quarter 1 basics
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
CO equation
co = HR x SV
HR and SV relationship
inverse so inc HR dec SV to maintain the CO
normal CO indexed
2.5 - 4
Tachycardia (inc HR so dec SV) is caused by
Hypovolemia, low BP, fight/flight or a fever
bradycardia (dec HR so inc SV) is caused by
arrhythmias, heart blocks or MI
if the HR >180 in a healthy person
the heart is beating too fast leaving no time for the ventricles to fill so SV cant compensate and CO will dec
SV depends on
preload, afterload and contractility
preload
how much the ventricles can fill/stretch so its affected by blood Volume/distribution and will inc with Fluid Overload (regurgitation)
inc preload causes
dilation and volume overload patterns
Frank Starling Law
inc Preload = inc Stretch = Inc Contraction so if more blood enters the ventricle more
contraction force is required to eject that blood
afterload
resistance the heart faces so it inc with systemic HTN (LV), pulmonary HTN/COPD (RV) or stenosis and causes hypertrophy which can lead to enlargement as the muscles give out
how afterload affects the atria
anything that inc LVEDP can cause the atria to dilate
VTI measures
how far blood travels back in a time period
PAP should be
<25 (>35 is abnormal)
if the heart is boot shaped
move up
continuity equation (gives AVA)
AVA = lvot x lvot VTI / AV VTI
TAPSE vs TDI of the Right heart
tapse measures how far the annulus moves toward the apex in systole while TDI measures the velocity of the annulus toward the apex
MCConnell's Sign indicates
acute PE (hypokinetic RV but the apex dips down)
CVP (central venous P) is the same as
RAP
TV vs MV
the TV is more apical
Bernoulli Equation (finds PAP)
PAPs = 4 V^2 + RAP
max normal aov velocity
<2.5m/s (severe >400)
HF findings
dec ventricular function, ventricular enlargement and possible regurgitation
left heart failure symptoms
breathing symptoms and fluid retention (from a backup of blood) causing weight gain/edema
how the heart will compensate for HF
inc HR to maintain co, hypertrophy from inc P or LVE to inc preload
hypertrophy is usually associated with
HFpEF since the large ventricles leave little room to fill causing diastolic dysfunction
enlargement is usually associated with
HFrEF since the walls are thin and cant contract to push more blood out causing systolic dysfunction
exertional angina is associated with a
70% reduction
resting angina is associated with a
90% reduction
Prinzmetal’s Variant Angina is caused by
coronary spasm (usually from drug use)
Prinzmetal’s Variant Angina can occur in
normal coronaries or adjacent to atherosclerosis
ST depression is associated with
acute coronary syndrome, hypertrophy or bundle branch blocks
STEMI will have inc
enzymes, creatine kinase and troponin
MI can cause
MR, pericardial effusion, aneurysm or VSD
% of people with Sudden cardiac death who die
80%
4-6 weeks after a MI can cause
LV wall thinning with inc echogenicity
Plaque vs thrombus
Plaque forms on artery walls while thrombus forms in areas of stasis
complete occlusion causes a
STEMI
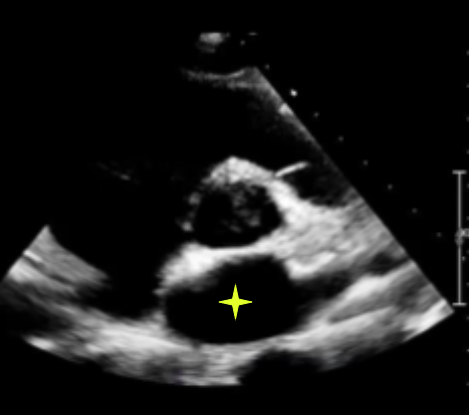
LA
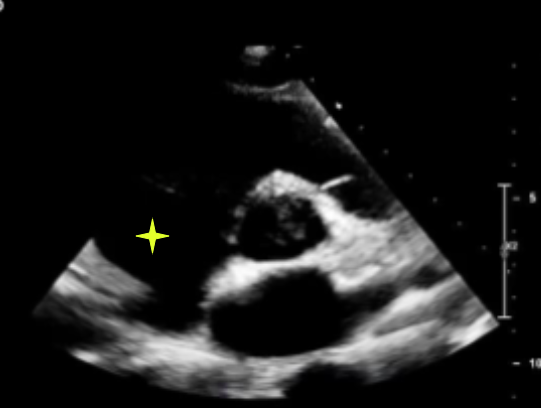
RA
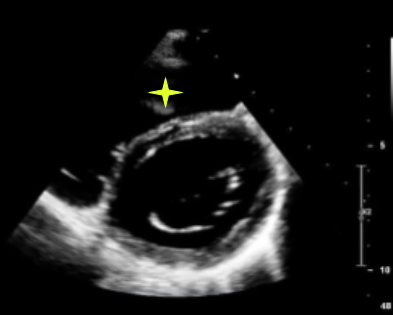
RV
most severe arrhythmia
vent fib
arrhythmia with a sawtooth pattern
a flutter
where should you measure for patients with a Sigmoid Septum
slightly apically
systolic click murmur indicates
MVP
what week is the heart fully developed
week 7
grade 3 diastolic dysfunction occurs when
E/A >2 (should be <0.8)
E/e’ should be
<14
septal e’ should be
>7 and lateral e’ should be >10
TR velocity should be
<2.8m/s
HFpEF parameters for diastolic dysfunction (only need 50% or more to occur)
E/e’ >14, septal e’ <7, lateral e’ <10, TR >2.8 and LA >34
grade II diastolic dysfunction occurs when (only need 2-3 to occur)
E/e’ >14, TR >2.8 or LA >34 (if only 1 is true then grade I)
AR PHT
>500 is mild but <200 is severe
AS AVA
>1.5 is mild but <1 is severe
mild MR/TR eroa is
<0.2 but severe is >0.4
systolic heart failure is caused by
dec contractility causing the heart to dilate (from MI, DCM or myocarditis)
diastolic heart failure is caused by
inc afterload causing the heart to hypertrophy (from HTN or AS)
both systolic and diastolic HF will
dec CO
E wave coordinates with
early filling
when measuring E wave use
time not slope
normal e wave decel time
>160
e’ refers to the
peak velocity of the MV annulus (LV dysfunction causes dec annular motion)
e’ is affected by
LV relaxation and filling P
if E/e’ is >14 there is
elevated LV filling P
elevated RVSP can indicate elevated
LAP

normal or grade 2 (pseudonormal)
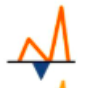
grade 1
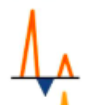
grade 3 restrictive (fuses with valsalva)
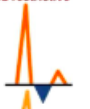
grade 4 fixed restrictive (doesnt change with valsalva)
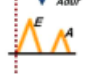
valsalva
normal
equation used to find PAP is called
Bernoulli
equation used to find AVA is called
continuity