Biotechnology
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Biotechnology
the manipulation of living organisms or their components to perform practical tasks or provide useful products
Examples of biotech use
Ex: solving crimes, paternity testing, testing for genes, bacteria have been engineered to produce human insulin
Commonly Used in Biotech
Restriction enzymes (endonucleases), DNA ligase, plasmid, bacteria/viruses, short tandem repeats
Restriction enzymes (endonucleases)
cut DNA at very specific sites (restriction sites)
-works on any species
What are the cut DNA pieces by restriction enzymes called? What is the name of the part that is single stranded
-resulting pieces are called restriction fragments
-part of the fragment is single stranded and is called the sticky end
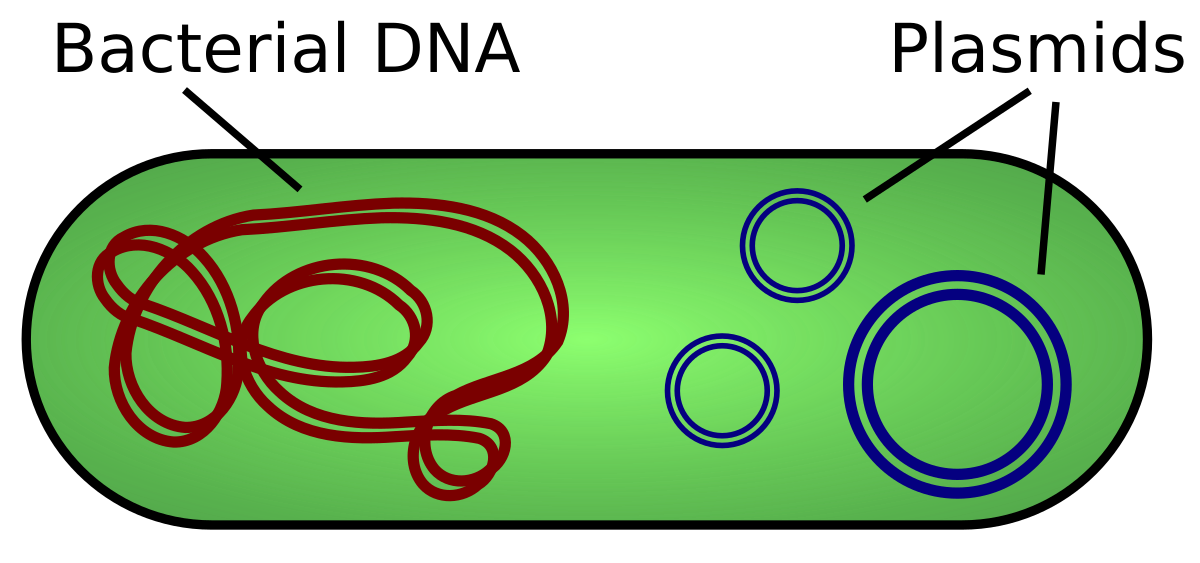
Plasmid
a small ring of bacterial DNA that carries accessory genes separate from those on a bacteria chromosome (ignore the larger one; usually the smaller ones)
-Often used to transfer genes into a bacteria or other type of cell in genetic engineering
Bacteria or Viruses
used as vectors to carry DNA to new cell (ex:bacteriophage)
Short Tandem Repeats
short repeated sequences of DNA (2-6 pairs) that account for approximately 3% of the human genome
-can be used in forensic studies (unique to individual)
-have a higher mutation rate than other areas of DNA
-inherited like an allele
Gel electrophoresis
-used on DNA or amino acids/proteins
-method of separating fragments of DNA (or proteins) based on size and charge
-each person’s DNA fragments are different sizes
-smaller particles move away from the origin
What cuts DNA into fragments and where?
-DNA is cut into fragments by restriction enzymes at restriction sites
How are DNA fragments moved?
By an electrical field or by electrical currents
What does PCR stand for?
Polymerase chain reaction
Polymerase chain reaction
-artificially copies DNA pieces in which the amount doubles every cycle
-amplifies minute quantities of DNA (100 bases)
What is used in PCR to separate the double helix of DNA?
thermocycler/ high heat is used
DNA Profiling
-using gel electrophoresis, PCR or DNA sequencing to solve crime using forensic evidence or for paternity testing
DNA Fingerprint
-an individual’s unique banding pattern of DNA fragments on an autoradiograph
-each band is a different DNA restriction fragment
-PCR can be used to make new fragments
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNP)
-most common genetic variation between people with a gene
-each SNP represents a difference in a single DNA nucleotide
-biological markers
-can be used to track inheritance within families
-appears in more than 1% of the population (less than 1% equals a mutation)
DNA or Amino Acid (RNA) Sequencing
-determines the sequence of nitrogenous bases on a gene or a strand of DNA/RNA or an entire genome using radioactive base pairs
-optic scanners and lasers read colors to create digital record of nitrogenous bases in a genome
Whole Genome Sequencing ( its uses as well an example)
Ex: Human Genome Project
-important uses: shows evolutionary links, treatment (personalized), can be used in diagnosis (gene testing)
-(another version can be used to determine sequence of amino acids in a protein)
Genetic databases
digital library that allow DNA sequences to be stored and studied easily
Genetic Transfer Using Plasmids
-creates GMOs
-inserts new gene into plasmid, which is then transferred to host
-1. isolate the gene to be moved and extract using restriction enzymes
-2. insert plasmid using ligase
-3. use a vector (bacteria/virus) to transfer plasmid into host
CRISPR
genetic engineering tools that acts as molecular scissors to target a chosen gene
Cas 9
-guided restriction enzyme that cuts DNA (used in CRISPR)
-becomes associated with an RNA guide that finds the correct area of DNA to edit
DNA Barcode
-created using short (600-700bp) units that are unique to a species
-can identify if species are in an area by testing water or soil samples
Clone
-genetically identical cells or organisms
-naturally occurs in mitosis, twins are natural clones
Short Tandem Repeats
-short repeated sequences of DNA (2-6 pairs)
-can be used in forensic studies/DNA profiling (unique to individual)
-have a higher mutation rate than other area of DNA
Gene Knockout
-using genetic engineering to inactivate or remove one or more specific genes
-allows scientists to investigate a gene’s function
Universal
all living organisms use the same codons to represent the same amino acids
Codons
3 nitrogenous base sequences each representing an amino acid (1 codon=1 amino acid)
Restriction enzymes (endonucleases)
cut DNA into fragments
DNA ligase
glues DNA fragments together
Complimentary base pairing
adenine always pairs with thymine, and guanine always pairs with cytosine (in RNA, T is replaced with U)
Taq DNA Polymerase
heat tolerant enzyme used in PCR to synthesize new DNA, can withstand heating and cooling denatured
-derived from bacteria
Genome
all genetic material in an organism
Cloning of Mammals (what animals are usually cloned?)
sheep, cows, and horses
How many animals are required in cloning?
3 animals
What are the steps in cloning?
-donates cell to be cloned
-donates egg (denatured)
-surrogate mother
The clone produced in cloning has identical DNA of the ____
First donor cell (First cell)