Comprehensive Study Flashcards for Adults Exam 1 in Medicine
1/212
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
213 Terms
(assist levels) independent
no assistance from devices or staff
Assist levels: Modified Independent
utilizes adaptive equipment to complete task
(assist levels) set up
helper does not need to be physically present during task but must provide set up of equipment for successful completion. (Places all items for grooming visible on sink, opens containers when delivering meal tray)
(assist levels) supervision or standby assist
needs cues, encouragement to complete. verbal or demonstration, no physical assistance is provided. Used if there are safety concerns
(assist levels) close supervision
physically present in room, within visual regard at all times
(assist levels) distant supervision
within visual regard most of the time, may not be physically present in room by standing where the helper can hear the person
(assist levels) contact guard assist
hand is place on the person some to all of the time, sometimes CGA is holding the gait belt or clothing item
(assist levels) min assist
client completes 75-99% of the task, may be a large task or the component of a task
(assist levels) mod assist
client completes 50-74% of the task
(assist levels) max assist
client completes 25-49 % of the task
(assist levels) dependent
client completes less than 24% of the task or does not participate
(process) initial interview
develop occupational profile by reviewing hisotry, needs, values, goals
(process) activity analysis
essential skill for OTs to understand components and skill requirements of a task
what is the goal of an activity analysis
client independence, discharge
therapeutic grading
the modification of activity demands to reduce or increase the activity's challenge level
what is the purpose of therapeutic grading
promoting psychomotor learning and increase occupational performance (grading up and down)
activity adaptation
Modifying or substituting objects used in performing the activity. (How they are always going to do the activity or use a tool)
Ex: apply velcro fastener on a purse, color code files for quick ref., wear a walkman/ipod to drown out background noise.
considerations of activity adaptation
make the activity therapeutic
grade the exercise
enable performance for those with physical impairments
address activities with long term participation to prevent cumulative trauma
biomechanical approach
principles of kinetics and kinematics are applied to understand normal movement. Effective interventions include working on ROM, strength, and endurance.
rehabilitation approach
uses approaches of remediation, compensation, adaptation or a combination of these approaches.
Neurodevelopmental approach
Definition-emphasizes individualized therapeutic handling based on movement analysis for habilitation and rehabilitation of individuals with neurological pathology.
Task oriented approach:
emphasizes the dynamic interaction between the person, the environment, the occupational performance task, and role performance and it suggests that behavior emerges from this dynamic interaction.
Motor learning theory
takes into consideration how skilled actions are acquired, modified, retained, and transferred as the result of practice. It promotes skill acquisition and generalization of learning.
Pain assessments
mcgill pain questionnaire
body diagrams
rating scales
face, legs, activity, cry, consolability behavioral scale
functional outcome measures
DASH, UEFI, american shoulder and elbow form, patient related tennis elbow evaluation, patient related wrist/hand evaluation, michigan hand questionnaire, patient related ulnar nerve eval, carpal tunnel symptoms severity scale and functional scale, barthel
DASH is higher the score, the
greater the disability
UEFI is higher the score
greater the ability, less disability
edema assessment
circumferential, figure 8, or volumetric
end feel
the quality of the movement a person senses when pressure is applied passively to a joint at the end of its available range of motion
normal end feels
soft, firm, hard
abnormal end feels
empty, capsular, hard, springy block, muscle spasm
muscle length test
a provedure to asses the length or passive extensibility of a muscle
determined by the distance between the proximal and distal ends of the muscle
muscle strength test
procedure used to test the motor strength of certain muscle groups
special tests are used to
confirm or deny a hypothesis
special tests result in varying specificity and sensitivity - specificity means
How well a test identifies clients who do not have the condition and correctly shows up as negative on the special test; when the test is positive you can be confident the condition is present (rules in the condition)
special tests result in varying specificity and sensitivity - sensitivity means
How well a test identifies clients with the condition and correctly shows up as a positive on the special test; when the test is negative, you can be confident the condition is not present (rules out the condition)
semmes weinstein is a standardized assessment is good for
identifying compression injuries such as carpal tunnel
two point discrimination is a standardized assessment good for
assessing sensibility after nerve laceration
vascular assessments
allen's test, capillary refill, adson's test
allen's test
A test for the patency of the radial artery after insertion of an indwelling monitoring catheter
capillary refill test
Assessed by observing the repercussion of the nail bed after the blood has been forcibly squeezed out by pressure. The clinician compresses the fingertip for several seconds until the nail bed has blanched. The clinical observes the length of time it takes to refill the capillary bed. Normal is less than 3 seconds. Any time equal or greater than 3 seconds is considered abnormal. This test is done to look for different vascular diseases, dehydration, hypothermia, and shock.
adson's test
thoracic outlet syndrome
(EKG) atrial depolarization
electrical impulse travels through the atria
(EKG) PR interval
AV conduction time; impulse travels from the atria to the AV node, and down the. bundle branches, to where the ventricles contract
(EKG) QRS complex
ventricular depolarization
(EKG) T-Wave
ventricular repolarization
(EKG) ST segment
Represents early ventricular repolarization
Measured from end of S wave to beginning of T wave
tachycardia
heart rate over 100
bradycardia
slow heart rate (less than 60 bpm)
atrial fibrilation
irregularly irregular. rate varies and depends on the conduction rate. no identifiable P waves. Baseline shows fibrillartory waves.
role of OT: levels of care in acute care
ER, ICU, acute general care unit
role of OT: goals
Improve client's independence, prevent complications like bedsores or delirium, and prepare for discharge
impacts of extended bedrest
loss of muscle strength, joint cnotractures, and decreased functional independence
typical preparation for a treatment session
review chart for status changes, appropriateness for therapy
inpatient acute rehab
requires three hours of therapy a day
sub acute rehab
one to three hours of therapy a day
24 hr supervision
long term acute rehab
for less medically stable patients, long term care
day rehab
up to three hours of therapy a day in an outpatient setting
outpatient OT
safe at home, able to travel, community access
home health therapy
home bound patients receiving therapy at home
Foley Catheter
flexible plastic tube used to drain the urinary bladder
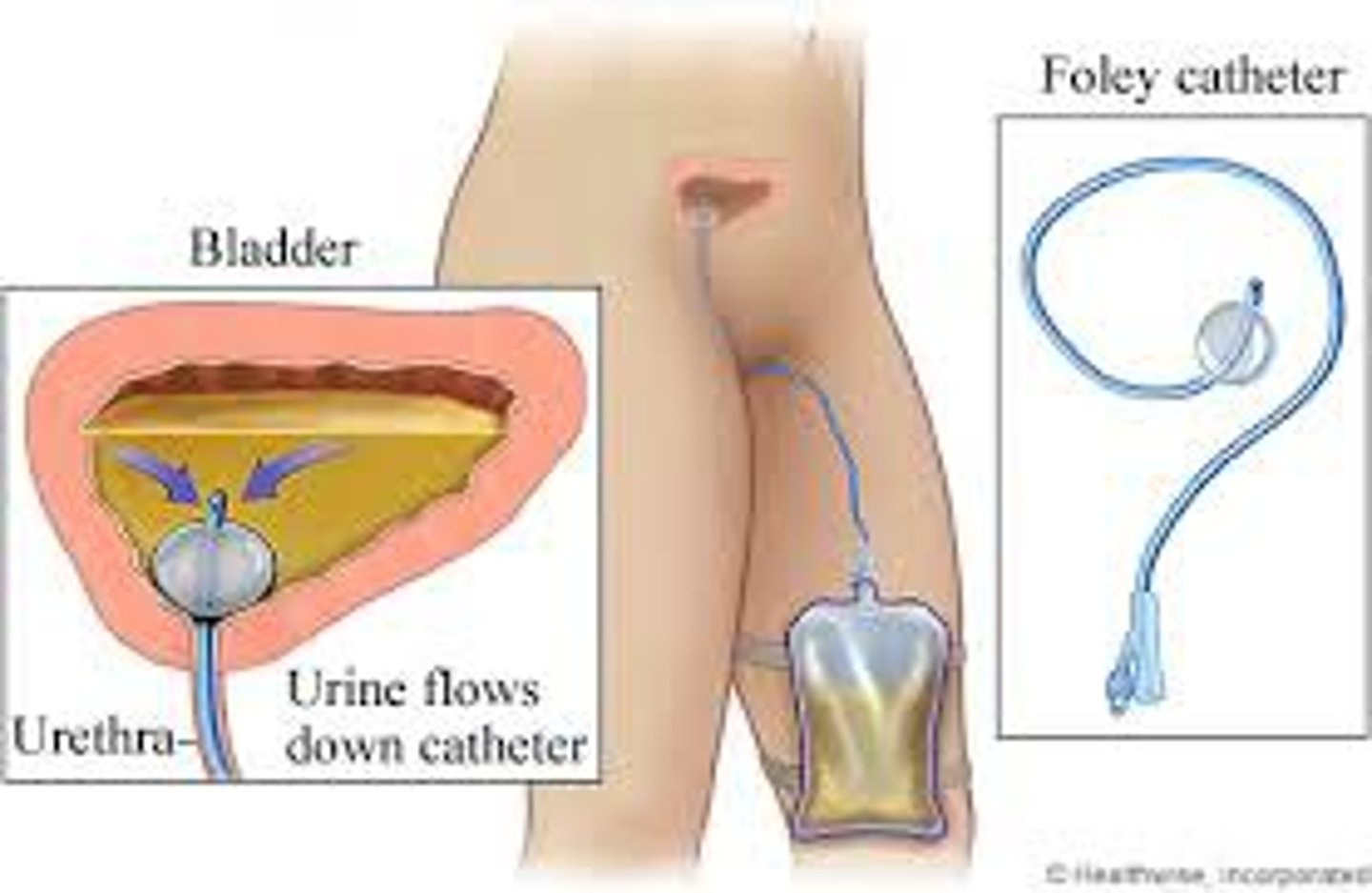
Foley Catheter; implications for therapy
Be cautious not to dislodge the catheter during mobility. Ensure the drainage bag is kept below the bladder level and the tube is off the floor to minimize infection risk.
texas catheter
condom catheter; for males; more temporary - this can dislodge easily
Nasogastric tube (NG)
tube inserted through the nose into the stomach
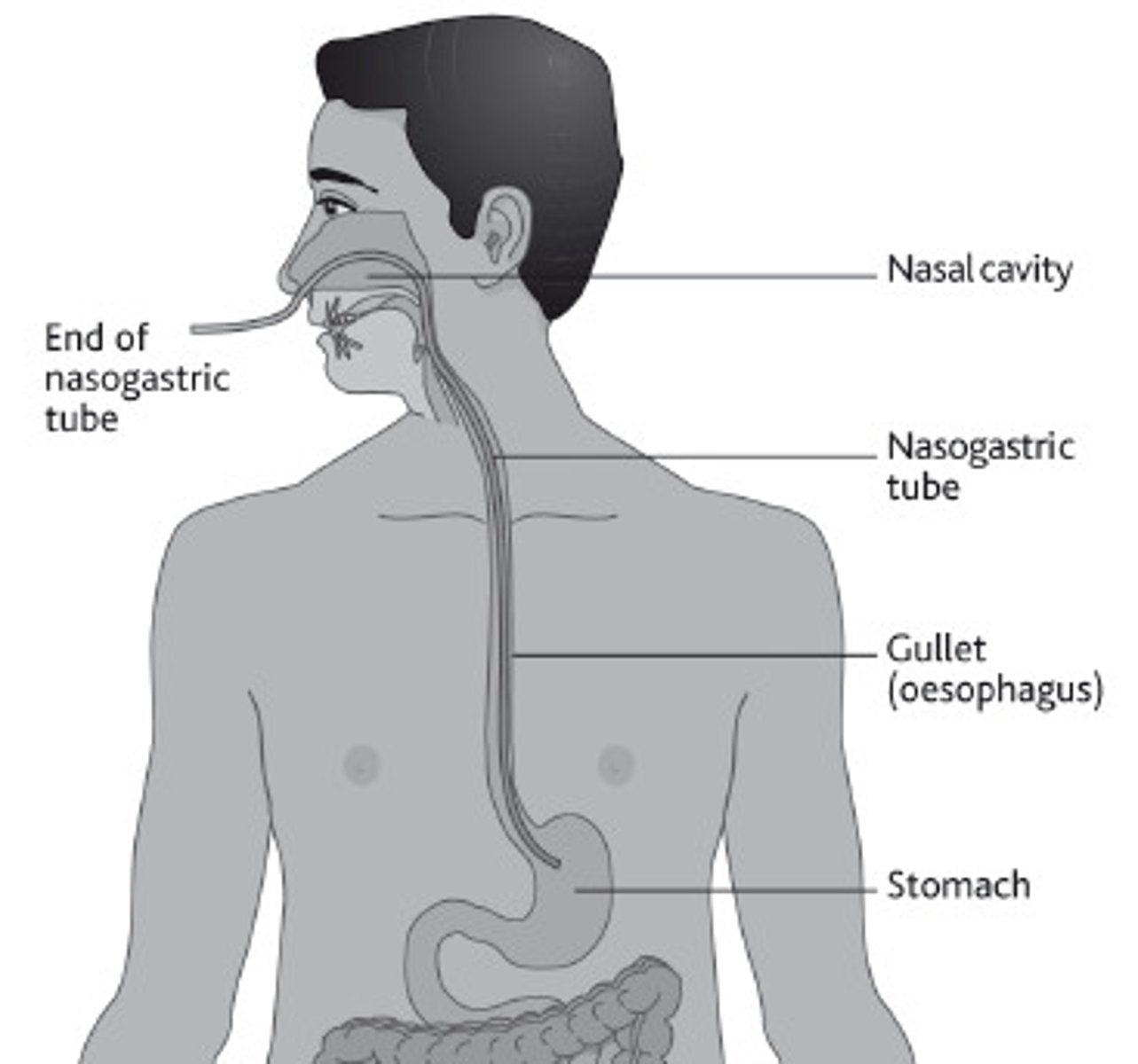
NG tube; implications for therapy
secure with tape, which may need re-securement if it comes loose.
Gastronomy Tube (G-Tube)
tube placed through the abdomen directly into the stomach and used to provide nourishment
G-tube: implications for therapy
monitor for signs of infection around the tube site and avoid pulling or irritating the tube during mobility
peripheral IV
short catheter inserted into any vein that is not in the chest or abdomen
peripheral IV; implications for therapy
keep the IV pump and pole in front of the payient to avoid tangling, be cautious of movement discomdort and consult with the nurse about disconnecting the IV if needed
Arterial line (a-line)
• Thin catheter inserted into an artery (commonly the radial a.) in order to monitor blood pressure and mean arterial pressure in real time. This catheter is more firm than an intravenous line (IV).
• Also used for collection of arterial blood gas.
• Displayed as a red wave form usually near the bottom on the monitor.
PICC line
a long term IV catheter inserted into a peripheral vein and advanced to larger veins near the heart for extended medicatino or nutrient delivery
central venous catheter
central IV line interseted into major veins terminating into the atrium
dialysis catheter
specialized central catheter used for dialysis, either inserted into the jugular or subclavian vein
nerve block
injection of regional anesthetic to stop the passage of sensory or pain impulses along a nerve path
Jackson Pratt Drain
hollow bulb-like device used to collect drainage
implications for therapy JP drain
secure the drain to prevent accidental bursting or pulling, attach it to the gown or hold it during mobility
chest tube
Catheter inserted through the thorax into the chest cavity for removing air or fluid; used after chest or heart surgery or pneumothorax.
implications for therapy; chest tube
keep the drainage system upright and below the level of insertion, there are no restrictions on movement but be mindful of patient discomfort
wound VAC
a device that uses negative pressure to promote wound healing and remove fluid and infectious waste
cardiac telemetry
monitors heart rhythms using 5-12 leads attached to the patients trunk
pulse ox
measures oxygen saturation in the blood
cardiac monitor
displays various vital signs including heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and Sp O2
therapy tolerance of inpatient rehab
must tolerate 3 hrs of therapy per day 5 days a week
(inpatient rehab) medical stability
patients transferred from hospitals or nursing homes
inpatient rehab - diagnosis requirement
stroke, spinal cord injury, major trauma, etc
ortho rehab - UE Eval
- Take history and occupational profile
- Observation : Posture, UE, spontaneous use, guarding, scar, wounds, trophic status
- Palpation (gentle): tenderness/pain, adhesions, pitting/brawny edema
- Perform specific tests or assessments: ROM, joint end feel, edema, vascular, sensation, strength, coordination, muscle length tests, functional assessments
adhesive capsulitis (frozen shoulder)
Decreased passive and active range of motion
More stiffness than pain
phases of frozen shoulder
freezing, frozen, thawing
frozen shoulder - freezing
2-9 months
frozen shoulder - frozen
up to 1 year
frozen shoulder - thawing
up to 26 months
in frozen shoulder, does a client go through all the phases
not always
frozen shoulder creates loss of motion
in external rotation , internal rotation , and abduction
treatment for frozen shoulder - non operative
pain management, stretching, strengthening
treatment for frozen shoulder - operative
manipulation under anesthesia or arthroscopic release
rotator cuff tear
traumatic rip of one or more of the muscles or tendons within the rotator cuff of the shoulder; can be partial or full thickness
rotator cuff tear - non operative treatment
early PROM, strengthening RC muscles, activity modification
rotator cuff tear - operative treatment
focus on regaining full ROM and progressing to ADL performance
which muscle is the most vulnerable to tearing in a rotator cuff tear?
supraspinatus
proximal humerus fracture
most common, most occur as a direct result of a fall on the shoulder or a direct blow to the humeral region