EBP Midterm Flashcards
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
Evidence based practice
Making a change in practice and evaluation of change for the patient, provider, and health care system. Quality, safety, and cost-effective outcomes.
Evidence Based practice
The use of best clinical evidence in making patient care decisions (combination of the best research evidence, clinical expertise, and patient values).
Evidence based Practice
The basis of nursing decisions —> Influences many recent clinical practice changes
Produces decisions that are clinically appropriate, cost effective, and result in positive client outcomes
NOT EBP
“one size fits all” approach to healthcare.
NOT EBP
A cost-cutting practice or method for rationing healthcare services.
Qualitative Research study
Dynamic design, holistic, context-bound, uses humans as instruments, qualitative information, seeks patterns.
Qualitative research Study
Goal: NOT hypothesis testing. Data is SUBJECTIVE. You can come up with your OWN theory.
Qualitative: Phenomenological
Seeks to understand and describe the universal essence of a phenomenon. Investigates everyday experiences of human beings while suspending the researchers’ preconceived assumptions about the phenomenon.
Example of Phenomenological
“how do cancer patients cope with a terminal diagnosis?”, “what are the experiences of long-term carers of family members with a serious illness or disability?”, ‘What is it like to survive a plane crash?”
Qualitative: Grounded theory
Method concerned with the generation/development of theory based on data. To study areas with little previous research. Create your own theory
Example of grounded theory
“the impact of technology on social interactions”, “the impact of poverty on health”, “the role of gender in academic performance”
Qualitative: Ethnographic
Holistic view of a culture. Research on social and behavioral sciences of cultures/societies.
Example of ethnographic
“shadowing a hospital floor to observe medical staff and how they deal with stress”, “researcher living and working with a community in an isolated village or tribe”, “observing a group of children playing”
Qualitative: Exploratory-descriptive
aims to explore and describe people’s experiences. Broad-ranging & systematic. To develop insight into clinical or practice problems.
Example of exploratory-descriptive
Examples: “studying the circumstances and contexts in which individuals experience loss”, ‘surveying patients who had a specific type of surgery to learn their feelings about the procedure, the doctor’s care, and their recovery”
Qualitative: Historical research
examining past events to draw conclusions and make predictions about the future. Studies past behavior, events, conditions.
Example of historical research
“examining the types of equipment used by nurses in another time period”, “studying field notes written by people who practiced as nurse midwives during the 1940s”.
Quantitative research
Orderly procedures, systematic/prespecified plan, control>context, formal measurement, empirical evidence, seeks generalizations
Quantitative: Descriptive
exploration and description of phenomena in real-life situations. New meaning discovered and description of concepts is established. Helps identify relationships.
Example of descriptive
how many calories do Americans consume per day?”, “what are the most important factors that influence the career choices of American university students?
Quantitative: Correlational
looks at relationship between 2+ variables. Determines strength and type of relationship. Explains what is seen. No cause and effect.
Quantitative: Correlational
“what is the relationship between respiratory symptoms and pain experiences in children and adolescents with sickle cell disease?”, “How does the placenta position in pregnancy contribute to risk of having a stillbirth?”
Quantitative: Quasi-experimental
examines cause and effect relationship. Less control by researcher than true experimental designs. Samples are NOT randomly selected. All variables in the study cannot be controlled by the researcher.
Example of quasi-experimental
One type is the control group pre-test post-test design: testing the effectiveness of an exercise intervention on nurses’ physical fitness using nurses from different units of a medical center, to be either an intervention group or a comparison group.
Quantitative; Experimental
controlled manipulation of at least one independent variable. Uses experimental and control groups. Random assignment of the sample to experimental and control groups. Highly controlled, objective, systematic studies.
Example of experimental
Example: testing an educational intervention to reduce the use of restraints in psychogeriatric nursing wards. Fifteen wards were randomly assigned to receive the intervention or not. In all, 120 nursing home residents were included in the analyses
Middle-range theory
a theory that focuses on a specific aspect of human experience (e.g., stress); more specific and more amenable to empirical testing.
Nursing theories and models: Examples of middle range theory
-Beck’s Theory of Postpartum Depression (2012)
-Mishel’s Uncertainty in Illness Theory (Mishel, 1990)
-Pender’s Health Promotion Model (2015)
Nursing theories and models: Practice theory
type of middle-range theory designed to propose specific approaches to particular nursing practice issues. Also called “prescriptive theories.” For example: “theory of heart failure self-care.”
Nursing theories and models: Conceptual model
more loosely structured than theories. Can serve as springboards for generating hypotheses. Abstractions assembled because of their relevance to a common theme. Provide a conceptual perspective on interrelated phenomena. Inductive approach.
Nursing theories and models: Roy’s adaptation model
a prominent nursing theory that views people as biopsychosocial beings who are constantly interacting with a changing environment
Nursing theories and models: Shared theories
explains a phenomenon specific to the discipline that developed the theory. Has a specific purpose or goal.
Examples of shared theories
· Bandura’s Social Cognitive Theory
· Prochaska’s Transtheoretical Model
· Becker’s Health Belief Model (HBM)
· Ajzen’s Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB)
19th century (1850)
Nursing research began in the ___ with Florence Nightingale
1851
she began her observations on nursing and healthcare in at the Kaiserswerth Deaconess home, Germany.
1853
Nightingale toured hospitals in France, Austria, and Italy.
1854-1856
During the Crimean war in ____: Nightingale used the battlefield hospitals as her research laboratory, where she conducted pioneering epidemiological research and statistical analysis. Her work established a link between health and environmental factors, such as fresh air, clean water, and sunlight. She also documented the relationship between the environment and health status of soldiers.
Grand theory
a theory that attempts to explain large aspects of human experiences.
Self-care deficit theory of nursing
Dorothy Orem: The goal is for individuals to initiate and perform self-care activities to maintain life, healthful functioning, and continual personal development.
Adaptation model
Sister Callista Roy: The goal is adaptation; a person’s adaptation level is constantly changing and is made up of focal, contextual, and residual stimuli.
Systems Model
Betty Neuman & Fawcett :This model is based on general systems theory and reflects the nature of living organisms as open systems that interact with each other and the environment.
Theory of Caring
Jean Watson: Human caring is a central process of life that influences health
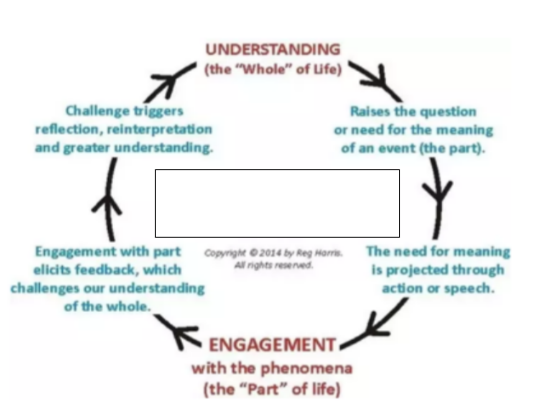
Hermeneutic Loop
is a process where you understand a text by constantly moving between the whole text and its individual parts. Your initial grasp of the entire text helps you interpret its parts, and understanding more parts improves your overall understanding. This back-and-forth process deepens comprehension.
Hermeneutic loop
Purpose of IRB
institutional review board is an administrative body established to protect the rights and welfare of human research subjects recruited to participate in research activities conducted under an affiliated institution.
IRB Functions
protection of rights and welfare, voluntary informed consent, benefits exceed risks.
Serves in IRB board
At least 5 members of varying backgrounds with experience and expertise in research.
Ethical principles: Respect for persons
- individuals should be treated as autonomous agents (self-determination in participation or withdrawing)
-persons with diminished autonomy are entitled to protection.
- Full disclosure, no deception, no coercion.
Ethical principles: __
Voluntary consent
Ethical principles; beneficience
-do not harm
- freedom from exploitation
-maximize possible benefits and minimize possible harms.
Ethical principles: Justice
"fairness in distribution" or "what is deserved.“ Even if the person chooses not to participate.
-to each person, an equal share
- to each person according to individual need
- to each person according to individual effort
-to each person according to societal contribution, and
-to each person according to merit
Ethical principles: Right to privacy
anonymity and confidentiality
Tuskegee Syphilis study
AA males were withheld treatment of syphilis. The U.S. Public Health Service (USPHS) Syphilis Study was conducted between 1932 and 1972 to observe the natural history of untreated syphilis. As part of the study, researchers did not collect informed consent from participants and they did not offer treatment, even after it was widely available.
All principles were violated (respect for persons, beneficence, justice)
Research subject’s rights
Right to self-determination
Right to privacy
Right to anonymity and confidentiality
Right to fair treatment
Right to protection from discomfort and harm
Children assent
Child’s affirmative agreement to participate in research. (7 years old or older) AND obtain permission from parents/guardians to participate in research. If child is less than 7 years old the assent is optional.
Framework
the abstract, theoretical basis for a study that enables the researcher to link the findings to nursing’s body of knowledge.
Theory
an integrated set of defined concepts and relational statements that present a view of phenomenon and can be used to describe, explain, predict, or control phenomena.
Hypothesis
a prediction that can be statistically tested and may be accepted or rejected. Prediction about the relationship of two or more variables.
Concept
Abstractly describe and name an object, idea, or phenomenon, thus providing it with a separate identity or meaning.
Associative Hypothesis
relationship between variables. When one variable changes, the other also changes.
Example of associative hypothesis
Ex: “children of overweight parents are more likely to be obese”.
Causal hypothesis
cause and effect relationship between variables.
Example of causal relationship
“after a diabetic education program, the patient will have: lower levels of hemoglobin A1c, greater knowledge about diabetes, fewer barriers to self-care, and greater self-efficacy”
Simple hypothesis
states the relationship (associate or causal) between 2 variables.
Example of simple hypothesis
“there is a direct relationship between the level of psychomotor coordination and the degree of self-esteem”.
Complex hypothesis
states the relationships (associative or causal) among 3 or more variables.
Example of complex hypothesis
“both men and women who participated in the CHIP (cardiac home information program) intervention would have lower levels of psychological distress, higher levels of physical functioning, and fewer adverse symptoms than women and men who did not participate in the program”.
Nondirectional hypothesis
relationship exists between variables, but the hypothesis does not predict the nature of the relationship.
Example of nondirectional relationship
“hours playing video games is related to body mass index in school-aged-children”
Directional hypothesis
the nature (positive or negative) of interaction between 2 or more variables is stated. Developed from theoretical framework, literature, or clinical practice. Uses terms such as positive, negative, increase, decrease, more, less, greater, higher, or lower.
Example of directional hypothesis
“parents will be more likely to misperceive the weight status of younger children”.
Null hypothesis
states there is no difference between variables; also called “statistical hypothesis”. Always non-directional.
Research hypothesis
states what the researcher thinks is true; there is a relationship between 2 or more variables. These are alternatives to the null hypothesis. (All hypotheses except the null are research hypotheses).
Basic research purpose
Generates and refines theory
Findings frequently not useful in practice
Includes lab investigations with animals or humans to promote further understanding of physiologic functioning, genetic, inheritable disorders, and pathological processes.
Example of basic research purpose
“Determining the effect of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise on pain-like behavior and NT-3 in an animal model of widespread pain"
Nursing research
Systematic inquiry to develop trustworthy evidence about issues of importance to nurses and their clients.
Nursing process
a systematic guide to client-centered care with 5 sequential steps. ADPIE.
Levels of research evidence
Informed consent
Essential information for consent.
Comprehension of consent information
Competence to give consent.
Voluntary consent
Essential information for informed consent
1. Introduction of research activities
2. Statement of research purpose
3. Selection of research subjects
4. Explanation of procedures
5. Description of risks and discomforts
6. Description of benefits
7. Disclosure of alternatives
8. Assurance of anonymity and confidentiality
9. Offer to answer questions
10. Voluntary participation
11. Option to withdraw
12. Consent to incomplete disclosure (deception sometimes necessary for human research)
The goal of QUAL research in EBP
To add on to previously studied research. To create new theories. NOT to test a hypothesis
initial step when developing a research study
IDENTIFY the research problem!!
Question
· Identifies relationships between variables and indicates the population to be studied.
· Narrower in focus than purpose and often specify only one or two research variables
Problem and purpose
· Should build on previous research
· Should influence nursing practice
· Promotes theory testing or development
· Addresses nursing research priorities
Feasibility
· Researcher expertise
· Money commitment/funding source
· Time commitment
· Availability of subjects, facilities, and equipment
· Ethical considerations
PICOT
Population of interest
Intervention or issue of interest
Comparison of interest
Outcome expected
Time needed for the intervention to achieve the outcome or the time in the course of disease/symptom that the intervention is applied
Inductive reasoning
moves from the specific to general; particular instances are observed and then combined into a larger whole or a general statement.
Examples of inductive reasoning
“a headache is an altered level of health that is stressful” “a terminal illness is an altered level of health that is stressful” Therefore; it can be induced that all altered levels of health are stressful.”
Deductive reasoning
moves from the general to the specific or from a general premise to a particular situation of conclusion.
Example of deductive reasoning
“All humans experience loss” “all adolescents are humans” Therefore it can be deducted that all adolescents
Independent variable
The stimulus or activity manipulated or varied by the research to cause an effect on dependent variables. The treatment or experimental variable. CAUSES the dependent variable to CHANGE. The independent variable does NOT change- the researcher controls it.
Dependent variable
The OUTCOME or response the researcher wants to predict or explain. Changes in the dependent variable are presumed to be caused by the independent variable.
Bracketing (qualitative research)
The process of identifying and holding in abeyance preconceived beliefs and opinions about the phenomenon under study. To reduce the influence of preconceptions on the research process. Set aside personal beliefs and assumptions.
Steps in QUANT studies
1
Identifying and understanding the nature of nursing phenomena and the relationships among the phenomena are examples of _______?
Description
Explanation
Prediction
Control
2
The beginning nurse researcher would like to investigate credible resources for implementing protocols in clinical practice. Which of the following would be considered empirical sources of nursing knowledge?
Reasoning, authority, and tradition
Quantitative, qualitative, and outcomes research
Care maps and protocols
Role modeling and trial and error
2
The nurse researcher is investigating outcomes research on nursing interventions. Which of the following examples would constitute outcomes research?
A comparison of two patient groups
Patient responses to nursing intervention
Patient tested before an intervention
A patient’s perception of the intervention
2
Tell whether the following statement is True or False.
Research findings increasingly must meet the test of being clinically significant, and medical practitioners have taken center stage in efforts to define clinical significance.
True
False
4
What is the best method of acquiring reliable knowledge on which to base a clinical practice?
Traditions and authority
Clinical experience and trial and error
Assembled information
Disciplined research
2
Tell whether the following statement is True or False.
Quantitative research attempts to identify a phenomenon.
a. True
b. False