XPhys Exam 1
1/244
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
245 Terms
how many kcal is a carb
4
how many kcal is a fat
9
how many kcal is a gram of protein
4
What type of exercise are carbs used the most
intense
what is gluconeogenesis
making new glucose in liver
what is glycogenolysis
breaking down glycogen
where is glycogen stored the most
skeletal muscle
What 3 places is glycogen stored?
liver, skeletal muscle, plasma glucose
how much carbs should a physically active person eat?
400-600g (60% daily total)
how much carbs should an althlete eat?
70% of total kcal
how does carb loading impact exercise
you can exercise at a higher intensity for longer
what does carb depletion do to fat and protein use
increases it
where are lipids stored? (4)
adipose tissue, intramuscular triglycerols, plasma FFA, and plasma TGs
how much fat intake is recommended?
20-35% of kcals
as exercise duration increases, fat use (increases/decreases)?
increases
what is the best intensity to burn fat
low intensity
how does fat / carb use change with training?
after training more fat is used first
how much protein intake is recommended?
0.8-2.0/ kg/ day
when does muscle protein synthesis occur the most
during recovery from exervise
what types of reactions are important in the ETC for resynthesizing ATP?
Redox
What are 4 factors that affect the rate of energy conversion?
enzymes, coenzymes, availability of substrates, and environmental factors
energy released form macronutrients gets used to…
rephosphorylate ATP
What are teh 3 energy systems for resynthesizing ATP?
ATP-PCr, glycolysis, and oxidative phosphorylation.
What does the relative contribution of the 3 energy systems depend on?
macronutrient availbility, exercise intensity, and need for energy
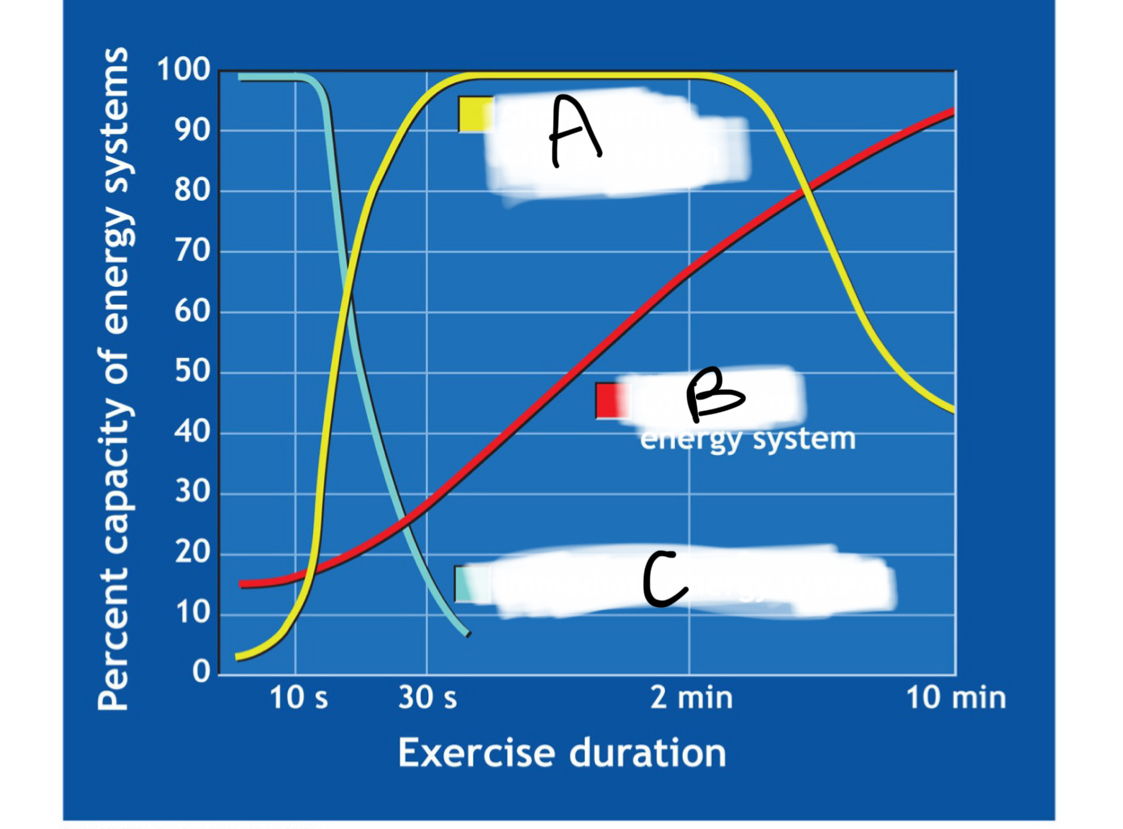
label A, B and C
A= glycolysis, B=oxidative phosphorylation, C= ATP-PCr
() systems produce energy faster than () systems
anaerobic; aerobic
anaerboic systems produce (more/less) energy than aerobic systems
less
energy systems/ processes producing the most E are located in the () of cells
mitochondria
T/F All energy systems are functioning all the time
True
Where does ATP-PCr occur?
in cytosol of muscle cells
What is the main enzyme in ATP-PCr
creatine kinase
Resting ATP stores would sustain resting energy needs for only ….
1-2 min
what are the reactants in ATP-PCR
ADP and creatine phosphate
resting PCr stores are ( ) resting ATP stores
the same as
What is the theory behind creatine supplementation
increased creatine can increase PCr levels increasing the duration of time that ATP-PCR supplies majority of energy during high-intensity activity.
T/F - creatine supplementation has an immediate effect?
false; it takes time to build stores
what enyme turns 2 ADP to ATP and AMP
Adenylate kinase
How many steps in glycolysis for glucose?
10
how many steps in glycolysis for glycogen
9
is glycolysis anaerobic or aerobic?
anerobic
where does glycolysis occur
cytosol
What is the first step of glycolysis?
glucose to G6P
what turns glucose into G6P
hexokinase
G6P turns to ____ in glycolysis?
fructose 6-P
what turns G6P to fructose 6P
glucose 6-phosphate isomerase
what does fructose 6-P turn into
fructose 1,6 bisphosphate
What turns fructose 6P to fructose 1,6 P
phosphofructokinase
what does fructose 1,6 P turn into
dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
what turns dihydroxyacetone phosphate into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate?
triosephosphate isomerase
What breaks apart fructose 1,6 bisphosphate into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate?
aldolase
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate turns into what next, and by what enzyme?
1,3 bisphosphoglycerate; glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
1,3 BPG turns into what next?
3-phosphoglycerate
what turns 1,3 BPG into 3-PG?
phosphoglycerate kinase
3-PG turns into what; by what enzyme?
2-phosphoglycerate by phosphoglyceromutase
2- PG turns into phosphoenol pyruvate by what enzyme
enolase
2 PG turns into what next?
phosphoenolpyruvate
PEP turns into what next>
pyruvate
what turns PEP to pyruvate?
pyruvate kinase
in what steps of glycolysis is ATP USED?
glucose to G6P , F6P to F1,6 BP (hexokinase and phosphofructokinase)
In what steps of glycolysis is ATP MADE?
1,3 BPG to 3PG and PEP to pyruvate (kinases)
What steps is NADH made in glycolysis?
G3P to 1,3 BPG
Each glucose when fully broken down forms two
lacatate or acetyl-CoA
what is the rate limiting enzyme of glycolysis
phosphofructokinase (PFK)
what is the net gain of glycolysis from glycogen?
3 ATP
what is the net ATP gain of glycolysis from glucose?
2 ATP
what affects the rate of ATP-PCr
the levels of PCr
() and () affect the rate of glycolysis
PFK, and glucose/glycogen storage
about () % of the potential energy in glucose is ultilized to produce ATP in glycolysis
3-5
how many atp does ATP-PCr yield
1
without sufficient oxygen glucose is converted to
lactate
what enzyme converts pyruvate to lactate
lactate dehydrogenase
where does lactate go durign exercise?
stays in muslce, and is transported to blood
what buffers lactate in blood?
bicarbonate
after cessation of exercise lactate is
converted back to glucose or used for energy
in the liver lactate can be
convered to glucose (stored as glycogen)
what two tissues can use lactate as energy?
brain and heart
When there is suffient oxygen pyruvate is converetd to ( ) by ( )
acetyl CoA; pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
how many atp is made from krebs?
2 (1 per cycle)
how many NADH frm glycolysis?
2
how many NADH from Krebs
6
how many FADH2 from Krebs
2
how many NADH from pyruvate→ acetyl coa
2
what is the rate-limiting step in Krebs?
isocitrate dehydrogenase
acetyl-coa combines with ( ) to make ( )
oxaloacetate; citrate
what turns acetyl coa and oxaloacetate into citrate?
citrate synthase
what does citrate turn into before isocitrate
cis-aconitate
what does citrate ultimately convert to ; by what enzyme?
isocitrate; aconitase
isocitrate converts to
oxalosuccinate
isocitrate —> oxalosuccinate by which enzyme?
isocitrate dehydrogenase
what does isocitrate ultimately convert to
alpha-ketogluterate
what turns isocitrate to a-ketogluterate
isocitrate dehydrogenase
what does a-ketogluterate turn into
succinyl-coa
what enzyme a-ketogluterate—> succinyl coa
a-ketogluterate dehydrogenase
succinyl coa turn into what; by what enzyme
succinate; succinyl-coa synthetase
succinate turns into ( ) by ( )
fumerate; succinate dehydrogenase
what does fumerate turn into
malate
what turns fumerate —> malate
fumerase
malate turns into
oxaloacetate
what enzyme converts malate—> oxaloacetate?
malate DH
in what step of krebs in ATP made?
succinyl coa—> succinate