Light/Pigments, Reactions of Photosynthesis, Chloroplast Structure, & Leaf Structure
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
What is ATP?
ATP stores energy until a cell needs it, and when it does require the energy, it breaks part of the ATP molecule to release energy.
Name the three parts (in order): The molecule on the top left, the molecule in the center, and the three groups on the right
Adenine, ribose, phosphate groups
What happens in ATP Decomposition?
The third phosphate group from the ATP molecule breaks off, releasing energy. The leftover molecule is ADP.
What is ADP?
Consists of adenine, ribose sugar, and two phosphate groups. Has less energy than ATP.
What happens during ATP Synthesis?
ADP it turned into ATP. Glucose is used to add a lone phosphate group to the other two phosphate groups in ADP
Where is energy stored within ATP?
Within the bonds of the three phosphate groups
What is the photosynthesis equation? (Format: (reactants) (requirements for transition to products [aka the arrow]) (products))
6H2O + 6CO2 (sunlight and chlorophyll) 6O2 + C6H12O6
What are autotrophs?
Beings that make their own food (plants)
What are heterotrophs
Beings that obtain food (animals)
What are photoautotrophs?
Beings that use sunlight to make their own food through photosynthesis
How much energy do shorter wavelengths have? What are examples of long wavelengths?
have more energy. gamma rays and X-rays
How much energy do longer wavelengths have? What is an example of a long wavelength?
Have less energy. radiowaves
What is the visible spectrum? How many nm?
The spectrum that contains visible light. 380 nm to 750 nm
What is sunlight made up of?
All visible wavelengths
What are pigments? Do we see absorbed colors or reflected colors?
Molecules that absorb and reflect certain wavelengths. We see reflected colors.
What is chlorophyll(s)? What kinds are there? What colors do they reflect and absorb?
Main photosynthetic pigments, all plants have chlorophyll a or b. Absorbs violet, blue, and red wavelengths while reflecting green and yellow wavelengths
What are accessory pigments?
Help absorb other wavelengths
Carotenoids
Accessory pigment that reflects red and orange
Xanthophylls
Accessory pigment that reflects yellow
Why do leaves change color in autumn?
Shorter days and cooler temps causes chlorophyll to break down. Accessory pigments can be seen
What is necessary for photosynthesis to occur (what do plants intake)?
Water, carbon dioxide, and sunlight.
What gas do plants give off during photosynthesis (what do plants output)?
oxygen
How does carbon dioxide enter the leaf?
Through the stomata
How does the plant break apart water molecules?
Using sunlight as energy
Is sunlight necessary for plants to stay alive?
Yes, however, if sugar water is given to the plant, it can temporarily survive.
Is oxygen necessary for plants to stay alive? Why?
Yes, it is used to breakdown the carbohydrate molecules that plants use for food. The plant would starve without it.
Glucose formula?
C6H12O6
Where is chlorophyll stored?
The chloroplast
What molecules are used for glucose to be made in photosynthesis? (describe process regarding ONLY the molecules)
Water molecules are split into separate oxygen and hydrogen atoms, in which excess oxygen is filtered out the leaf while hydrogen bonds with carbon dioxide.
What two colors do chlorophyll a absorb the most?
Violet and red
What two colors does chlorophyll b absorb the most?
Blue and red
What do chlorophyll a and b absorb the least (reflect)
green
Site of photosynthesis?
chloroplast
What is the thylakoid membrane? (Description; what it contains; site of what reaction; where)
disk-like stacks of inner membrane; contain pigments and enzymes; site of light dependent reactions; in the chloroplast
What is the stroma? (description; what does it contain; site of what; where)
Fluid filled space; contains enzymes and DNA; site of light independent reactions; in the chloroplast
What is Grana?
Stack of thylakoid membranes; in the chloroplast
What are photosynthetic pigments? (where; purpose; includes what)
In the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast; absorb light for photosynthesis; include chlorophyll
What is used in light independent reactions? (2 things)
ATP and NADPH
Where is glucose made? With what energy? What kind of reaction is it?
In the stroma of the chloroplast; with ATP and NADPH; light independent reaction
Where is excess oxygen produced in during photosynthesis? What kind of reaction is it?
The thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast; light dependent reaction
Light dependent reaction process? Ultimately, what are the three products?
Chlorophyll absorbs light to split water into oxygen and hydrogen atoms. Oxygen gas is given off as a byproduct. Ultimately, O2, ATP, and NADPH are the products.
How are ATP and NADPH formed? What are they used for?
From light dependent reactions, and are then used in light independent reactions
What are light independent reactions also called?
The Calvin Cycle
Can light independent reactions use light?
Yes, with or without light.
Light independent reaction process?
Carbon dioxide from the environment combines with ATP and NADPH from light reactions to bond with hydrogen from split water molecules and make glucose in the stroma
What is glucose used for in light independent reactions?
To make sucrose, cellulose, other carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and more
What is photolysis?
Process of water being split by light
What is the main photosynthetic organ of the plant?
The leaf
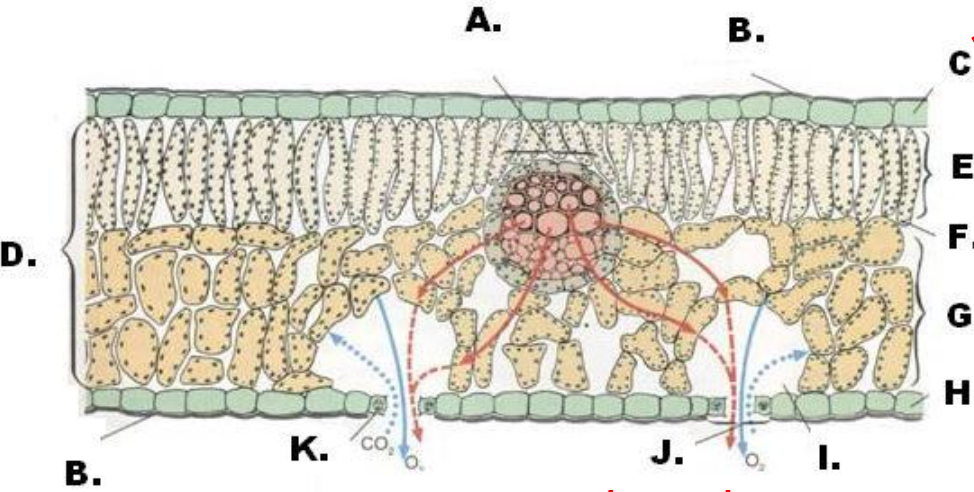
Answer in alphabetical order: (From A to K)
Vein, cuticle, upper epidermis, mesophyll, palisade mesophyll, chloroplast, spongy mesophyll, lower epidermis, air space, stomata, guard cell.
Why (in flowering plants) are leaves flat?
To maximize light absorption and control gas exchange
What covers the upper surface of leaf-functions in protection and secretes the cuticle?
The upper epidermis
What is the opening or pore in the epidermis that allows for diffusion of gases and water vapor?
stomata
What consists of xylem and phloem tissues and supplies water and minerals to leaf and carries products of photosynthesis to other plant parts?
the vein/vascular bundle
What holds air?
air space
What is the mesophyll layer that contains the most chloroplasts, where most photosynthesis occurs?
Paliside mesophyll
What is the mesophyll layer that contains air spaces for gas storage?
Spongy mesophyll
What is the waxy coating that prevents drying out and protects the leaf?
Cuticle
What covers the lower surface of the leaf-functions in protection and secretes the cuticle?
Lower epidermis
What is the tissue that contains the palisade and spongy layers?
mesophyll
What surrounds the stomata to open and close them in response to environmental conditions, as well as permit gas exchange and regulate water loss?
Guard cells
What is the site of photosynthesis and has chlorophyll and other pigments for light absorption?
Chloroplast
What is the vascular tissue that transports sugars throughout the plant?
Phloem
What is the vascular tissue that transports water and minerals throughout the plant?
Xylem
Why would the stomata open? (3 reasons)
To take in water, to take in carbon dioxide diffuse, and for oxygen gas to diffuse out.
Why does the stomata close? (regarding water)
Water is lost to evaporative forces when the stomata are open. It would close in hot/dry environments.
When are stomata open?
They remain open in the day when photosynthesis is occurring and sugars are being made, and oxygen is being created that has to be diffused out. However, cacti have their stomata open at night when temps are low to minimize evaporative water loss.
What is evaporative water loss from leaves and other aboveground plant parts called?
Transpiration
How are guard cells regulated?
Through osmosis. When in a hypotonic environment, guard cells swell and open the stomata to gain water. When in a hypertonic environment, guard cells lose water and close the stomata to hold water.
Relationship of light intensity/concentration of carbon dioxide to the rate of photosynthesis
Both are necessary for photosynthesis to occur, and the rate will exponentially increase with both factors. However, to a certain extent, it will barely increase the rate of photosynthesis.
Relationship of temperature to the rate of photosynthesis
The rate of photosynthesis will increase while temperature is increasing until before 30 C, in which it will then decrease until 40 C, when the rate is 0.