Evaluating Research FINAL
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
This research is considered more humanistic, more descriptive, and harder to measure:
Qualitative research
HIPP, PPI, plagiarism, and risk to participants are all part of _______ ______.
ethical considerations - maybe research integrity
A perfect experiment can be performed. T or F
False
Correlation implies causation T or F
False
______ ______ design allows scientists to reduce the number of groups used in Solomon Design
two-group (comparing two groups of participants
Research allows clinicians and scientists to test questions empirically True or False
true
A research question (or PICO), hypothesis, and rationale are necessary to write a _____ ______.
research paper - Literature review
______ describes human behavior, processes, & phenomena
naturalistic observation? (Observational research and survey
Matching is important because/for (3 things):
cross sectional studies- comparing groups of different ages or severities
nonequivalent groups- matching groups with characteristics that may influence DV
longitudinal design
can match across preferred attributes
provides a control group
A test can be reliable but not valid - True or False
True
In research, ______ & ______ are both about how well a method measures something.
reliability and validity
______ is a form of reliability that is the extent to which a measure is consistent within itself
internal reliability ( split half method) experimental slide
Construct validity is part of:
content-related validity (appropriate content0 - does the test relate to underlying theoretical concepts
Morality and/or attrition refer to what:
attrition refers to the dropping out of participants in a study
A test can be valid but not reliable - True or False
False
Being concise and clear are ways to address _____ concerns in survey research.
response bias???
A Mixed Experimental design utilize what types of data?
qualitative and quantitative data
The simplest factorial design is
two by two design
Exploratory sequential design follows the order
Qualitative Data Collection and Analysis - Builds to - Quantitative Data Collection and Analysis - Interpretation
The advantage of multiple baseline design in SSD are:
look at different behaviors across 2 or more situations or same behavior across 2 or more settings - useful when looking at generalization
A design that follows a group of participants for three years is called:
longitudinal study
Explanatory sequential follows what order for data acquisition and analysis?
Quantitative Data Collection and Analysis - Follow up with 0 Qualitative Data collection and Analysis - Interpretation
Name one advantage of SSD
•Focuses on individuals
•Detailed analysis of treatment “responders” and “non-responders”
•Ideal for low-incidence populations/disorders
•Cost-effective
•Looks for effects large enough to detect through visual inspection
•Does not require complicated statistics
•Identifies interventions that are appropriate for large-scale analysis
•Clinically relevant and practical

Review articles synthesize evidence- True or False
True (detailed strategy, extract points related to the strategy, examine design and then include or exclude articles.
Statistical analysis can be divided into _____ & ______ statistics.
descriptive and inferential
The most common procedure used for analyzing the different between 2 means is a ___ - _____.
t-test??
The ________ is usually set at 0.05, called the probability value, and used to reject or accept the null hypothesis.
P-value
The tail of positively skewed mean distribution is on the ______.
right side of distribution

The tail of negatively skewed mean distribution is on the ______.
left side
The 3 phases of the qualitative research cycle are:
Collect data, code data, provide summary
The 3 ways to analyze qualitative research are:
thematic analysis, conversational analysis, phenomenology, grounded theory, ethnography
When collecting/analyzing data, challenged to survey research are: (name 3)
nonresponse bias, social desirability bias, partial completion, Christmas tree responses, DK/Na alternative
An example of an attribute is _____ (just name one).
age, gender, language
The most basic SSD design for analysis is _______.
AB (baseline prior to intervention. treatment is introduced and changes in depend variables are noted
Survey & observational research are this type of research:
Hint: (qualitative/quantitative/mixed)
qualitative (probably mixed)
Any variable that has the potential to affect the study and was not purposefully introduced is called a(n) ______ _______.
extraneous/confounding
A dependent variable (DV) is also called the ______ variable.
Outcome - (what is being measure- frequency, duration, accuracy)
An independent variable (IV) is also called the “I” or the ______, in the PICO question.
Intervention ( drugs, sleep, exercise)
The purpose of Correlational Research is what?
to understand and find relationship between two variables
This research design is called the “N of 1”
Single-case design
¡R - Group of randomly assigned individuals
¡N - Group not/semi-randomly assigned
¡O - Observation (you take data here)
¡Xn - Experimental Group in the n condition (e.g., X1 vs X2)
¡Ø / - No experimental condition

mixed method might be hard why?
more resource intensives (like two studies) can end up with an overwhelming amount of data, difficulty in integrating the data all together
Observational - naturalistic observation vs participant observation
naturalistic- study behaviors of people or animals as they act in everyday environment.
participant observation- researcher joins group being observed- or makes presence known
stratified sampling vs simple random sampling
stratified sampling- population is divided into subgroups and then is randomly selected
simple random- selecting individuals randomly from entire population
Myths of SSED
•SSED is non-experimental
•SSED is not an established/valid research method
•SSED cannot determine causality
•SSED has only one participant
•SSED is really complicated

reliability refers to what and validity refers to what
reliability refers to consistency of measure (whether the results can be reproduced under the same conditions)
validity- refers to accuracy of a measure (whether the results represent what they are supposed to measure
Elements of a research paper
Introduction- meant to hook reader with research question
Body- main argument, or rationale, contains headings, subheadings, and the paragraphs
Conclusion - summarizes key points
levels of measurement in order
Ratio - highest
Interval
Ordinal
Nominal - lowest
Ratio -
Interval -
Ordinal -
Nominal -
Ratio- true zero exists- no quantity less than zero
Interval- I.Q test - 120 is better than 60 but person is not twice as smart Temp - no absolute zero
Ordinal- can be ordered least to greatest. Education attainment
Nominal Gender- male female - categories not more or less than one another
____ are often the primary means of displaying and interpreting data in a single subject design
graphs
scatterplot used for-
studying the relationship between two variables
range vs mode vs median
used to identify highest and lowest scored
mode- data that occurs most frequently in a set of data
median- middle score when numbers are lines up least to most
standard deviation
value that shows the relation that individual scores have to the mean of the sample
coefficient of variation
often more meaningful to express SD as a percentage of what is being measured
what is standard score (z score)
represents number of standard deviation units a specific score differs from the mean
what is kurtosis
the peakedness (how flat or sharp) is peak- negative flatter than normal
PICO
Population/problem
Intervention
Comparison
Outcome
What are some drawbacks to mixed-methods
more resource intensive
can end up with an overwhelming amount of data
Difficulty in integrating the data together
May affect IV/DV relationship but is out of experimenter control
Sometimes difficult or impossible to control, but can try:
Elimination
Randomization – very difficult to do
Build into design
Match participants
Statistically equate groups

extraneous
benefits of SSED
•Focuses on individuals
•Detailed analysis of treatment “responders” and “non-responders”
•Ideal for low-incidence populations/disorders
•Cost-effective
•Looks for effects large enough to detect through visual inspection
•Does not require complicated statistics
•Identifies interventions that are appropriate for large-scale analysis
•Clinically relevant and practical

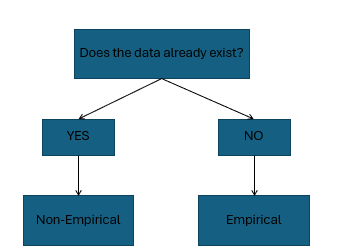
empirical vs non-empirical S