General Radiography QC
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
What is the goal of SC35?
Protect all individuals who may be exposed to radiation derived from X-ray equipment
The three principal objectives of SC35
Minimize patient exposure
Ensure X-ray workers are protected
Protection of the public in areas where X-rays are present
What does a quality assurance program include?
Policies and procedures
Education and training
Departmental guidelines
Radiation safety
Preventative maintenance
Quality control
What are the levels of QC testing and who completes which?
Noninvasive/simple: technologist
Noninvasive/complex: QC technologist
Invasive/complex: Engineer or physicist
When is acceptance testing performed? What is the purpose?
All new or repaired equipment, establish a baseline for future QC
When is routine testing performed? What is the purpose?
After a predetermined amount of time has elapsed, diagnose any changes in performance before an issue presents itself
What is quality management?
The act of overseeing all activities and tasks needed to maintain a desired level of excellence
The responsibilities of which personnel are outlined in SC35? (7)
Owner
User
Operator
Medical physicist/radiation safety officer
Referring physician
Information systems specialist
Repair & maintenance personnel
What are the medical physicist/radiation safety officers responsibilities?
Establish safe working conditions
Ensure procedures are being followed
Perform routine checks on equipment
Record radiation surveys
What are the referring physician/practitioner’s responsibilities?
Ensure imaging is justified
Use experience, judgement and common sense
Consider alternative options (MRI, US)
What is the annual body dose limit for the technologist?
20 mSv
What is the annual body dose limit for the public?
1 mSv
What is the annual eye dose limit for the technologist?
150 mSv
What is the annual skin dose limit for the technologist?
500 mSv
What is the annual hand dose limit for the technologist?
500 mSv
What is the annual organ dose limit for the technologist?
500 mSv
What is the annual organ dose limit for the public?
50 mSv
What is the annual eye dose limit for the public?
15 mSv
Precision vs accuracy
Precision: consistency to create the same results after multiple tests
Accuracy: ability to measure what is meant to be measured
3 parts of a QC program for radiographic equipment
Visual inspection
Environmental inspection
Performance testing
What are the daily visual inspection tasks?
Look for loose or broken components
Cleanliness
Check for vibration or motion
What are the weekly visual inspection tasks?
Look for dust and dirt in reception area
CR and laser scanning digitizer
DR and fluoroscopic systems
What is included in an environmental inspection?
Mechanical and electrical safety
Cable coverings
Equipment grounding
Tube lubrication
What is the SC35 equipment warmup recommendation?
Follow manufacturers recommendation
Repeat warm-up after an extended period of time with no imaging
What type of detectors are used in QC radiation measurment?
Ion chamber
Proportional counter
Geiger-muller counter
What does an ion chamber do?
Measures ion pairs created within a gas caused by incident radiation
What voltage are ion chambers used?
100-300V
What is kVp accuracy?
Determining any variation between stated kVp and actual kVp
What can cause discrepancies in kVp?
Line voltage
Faulty cables
Tungsten vaporization
Autotransformer issue
kVp selection circuitry
kVp accuracy acceptance limit SC35
±10%
kVp accuracy testing frequency SC35
Annual
What is HVL?
The amount of filtration needed to reduce the exposure by 50%
With no filtration, skin dose can increase by __%
90%
How is HVL tested?
Exposures are made at 70 kVp
1mm aluminum filters are gradually added until until exposure is halved
SC35 HVL acceptance limit
2.5mmAL or more at 70 kVp
SC35 HVL testing frequency
Annual
What is reproducibility of exposure?
Ability of a radiographic unit to produce the same exposure throughout a short period
SC35 reproducibility of exposure limits
Coefficient of variation within 0.05
Of 10 measurements, none may differ more than 15% of the mean
SC35 reproducibility of exposure testing frequency
Annual
What is mAs linearity?
Production of a constant amount of radiation for different combinations of mA and time
How is mAs linearity testing performed?
Several exposures are taken with increasing mAs and compared to the previous
SC35 mAs linearity acceptance limits
Adjacent exposures must not differ by more than 10% of their sum
SC35 mAs linearity testing frequency
Annual
SC35 timer accuracy
Must automatically terminate if a predetermined amount of x-ray pulses have been detected
Operator must be able to terminate at any time
Must automatically reset to zero if exposure is terminated
Irradiation is not possible at zero, off or unmarked settings
SC35 AEC consistency with varying kVp acceptance limit
0.15 variation in optical density
SC35 AEC consistency with varying part thickness acceptance limit
0.2 variation in optical density
SC35 AEC reproducibility acceptance limit
0.10 variation in optical density
SC35 collimation acceptance limit
Misalignment within ±2%
Size of field within 3% of SID
Total misalignment must not exceed 4% of SID
SC35 light field/radiation field alignment acceptance limits
±2% of SID
SC35 Image receptor / radiation field alignment acceptance limit
Within 3% of SID
SC35 Beam perpendicularity acceptance limits
Within 2% of SID
What is focal spot blooming?
The increase in focal spot size with age, use and high mA station use
What does focal spot size determine?
Spatial resolution and detail
What QC tests evaluate focal spot blooming?
pinhole camera
focal spot test tool
Lead aprons must me what thickness at 100 kV or less, 100 to 150 kV and 150 kV or more
>100: 0.25mmPb
100-150: 0.35mmPb
150+: 0.5mmPb
How often should lead be inspected?
Annually
SC35 lead defect acceptance limits
Total defect area greater than 670mm2
Defect in the thyroid or gonad area greater than 5mm in diameter
What should lead thickness be in interventional procedures?
0.5mm Pb in the front
0.25mm Pb in the back
Thyroid shield Pb thickness
0.5 mm
Gonadal shield thickness
minimum 0.25mm
minimum 0.50mm at 150 kV
Lead glove thickness
0.25mm Pb
Rolly shield thickness
0.50mm Pb
SC35 recommended repeat rate
Less than 5%
Bit depth
Number of bits in a pixel = shades of grey
Bit depth formula
2^n
(n=number of bits)
How are electronic display devices tested?
SMPTE test pattern or AAMP TG-18-QC test pattern
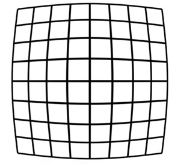
What type of distortion is this?
Barrel
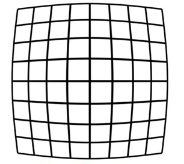
What type of distortion is this?
Pincushion
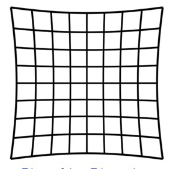

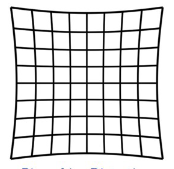
What is this?
AAPM TG-18 test pattern

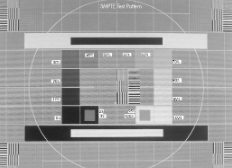
What is this?
SMPTE test pattern
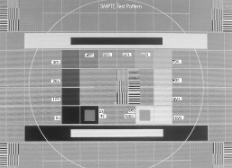
At what distance should test patterns be viewed?
30 cm
How often should an imaging plate be cleaned?
Monthly