UA&BF Renal Function, Renal Dz, and Renal Dz
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/130
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:08 AM on 2/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
1
New cards
The Urinary Tract
Kidney, Bilateral Ureters, Bladder, Urethra
2
New cards
Internal Gross Anatomy of Kidney
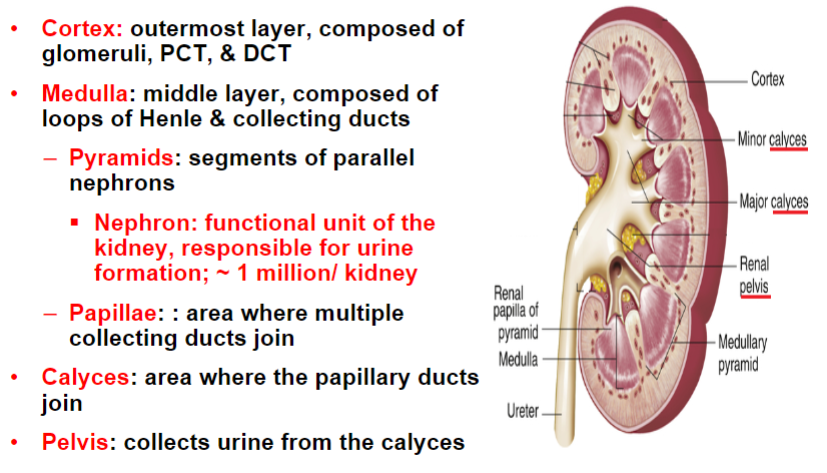
3
New cards
Nephrons are composed of two parts
Renal Corpuscle and Renal Tubules
4
New cards
Renal Corpsucle
Where blood is filtered; consists of the glomerulus and Bowmans’s capsule
5
New cards
Renal Tubules
Where selective reabsorption and secretion occurs; consists of the PCT(main site for reabsorption), loop of Henle(conserves water and creates hyperosmotic gradient), DCT(solute adjustment(aldosterone)), and CD(Final solute adjustment(aldosterone) and concentration(ADH))
6
New cards
The two kinds of nephrons
Cortical(85%) and Juxtamedullary(15%)
7
New cards
Cortical nephrons
Short loops of Henle; removal of waste products and reabsorption of nutrients
8
New cards
Juxtamedullary nephrons
Longer loops of Henle; concentrate urine
9
New cards
Renal Blood Circulation
Renal Artery(afferent arteriole and efferent arteriole) → Peritubular Capillary/PCT → Vasa Recta/Loop of Henle(maintains osmotic gradient necessary for renal concentration) → Peritubular Capillary/DCT → Renal Vein
10
New cards
Afferent arteriole
Large arteriole carrying blood to the glomerulus
11
New cards
Efferent arteriole
Smaller arteriole carrying blood away from the glomerulus
12
New cards
Functions of the Kidney:
Excretory: Eliminates toxic substances and waste
Regulatory: Maintains body electrolyte, fluid, and acid/base balance
Endocrine: Primary: produce hormones(rennin, erythropoietin, and prostaglandins); Secondary: Activate hormones produces elsewhere(Vitamin D)
Regulatory: Maintains body electrolyte, fluid, and acid/base balance
Endocrine: Primary: produce hormones(rennin, erythropoietin, and prostaglandins); Secondary: Activate hormones produces elsewhere(Vitamin D)
13
New cards
Urine Production is dependent on
Renal blood flow, glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, and tubular secretion
14
New cards
Characteristics of Glomerular Filtration
Passive & nonselective filtration of blood
15
New cards
Glomerular Filtration Factors
Size/Charge(Glomerular Filtration Barrier) and Pressure(Net Positive Pressure)
16
New cards
Glomerular Filtration Barrier
3 layers based on size and charge.
1. Capillary endothelium- contains pores called fenestrations
2. Glomerular basement membrane- shield of negativity
3. Visceral epithelium- contains podocytes
1. Capillary endothelium- contains pores called fenestrations
2. Glomerular basement membrane- shield of negativity
3. Visceral epithelium- contains podocytes
17
New cards
Net Positive Pressure in Glomerulus
Hydrostatic pressure; Blood colloid osmotic(oncoid) pressure; capsular hydrostatic pressure
18
New cards
Glomerular filtration pressures are regulated by…
Juxtaglomerular apparatus by controlling arteriole size.
Low systemic BP leads to larger afferent and smaller efferent.
High systemic BP leads to smaller afferent and larger efferent.
Low systemic BP leads to larger afferent and smaller efferent.
High systemic BP leads to smaller afferent and larger efferent.
19
New cards
Glomerular Filtration Rate(GFR)
Volume of plasma filtered by glomeruli per minute; normal GFR is about 120mL/min
20
New cards
Low GFR indicates
loss of glomerular filtration function & diminished renal function
21
New cards
How can GFR be estimated
eGFR or “clearance” test to evaluate glomerular function
22
New cards
Glomerular filtration results in what
Ultrafiltrate comprised of water, glucose, Na, Cl, other ions, HCO3, amino acids, small MW proteins, urea, uric acid, and creatinine. It has the same SG & pH of plasma
23
New cards
Tubular reabsorption and secretion is…
Selective
24
New cards
Tubular reabsorption returns water and useful nutrients to the blood via
Passive diffusion: Simple diffusion down a concentration gradient.
Active diffusion: Requires a protein carrier and energy
Active diffusion: Requires a protein carrier and energy
25
New cards
Active diffusion in tubular reabsorption is dependent on
Renal threshold: The plasma concentration at or above which increased amount of urine is excreted.
E.g. Glucose=160-180mg/dL
E.g. Glucose=160-180mg/dL
26
New cards
Tubular secretion results in 3 possible out comes for hydrogen ions, describe them.
1. Secreted protons combine w/ ammonia to excrete excess protons in the urine as ammonium ions
2. Secreted protons combine w/ phosphate ions to excrete excess protons in the urine as dihydrogen phosphate ions
3. Secreted protons combine w/ filtered HCO3 to return the buffer to the blood
27
New cards
Renal Concentrating function depends on
Creating and maintaining a hypertonic medulla which is necessary for the reabsorption of water by the descending loop of Henle & CD
28
New cards
Describe the Countercurrent Multiplier Mechanism
Because in the LoH the descending limb is permeable to only water(passive) and the ascending limb is permeable to only salts(active), this helps create the hypertonicity of the medulla. This has the main function of conserving water.
The term itself refers to how the filtrate flows in opposite direction up and down the LoH
The term itself refers to how the filtrate flows in opposite direction up and down the LoH
29
New cards
Describe the Countercurrent Exchange Mechanism
Refers to how the filtrate of the LoH flows opposite to the blood in the Vasa Recta.
Requires that the blood in the Vasa Recta flow opposite to the LoH at a very slow rate.
On the descending portion, salt is reabsorbed into the blood while water is secreted.
On the ascending portion, salt is secreted into the interstitium, while water is reabsorbed
Requires that the blood in the Vasa Recta flow opposite to the LoH at a very slow rate.
On the descending portion, salt is reabsorbed into the blood while water is secreted.
On the ascending portion, salt is secreted into the interstitium, while water is reabsorbed
30
New cards
Which part of the Loop of Henle is permeable to Urea?
Medullary collecting duct
31
New cards
Describe the concept of Urea Trapping.
Net effect is to trap urea in the renal medulla, raising the osmotic activity of the interstitial fluid
32
New cards
Know the hormones produced by the kidney, their source, stimulating factor for synthesis, and action
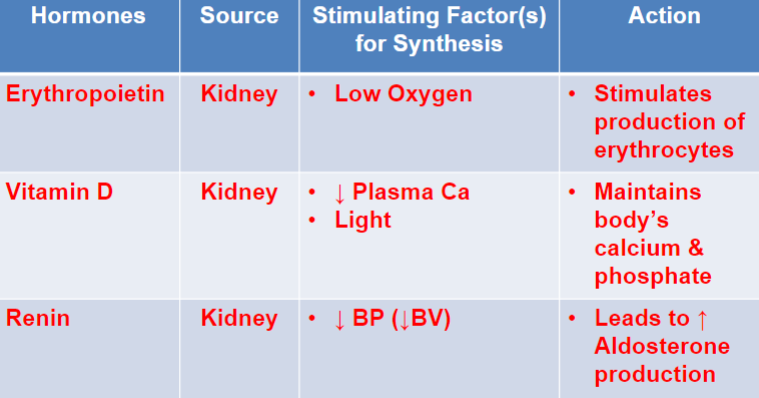
33
New cards
Know the hormones regulated by the renal system, their source, stimulating factor for synthesis, and action
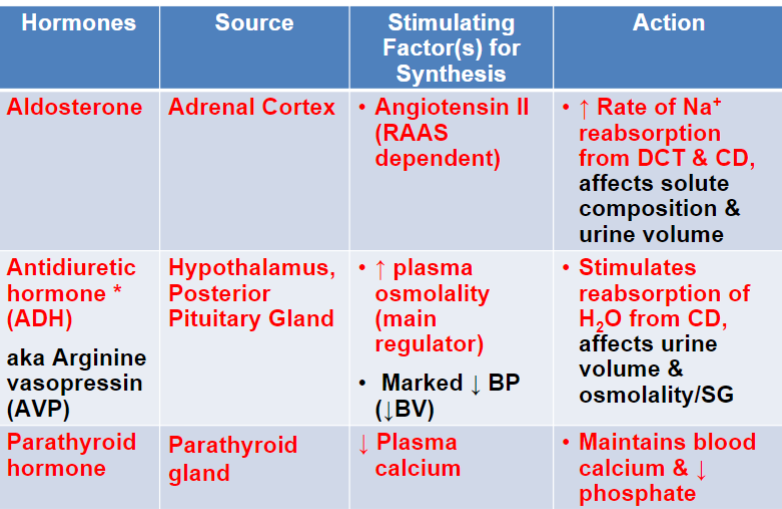
34
New cards
Function of RAAS
Maintains body’s BP by increasing sodium reabsorption in the DCT & blood vessel constriction.
When BP is high, rennin secretion is inhibited and sodium secretion is enhanced.
When BP is high, rennin secretion is inhibited and sodium secretion is enhanced.
35
New cards
Where is ADH made and what does it do?
Made in the hypothalamus and stimulates renal water reabsorption in DCT and CD
36
New cards
Give an in depth definition of how ADH is released and its impact
High blood osmolality and a marked decrease in BP stimulates its release.
Increased blood osmolality = Increased ADH = Blood Osmolality decrease, Urine becomes more concentrated and less urine volume.
\
Decreased blood osmolality = decreased ADH = Urine volume increases and is more dilute
Increased blood osmolality = Increased ADH = Blood Osmolality decrease, Urine becomes more concentrated and less urine volume.
\
Decreased blood osmolality = decreased ADH = Urine volume increases and is more dilute
37
New cards
What is the function of the PCT?
Reabsorbs: Na, Cl, K, bicarbonate, amino acids, glucose, urea, Ca
Secretes: Protons and NH3
Secretes: Protons and NH3
38
New cards
What is the function of the descending loop of Henle?
Only reabsorbs water
39
New cards
What is the function of the ascending loop of Henle?
Reabsorbs: Na and Cl
Secretes: Urea
Secretes: Urea
40
New cards
What is the function of the DCT?
Reabsorbs: Na(exchanges for aldosterone)
Secretes: Protons, K, bicarbonate, NH4
Secretes: Protons, K, bicarbonate, NH4
41
New cards
What is the function of the collecting duct?
Reabsorbs: Na(aldosterone), water(ADH), and urea
42
New cards
How much reabsorption occurs in the PCT
80% of all tubular reabsorption.
100% of glucose and amino acids(up to renal threshold)
70% of salts and water
100% of glucose and amino acids(up to renal threshold)
70% of salts and water
43
New cards
What percentage of urine composition do solutes make up?
5%, the rest is water
44
New cards
What are the major organic solutes in urine?
Urea > Uric acid > Creatinine
Urea and creatinine can be used to ID a fluid as urine
Urea and creatinine can be used to ID a fluid as urine
45
New cards
What are the major and minor inorganic solutes in urine?
Major: Cl > Na > K
Minor: Phosphates & NH4
Minor: Phosphates & NH4
46
New cards
Aside from the organic and inorganic solutes, what other solutes may be found in urine
Medications
47
New cards
What formed elements can be found in urine and what can they indicate?
Cells, casts, crystals, mucus, and bacteria
Pathogenic when increasing excessively
Pathogenic when increasing excessively
48
New cards
What is the urine composition volume?
RR: 600-2000
Average: 1200-1500
Average: 1200-1500
49
New cards
What is the RR pH of blood and urine
Blood: 7.35 - 7.45
Urine: 4.5-8
Urine: 4.5-8
50
New cards
What is the SG for urine composition
RR: 1.003 - 1.035
Ultrafiltrate: 1.010
Ultrafiltrate: 1.010
51
New cards
What makes the solute composition of urine vary?
Hydration, metabolism, Dz processes, medications(diuretics)
52
New cards
What are the two categories of Renal Diseases
Based on structure initially affected and based on the time course of the disease
53
New cards
What are 4 renal structures that can be effected by renal diseases
Glomerular, tubular, interstitial, and vascular
54
New cards
What are the two types of renal diseases based of the time course of the disease
Acute Renal Failure: Rapid, within days to weeks
Chronic Renal Failure: Gradual loss of function, within years
Chronic Renal Failure: Gradual loss of function, within years
55
New cards
What can a UA diagnostics test show about Renal Disease?
Glomerular damage or inflammation: Proteins present
Tubule damage: Renal tubular epithelial cells present
Infection: Bacteria, yeast, WBC present
Tubule damage: Renal tubular epithelial cells present
Infection: Bacteria, yeast, WBC present
56
New cards
What can a blood test show about Renal Diseases
Impaired filtering function: Increased BUN and creatinine
Renal loss: Decreased protein(albumin)
Renal loss: Decreased protein(albumin)
57
New cards
Aside from blood and UA tests, what are the other two types of diagnostic tests used to identify renal disease
Ultrasounds and kidney biopsy
58
New cards
What are the 5 categorizations for glomerular disease
Primary: Directly and specifically attacks only the glomeruli
Secondary: Systemic disease
Idiopathic: unknow cause
Acute: Quick
Chronic: Gradual
Secondary: Systemic disease
Idiopathic: unknow cause
Acute: Quick
Chronic: Gradual
59
New cards
Describe the two possibilities of pathogenesis of glomerular injury
1. Immunological: most common
1. Circulating Immune complexes trapped in glomeruli
2. Auto-abs
2. Non immunological
1. Diabetic nephropathy
2. Exposure to toxins/chemicals
60
New cards
Understand the Glomerular Disease classification chart
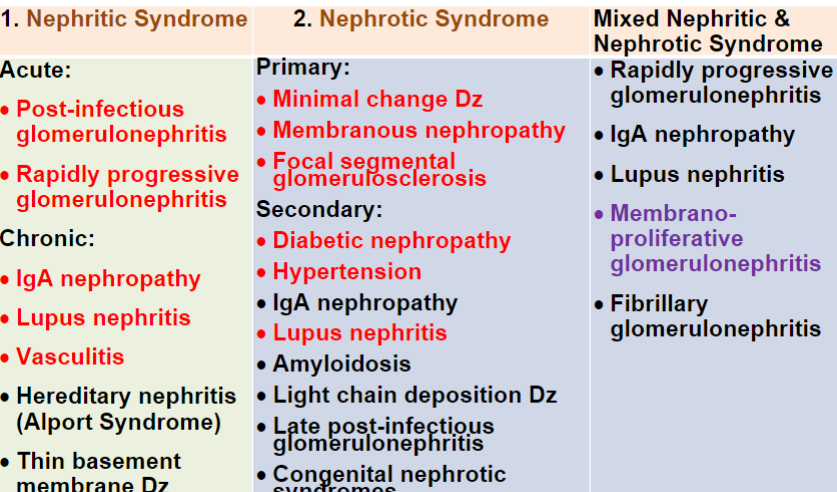
61
New cards
Nephritic syndrome is a…
Sterile glomerular inflammation that can be either acute or chronic
62
New cards
Nephritic syndrome is characterized by…
Hematuria w/ dysmorphic RBC casts(RBC, granular, hyaline) and proteinuria
Other signs include oliguria
Other signs include oliguria
63
New cards
Describe Acute Glomerulonephritis
Inflamed and enlarged glomeruli.
Causes are immunological, often infections like post-strep A
Characterized by: Hematuria, RBC casts, and proteinuria
Causes are immunological, often infections like post-strep A
Characterized by: Hematuria, RBC casts, and proteinuria
64
New cards
Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis is a more serious form of acute glomerulonephritis that…
Progresses to renal failure within weeks - months
65
New cards
Describe what occurs during rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis as well as what accompanies it.
Macrophages damage capillary walls and Fibrin causes permanent damage to capillary tufts.
It is often accompanied by microscopic glomerular crescent formations.
It is often accompanied by microscopic glomerular crescent formations.
66
New cards
What does the UA of rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis show?
Typical glomerulonephritis(dysmorphic RBC, RBC casts, proteinuria), but eventually progresses to more severe hyperproteinuria & decreased GFR
67
New cards
Chronic glomerulonephritis results from ___ and may eventually progress to _
Progressive, irreversible damage to the glomeruli; ESRD w/ anuria
68
New cards
What would a UA test of chronic glomerulonephritis show and what are some other signs of it?
UA: Hematuria, RBC casts, proteinuria, and broad and waxy casts
\
Other signs: Oliguria and HTN
\
Other signs: Oliguria and HTN
69
New cards
What are the causes of chronic glomerulonephritis
1. IgA nephropathy(Berger’s Dz)
1. IgA complexes deposit on and inflame the glomerular membrane
2. Dx is based on UA & Renal biopsy(deposition of IgA & complement)
2. Lupus nephritis
1. Antibodies attack the glomeruli and leave scarring
70
New cards
Describe nephrotic syndrome and its characteristics
Excessive permeability to plasma proteins in the glomerulus due to GBM change.
Characterized by: Massive proteinuria and lipiduria(oval fat bodies and fatty casts), no or mild hematuria.
Other signs: edema
Characterized by: Massive proteinuria and lipiduria(oval fat bodies and fatty casts), no or mild hematuria.
Other signs: edema
71
New cards
What are the 3 kinds of primary nephrotic syndrome?
Minimal change Dz, Membranous nephropathy, and Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
72
New cards
Describe Minimal change Dz of primary nephrotic syndrome
Allergic reaction, immunization, auto-immune d/o.
Primary cause of nephrotic syndrome in children.
Little evidence of glomerular scarring in kidney biopsy.
UA shows heavy proteinuria and lipiduria
Primary cause of nephrotic syndrome in children.
Little evidence of glomerular scarring in kidney biopsy.
UA shows heavy proteinuria and lipiduria
73
New cards
Describe Membranous nephropathy of primary nephrotic syndrome
Unusual deposits of IgG and C3 immune deposits
74
New cards
Describe Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis of primary nephrotic syndrome.
Scarring of some glomeruli.
Secondary to other D/O(HIV or drugs-heroin & analgesic abuse.
Deposits of IgM & complement C3
Secondary to other D/O(HIV or drugs-heroin & analgesic abuse.
Deposits of IgM & complement C3
75
New cards
What are the two most common causes of Secondary Nephrotic Syndrome
Diabetic Nephropathy and Hypertension(HTN)
76
New cards
Describe diabetic nephropathy and how it relates to Secondary Nephrotic Syndrome
Most common cause of ESRD.
Thickening of the glomerular basement membrane because of increased deposition of glycosylated proteins and sclerosis of vascular structure.
Thickening of the glomerular basement membrane because of increased deposition of glycosylated proteins and sclerosis of vascular structure.
77
New cards
Tubular D/O may:
1. Effect (One/multiple) structures
2. Manifest w/ (focalized/generalized) dysfunction
3. Be (Hereditary/acquired)
4. Be (primary/secondary) to other Dz processes
\
1. Effect (One/multiple) structures
2. Manifest w/ (focalized/generalized) dysfunction
3. Be (Hereditary/acquired)
4. Be (primary/secondary) to other Dz processes
\
1. Both
2. Both
3. Both
4. Both
78
New cards
Understand this chart of tubular D/O
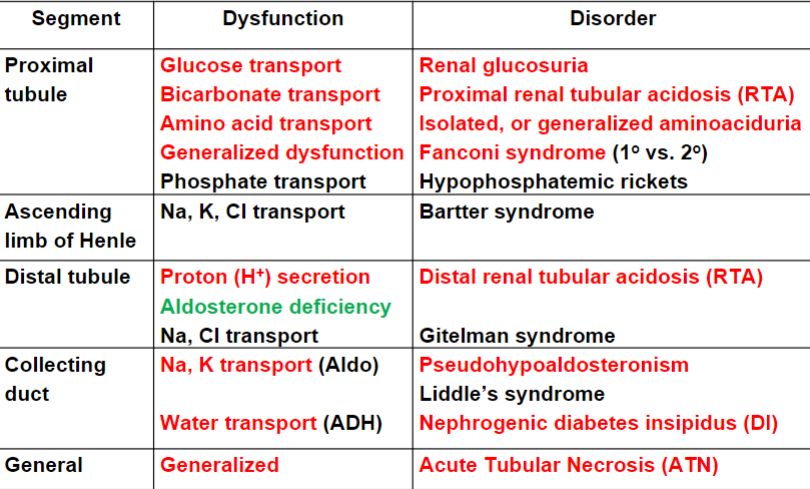
79
New cards
Describe what Renal Glucosuria is and what a UA test would show.
Occurs in PCT
Only affects reabsorption of glucose
UA: Consistent glycosuria w/ normal blood glucose(benign)
Only affects reabsorption of glucose
UA: Consistent glycosuria w/ normal blood glucose(benign)
80
New cards
Understand this graph of Renal Tubular Acidosis(RTA)
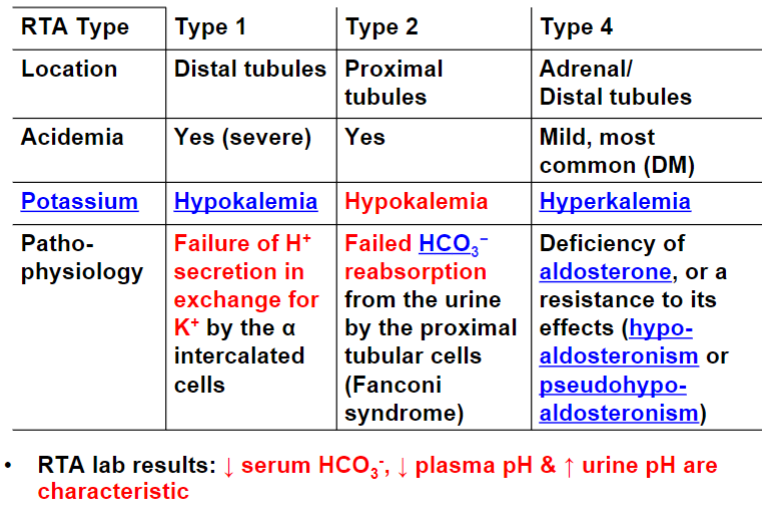
81
New cards
Describe Cystinuria
Inherited defect in the renal PCT transporter protein that reabsorbs cystine and dibasic amino acids.
Excessive cystine from crystals in urine at an early age.
Excessive cystine from crystals in urine at an early age.
82
New cards
Describe Cystinosis
Inherited disease resulting in intracellular deposits of cystine.
Kidney and PCT cells are damaged, losing ability to normally reabsorb filtrate components
Kidney and PCT cells are damaged, losing ability to normally reabsorb filtrate components
83
New cards
What would a UA show of cystinuria and cystinosis
Cystine crystals and all filtered substances in urine
84
New cards
What is Fanconi’s syndrome and how does one get it? What would a UA of it show
Generalized PCT reabsorption failure
\
May be inherited w/ another genetic disorder or acquired in patients treated w/ nephrotoxic drugs
\
UA: Glucosuria w/ normal blood glucose, generalized aminoaciduria, phosphaturia, and increased urine pH
\
May be inherited w/ another genetic disorder or acquired in patients treated w/ nephrotoxic drugs
\
UA: Glucosuria w/ normal blood glucose, generalized aminoaciduria, phosphaturia, and increased urine pH
85
New cards
What is renal Pseudohypoaldosteronism and who is most commonly affected by it
Renal tubules are unresponsive to aldosterone.
Most commonly affect infants w/ renal salt wasting(Increased urinary Na, Cl) & a normal GFR
Most commonly affect infants w/ renal salt wasting(Increased urinary Na, Cl) & a normal GFR
86
New cards
What is Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus and What Characterizes it?
Failure of tubules to respond to ADH
Characterized by: polydipsia, polyuria, and a large volume(diuresis) of very dilute urine
Characterized by: polydipsia, polyuria, and a large volume(diuresis) of very dilute urine
87
New cards
What is Acute Tubular Necrosis(ATN) and what would a UA test of it show?
Destruction of renal epithelial cells.
UA: Renal tubular epithelial(RTE) cells, hematuria, casts(especially RTE casts)
UA: Renal tubular epithelial(RTE) cells, hematuria, casts(especially RTE casts)
88
New cards
What causes rapid onset of ATN
Ischemic damage and nephrotoxin damage(Hgb, Mgb, nephrotoxic abx, and ethylene glycol)
89
New cards
What do tubulo-interstitial diseases and UTIs have in common? What conditions do they include
They affect both the tubules and the interstitium.
Include
* Acute Interstitial Nephritis(AIN)
* Urinary Tract Infection(UTI)
* Upper UTI: pyelonephritis
* Acute pyelonephritis
* Chronic pyelonephritis
* Lower UTI
* Cystitis: Bladder Infection
* Urethritis: Urethra Infection
Include
* Acute Interstitial Nephritis(AIN)
* Urinary Tract Infection(UTI)
* Upper UTI: pyelonephritis
* Acute pyelonephritis
* Chronic pyelonephritis
* Lower UTI
* Cystitis: Bladder Infection
* Urethritis: Urethra Infection
90
New cards
What is Acute Interstitial Nephritis(AIN) and what would a UA test show?
Allergic reaction to medication or toxins can cause inflammation of the interstitium.
UA: Increased eosinophils w/o bacteria(called sterile pyuria)
UA: Increased eosinophils w/o bacteria(called sterile pyuria)
91
New cards
Describe Acute Pyelonephritis; what it is, its 2 possible causes, and what a UA test of it would show.
Infection of the kidneys
Causes:
* Bacteria ascend through ureters from lower UTI
* Bacteremia w/ bacteria localizing in the kidney
UA: Leukocyte esterase(+), nitrite(+/-), pyuria, WBC casts, bacteriuria, and bacterial casts
Causes:
* Bacteria ascend through ureters from lower UTI
* Bacteremia w/ bacteria localizing in the kidney
UA: Leukocyte esterase(+), nitrite(+/-), pyuria, WBC casts, bacteriuria, and bacterial casts
92
New cards
Describe Chronic Pyelonephritis and what a UA test would show.
Chronic inflammation resulting in permanent scarring progressing to renal failure.
Most serious tubulointerstital D/O
UA:
* Early stage: Same as acute pyelonephritis
* Late stage: Casts(WBC, bacteria, granular, broad & waxy), proteinuria, hematuria, decreased SG
Most serious tubulointerstital D/O
UA:
* Early stage: Same as acute pyelonephritis
* Late stage: Casts(WBC, bacteria, granular, broad & waxy), proteinuria, hematuria, decreased SG
93
New cards
What are Cystitis and Urethritis; what are they caused by and what would a UA test show?
Bacterial infection of lower UT
85% are caused by gram negative enteric bacteria(E. Coli)
UA: Many WBC, leukocyte esterase(+), bacterial nitrate(+/-)
85% are caused by gram negative enteric bacteria(E. Coli)
UA: Many WBC, leukocyte esterase(+), bacterial nitrate(+/-)
94
New cards
Describe vascular disease.
One of the most common kidney Dz
Damage or narrowing of renal artery or intrarenal arterioles leading to ischemia(decreased perfusion of kidney)
Serum potassium decrease, urine potassium increase
Damage or narrowing of renal artery or intrarenal arterioles leading to ischemia(decreased perfusion of kidney)
Serum potassium decrease, urine potassium increase
95
New cards
What is Acute Renal Failure? What are it’s symptoms? What would test results show?
Rapid and severe loss of renal function(reversible).
Symptoms: Oliguria
Test results: GFR decrease and azotemia(blood BUN & creatinine levels increase); isosthenuria(lack of renal concentrating ability)
Symptoms: Oliguria
Test results: GFR decrease and azotemia(blood BUN & creatinine levels increase); isosthenuria(lack of renal concentrating ability)
96
New cards
Understand this acute renal failure chart.
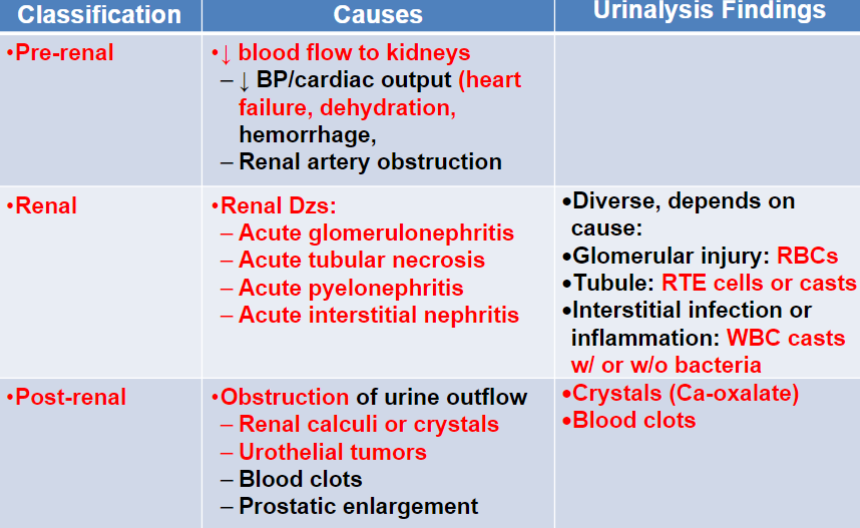
97
New cards
What is chronic renal failure? What are the test results for it vs the test results for ESRD?
Progressive, chronic loss of renal function.
Test results: Gradual decrease in GFR
Test results for ESRD:
* Marked decrease in GFR
* UA: Casts(granular, broad & waxy), Isosthenuria(loss of kidney concentrating function), significant proteinuria, glycosuria
\
Test results: Gradual decrease in GFR
Test results for ESRD:
* Marked decrease in GFR
* UA: Casts(granular, broad & waxy), Isosthenuria(loss of kidney concentrating function), significant proteinuria, glycosuria
\
98
New cards
Understand this table about the stages of chronic kidney disease
99
New cards
What are renal calculi(kidney stones) and what are the precipitating factors for them?
Solid mineral salts are formed in the renal calyces, pelvis, ureters, or bladder.
Precipitating factors:
* Increase in urinary concentration(dehydration)
* Urinary stasis
* Favorable pH, varies depending on type
* Presence of a foreign seed body
\
Precipitating factors:
* Increase in urinary concentration(dehydration)
* Urinary stasis
* Favorable pH, varies depending on type
* Presence of a foreign seed body
\
100
New cards
What are the most common types of kidney stones and what do UA findings show?
Most renal calculi contain calcium ions(80%), a/w renal failure.
Uric acid a/w gout
phosphate a/w UTI
UA: Hematuria, crystals
Uric acid a/w gout
phosphate a/w UTI
UA: Hematuria, crystals