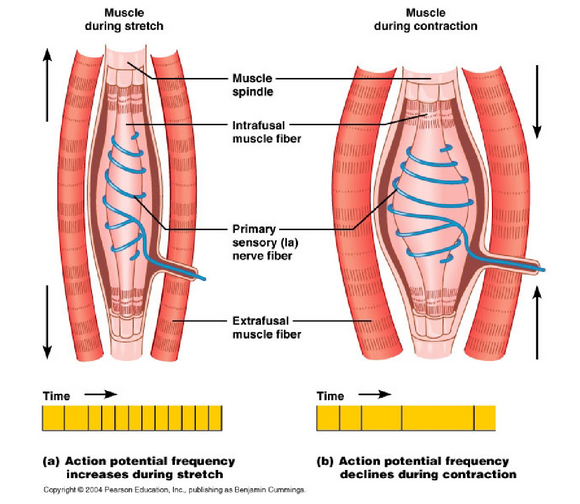
How do muscle fibres detect movement
when intrafusal muscle fibres contract, nerve fibres are stretched, sending information forward
Approximately how many muscle fibres are connected to each golgi tendon organ?
10-15
How do golgi tendon organs detect movement (2 points)
sensory dendrites of afferent nerves are interwoven with collagen fibres
when the muscle contracts, the collagen fibres are pulled tight, activating the afferent neuron
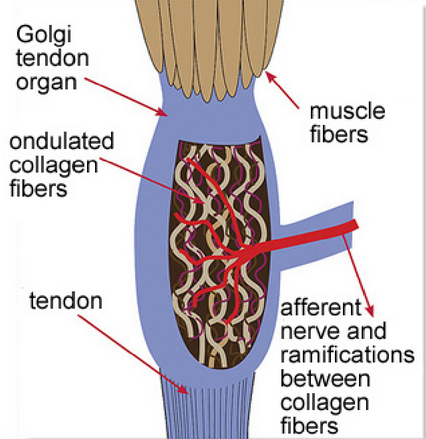
How does the golgi tendon organ act as a failsafe (2 points)
the golgi organ has a disynaptic (inter neuron) connection to its own neuron
if a muscle is subject to so much tension that itt’l be damaged, it produces a powerful activation of that inhibitory inter neuron that stops the lower motor neuron firing