MMSC 407 - Vitamins
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
How are vitamins identified?
By letter, number to indicate dif forms
Fat-soluble vs. Water-soluble vitamins
Fat-soluble vitamins remain in system for longer, whereas water-soluble vitamins are shed in urine within 24 hours
Fat-Soluble vitamins
A, D, E, K
Dietary sources of Vitamin A
leafy green vegetables, orange/yellow vegetables, tomatoes, red bell pepper, cantaloupe, mango, beef liver, fish oils
Symptoms of vitamin A deficiency
Dry skin, dry eyes, night blindness, infertility, delayed growth (in children), poor wound healing, acne
In developing nations, where vit A deficiency is more severe (malnutrition), responsible for upper/lower respiratory infections
What is hypervitaminosis A?
Results from taking high-dose supplements over long periods of time - Vit A is a fat soluble vitamin so it is stored in the liver and can lead to toxicity and sxs (vision changes, bone swelling, mouth ulcers, confusion)
What vitamin should pregnant women avoid taking too much of?
Vitamin A
Recommended daily allowance (RDA) of vitamin A
Given as retinol activity equivalents to account for different bioactivities of retinol and provitamin A carotenoids (converted to retinol)
-14-51+: 900 (males) and 700 (females)
-14-18: 750mcg (pregnancy) and 1200 (lactation)
-19-50: 770mcg (pregnancy) and 1300 (lactation)
Vitamin A reference range
15 - 60 ug/dL
Chemistry of vitamin A
retinols, beta-carotene
Chemistry of Vitamin E
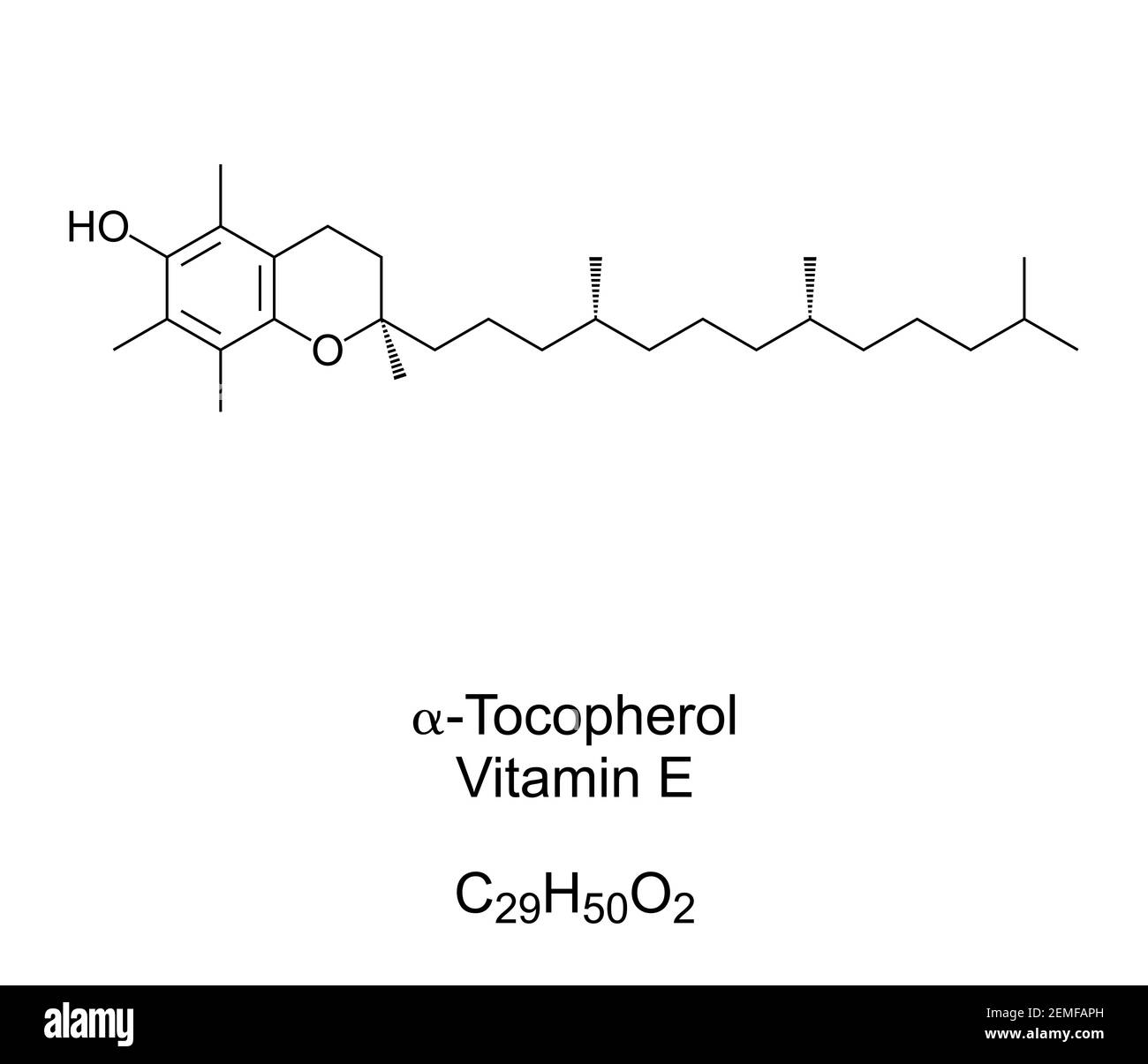
alpha-tocopherol is the only form of vit E used by the human body (easily absorbed into skin)
Main role of alpha-tocopherol (vit E)
Act as an antioxidant, scavenging free radicals that can damage cells
Dietary sources of Vitamin E
Best natural sources of vit E: Vegetable oils (wheat germ, sunflower, and safflower oils are the best source of vit E), Nuts (esp. Almonds), seeds
Provide some vit E: Green vegetables, added to breakfast cereals, fruit juices, margarines
Causes of vitamin E deficiency
Rare in healthy people; Commonly linked to certain diseases in which fat is not properly digested or absorbed (Crohn's disease, cystic fibrosis, AVED) - Vit E needs some fat for the digestive system to absorb it
Symptoms of vitamin E deficiency
Nerve and muscle damage, loss of body movement control, muscle weakness, vision problems, weakened immune system
Vitamin E toxicity
Relatively large amounts of vit E are usually not harmful, but may cause muscle weakness, fatigue, nausea, and diarrhea. The most significant risk is bleeding (doses of >1000 mg/day)
Reference range of vitamin E
Adult: 5.5-17ug/mL
Children: 3-18.4 ug/mL
Two forms of vitamin K
Phylloquinone (green leafy vegetables)
Menaquinones (some animal foods and fermented foods; also produced by bacteria in the body)
Major role of Vitamin K
Key role in coagulation (prevents excessive bleeding)
Also has roles in bone development and cardiovascular health
Vitamin K toxicity
Vit K toxicity is extremely rare; Only reported toxicity comes from menadione (nutritional supplement in animal feed - humans should not be consuming this). Sxs of vit K toxicity include jaundice, hyperbilirubinemia, hemolytic anemia, and kernicterus in infants
Vitamin K deficiency leads to...
Significant bleeding, poor bone development, osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease
Vitamin K reference range
0.2-3.2 ng/mL - BUT impaired blood clotting has been associated with levels below 0.5 ng/mL
Common name of vitamin B1
Thiamine
How does thiamine enter the body?
Thiamine is absorbed in the blood from the GI tract
_________________
Chemistry of Vit B1
Pyrophosphate groups
Dietary sources of vitamin B1
Fortified breakfast cereals, pork, fish, beans/lentils, green peas, enriched cereals/breads/noodles/rice, sunflower seeds, yogurt
Role of vitamin B1
Helps the body's cells change carbohydrates into energy; Role in muscle contraction and conduction of nerve signals
RDA for thiamine (vit B1)
RDA thiamine for men over 19: 1.2 mg daily
RDA thiamine for women over 19: 1.1 mg daily
Pregnant and lactating women: 1.4 mg daily
Symptoms of thiamine deficiency
Early (vague) symptoms - Fatigue, irritability, poor memory, loss of appetite, sleep disturbances, abdominal discomfort, weight loss
Severe thiamine deficiency (beri-beri) - Nerve, heart, and brain abnormalities. Wet beri-beri: cardiovascular sxs; Dry beri-beri: Nervous system sxs
Vitamin B1 toxicity
Unlikely to reach a toxic level of B1 from food alone (because it is water-soluble). The body will absorb less of the nutrient and flush out any excess through urine
No levels of thiamine have been established for toxicity
Laboratory assessment of vitamin B1
No toxicity established, so this is not done often
The biologically active form of B1 (thiamine pyrophosphate) is best measured in whole blood (EDTA). Reflects intake
** The test offered by LabCorp has not yet been cleared or approved by the FDA
Common name vitamin B2
Riboflavin
Role of riboflavin
Helps to maintain normal levels of homocysteine
What does riboflavin look like when exposed to UV light?
Riboflavin will turn yellow, naturally fluorescent
Exposure to UV light inactivates riboflavin - Lengthy light therapy to treat jaundice in newborns or skin disorders can lead to riboflavin deficiency
Sources of vitamin b2
90% of dietary riboflavin is in the form of FAD or FMN
Where is riboflavin absorbed and stored?
Absorbed in proximal small intestine
Stored in liver, hearts, and kidneys (excess excreted in urine)
Where is riboflavin produced in the body?
Bacteria in the large intestine produce riboflavin ______________-
Dietary sources of Vit B2
Eggs, organ meats (kidney/liver), lean meats, milk, some vegetables, grains and cereals are fortified with riboflavin
In most foods is in the form of FAD (although the main form in eggs and milk is free riboflavin)
What is a stable and sensitive measure of riboflavin deficiency?
Erythrocyte glutathione reductase activity coefficient (EGRAC) - Based on ratio between this enzymes in vitro activity in the presence of FAD to that without added FAD
What value of EGRAC indicates adequate riboflavin status?
< 1.2 is adequate
1.2-1.4 is marginal deficiency
>1.4 indicates riboflavin deficiency
Fluorometric measurement of urinary excretion to measure riboflavin
Fluorometric measurement of urinary excretion over 24 hours (total amount of riboflavin excreted) - Typically reflects dietary intake
Healthy adult riboflavin secretion ____________--
RDA riboflavin
Not very different for males and females until older age (1.3 mg males; 1.1 mg females); Increases with age; More required during pregnancy
For babies, we cannot overload with B2
Function of vitamin B6
Coenzyme in more than 100 reactions; Mostly concerned with protein metabolism
PLP and PMP are involved in amino acid metabolism
PLP is involved in __________
-Structure Identifier: “N” in the ring structure
Average vit B6 intake
Men: 2 mg/day
Women: 1.5 mg/day
Dietary sources of vit B6
Chickpeas, tuna, salmon, potatoes, turkey, bananas, fortified cereals, many more!
With B6 provided in supplements, intake is often not enough to reach the appropriate level
What affects your ability to uptake vit B6?
Smoking (first or second hand); levels are lower in women than men, in underweight people, and in black than white
Vitamin B6 Deficiency
Uncommon; Usually associated with deficiencies in other B vitamins; Causes biochemical changes that become more obvious as deficiency progresses
Symptoms of severe vit B6 deficiency
Microcytic anemia, dermatitis with scaling on lips and cracks at corners of mouth, glossitis (swollen tongue), depression and confusion; weakened immune system
Infants (mod deficiency): Irritability, abnormally acute hearing, convulsive seizures
Causes of vit B6 deficiency
End-stage renal disease; kidney diseases; malabsorption syndromes
Common name for vit B12
Cyanocobalamin (Co+ in center of molecule - important)
"Cobalamins"
Why is B12 important?
Vit B12 is required for the development, myelination, and function of the CNS; healthy RBC formation; DNA synthesis
Cofactor for two enzymes (methionine synthase, L-methylmalonyl-CoA mutase)
RDAS for vit B12
Not many differences between genders; (2.4 mcg for men & women) Higher during pregnancy and lactation (2.6 for pregnant & 2.8 lactating)
Cannot give too much to infants
Dietary sources of vit B12
Beef liver (71% wow!), clams, nutritional yeast, salmon, tuna, milk, yogurt
Causes of vit B12 deficiency
Difficulty absorbing B12 from food, lack of intrinsic factor (pernicious anemia), GI surgery, prolonged use of certain medications
Clinical Manifestations of Vit B12 deficiency
Megaloblastic anemia (large, nucleated RBCs), low counts of WBCs/PLTs, glossitis, fatigue, palpitations, pale skin, dementia, weight loss, infertility
Pregnant women: Neural tube defects
RDA vitamin C for healthy adult nonsmokers (male vs female) and children
Males: 105.2 mg/day
Females: 83.6 mg/day
Reference Range: 0.6-2mgdL mg/day
What does vitamin C deficiency cause?
Scurvy
As vit C levels drop, collagen synthesis slows, connective tissues become weak causing petechiae, ecchymoses, purpura, joint pain. As scurvy worsens, you will eventually see depression and swollen, bleeding gums or loss of teeth. Increased bleeding may lead to iron deficiency anemia
Fatal if untreated
Groups at risk of vitamin C inadequacy
Smokers / subject to secondhand smoke
Infants fed with evaporated or boiled milk
Tolerable upper intake levels of vitamin C for adults
2000 mg
Name for vitamin B7
Biotin (vitamin H)
Major role of biotin
Cofactor for five carboxylases (catalyze steps in metabolism of fatty acids, glucose, and amino acids
Role in histone modifications, gene regulation, and cell signaling
RDAs vitamin B7 (healthy adults)
30mcg
Dietary sources of biotin
Beef liver, egg, salmon, pork chop, hamburger, sunflower seeds, sweet potato, almonds
What do high levels of biotin interfere with?
High intake of biotin (hair/skin/nail vitamins) may interfere with diagnostics assays that measure thyroid hormones or troponin tests to diagnose congestive heart failure (falsely normal or abnormal results)
Name for vitamin B9
Folic acid
Vit B9 molecule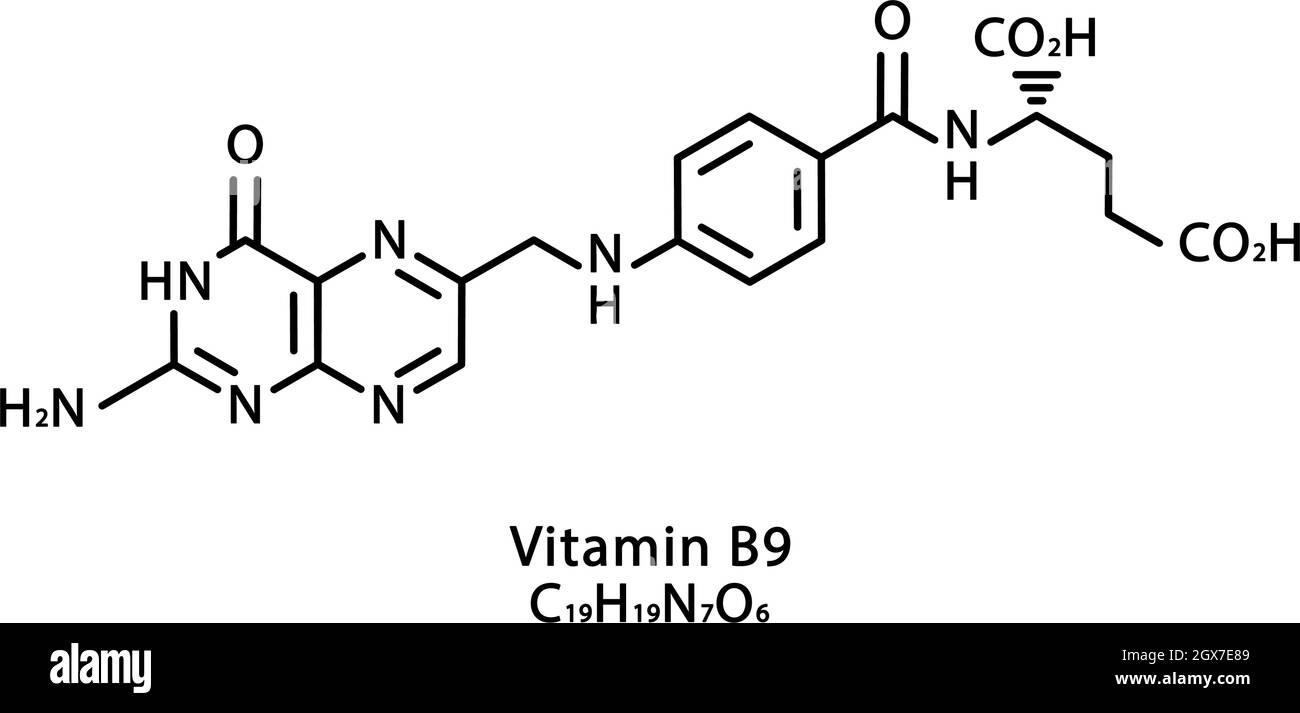
Very large; Variable R groups
Which form of vitamin B9 is absorbed better than from food sources and why?
Folate - Helps form DNA and RNA and is involved in protein metabolism. Folate is also needed to produce healthy RBCs and is critical during periods of rapid growth (pregnancy and fetal development)
Dietary sources of folic acid
Dark green leafy vegetables, beans, peanuts, sunflower seeds, fresh fruits, whole grains, liver, aquatic foods, eggs
Effect of alcoholism on folic acid
Alcoholism interferes with the absorption of folate and speeds the rate that folate breaks down and is excreted from the body
Effect of intestinal surgeries or digestive disorders that cause malabsorption
Anything that causes intestinal malabsorption will give problems with maintaining folate levels (celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease)
Effect of mutated MTHFR gene
With a mutated MTHFR gene, people cannot convert folate to its active form to be used by the body
RDA Folic Acid
mg of DFE (Dietary folate equivalents)
Adults: 400 mg DFE
Pregnant women: 600 mg DFE
Lactating women: 500 mg DFE
People who drink alcohol should aim for at least 600 mg DFE of folate daily since alcohol can impair its absorption
Name for vitamin B3
Niacin (nicotinic acid)
Function of niacin
All tissues (except skeletal muscle) in the body convert absorbed niacin into its main metabolically active form, coenzyme NAD. Many enzymes require NAD to catalyze reactions in the body. NAD is also converted into NADP
-More than 400 enzymes require NAD to catalyze reactions in the body,
What is the most sensitive and reliable measure of niacin status?
24 HOUR URINE
Urinary excretion of N1-methyl-nicotinamide and N1-methyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide
RDA niacin (adults)
Males: 16 mg NE
Females: 14 mg NE
Pregnant women: 18 mg NE
*Levels are same for male and female until puberty
Dietary sources of niacin
Beef liver, chicken breast, marinara sauce, turkey breast, salmon, tuna, pork tenderloin, ground beef, brown rice, peanuts, fortified breakfast cereals
Effects of niacin deficiency
Pellagra - Pigmented rash or brown discoloration on skin exposed to sunlight; The skin also develops a roughened, sunburned-like appearance; Bright red tongue and changes in the digestive tract leading to vomiting, constipation, or diarrhea
Neurological symptoms: Depression, apathy, loss of memory, aggression, paranoia, suicidal behaviors, auditory/visual hallucinations
Name for vitamin B5
Pantothenic Acid
Main function of pantothenic acid
Synthesis of coA (coA is essential for fatty acid synthesis and degradation) and acyl carrier protein (fatty acid synthesis)
What is the most reliable indicator of pantothenic acid? Normal values?
Urinary concentrations are reliable because they relate to dietary intake. With a typical American diet, the urinary excretion rate for pantothenic acid is 2.6 mg/day
-less than 1mg/day suggest deficiencies
RDA pantothenic acid
5 mg healthy adults
Pregnancy: 6 mg
Dietary sources of pantothenic acid
Beef liver, fortified breakfast cereals, shitake mushrooms, sunflower seeds, chicken breast, avocados, milk, potatoes, egg, greek yogurt
Proposed effect of vitamin B5 on hyperlipidemia
Because of B5's role in triglyceride synthesis and lipoprotein metabolism, experts have hypothesized that pantothenic acid supplementation might reduce lipid levels in patients with hyperlipidemia
Units of measurement for trace elements
ug/dL or mg/kg
What enzyme is required for transport and storage of reactive metal ions?
Metalloproteinase
Causes of deficiency of trace elements
Lack of absorption
Liver/bowel/renal disease
Catabolic responses to injury, infection, and disease
Innate trace element diseases we will test for in a newborn
Iron, copper, zinc, molybdenum, selenium, iodine
Where is chromium found in blood?
Bound to plasma protein - transferrin
Accumulates in liver, spleen, soft tissue, and bone
What is the best test method for chromium?
Urinalysis (per 24 hours)
Levels are related to recent chromium intake, NOT good indicators of chromium body stores
Cr levels can also be found in hair/nails
Adequate intakes (AIs) for chromium for adults
Males: 35 mcg
Females: 25 mcg
More during pregnancy and lactation
Dietary sources of chromium
Grape juice, ham, english muffin, brewer's yeast, orange juice
Role of chromium in metabolic syndrome
Studies have shown that if we give chromium supplements to patients with metabolic syndrome, they have shown benefits
Where do we get cobalt?
Cobalt must be supplied by diet
Which vitamin is cobalt a component of?
Vitamin B12
Major roles of cobalt
Cobalt is very important for forming amino acids and some proteins to create myelin sheath in nerve cells
Industrial exposure to cobalt
Cobalt is not highly toxic, but high doses will produce adverse clinical manifestations
Symptoms of high dose cobalt exposure
Contact dermatitis, respiratory sensitization, asthma, shortness of breath, decreased pulmonary function
Blood reference range for cobalt
< 10 nmol/L
(higher suggests environmental exposure or joint replacement)
Dietary sources of cobalt
Fish, nuts, green leafy vegetables, cereals (oats)