Cybersecurity - ALL TERMS (Original by kasenso20)
1/327
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Compared to the other Cisco Cybersecurity flashcards, this one focuses more on all the terms and in-depth info. Do not credit me. Flashcards are made by kasenso20 on Quizlet. (https://quizlet.com/330496993/cybersecurity-flash-cards/)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
328 Terms
What is cybersecurity
preventing the unauthorized access to data and information systems
what three goals does cybersecurity have
confidentiality, integrity, accessibility
what is the confidentiality goal of cybersecurity
ensuring no one with authorized can access information
what is the integrity goal of cybersecurity
ensuring the data hasn't been manipulated and is accurate
what is the availability goal of cybersecurity
ensuring the systems are available to the end users
what are the three main methods or controls that shape cybersecurity?
people, process, technology
what is the role of people in cybersecurity
- giving people the skills and information to implement an effective cybersecurity program
- training, awareness, building skills
what is process in cybersecurity
the policies and organizational procedures used to implement and manage the cybersecurity program
what role does technology play in cybersecurity
the tools or controls used to implement the cybersecurity lifecycle
what is the cybersecurity lifecycle
the components of cybersecurity according to NIST
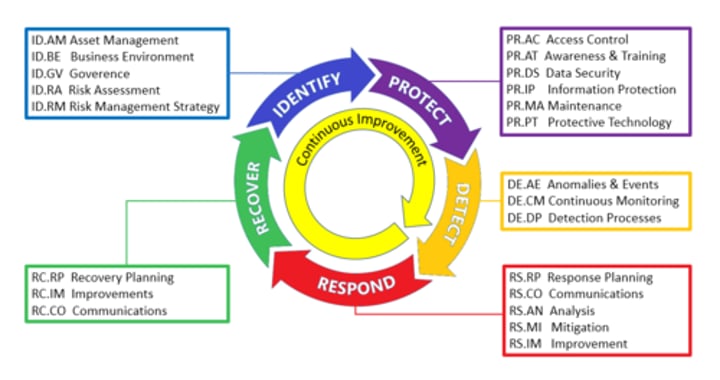
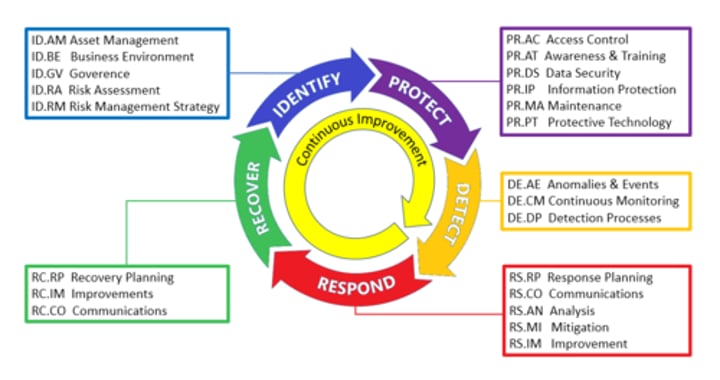
what are the NIST components of the cybersecurity lifecycle
identify, monitor, protect, detect, respond, recover
what is the old model to approach cybersecurity
the perimeter model (hard shell, soft inside)
why is the perimeter model not fully effective in cybersecurity
- the perimeter is not perfect and is only one layer
- you have to violate the perimeter all the time to share information between authorized users
- too many doors and windows
What is the Identify function in the NIST model?
Identify
The Identify Function assists in developing an organizational understanding to managing cybersecurity risk to systems, people, assets, data, and capabilities. Understanding the business context, the resources that support critical functions, and the related cybersecurity risks enables an organization to focus and prioritize its efforts, consistent with its risk management strategy and business needs.
Examples of outcome Categories within this Function include:
Identifying physical and software assets within the organization to establish the basis of an Asset Management program
Identifying the Business Environment the organization supports including the organization's role in the supply chain, and the organizations place in the critical infrastructure sector
Identifying cybersecurity policies established within the organization to define the Governance program as well as identifying legal and regulatory requirements regarding the cybersecurity capabilities of the organization
Identifying asset vulnerabilities, threats to internal and external organizational resources, and risk response activities as a basis for the organizations Risk Assessment
Identifying a Risk Management Strategy for the organization including establishing risk tolerances
Identifying a Supply Chain Risk Management strategy including priorities, constraints, risk tolerances, and assumptions used to support risk decisions associated with managing supply chain risks
what is the Protect function in the NIST model
The Protect Function outlines appropriate safeguards to ensure delivery of critical infrastructure services. The Protect Function supports the ability to limit or contain the impact of a potential cybersecurity event.
Examples of outcome Categories within this Function include:
Protections for Identity Management and Access Control within the organization including physical and remote access
Empowering staff within the organization through Awareness and Training including role based and privileged user training
Establishing Data Security protection consistent with the organization's risk strategy to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information
Implementing Information Protection Processes and Procedures to maintain and manage the protections of information systems and assets
Protecting organizational resources through
Maintenance, including remote maintenance, activities
Managing Protective Technology to ensure the security and resilience of systems and assists are consistent with organizational policies, procedures, and agreements
What is the Detect function in the NIST model?
Detect: Identifying the occurrence of a cybersecurity event (an incursion or attempted incursion) in a timely manner
Details:
The Detect Function defines the appropriate activities to identify the occurrence of a cybersecurity event. The Detect Function enables timely discovery of cybersecurity events.
Examples of outcome Categories within this Function include:
Ensuring Anomalies and Events are detected, and their potential impact is understood
Implementing Security Continuous Monitoring capabilities to monitor cybersecurity events and verify the effectiveness of protective measures including network and physical activities
Maintaining Detection Processes to provide awareness of anomalous events
What is the Respond function in the NIST model?
To take action regarding . detected cybersecurity incident to minimize impact
Details:
The Respond Function includes appropriate activities to take action regarding a detected cybersecurity incident. The Respond Function supports the ability to contain the impact of a potential cybersecurity incident.
Examples of outcome Categories within this Function include:
Ensuring Response Planning process are executed during and after an incident
Managing Communications during and after an event with stakeholders, law enforcement, external stakeholders as appropriate
Analysis is conducted to ensure effective response and support recovery activities including forensic analysis, and determining the impact of incidents
Mitigation activities are performed to prevent expansion of an event and to resolve the incident
The organization implements Improvements by incorporating lessons learned from current and previous detection / response activities
What is the Recover function in the NIST model
To maintain plans for resilience and to restore services impaired during cybersecurity incidents
Details:
The Recover Function identifies appropriate activities to maintain plans for resilience and to restore any capabilities or services that were impaired due to a cybersecurity incident. The Recover Function supports timely recovery to normal operations to reduce the impact from a cybersecurity incident.
Examples of outcome Categories within this Function include:
Ensuring the organization implements Recovery Planning processes and procedures to restore systems and/or assets affected by cybersecurity incidents
Implementing Improvements based on lessons learned and reviews of existing strategies
Internal and external Communications are coordinated during and following the recovery from a cybersecurity incident
Why systems are vulnerable
- Accessibility of networks via unauthenticated sources (e.e., open to the internet)
- Hardware problems (breakdowns, configuration errors, damage from improper use or crime, failure to maintain patches to the hardware such as a firmware update.
- Software Problems (programming or installation errors, unauthorized changes, failure to maintain patches to the software)
- Use of networks/computers outside of firm's control
- Loss and theft of end points with authenticated access to the systems such as portable devices
Internet Vulnerabilities
- Network open to anyone
- Size of internet means abuses can have wide impact
- Use of fixed internet addresses (IPs) with cable/DSL modems creates fixed targets for hackers
- encrypted VOIP
- E-mail, P2P, IM
Wireless Security Challenges
- Smartphones as vulnerable as computers
- Radio frequency bands easy to scan
- SSIDs (service set identifiers)
> Identify access points
> Broadcast multiple times
> Can be identified by sniffer programs
What is War Driving
Eavesdroppers drive by buildings and try to detect SSID and gain access to network and resources
> Once access point is breached, intruder can use OS to access networked drives and files
Malware (forms of)
- Viruses
- Worms
- Trojan horses (Software that appears benign but does something other than expected)
- SQL Injection attacks (Hackers submit data to Web forms that exploits site's unprotected software and sends rogue SQL query to database)
Viruses
Rogue software program that attaches itself to other software programs or data files in order to be executed
Worms
Independent programs that copy themselves from one computer to other computers over a network.
Worms and Viruses spread (propagated) by
- Downloads
- E-mail, IM attachments
- Downloads on web sites and social networks
- Shared USB drives
spyware
- Small programs install themselves surreptitiously on computers to monitor user Web surfing activity and serve up advertising
- Key loggers
> Record every keystroke on computer to steal serial numbers, passwords, launch Internet attacks
- Other types:
> Reset browser home page
> Redirect search requests
> Slow computer performance by taking up memory
Cybervandalism
Intentional disruption, defacement, destruction of Web site or corporate information system
A common tactic of Hacktivist
Spoofing
- Misrepresenting oneself by using fake e-mail addresses or masquerading as someone else
- Redirecting Web link to address different from intended one, with site masquerading as intended destination
Sniffer
- Eavesdropping program that monitors information traveling over network
- Enables hackers to steal proprietary information such as e-mail, company files, and so on
Denial of Service attacks (DoS)
Flooding server with thousands of false requests (such as trying to login to the website) to crash the network
Distributed Denial of Service attacks (DDoS)
Use of numerous computers to launch a DoS so that the defender cannnot stop the attack by only blocking the one IP address where the attack arose
Identity Theft
Theft of personal Information (social security ID, driver's license, or credit card numbers) to impersonate someone else
Phishing
Setting up fake Web sites or sending e-mail messages that look like legitimate businesses to ask users for confidential personal data.
Evil Twins
Wireless networks that pretend to offer trustworthy Wi-Fi connections to the Internet
Computer Crime
- Defined as "any violations of criminal law that involve a knowledge of computer technology for their perpetration, investigation, or prosecution"
> National Information Infrastructure Protection Act in 1996 makes virus distribution and hacker attacks to disable Web sites federal crimes (up to 20 years in jail).
- Computer may be target of crime, for example:
> Breaching confidentiality of protected computerized data
> Accessing a computer system without authority
- Computer may be instrument of crime, for example:
> Using e-mail for threats or harassment
> Theft of Intellectual property
Trade Secret = company secret, not public information
Patent = Protects invention or process for 20 years
Copyright = Protects ownership of the property for the life of the creator plus 70 years
Espionage or Trespass
- Individual attempts to gain illegal access to organizational information
- Competitive intelligence: Legal information gathering
- Industrial espionage: Crosses the legal boundary
Cyberterrorism and Cyberwarfare
- Attack via the Internet using a target's computer systems to cause physical, real-world harm
- Usually employed to carry out a political agenda
- Supervisory control and data acquisition (the systems that run the real world systems such as manufacturing plants, the power grid and such.(SCADA) or Industrial Control Systems (ICS) attacks
- SCADA systems control chemical, physical, or transport processes (i.e., oil refineries, water and sewage treatment plants, electrical generators, and nuclear power plants)
- 1982 Soviet Gas Pipeline / Farewell Dossier
Internal Threats: Employees
- Security threats often originate inside an organization
- Inside knowledge
- Sloppy security procedures
> User lack of knowledge
- Social engineering:
> Tricking employees into revealing their passwords by pretending to be legitimate members of the company in need of information
One in five employees would sell the passwords they use at work to access employer networks if they were asked (US is highest country)
Software Vulnerability
- Commercial software contains flaws that create security vulnerabilities
> Hidden bugs (program code defects)
* Zero defects cannot be achieved because complete testing is not possible with large programs
> Flaws can open networks to intruders
- Patches
> Small pieces of software to repair flaws
> Exploits often created faster than patches can be released and implemented
Business Value of Security and Control
- Failed computer systems can lead to significant or total loss of business function.
- Firms now are more vulnerable than ever.
- Confidential personal and financial data
> TARGET Customer Breach - Estimated costs $61M (as of 2-26-14)
- Trade secrets, new products, strategies
- A security breach may cut into a firm's market value almost immediately.
- Inadequate security and controls also bring forth issues of liability.
Legal and regulatory requirements for electronic records management and privacy protection
-GDPR: Global Data Protection Regulations (EU only regulation)
- HIPAA: Medical security and privacy rules and procedures
- Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act: Requires financial institutions to ensure the security and confidentiality of customer data
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act: Imposes responsibility on companies and their management to safeguard the accuracy and integrity of financial information that is used internally and released externally
Electronic Evidence
- Evidence for white collar crimes often in digital form
> Data on computers, e-mail, instant messages, e-commerce transactions
- Proper control of data can save time and money when responding to legal discovery request
Computer Forensics
- Scientific collection, examination, authentication, preservation, and analysis of data from computer storage media for use as evidence in court of law
- Includes recovery of ambient and hidden data
Information Systems Controls
- Manual and automated controls
- General and application controls
General Controls
- Govern design, security, and use of computer programs and security of data files in general throughout organization's information technology infrastructure
- Apply to all computerized applications
- Combination of hardware, software, and manual procedures to create overall control environment
Types of General Controls
- Software controls
- Hardware controls
- Computer operations controls
- Data security controls
- Implementation controls
- Administrative controls
Application Controls
- Specific controls unique to each computerized application, such as payroll or order processing
- Include both automated and manual procedures
- Ensure that only authorized data are completely and accurately processed by that application
- Include:
> Input controls
> Processing controls
> Output controls
Risk Assessment
Determines level of risk to firm if specific activity or process is not properly controlled
- Types of threat
> Probability of occurrence during year
> Potential losses, value of threat
> Expected annual loss
Security Policy
- Ranks information risks, identifies acceptable security goals, and identifies mechanisms for achieving these goals
- Drives other policies
> Acceptable use policy (AUP): Defines acceptable uses of firm's information resources and computing equipment
> Authorization policies:
Determine differing levels of user access to information assets
Identity Management
- Business processes and tools to identify valid users of system and control access
> Identifies and authorizes different categories of users
> Specifies which portion of system users can access
> Authenticating users and protects identities
- Identity management systems
> Captures access rules for different levels of users
Disaster Recovery Planning
Devises plans for restoration of disrupted services
Business continuity planning
Focuses on restoring business operations after disaster
IS Audit or Assessment
- Examines firm's overall security environment as well as controls governing individual information systems
- Reviews technologies, procedures, documentation, training, and personnel.
- May even simulate disaster to test response of technology, IS staff, other employees
- Lists and ranks all control weaknesses and estimates probability of their occurrence
- Assesses financial and organizational impact of each threat
Internal Auditors
Part of accounting internal auditing that validates policies and procedures are being followed
External Auditors
Review internal audit results and perform independent information systems audit
ISACA (Information Systems Audit and Control Association)
ISACA now goes by its acronym only, to reflect the broad range of IT governance professionals it serves.
Risk
The probability that a threat will impact an information resource
Risk Management
Identify, control, and minimize the impact of threats
Risk Analysis
- Prioritize assets (probability x value)
- Compare cost of security breach vs. cost of control
Risk Mitigation
- Organization takes concrete actions against risk
- Implement controls and develop recovery plan
- Three strategies:
Risk acceptance: Accept the potential risk, continue operating with no controls, and absorb any damages that occur
Risk limitation: Limit the risk by implementing controls that minimize the impact of threat
Risk transference: Transfer the risk by using other means to compensate for the loss, such as purchasing insurance
Identity Management Software
- Automates keeping track of all users and privileges
- Authenticates users, protecting identities, controlling access
Authentication
- Password systems
- Tokens
- Smart cards
- Biometric authentication
Firewall
- Combination of hardware and software that prevents unauthorized users from accessing private networks
- Technologies include:
> Static packet filtering
> Stateful inspection
> Network address translation (NAT)
> Application proxy filtering
Intrusion Detection Systems
- Monitors hot spots on corporate networks to detect and deter intruders
- Examines events as they are happening to discover attacks in progress
Antivirus and Antispyware software
- Checks computers for presence of malware and can often eliminate it as well
- Requires continual updating
Whitelisting and Blacklisting
- Whitelisting: Allows acceptable software to run / connections/email accepted
- Blacklisting: Allows everything to run unless it is on the blacklist
Encryption
- Transforming text or data into cipher text that cannot be read by unintended recipients
- Two methods for encryption on networks
> Symmetric key encryption
> Public Key encryption
Symmetric Key Encryption
Sender and receiver use single, shared key
Public Key Encryption
- Uses two, mathematically related keys: Public key and private key
- Sender encrypts message with recipient's public key
- Recipient decrypts with private key
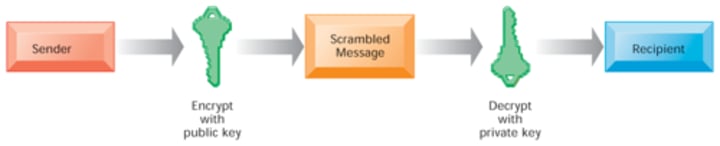
Digital Certificate
- Data file used to establish the identity of users and electronic assets for protection of online transactions
- Uses a trusted third party, certification authority (CA), to validate a user's identity
- CA verifies user's identity, stores information in CA server, which generates encrypted digital certificate containing owner ID information and copy of owner's public key
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
- Use of public key cryptography working with certificate authority
- Widely used in e-commerce
Ensuring System Availability
Online transaction processing requires 100% availability, no downtime
Fault-Tolerant Computer Systems
- For continuous availability, for example, stock markets
- Contain redundant hardware, software, and power supply components that create an environment that provides continuous, uninterrupted service
High-Availability Computing
- Helps recover quickly from crash
- Minimizes, does not eliminate, downtime
Recovery Oriented Computing
Designing systems that recover quickly with capabilities to help operators pinpoint and correct faults in multi-component systems
Security in the Cloud
- Responsibility for security resides with company owning the data
- Firms must ensure providers provides adequate protection:
> Where data are stored
> Meeting corporate requirements, legal privacy laws
> Segregation of data from other clients
> Audits and security certifications
- Service level agreements (SLAs)
Securing Mobile Platforms
- Security policies should include and cover any special requirements for mobile devices
> Guidelines for use of platforms and applications
- Mobile device management tools
> Authorization
> Inventory records
> Control updates
> Lock down/erase lost devices
> Encryption
- Software for segregating corporate data on devices
Software Metrics
Objective assessments of system in form of quantified measurements
> Number of transactions
> Online response time
> Payroll checks printed per hour
> Known bugs per hundred lines of code
Walkthrough
Review of specification or design document by small group of qualified people
Debugging
Process by which errors are eliminated
Information Systems and Ethics
- Information systems raise new ethical questions because they create opportunities for:
> Intense social change, threatening existing distributions of power, money, rights, and obligations
> New kinds of crime
IS Policies MOST IMPORTANT ONE
IT equipment issued by the company is corporate property. Anything you use the equipment for can be monitored and reviewed.
Access
Ability to make use of any information system (IS) resource. Ability and means to communicate with or otherwise interact with a system, to use system resources to handle information, to gain knowledge of the information the system contains, or to control system components and functions.
Access Control
The process of granting or denying specific requests to: 1) obtain and use information and related information processing services; and 2) enter specific physical facilities (e.g., federal buildings, military establishments, border crossing entrances).
Access Control List (ACL)
1. A list of permissions associated with an object. The list specifies who or what is allowed to access the object and what operations are allowed to be performed on the object. 2. A mechanism that implements access control for a system resource by enumerating the system entities that are permitted to access the resource and stating, either implicitly or explicitly, the access modes granted to each entity.
Access Control Lists (ACLs)
A register of: 1. users (including groups, machines, processes) who have beengiven permission to use a particular system resource, and
2. the types of access they have been permitted.
SOURCE: SP 800-12
Access Control Mechanism
Security safeguards (i.e., hardware and software features, physical
controls, operating procedures, management procedures, and various
combinations of these) designed to detect and deny unauthorized
access and permit authorized access to an information system.
SOURCE: CNSSI-4009
Access Level
A category within a given security classification limiting entry or
system connectivity to only authorized persons.
SOURCE: CNSSI-4009
Access List
Roster of individuals authorized admittance to a controlled area.
SOURCE: CNSSI-4009
Access Point
A device that logically connects wireless client devices operating in
infrastructure to one another and provides access to a distribution
system, if connected, which is typically an organization's enterprise
wired network.
SOURCE: SP 800-48; SP 800-121
Accountability
The security goal that generates the requirement for actions of an
entity to be traced uniquely to that entity. This supports nonrepudiation,
deterrence, fault isolation, intrusion detection and
prevention, and after-action recovery and legal action.
SOURCE: SP 800-27
Principle that an individual is entrusted to safeguard and control
equipment, keying material, and information and is answerable to
proper authority for the loss or misuse of that equipment or
information.
SOURCE: CNSSI-4009
Active Attack
An attack that alters a system or data.
An attack on the authentication protocol where the Attacker
transmits data to the Claimant, Credential Service Provider,
Verifier, or Relying Party. Examples of active attacks include
man-in-the-middle, impersonation, and session hijacking.
Active Content
Electronic documents that can carry out or trigger actions
automatically on a computer platform without the intervention of a
user.
Software in various forms that is able to automatically carry out or
trigger actions on a computer platform without the intervention of a
user.
Active Security Testing
Security testing that involves direct interaction with a target, such as
sending packets to a target.
Adequate Security
Security commensurate with the risk and the magnitude of harm
resulting from the loss, misuse, or unauthorized access to or
modification of information.
Security commensurate with the risk and magnitude of harm resulting
from the loss, misuse, or unauthorized access to or modification of
information.
Note: This includes assuring that information systems operate
effectively and provide appropriate confidentiality, integrity, and
availability, through the use of cost-effective management, personnel,
operational, and technical controls.
Administrative Account
A user account with full privileges on a computer.
Advanced Persistent Threats(APT)
An adversary that possesses sophisticated levels of expertise and
significant resources which allow it to create opportunities to achieve
its objectives by using multiple attack vectors (e.g., cyber, physical,
and deception). These objectives typically include establishing and
extending footholds within the information technology infrastructure
of the targeted organizations for purposes of exfiltrating information,
undermining or impeding critical aspects of a mission, program, or
organization; or positioning itself to carry out these objectives in the
future. The advanced persistent threat: (i) pursues its objectives
repeatedly over an extended period of time; (ii) adapts to defenders'
efforts to resist it; and (iii) is determined to maintain the level of
interaction needed to execute its objectives.
Adversary
Individual, group, organization, or government that conducts or has
the intent to conduct detrimental activities.
Alert
Notification that a specific attack has been directed at an
organization's information systems.