The Evolution of Populations and Hardy-Weinberg Principle
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Darwin's Theory
Evolution based on genetic variation.
Mendelian Genetics
Supports Darwin's theory of evolution.
Discrete Characters
Classified on an either-or basis.
Quantitative Characters
Vary along a continuum within populations.
Microevolution
Change in allele frequencies over generations.
Point Mutations
Changes in one DNA base.
Chromosomal Mutations
Alterations in chromosome structure.
Sexual Recombination
Main contributor to genetic variation.
Crossing Over
Exchange of genetic material during meiosis.
Independent Assortment
Random distribution of chromosomes during meiosis.
Gene Pool
All alleles for all genes in a population.
Diploid Species
Have two alleles for each gene.
Fixed Allele
Only one allele present in a population.
Hardy-Weinberg Principle
Allele frequencies remain constant without evolution.

Equilibrium
Constant allele and genotype frequencies.
Hardy-Weinberg Conditions
No mutations, random mating, no selection.
Allele Frequencies
Proportions of alleles in a population.
Genotypic Frequencies
Proportions of different genotypes in a population.
p
Frequency of dominant allele.
q
Frequency of recessive allele.
p²
Frequency of homozygous dominant genotype.
2pq
Frequency of heterozygous genotype.
q²
Frequency of homozygous recessive genotype.
Calculating q
Square root of homozygous recessive individuals.
Founder Effect
Small group isolated from larger population.
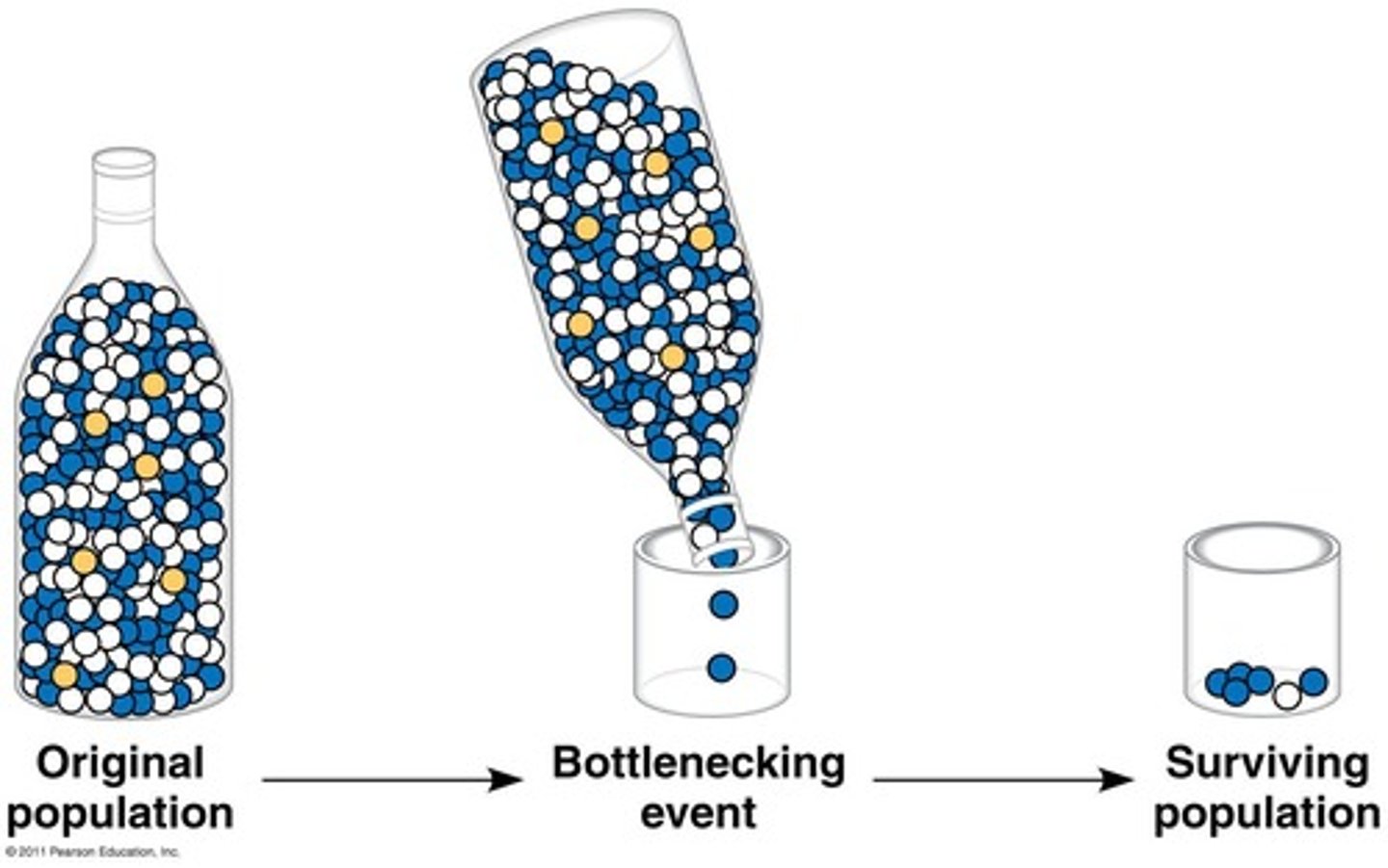
Bottleneck Effect
Population size drastically reduced by environmental change.
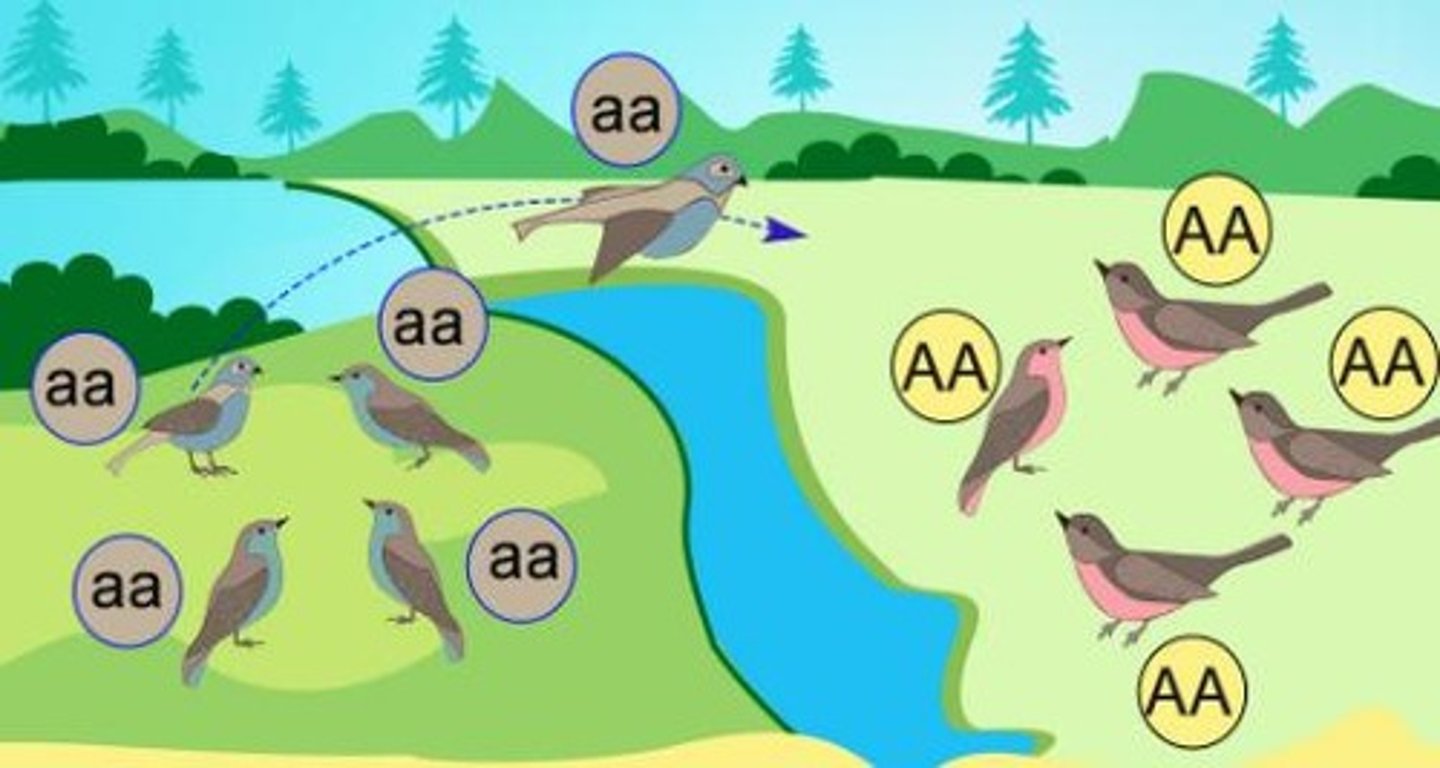
Gene Flow
Movement of individuals between populations.
Natural Selection
Survival of individuals with favorable traits.
Directional Selection
One extreme phenotype favored.
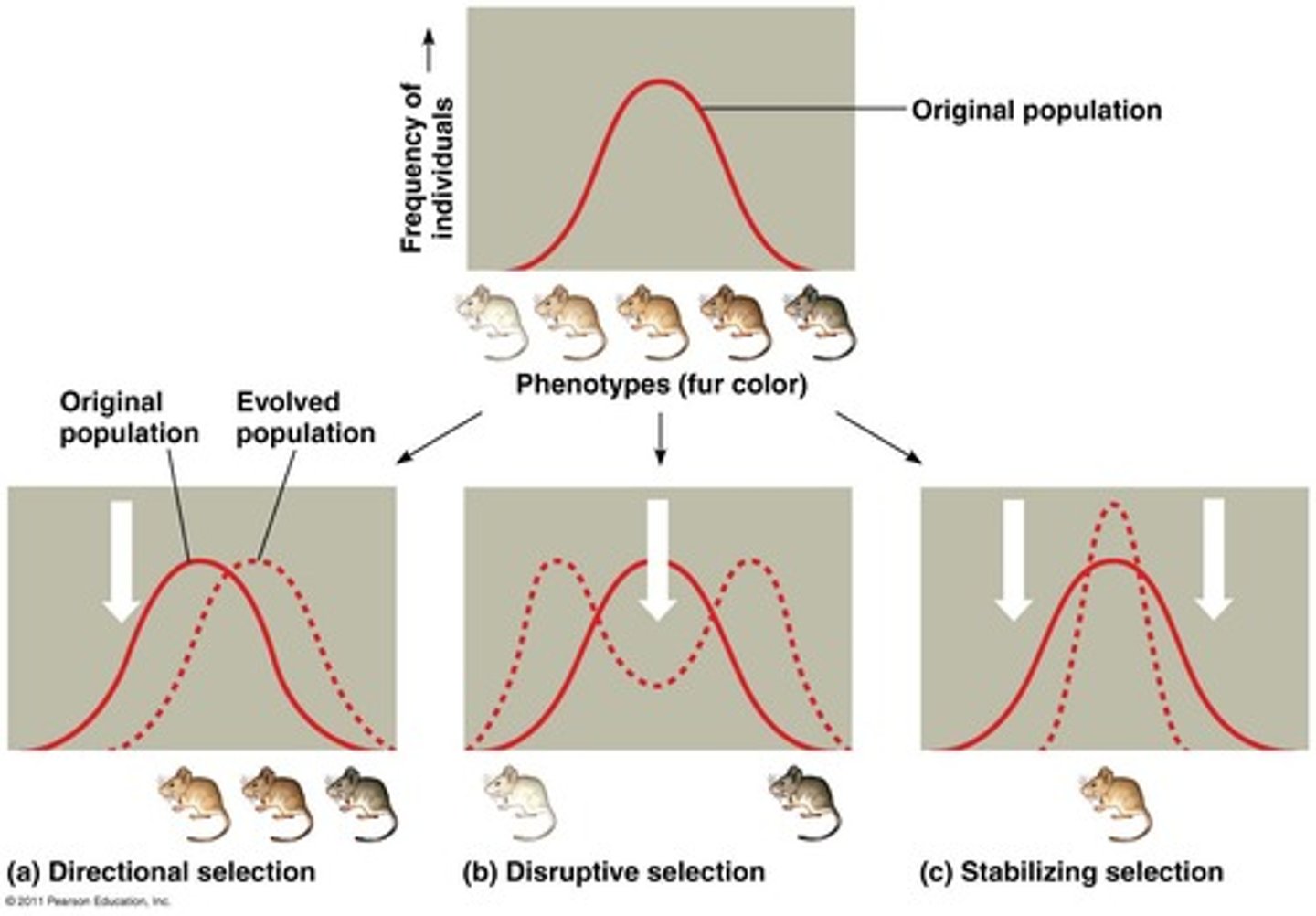
Disruptive Selection
Both extreme phenotypes favored.
Stabilizing Selection
Intermediate phenotype favored.
Sexual Selection
Individuals with certain traits more likely to mate.
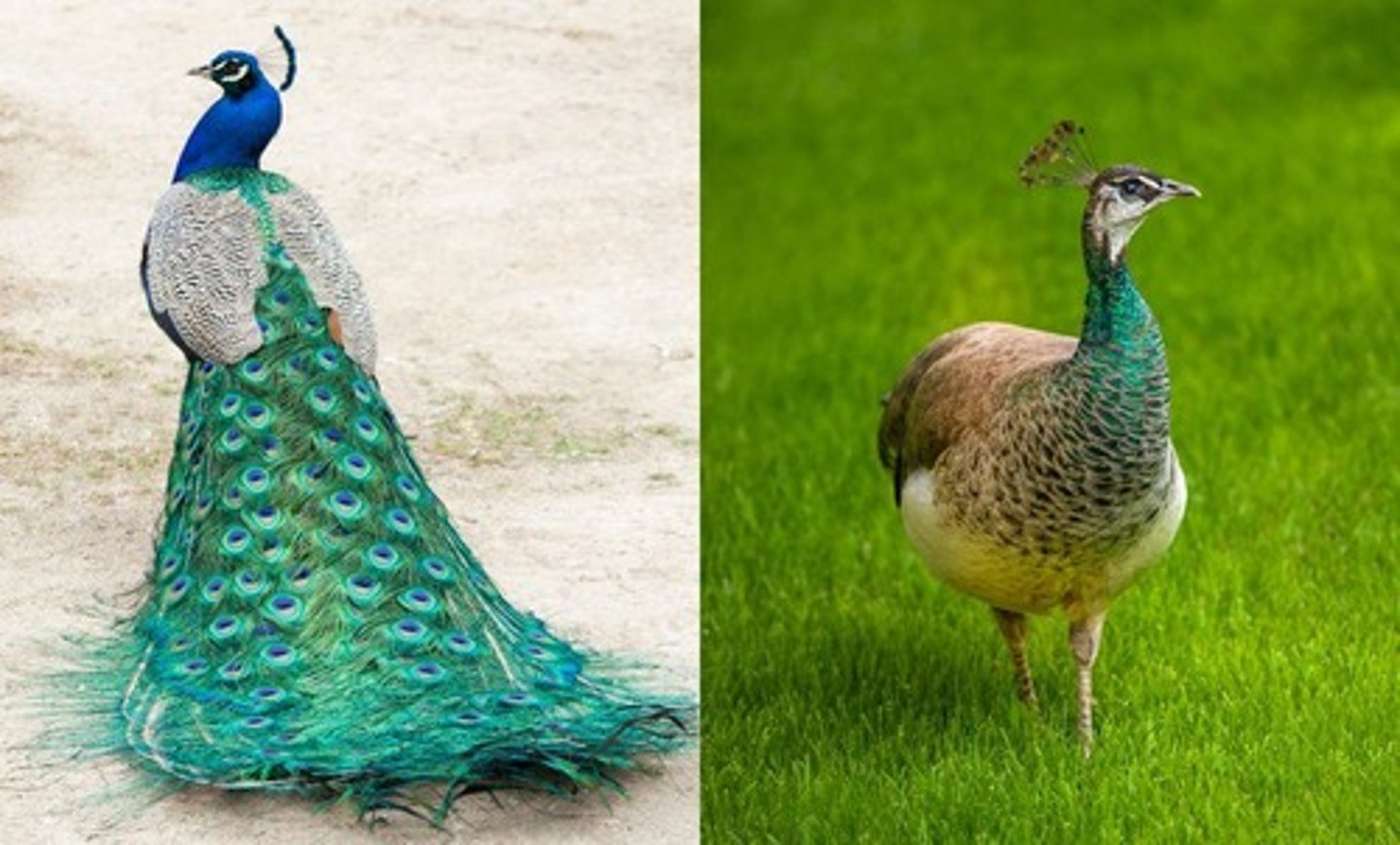
Sexual Dimorphism
Differences in appearance between sexes.

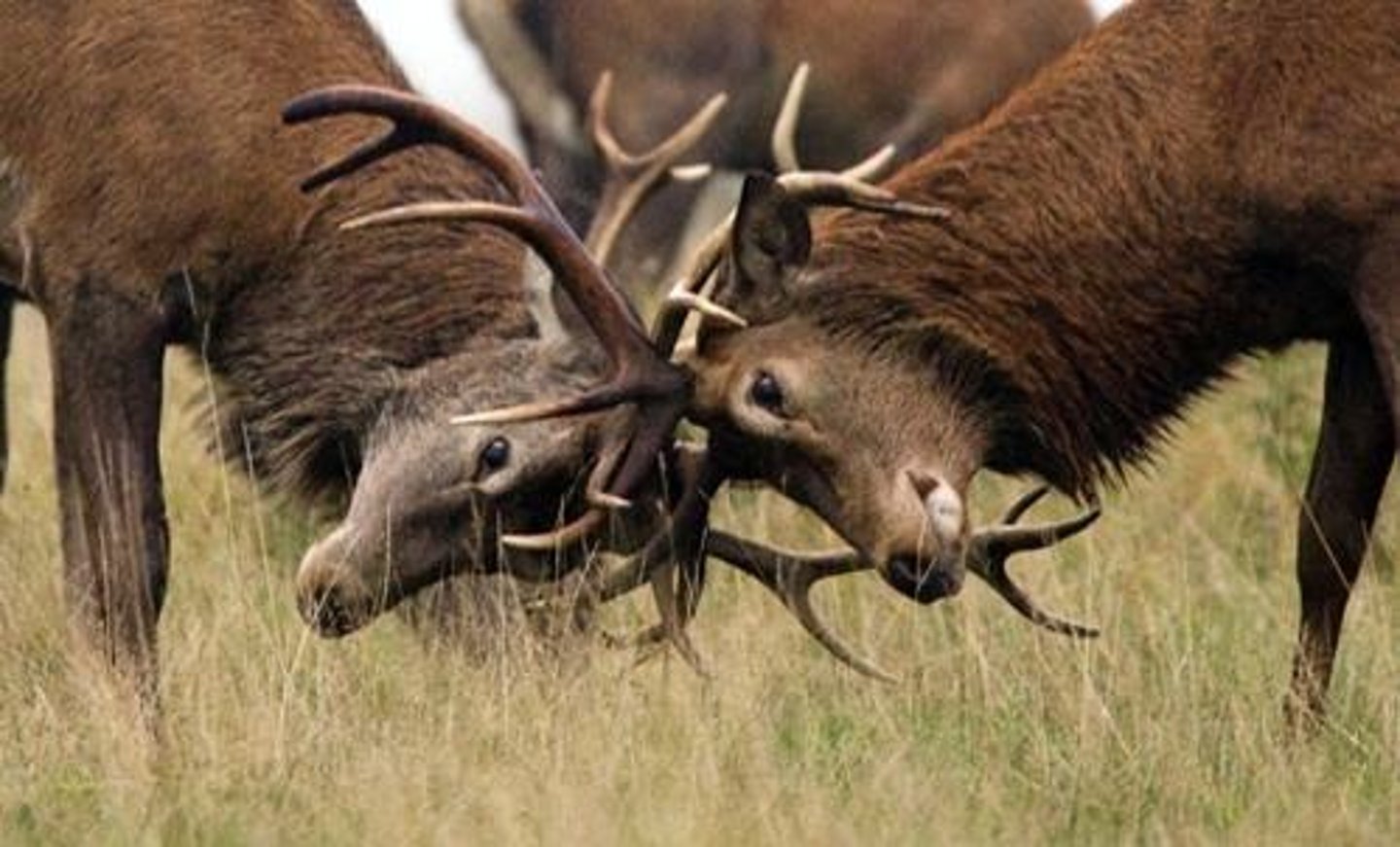
Intrasexual Selection
Competition within the same sex.

Intersexual Selection
Mate choice by the opposite sex.
Diploidy
Hides recessive alleles in heterozygotes.
Heterozygote Advantage
Higher fitness than homozygous individuals.
Historical Constraints
Evolution limited by past adaptations.
Genetic Variation Preservation
Maintaining diversity in a population.
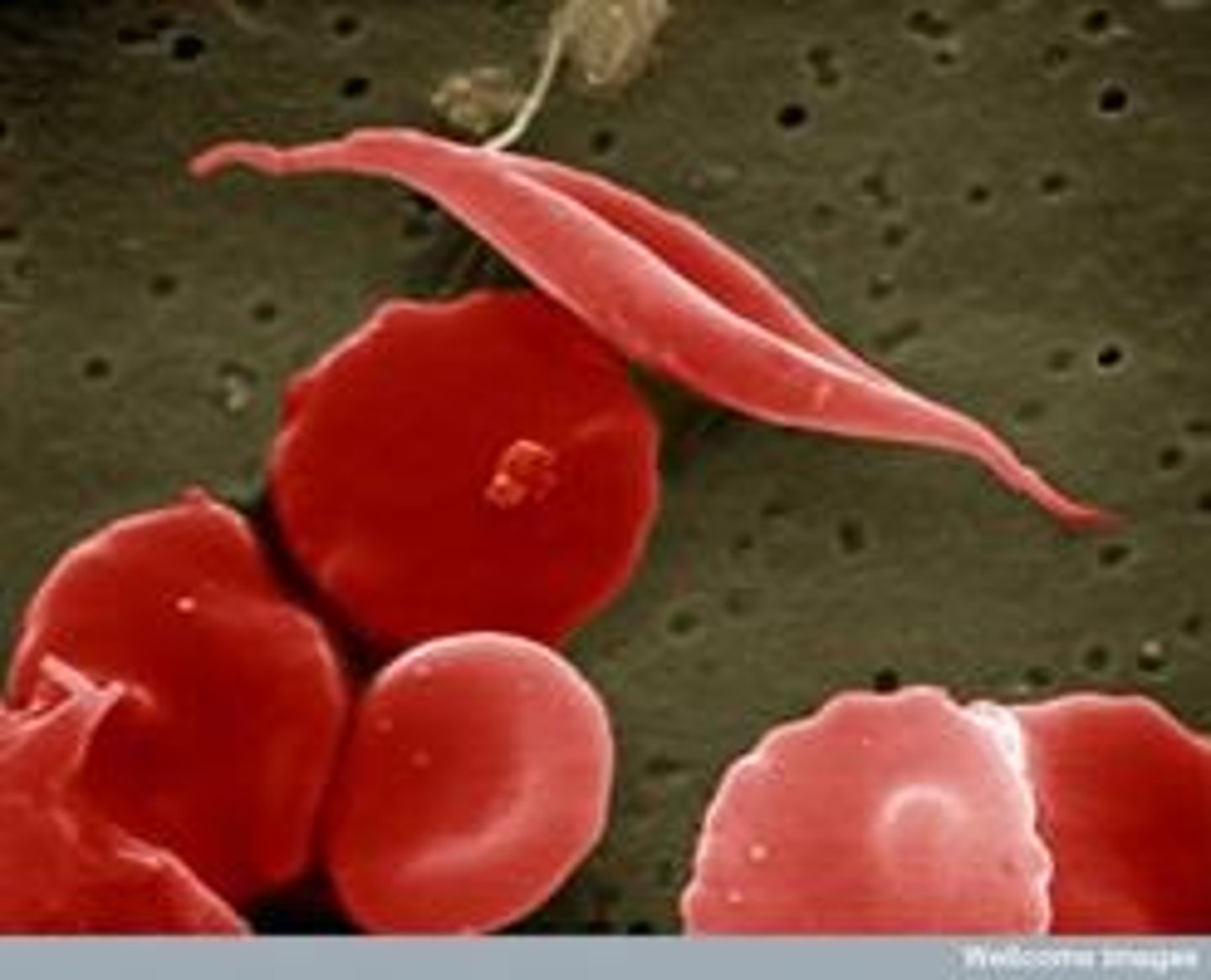
Sickle Cell Disease
Example of heterozygote advantage.
Genotype Frequencies Calculation
Using p and q to find frequencies.
Phenotypic Variation
Differences in observable traits among individuals.
Evolutionary Compromises
Adaptations often involve trade-offs.
Scarlet Moth Example
Calculate frequencies in a population of moths.
Albinism in Squirrels
Example of calculating allele frequencies.
Mice Population Example
Calculate genotype frequencies from given data.