HSE Module 4.3 Heat and Temperature Hazards
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Heat and Temperature Hazards
Operations with high potential of causing heat stress normally involve high temperatures, radiant heat sources, high humidity, direct physical contact with hot objects.
The American Conference of Government Industrial hygienists 1992 (ACGIH) states that workers should not be permitted to work when their deep body temperature exceeds 38º C.
Potential Heat Stress Operation
Iron and steel foundry
Electrical utilities (boiler room)
Bakeries, food canneries
Chemical plants
Construction, refining, asbestos removal
Hazardous waste site (require wearing impermeable protective clothing)
Temperature
The degree of hotness or coldness of a body or environment (corresponding to its molecular activity) that can be measured using a thermometer
Heat
A form of energy that can be transferred from one system to another system as a result of temperature difference (from high to low temperatures)
WET BULB GLOBE THERMOMETER (WBGT)
Most accurate measurement of heat hazards
Takes into account humidity, radiant heat and air temperature
Reading lower than regular thermometer
Testing should be done under normal working conditions as close to the works as possible
When our deep body temperature is between 20-27 degree C
Our body are in comfort zone.
We can perform our work at maximum efficiency
when temperature goes >27 degree C
We start to feel discomfort, irritate, lost concentration and efficiency in mental tasks
leading to mental problem
As the temperature goes even higher
we start losing efficiency in skilled tasks committing more errors causing more incidents…
Our body system starts to be dysfunctional leading to physiological problems such as fatigue and threat of exhaustion.
The maximum temperature tolerance is 35 to 40 degree C
Our body could not tolerate at this temperature, this conditions can lead to fatality.
Body Clues of High temperature
Lack of sweating
Hot Dry Skin
Headaches
Weakness
Dizziness
Nausea
No appetite
Short of breath vomiting
Factors affecting Heat Stress
Intensity of the heat
Duration of the exposure period
Tasks involved
Person performing the tasks
Presence of other stresses
Causal Factors:
Personal factor
Age, weight, degree of fitness, degree of acclimatization, metabolism, use of drug or alcohol, type of clothing worn, hypertension
Causal factors:
Environmental factor
Radiant heat, air movement, conduction, relative humidity
The severity at which a person will burn is based mainly on the depth to which the burn penetrates, which is dependent on:
Intensity of thermal energy transfer through
Radiation
Convection
Conduction
Absorptivity of the skin
Length of exposure
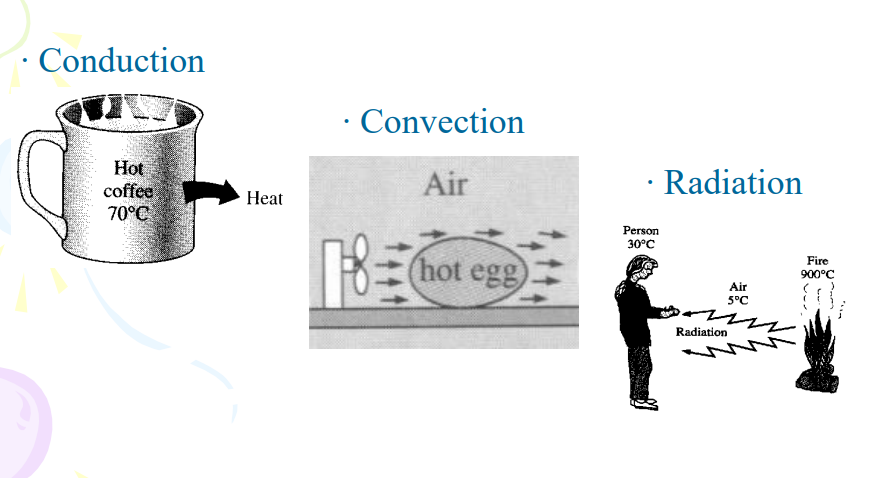
Heat Disorder and Health Effects:
Heat cramps
Involve muscular pains and spasms, cold sweating and vomiting. Generally, occurs due to a depletion of salt and potassium.
Action: Replenish the body’s salt and potassium supply orally. (Commercially produce liquids with proper quantity of salts, potassium, electrolytes and other elements)
Heat Disorder and Health Effects:
Heat Exhaustion
Next step after heat cramp. May lose the ability to stand erect. Water or salt depletion. Body becomes dehydrated.
Action: Move person to a cool, but not cold environment and allowed to rest lying down. Fluids should be taken slowly but steadily by mouth until the urine volume indicates that the body’s fluid level is once again in balance.
Heat Disorder and Health Effects:
Heat Stroke
More serious than heat cramps or exhaustion. patient will have a temperature of 105 degree F (40.5 degree C) or more, with corresponding hot skin, but it will be dryy, with no perspiration.
Action: Immediately reduce his or her body core temperature. Victim should be immersed in chilled water if facilities are available.
Controlling And Preventing Heat Stress
Engineering controls: ventilation, shielding, cooling fans etc
Work practice: provide plenty of drinking water, first aids training
Alternating work and rest periods
Acclimatization to the heat through short exposure
Employee education
Heat Stress Card: OSHA publication 3154
Classification of Burn Severities
Tolerance to burns:
the ability of a person to survive exposure to heat is governed by 2 factors:
Tolerance to pain
Heat-exposure level at which second-degree burns begin
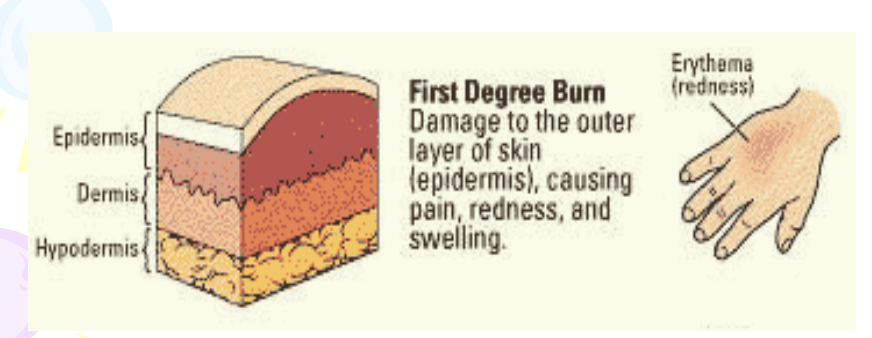
First-degree burn
Only cause a redness of the skin, which indicates a mild inflammation. The most common is sunburn. All are considered minor.
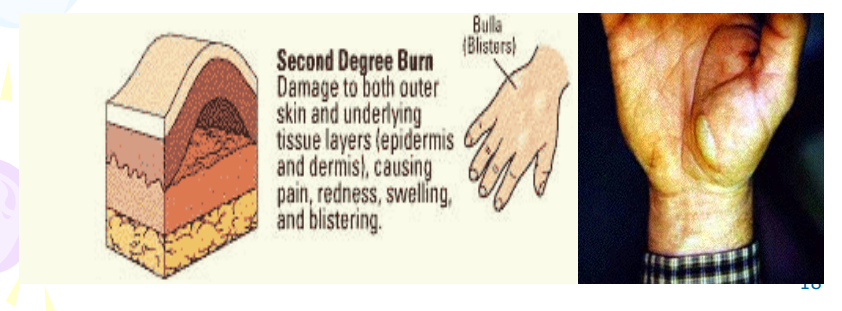
Second-degree burn
Blister of the skin will form, and in severe cases, fluid will collect under the skin. Sometimes more painful than 3rd degree based on nerve ending not damaged. Considered minor when only 15% of the body covered
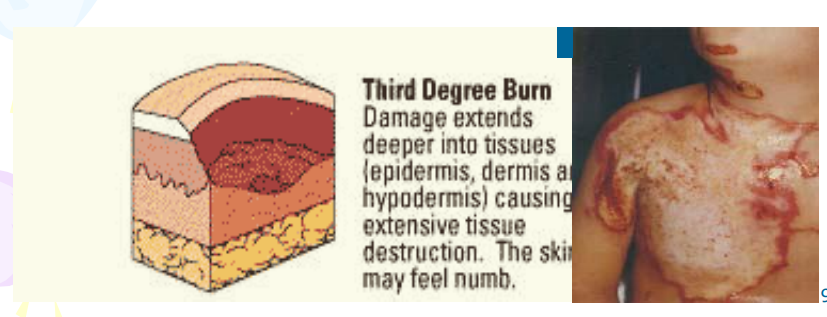
Third-degree burn
Burns the skin, subcutaneous tissue, red blood cells, capillaries, and sometimes muscle are destroyed. burned skin may be white, light gray, or even charred black. Considered minor when only 2% of the body is covered.
Treatment for first-degree burns:
Soak in cool water for a few minutes
Apply antibiotic ointment
Cover with clean, dry bandage
Take acetaminophen or ibuprofen
Treatment for second- degree burns
Soak in cool water for several minutes
Apply antibiotic ointment
Cover with non-stick bandage
Change your bandage daily
Take acetaminophen or ibuprofen
Treatment for third or fourth- degree burns
Seek immediate medical help
Elevate burned body part above heart
Seek medical attention if your burn is:
larger than 3 inches in diameter
Located on:
Face
Hands
Feet
Groin
Buttocks
Over a major joint