5.2 - Marshallian externalities & multiple equilibria
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Marshallian externalities
Local positive externalities that increase with size of industry
Lead to geographical agglomeration
Local knowledge spillovers
Input-output linkages
L market pooling etc
Static model - can switch equilibria with out any fundamental changes
Dynamic CA changes fundamentals
Marshallian externalities (ME) model - Harrison & Rodriguez-clare (2010) - Assumptions
Small open economy
2 sectors & 1 FofP (L)
Sector 1 has constant RtS (& no externalities)
Sector 2 has ME (constant RtS at firm level but L can have increasing productivity)
Marshallian externalities (ME) model - Harrison & Rodriguez-clare (2010) - Results
Under certain conditions, multiple equilibria arise
Equilibria in complete specialisation in 2 superior to 1
Economy has latent advantage in 2 but due to coordination failures it fails to exploit it (specialises in 1)
As externalities take time to realise, countries may have dynamic CA in sector not currently specialised in
may justify protection / IIP - policy can swap it to new CA without any fundamental changes
Marshallian externalities (ME) model - Harrison & Rodriguez-clare (2010) - maths
1: L produces λ1 units of 1
2: L produces λ2(1+αMin(Lbar,L2)
externalities increasing with employment but exhausted when L in sector teaches Lbar
θ ≡ 1 + αLbar > 1 = max benefits from clustering in 2 1 + α = max benefits
If L2 > Lbar the max level of productivity = θλ2
p* is world price of good 2 p*=p*2 / p*1
Marshallian externalities (ME) model - Harrison & Rodriguez-clare (2010) - specialisation in good 1
wage = λ1p*1 if specialised in good 1
unit cost of producing 2 (with no cluster benefits) = w/λ2 = p*
Hence, complete specialisation in good 1 is an equilibrium if and only if p* <= λ1/ λ2
p*=p*2 / p*1 = (w/λ2) / (w/λ1) = λ1/ λ2
Marshallian externalities (ME) model - Harrison & Rodriguez-clare (2010) - specialisation in good 2
wage = λ2p*2θ
Hence, complete specialisation in good 2 is an equilibrium if and only if θp* >= λ1/ λ2
p*=p*2 / p*1 = (w/θλ2) / (w/λ1) = λ1/θλ2
Marshallian externalities (ME) model - Harrison & Rodriguez-clare (2010) - multiple equilibria
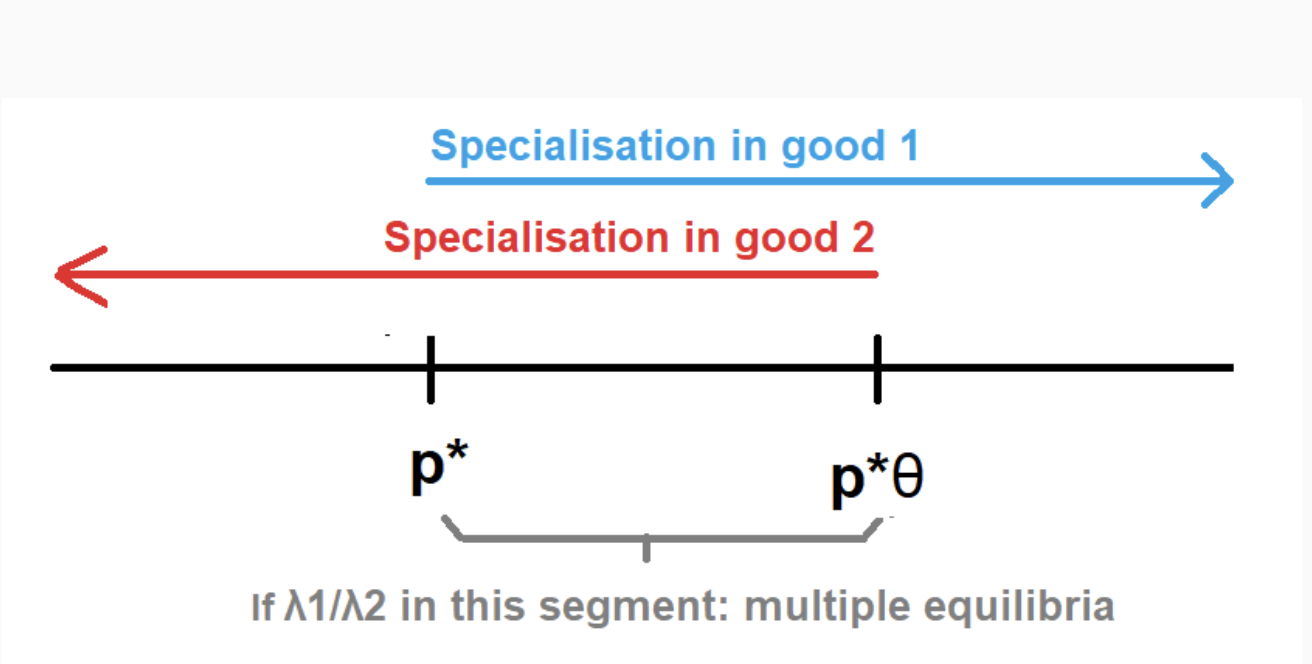
There is multiple equilibria if and only if:
p* <= λ1/ λ2 <= θp* CONDITION 1
θ > 1 as α > 0 & θ = 1 + α
If no externalities then p* only equilibrium
Marshallian externalities (ME) model - Harrison & Rodriguez-clare (2010) - multiple equilibria graph
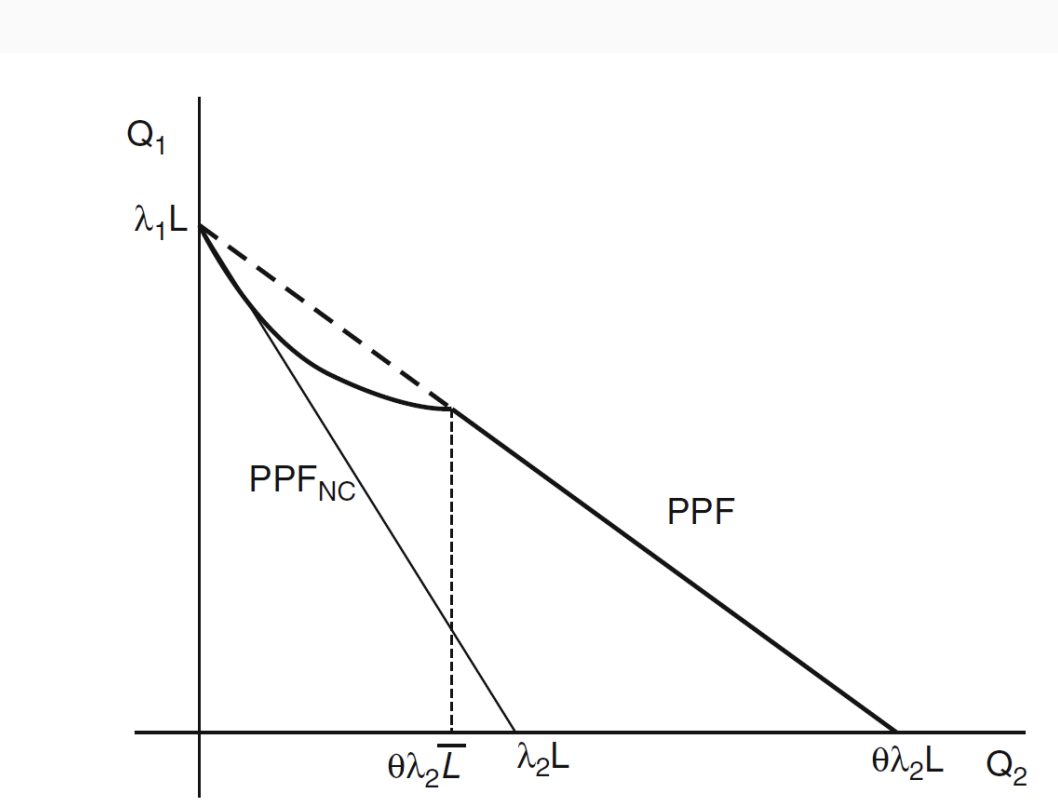
θ = λL (determined by L assigned to each sector)
Externality causes line to turn as L increase = externality UP = Productivity UP
Turns until limit of Lbar then back to linear PPF with 1 factor
Marshallian externalities (ME) model - Harrison & Rodriguez-clare (2010) - wages in multiple equilibria
If complete specialisation in 1: w = λ1p*1
2: w = λ2p*2θ
Therefore if condition 1 satisfied then w2 > w1
Marshallian externalities (ME) model - Harrison & Rodriguez-clare (2010) - latent CA (LCA)
LCA in good i if: OC of this good when ME realised < pw
For good 1: λ2θ/ λ1 <= 1/p*
For good 2: λ1/ λ2θ <= p*
Specialisation may still occur in 1 as nation has static CA in it and so isnt realising all ME
Marshallian externalities (ME) model - Harrison & Rodriguez-clare (2010) - Using a tariff
By using a tariff, consumers only see modified p - may cause switch to better equilibrium → Welfare rises
If p2 price increased enough by t → OC of producing 1 high enough to switch specialisation to 2
p = p*t2 = p*2t2 / p*1 > p*
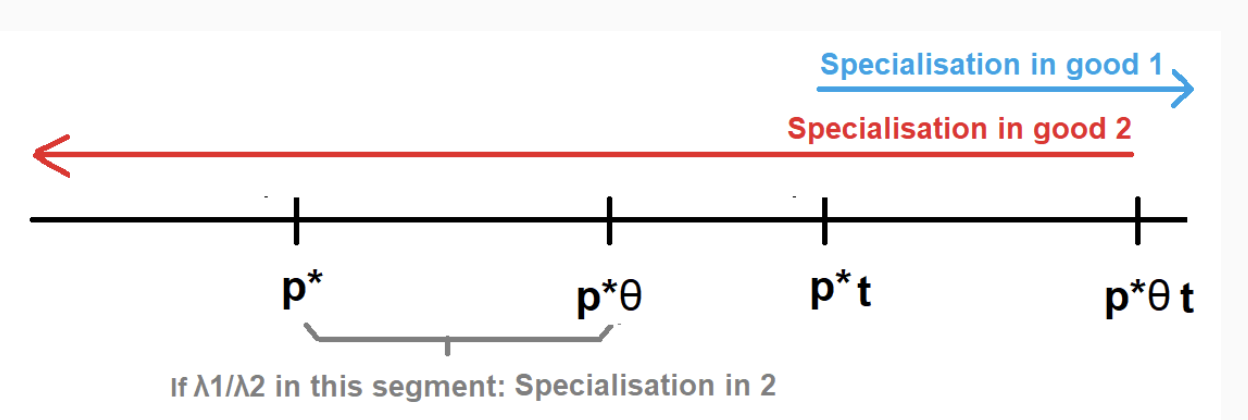
Once economy has switched specialisation then tariff can be removed
Marshallian externalities (ME) model - Harrison & Rodriguez-clare (2010) - Endogenous prices
Previously we have assumed p* is exogenous - in reality p* is determined by RoW productivity
Rich nations already enjoy lower costs of cluster in 2
lower costs shown by p*
For developing nation to have LCA in 2 it must have deep parameters to sustain advantage
α & Lbar need to be higher than in developed
Large developing can realise more ME as shift moreL
Technology affects α but unlikely to only affect developing
Marshallian externalities (ME) model - Harrison & Rodriguez-clare (2010) - Endogenous prices implications on model
Assume 2 is K & H intensive relative to 1
Specialising in 1 = low levels of K&H + lower TFP
By shifting specialisation to 2 through policy, endogenous accumulation of K&H
Low K stock & TFP in developing caused by not exploiting LCA
Either cant exploit or not enough access to K market to exploit
Marshallian externalities (ME) model - Harrison & Rodriguez-clare (2010) - Dynamic externalities problem
Model is static not dynamic
With international knowledge spillovers we have to add conditions for specialisation transition from 1 → 2
took China 20-30yrs to realise gains
2 needs large externalities + improvement in productivity at fast pace
Faster change = more benefits & shorter protection
Protection losses < discounted gains
Marshallian externalities (ME) model - Harrison & Rodriguez-clare (2010) - Dynamic externalities problem & policy
Policy needs to shift resources quickly
OR a large enough externality underlying to get to new equilibrium quickly naturally
Marshallian externalities (ME) model - Harrison & Rodriguez-clare (2010) - Exceptionality
Does a policy to achieve LCA pass Mill test
if all economies protect some industry to achieve LCA then not optimal - even with productivity gains
Never reach frontier as efficient for producers to stop producing before CA level (p < p*)
Protection only passes Mill test only if nation has LCA in protected sector
China has LCA as largest economy of L in Manu
Realised the gains so other similar nation (india) cant overturn its realisation
India may have own LCA in tech but needs exceptionality to force switch in specialisation