SPH3U1 - Physics Unit 1
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Kinesmatics
The study of motion/how objects move
Scaler Quantities
A quantity that has only magnitude (size)
Ex: Distance
Vector Quantities
A quantity that has both magnitude and direction
Ex: Velocity - Measures speed and direction
Reference point
A place or object used for comparison to determine if something is in motion
Position
The distance and direction of an object from the reference point
Displacemnet
Change in position of an object
Formula:
Total displacement if an object moves more than once
Formula:
Vector Scale Diagram
Vectors associated with total displacements drawn to a proportionate scale.
Ex:
Directed line Segment
A straight line between 2 points with a specific direction
Difference between speed and velocity
Speed - Deals with how fast an object moves
Velocity - Deals with how fast and what direction an object moves
Average Speed
Vav = Avg Speed
Δd = Total distance
Δt = Total time
Average Velocity
Vav = Avg Velocity
Δd = Total distance + direction
Δt = Total Time
Motion with uniform/constant velocity
Object travels in a straight line with a constant velocity
Motion with non-uniform/constant velocity
Motion in which the object’s speed changes or the object does not travel in a straight line
Ex: Traveling at a constant velocity, but in multiple directions
What is acceleration
Rate of change of velocity (m/s²)
Position-Time Graph: Horizontal Line ABOVE X-Axis
No velocity - object at rest
Slope = 0
Stationed east of the reference point
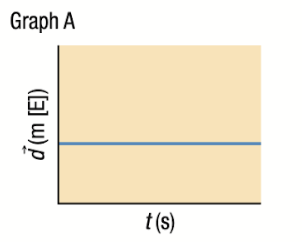
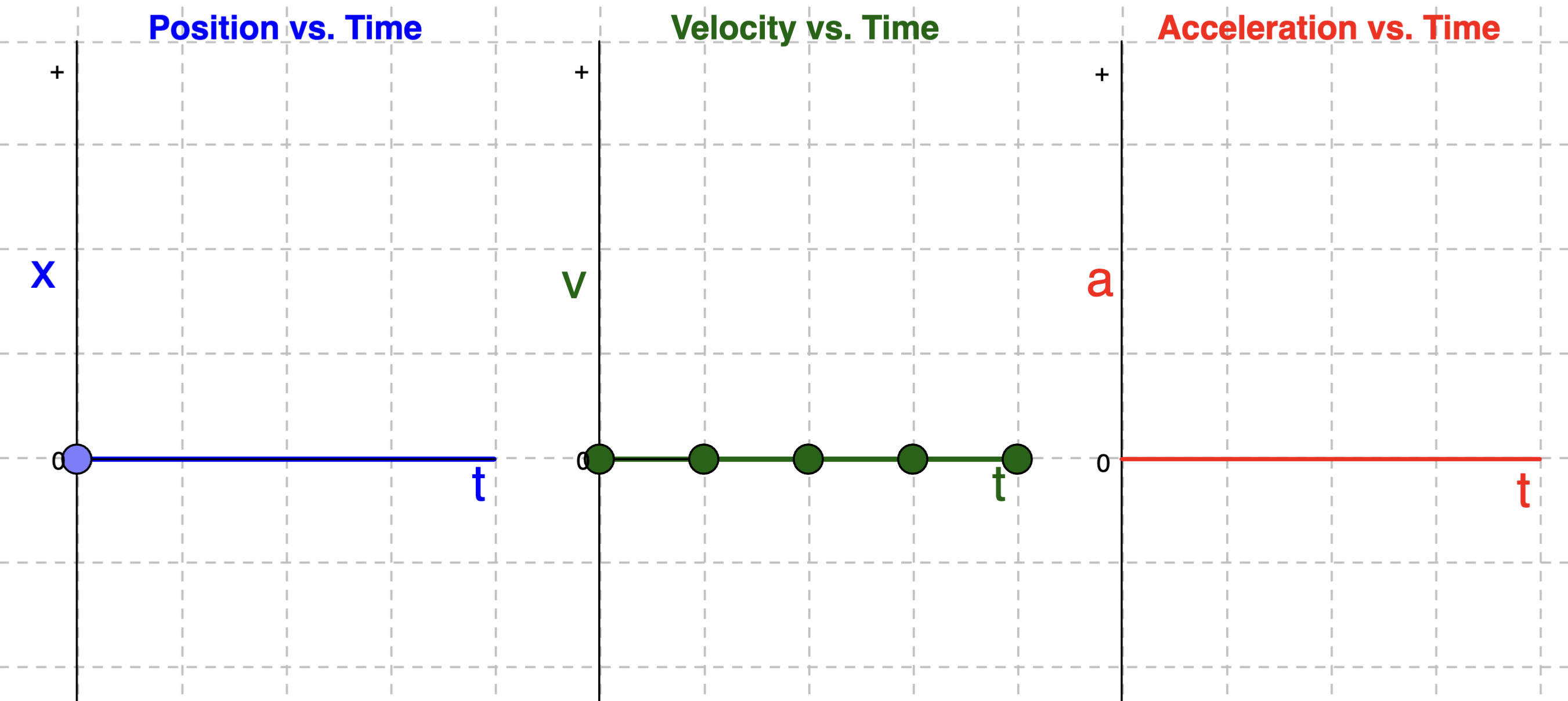
Velocity and Acceleration Time Graphs if position-time graph is a horizontal line ABOVE x-axis
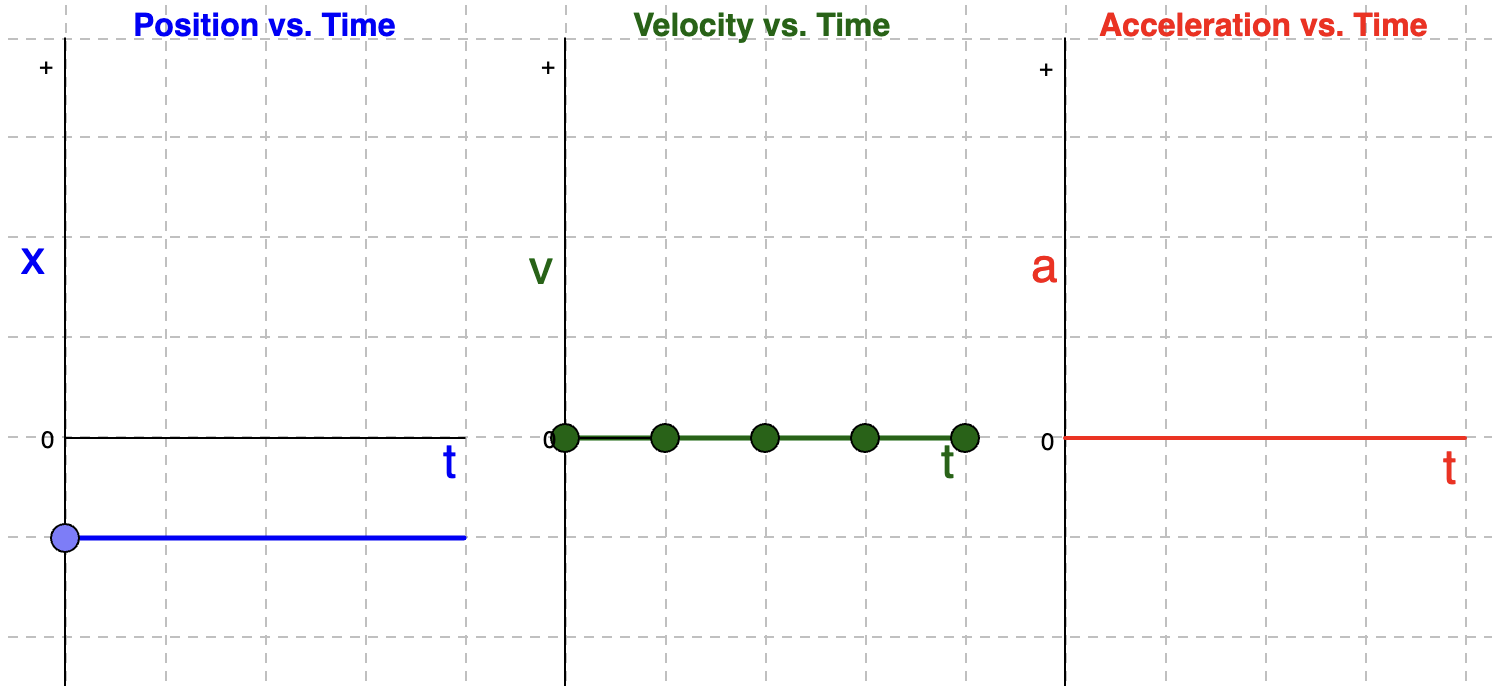
Position-Time Graph: Horizontal Line BELOW X-Axis
No velocity - object at rest
Slope = 0
Stationed WEST of reference point
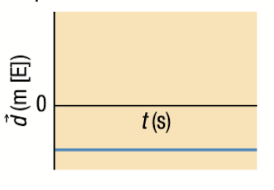
Velocity and Acceleration Time Graphs if position-time graph is a horizontal line BELOW x-axis
Position-Time Graph: Gradual Positive Slope
Straight Line = Constant Velocity
Positive Slope = Displacement in y-axis indicator
Y-axis title indicates direction
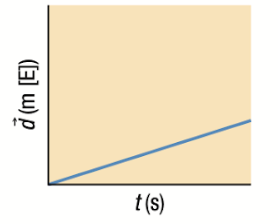
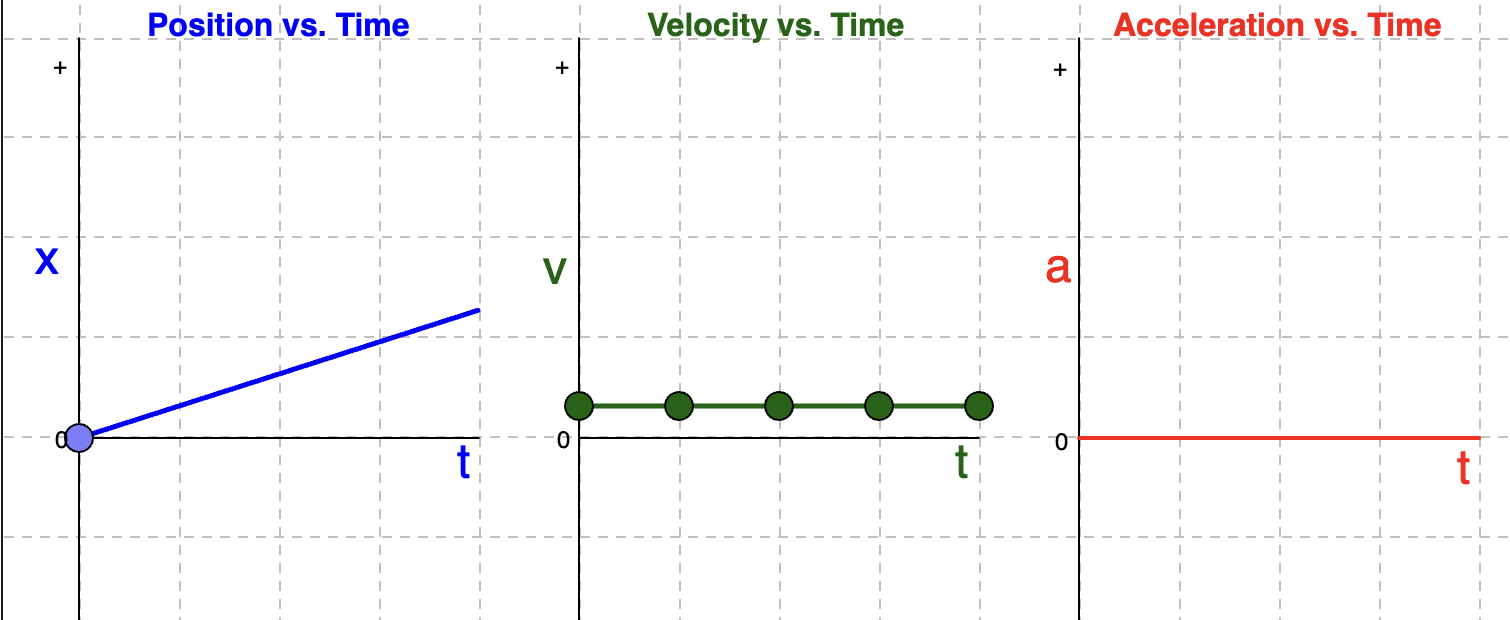
Velocity and Acceleration Time Graphs if position-time graph is a gradual positive slope
Position-Time Graph: Steep Positive Slope
Straight Line = Constant Velocity
Positive Slope = Displacement in y-axis indicator
Y-axis title indicates direction
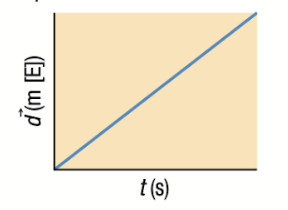
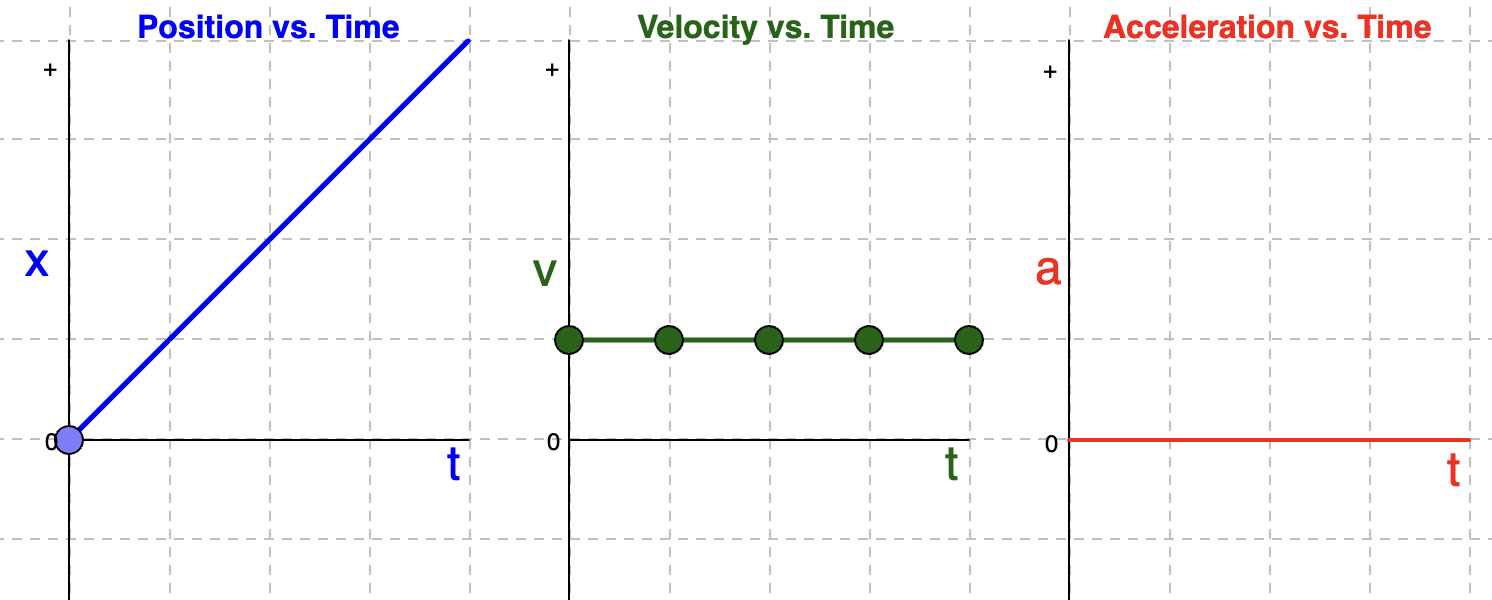
Velocity and Acceleration Time Graphs if position-time graph is a STEEP positive slope
Position-Time Graph: Negative Slope
Straight line = Constant Velocity
Negative Slope = Displacement in a negative Eastward direction until it passes the reference point.
If slope passes the x-axis or reference point object starts moving in the opposite direction
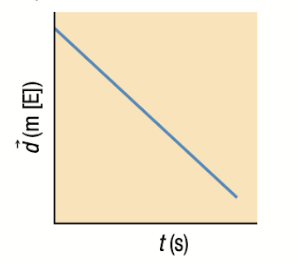
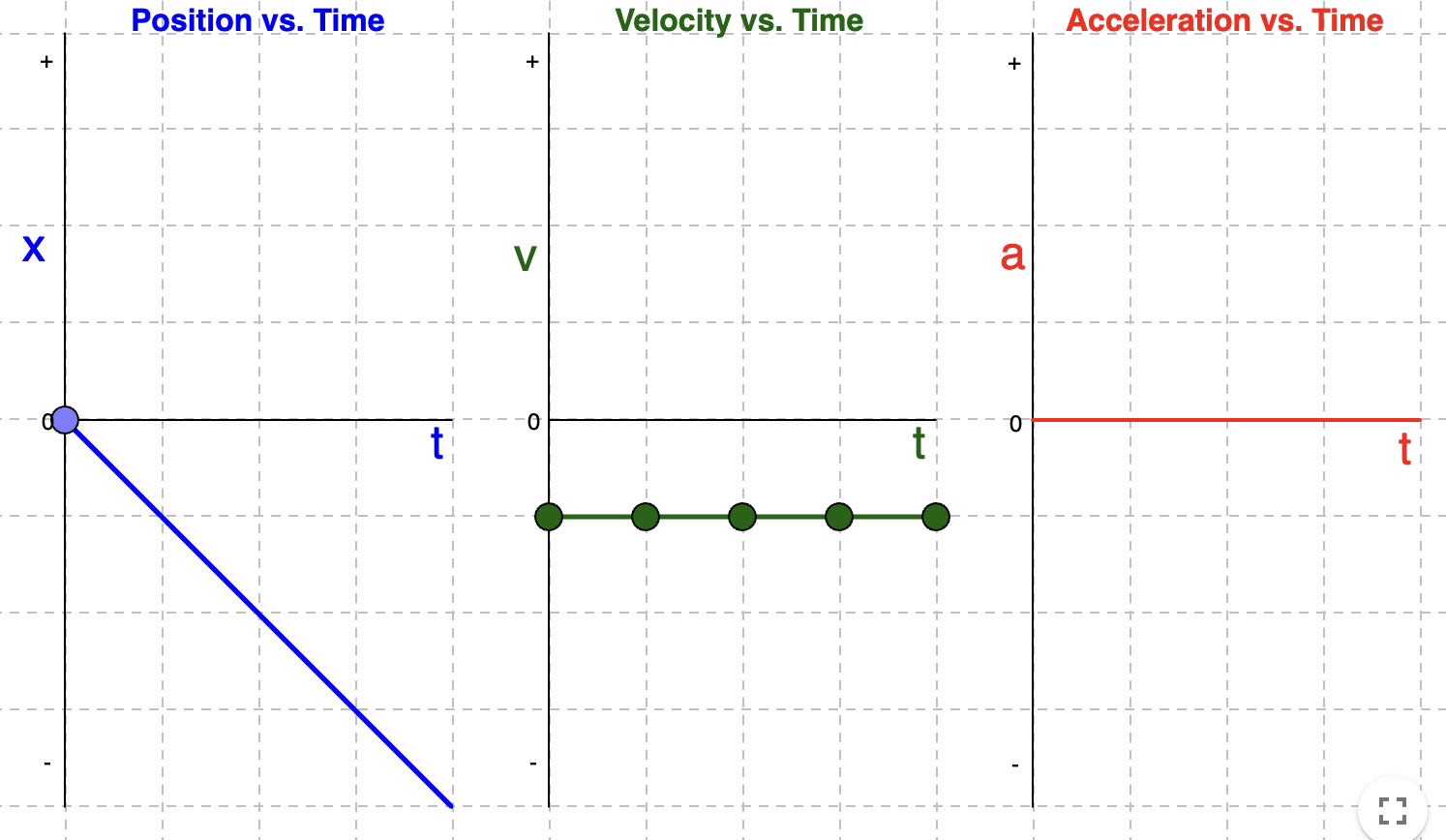
Velocity and Acceleration Time Graphs if position-time graph is a negative slope
Position-Time Graph: Positive Parabola ABOVE the horizontal line
Object speeding up EASTWARD
Upward parabola above X-Axis = Object speeding up
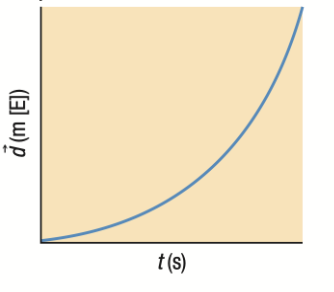
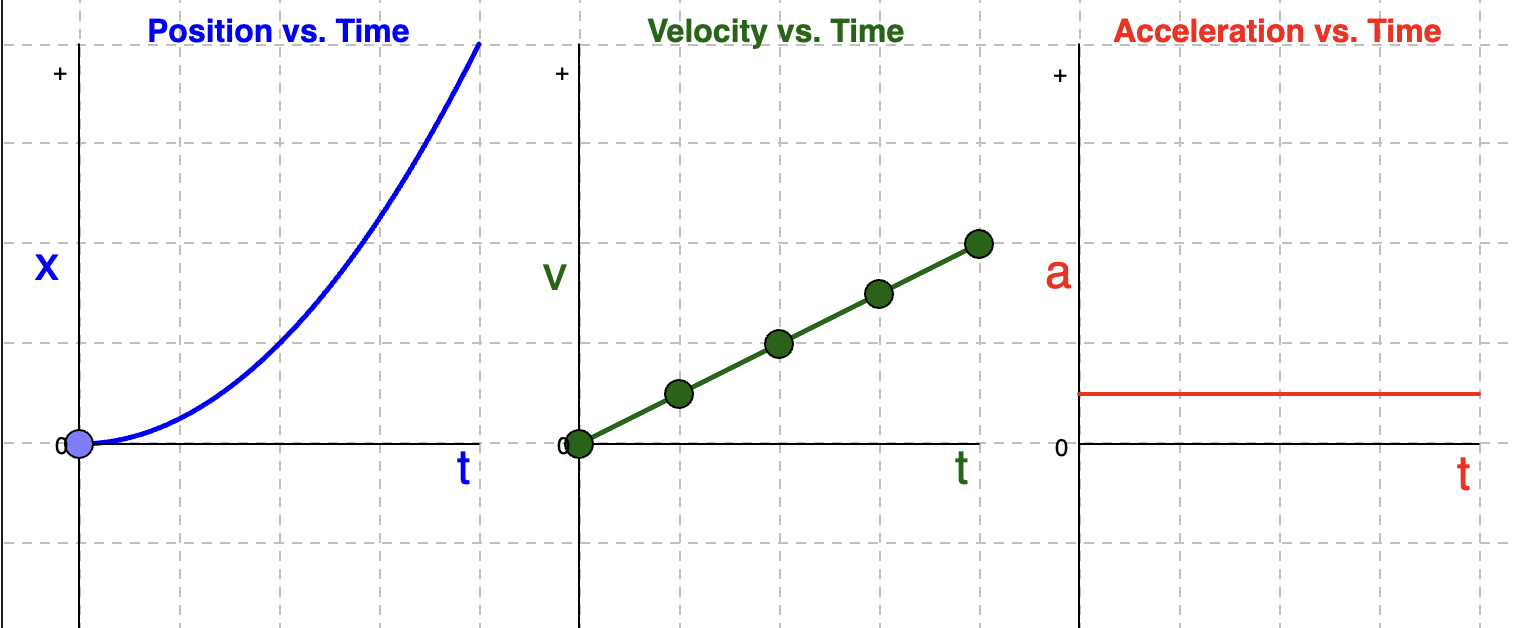
Velocity and Acceleration Time Graphs if position-time graph is a Positive Parabola ABOVE the horizontal line
Position-Time Graph: Positive Parabola BELOW the horizontal line
Object slowing down WESTWARD
Negative velocity
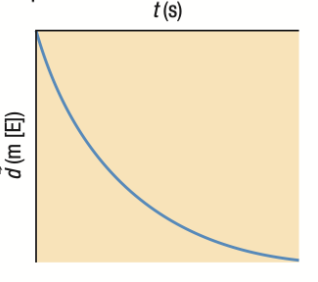
Velocity and Acceleration Time Graphs if position-time graph is a Positive Parabola BELOW the horizontal line
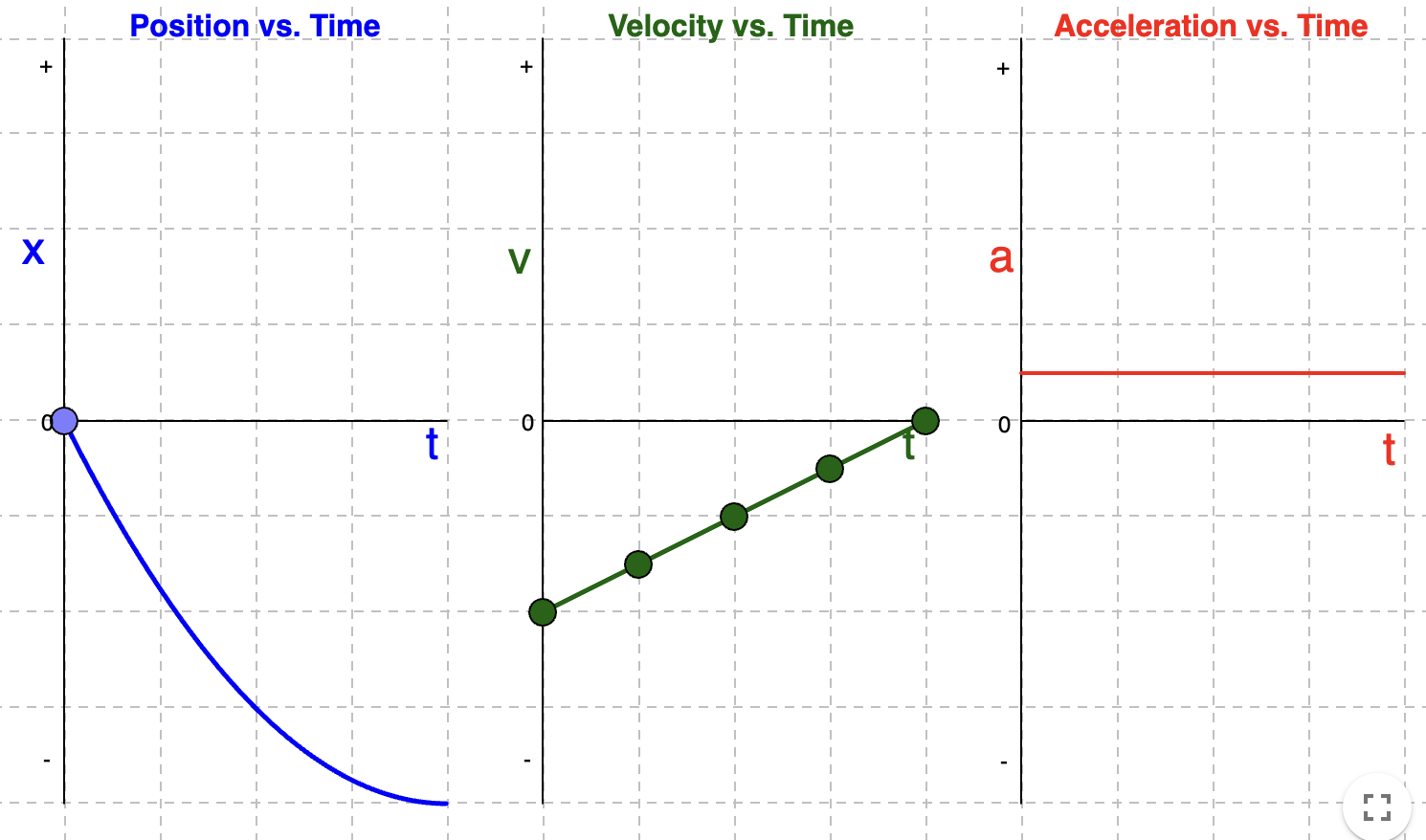
Position-Time Graph: Negative Parabola ABOVE the horizontal line
Object slowing down EASTWARD
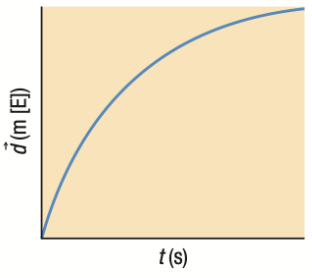
Velocity and Acceleration Time Graphs if position-time graph is a Negative Parabola ABOVE the horizontal line
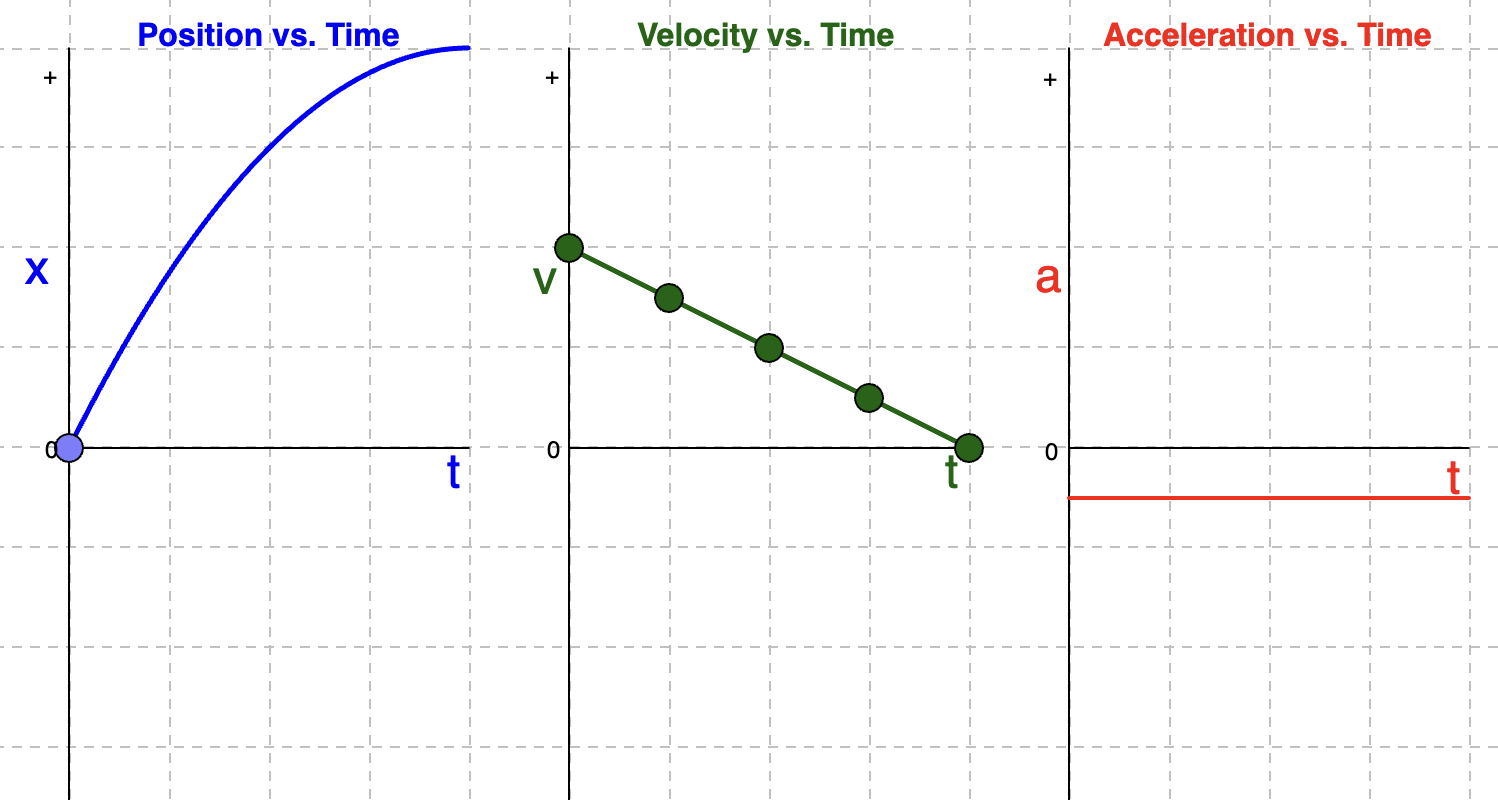
Position-Time Graph: Negative Parabola BELOW the horizontal line
Object speeding up WESTWARD - moving in a negative direction
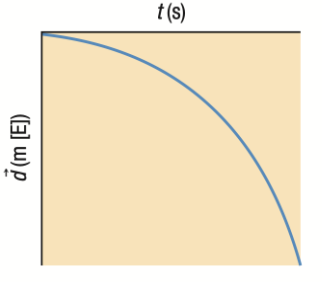
Velocity and Acceleration Time Graphs if position-time graph is a Negative Parabola BELOW the horizontal line
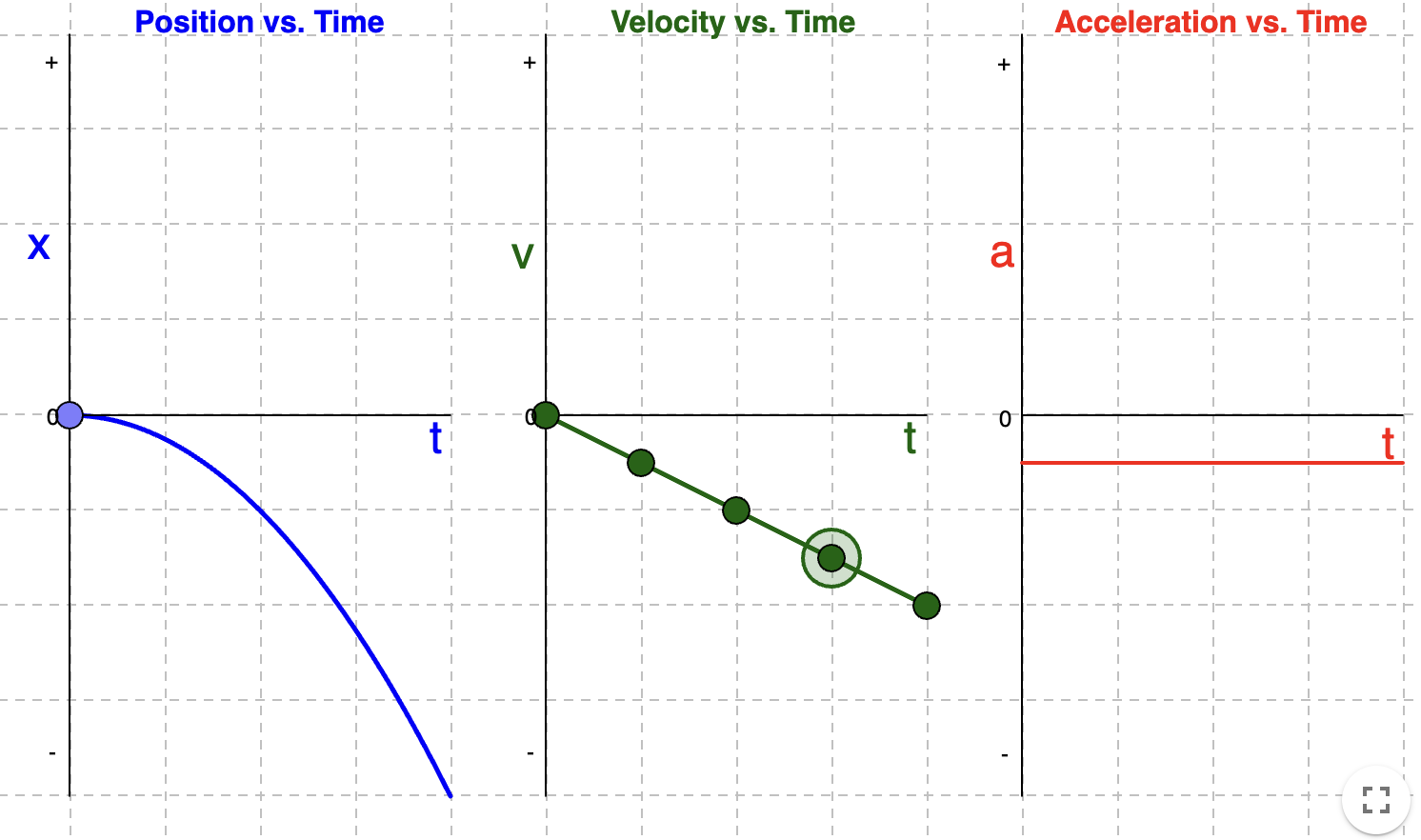
How to go from time graph to time graph
Position —> Velocity —> Acceleration
Find the SLOPE
Acceleration —> Velocity —> Position
Find the AREA
Instantaneous Velocity
Velocity at a specific interval of time
Ex: A car is moving for 10 seconds, and you must find the instantaneous velocity from 6-7 seconds
Equation 1
Variables Found: Δd, Δt, Vf, VI
Variables Not Found: aav
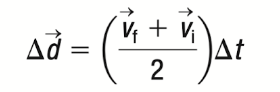
Equation 2
Variables Found: Δt, Vf, VI, aav
Variables Not Found: Δd
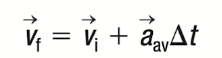
Equation 3
Variables Found: Δd, Δt, VI, aav
Variables Not Found: Vf
When trying to find Δt it can be tricky if initial velocity is not 0
However, using quadratic equations (ax2+bx+c) it can be solved by rearranging the formula and using the quadratic formula to find the roots.
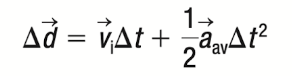
Equation 4
Variables Found: Δd, Vf, VI, aav
Variables Not Found: Δt
Equation 5
Variables Found: Δd, Δt, Vf, aav
Variables Not Found: VI
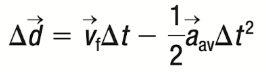
What is the value of g
g = 9.8m/s²
Object’s acceleration if moving up or down
If the object is moving down, the g = -9.8m/s2
If the object is moving up, the g = 9.8m/s2
Positive and Negative Convention
If the object is moving left and down then it is going to be NEGATIVE (-)
If the object is moving right or up then it is going to be POSITIVE (+)
Steps in solving problems involving gravitational pull:
Question: A flowerpot is knocked off a window ledge and accelerates uniformly to the ground. If the window ledge is 10.0 m above the ground and there is no air resistance, how long does it take the flowerpot to reach the ground?
Using equation 3:
find the variables that have been given
In this case:
Required: Time
Rearrange the formula to isolate the variable →
ViΔt is canceled out due to initial velocity being 0
Lastly, plug in the numbers