8. Multiple Regression
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What does change in a multiple regression compared with other types?
we build a model to explain the variance using a linear equation
we test how well the variability of the scores is explained by the model (R2 and significance of F)
usual assumptions apply inc. Homoscedasticity and normally distributed residuals
What are the features new in multiple regression compared with other types?
model built using more than one predictor
examine how much each predictor contributes to predicting the variability of the outcome measure (forced entry and hierarchical regression)
compare different models predicting the same outcome (hierarchical regression)
new checks on the data for assumptions and issues
What is the difference between R2 and adjusted R2?
R2 tells us the estimate for our sample. Will be an overestimate of the real R2 in the population
Adjusted R2 is an estimate for the population. Adjusted down to allow for the overestimation of R2. Better reflection of the real R2
the adjustment relates to sample size (bigger sample = less need for adjustment
What determines the degrees of freedom for the regression?
number of predictors (k)
What is the role of b values in multiple regression?
we can get individual bs for each of our predictors
they are the estimate of the contribution while controlling for the other variables
estimate of the individual contribution of each predictor
What makes us the equation in multiple regression?
we have a number of predictors to add to the equation
there is still one intercept b0
however, there is more than one predictor
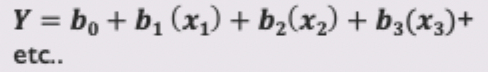
What are the 3 questions we can ask in multiple regression?
How much of the variance in wellbeing does the overall model with the five predictors accounts for? (similar to simple)
Do all the predictors contribute to the model?
How do all the predictors contribute to the model? Can we tease apart the contribution of individual predictors?
Why do we need beta weights in multiple regression?
Normal bs are affected by the distribution and type of score. Can use them in equations but can’t compare them esp. if they are different measures (IQ vs Age vs GPA)
So we standardise. Standardised score is simply the number of SDs from the mean of the scores.
We can then compare the contribution of each variable to the outcome, in terms of standard deviations.
What does the beta weight 0.594 show?
As our predictor increases by one standard deviation, the outcome increases by 0.594 of a standard deviation
What does the beta weight of -0.126 show?
As the predictor increases by one standard deviation, the outcome decreases by 0.126
What does testing each regression coefficient (b) in multiple regression tell us?
Whether each predictor contributes uniquely to explaining the outcome, after controlling for other predictors.
What statistical test is used to determine if a regression coefficient is significantly different from zero?
A t-test
What does it mean if a predictor is “significant” in a multiple regression model?
The predictor has a statistically significant unique effect on the dependent variable (p < .05).
What does the 95% confidence interval for a regression coefficient represent?
A range of values within which the true population coefficient is likely to fall.
How do you know from the confidence interval whether a predictor is significant?
If the 95% CI does not include zero, the predictor is significant.
This is directly linked to the t-test:
If the CI does not include 0, the coefficient is significantly different from zero → predictor is significant
If the CI does include 0, then zero is a plausible value → predictor is not significant
This is because CI-based significance testing aligns with t-tests at the same confidence level.
How come correlations show significant relationships between almost all big 5 factors but regression only shows that extraversion and conscientiousness are significant?
the regression analysis controls for the other variables when estimating significance and importance
the bn and beta’s are better estimates of the contribution of individual predictors
you can’t really trust your correlations, they are just an estimate of the two variables relationship without the other variables taken into consideration
How can we introduce categorical variables into regression?
Dummy coding using 1s and 0s
e.g. a two-level variable (gender) could be coded 0 for female and 1 for male
a way to introduce more levels
the variable is then entered in as you would a non-dummy variable
What does it mean if the b/beta value is positive in the Dummy variables output?
the category coded as 1 is higher in the outcome variable than the category coded as 0
What does it mean if the b/beta value is negative in the Dummy variables output?
The category coded as 0 is higher in the outcome variable
What are the usual assumptions that also apply for multiple regression?
variable type: outcome must be continuous (predictors can be continuous or discrete)
non-zero variance
independence
linearity
homoscedasticity
normally distributed errors
check for outliers and influential cases
What is multicollinearity?
multicollinearity exists when predictors are highly correlated with eachother
if predictors are highly correlates it’s difficult to separate them. All measuring similar thing
this assumption can be checked with collinearity diagnostics
How can multicollinearity affect findings?
can undermine your findings
b can be unstable (vary from sample to sample)
difficult to say which predictor is important
less likely to find a result if you have multicollinearity
What can we look for in output to determine multicollinearity?
the VIF is a measure of each predictor’s relationship with other predictors - we want this to be low: anything close to 10 is an issue
tolerance is 1 divided by the VIF, should be above 0.2
How do we check for outliers and influential cases?
check for high standardised residuals: only about 5% should be over 2 SD
Cook’s distance: measure of influence of each case on the model. most if not all cook’s distances should be below 1
What can we do if we violate the assumptions for multiple regression?
Robust regression (regression without the assumptions)
Bootstrapping: a method of finding results and their significance that doesn’t rely on underlying distributions, relies on “resampling”
can be used in regression to derive both the coefficients and the associated tests of significance
Why might we use hierarchical regression?
as a different way to introduce variables in the analysis
How do we perform hierarchical regression?
We add the variables into the equation in steps
We add the control variable in first. Examine the R2 and its significance.
Then add the variable we are interested in and run the analysis again
This gives us two models
We are interested in the change of predictive power from Model 1 to 2
How can we compare between models in hierarchical regression?
The F ratio change compares the models and tells us there is a significant improvement in variance explained in model 2
How is F change calculated?
(SSreg model 2) - (SSreg Model 1)
divided by df of change
divided by MS residual of model 2