IT & Informatics Exam Keywords
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Human - Centered Design
The process that ensures that the designs match the needs and capabilities of the people for whom they are intended.
Ethics and Social Responsibility
Responsibility in promoting ethical and socially responsible technological solutions.
Technology as Applied Science
The misconception that all technology solely comes from the application of scientific principles. These technologies were made by accident or didn't have any prior theoretical descriptions (like physics/math) to help guide its development.
Technology as Hardware
They are extraneous imperfections which undermine the efficiency of the machine. Physical hardware alone is not sufficient for there to be technology.
Technology as Rules
A series of steps that accomplish some goal. As society develops, more and more aspects of social life become more systemized in terms of system of rules.
Technology as Systems
In the system approach to technology, the user is inside the technology as designers, owners, administrators, advertisers, and propagandists channel the technology in one direction rather than another, and workers, consumers, and citizens are themselves channeled in one direction or another.
The idea is that technology is not neutral or isolated, but is deeply embedded in a broader system of social, economic, and political relationships.
Approach - Recognizes that technology doesn't simply function in a vacuum but is shaped by the actions, decisions, and intentions
Lessig's Pathetic Dot
A simple but powerful visual representation of forces that regulate human behavior, often depicted as a dot (representing an individual) influenced by four forces, that are, market, law, norms, and architecture.
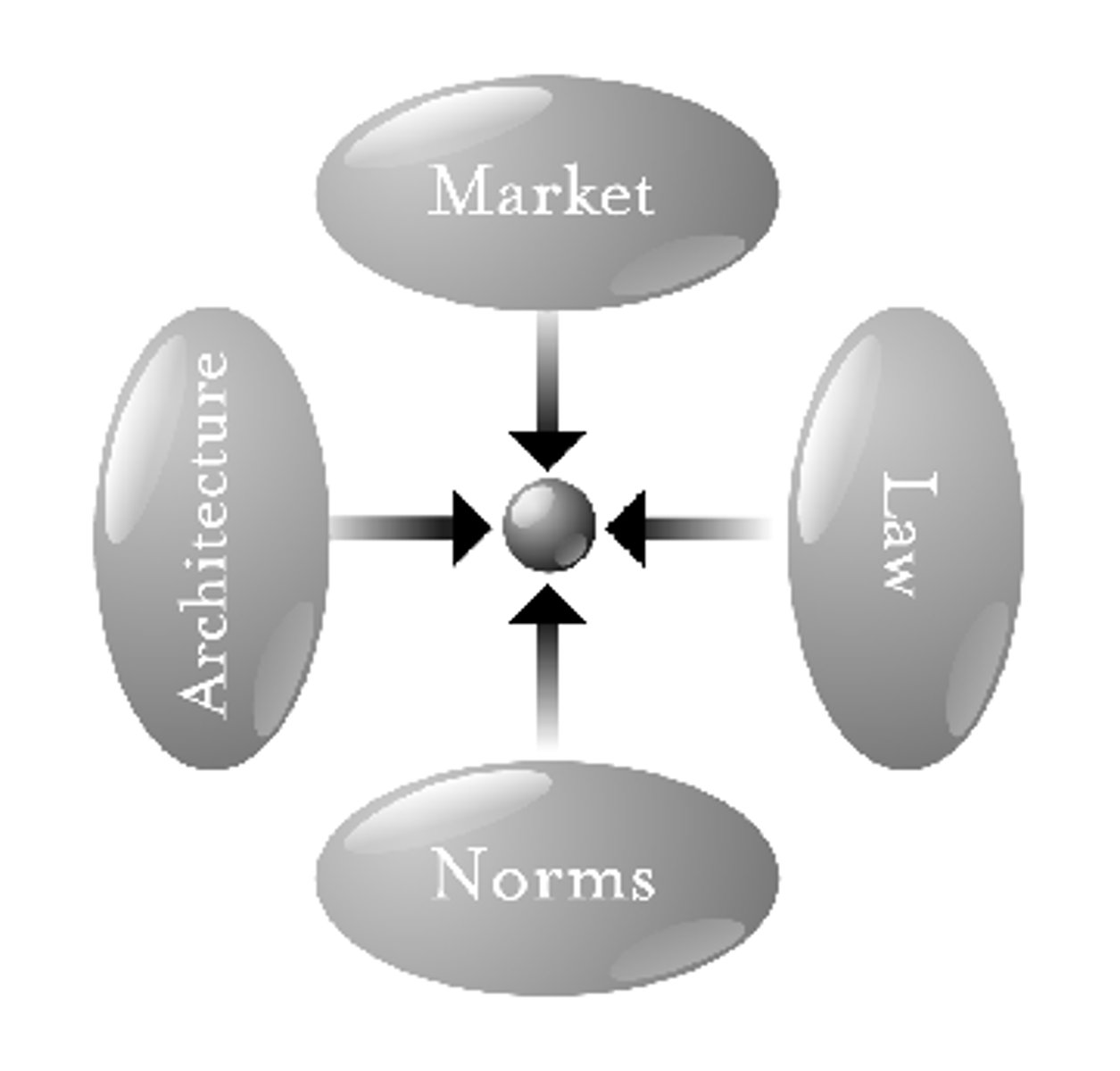
Market
Any arrangement that allows buyers and sellers to exchange things.
Law
Government regulations that impose penalties or restrictions, and bans certain products or actions with the consequence of penalty.
Norms
Rules and expectations by which a society guides the behavior of its members.
Architecture
The physical or digital structures that shape behavior and focus on the built environment.
Design
Changing some part of the world from its current state to preferred state.
DARPA (The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency)
Research and development wing of the United States Department of Defense. Initially focused on military technology, aimed to create a communication network that could survive a nuclear attack.
They built the ARPANET
ARPANET
The precursor to the Internet, was created to allow multiple computers to communicate by sending small packets of data across a network (packet switching). DARPA created ARPANET.
TCP (Transmission Control) /IP (Internet) Protocols
A set of rules which allow multiple computers to communicate over a network.
Human Protocol
A set of rules/way that describes how humans shows interact.
Traceroute
A diagnostic tool used to trace the path that data travels between nodes. Typically used to identify network problems or inefficient routing practices.
Ping
This command checks if an IP address is reachable or not.
This is done by measuring the round-trip time it takes for a message to travel from the source (your computer) to the destination IP address and back
Sends a small data packet called an ICMP ECHO REQUEST, a type of Internet Control Message Protocol, if the target is reachable and operational —> then the target device responds with an ICHO Echo Reply
DNS (Domain Name Service)
This is a system that connects website names with their IP addresses.
CERN (The European Organization for Nuclear Research)
Known for its physics equipments and also provides data for online users; Tim Bernes-Lee came from this organization to later create the World Wide Web
PageRank
Algorithm developed by Google that ranks web pages based on the number of connections to that particular web page.
Link to your website counts as a vote to your website → (the more hyperlinks, the better —> because it means your website is probably more important or valuable than the others (links from high-ranking pages like official university websites and trusted news outlets get votes)
Simulates a random web surfer who clicks on links randomly. The likelihood of a user landing on a particular page determines its PageRank score.
Dunbar's Number
The idea that a person can only have a limited number of close relationships, probably around 150.
Degrees of Connection
This is the number of direct relationships that separates two individuals.
Explicit Knowledge
Type of knowledge that is easily communicated and available to everyone.
Implicit Knowledge
Type of knowledge that a person cannot consciously recall or explain but that nevertheless affects the person's thinking or behavior.
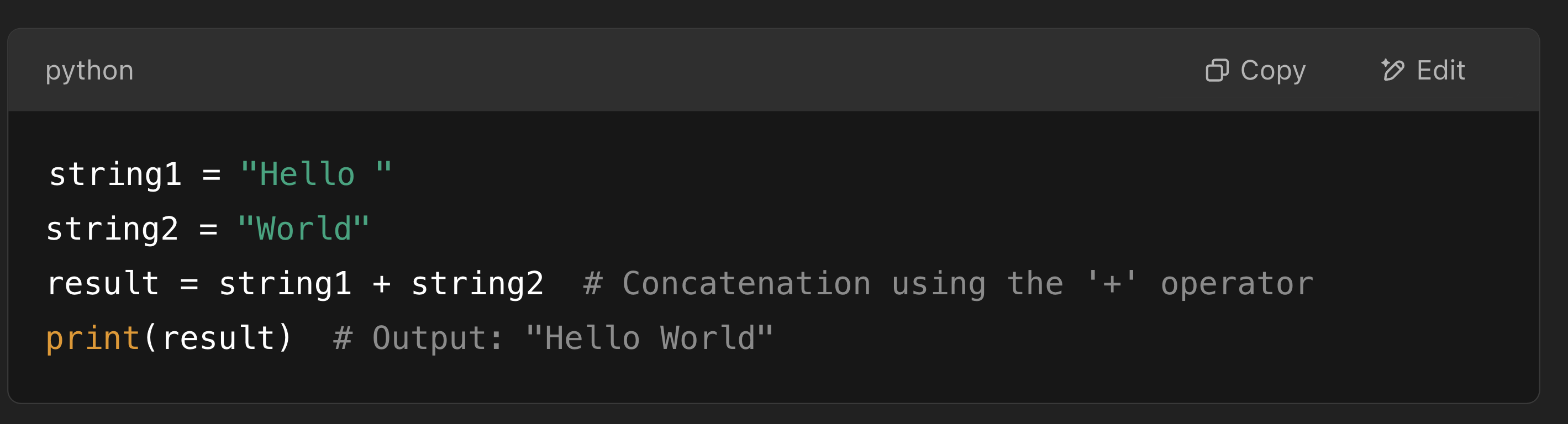
Concatenation
Joins together two or more strings end-to-end to make a new string.
Casting
Converts one data type to another.
Often necessary when you need to perform operations on differently types of data that aren't automatically compatible or when you want to explicitly convert between types for certain operations
CIA triad: Protecting Confidentiality
Protecting authorized restrictions on information access and disclosure.
CIA triad: Protecting Integrity
Protecting against improper modification.
CIA triad: Protecting Availability
Protection that ensures timely access to all the information required.
DoS - Denial of Service
An attack on a computer resource that prevents it from performing its normal operations, usually by overwhelming it with large numbers of requests in an effort to monopolize its resources.
Non - repudiation (Proof)
It is an assurance that the sender of information is provided with proof of delivery and the receiver is provided with proof of the sender's identity.
Social Engineering
Techniques that trick a person into disclosing confidential information.
Phishing
Deceiving users to click on malicious links through emails, phone calls, or even messages.
Pretexting
A form of social engineering in which one individual lies to obtain confidential data about another individual
Baiting
Getting a target user to perform an action by offering something tempting.
Tailgating
When an unauthorized individual enters a restricted-access building by following an authorized user.
Dumpster Diving
The act of digging through trash receptacles to find information that can be useful in an attack (discarded materials —> printed documents, old hardware, sticky notes, and receipts and invoices)
Penetration Testing
Involves traversing vulnerabilities and traversing the network using special tools to see if there is a likelihood of attack or weakness to attack.
Multi - Factor Authentication (MFA)
A security process that requires multiple steps to log in to an account.
Trace Data
Footprints you leave behind that you cannot see.
Metadata
Data that provides information about other data.
Fingerprinting
A technique used to track individuals based on unique data points about their devices, browser settings, and online behaviors, much like how physical fingerprints identify individuals uniquely.
National Security Agency (NSA)
Responsible for surveillance, codebreaking, and national security.
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
A symmetric encryption standard used by the NSA to secure data.