Bio 102 Lab Exam 2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
UMKC
Last updated 5:55 PM on 4/30/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
1
New cards
Once mitosis is complete, the two new daughter cells EACH have
The same number of chromosomes as the parent cell and each other
2
New cards
how many daughter cells are created after mitosis and cytokinesis are complete?
2
3
New cards
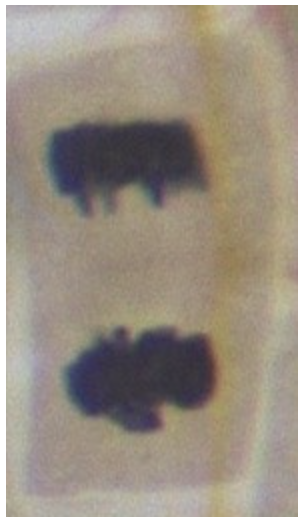
What phase is this image?
Telophase
4
New cards

What phase is this image?
Metaphase
5
New cards

What phase is this image?
Anaphase
6
New cards
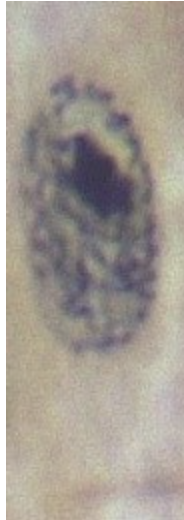
What phase is this image?
Prophase
7
New cards
During the typical cell cycle, does the DNA replicate during interphase or mitosis?
Interphase
8
New cards
Why is it critical that gametes are haploid cells and not diploid cells?
during fertilization, the fusion of two haploid gametes results in a diploid zygote with the correct number of chromosomes. If gametes were diploid, the resulting zygote would have double the number of chromosomes, leading to developmental abnormalities and potential infertility.
9
New cards
What are homologous chromosomes?
Homologous chromosomes are a pair of chromosomes that contain the same genes in the same order but may have different versions of those genes. One homologous chromosome is inherited from the mother and the other from the father. They are similar in size, and shape, and carry genetic information for the same traits.
10
New cards
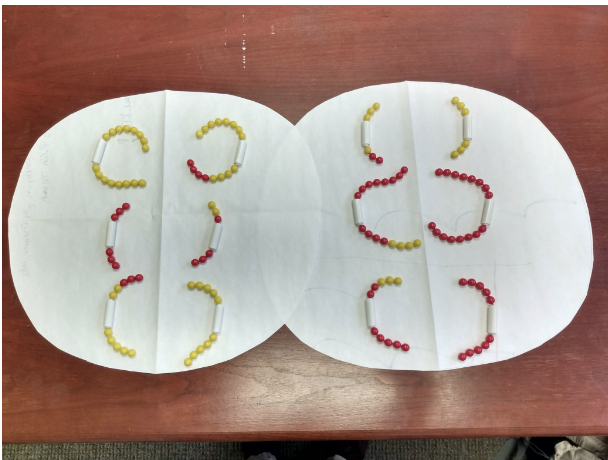

What phase of meiosis is this image?
Anaphase II
11
New cards
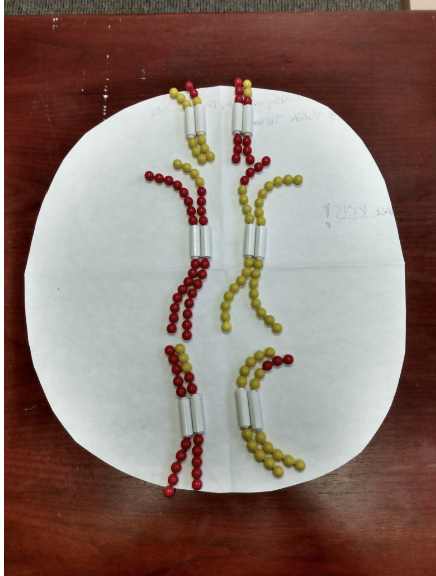

What phase of meiosis is this image?
Metaphase I
12
New cards
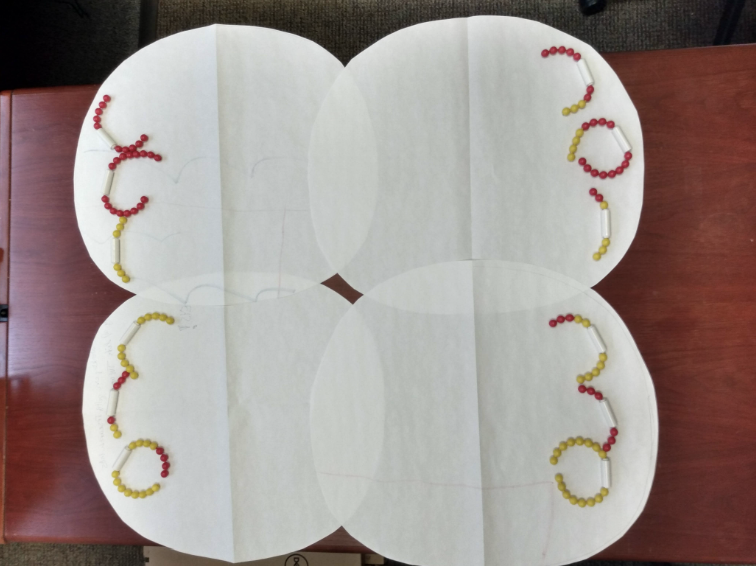

What phase of meiosis is this image?
Telophase II
13
New cards
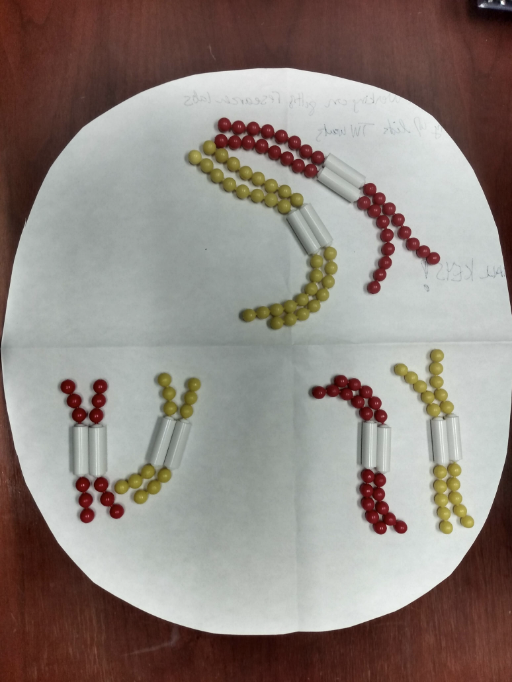
What phase of meiosis is this image?
Prophase I
14
New cards
How many daughter cells are created after meiosis and cytokinesis are complete?
4
15
New cards
If you begin with a parent cell that has 12 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will each of the daughter cells have after meiosis and cytokinesis are complete? Will these daughter cells be diploid or haploid cells?
6, haploid
16
New cards
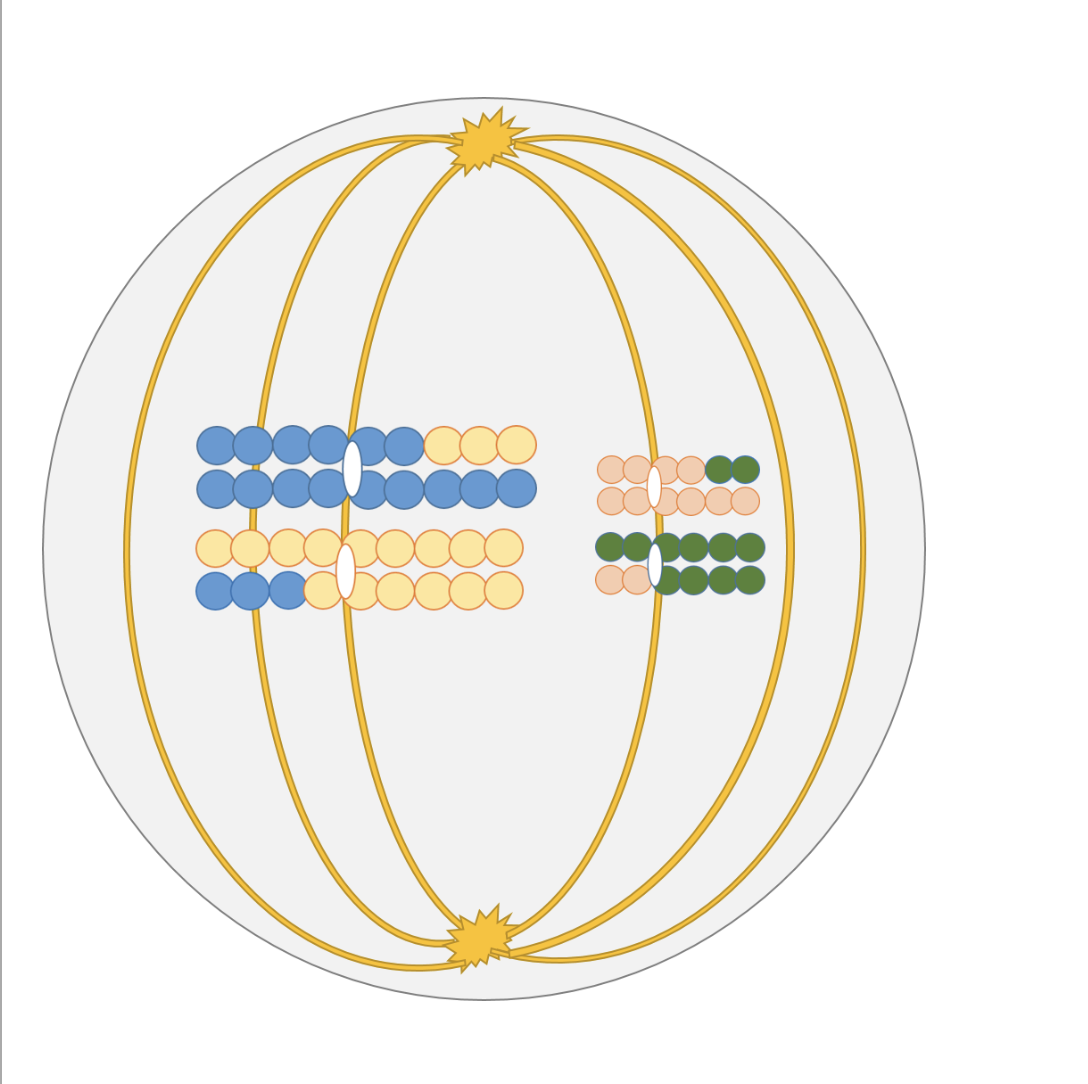
Is this cell undergoing mitosis or meiosis?
Meiosis
17
New cards
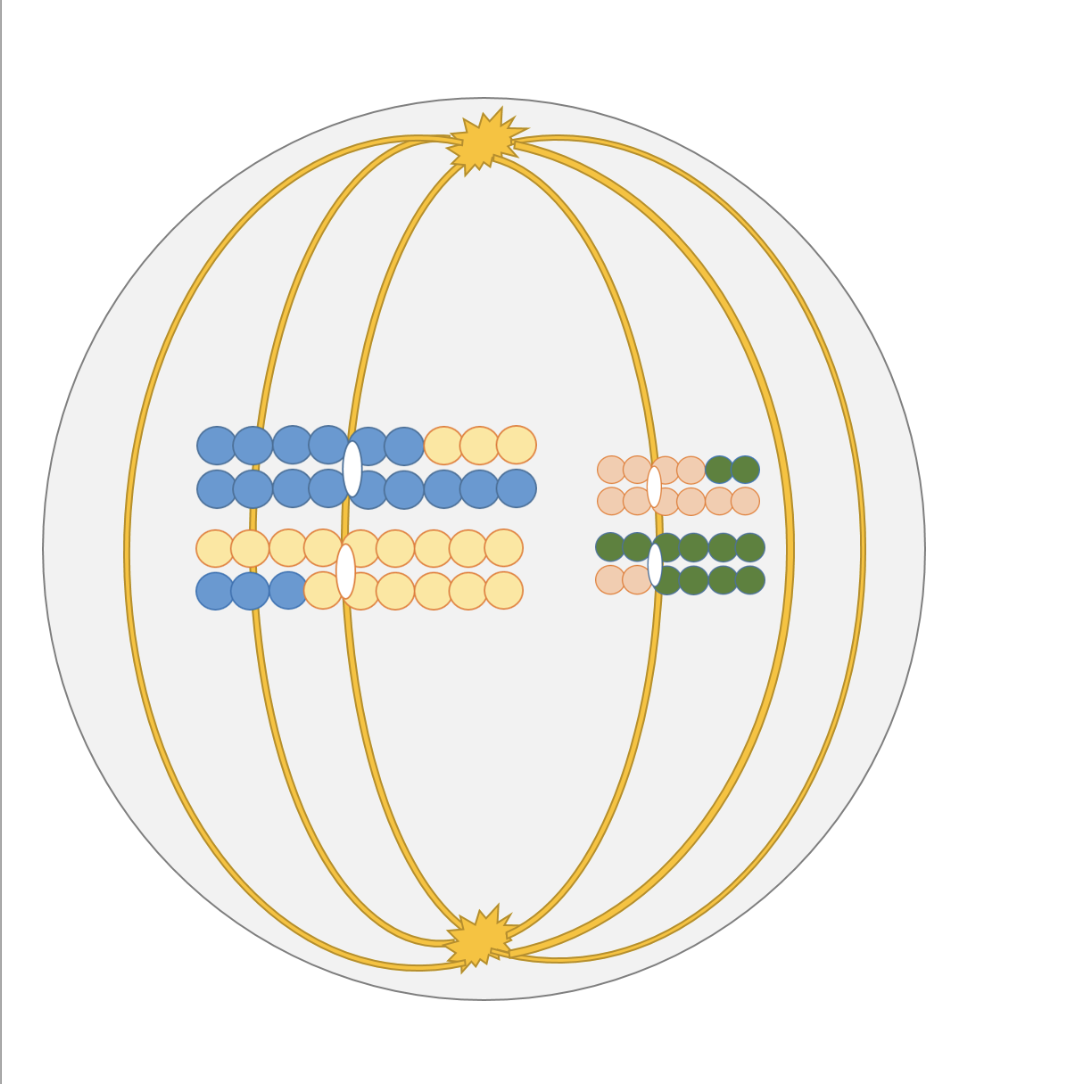
How do you know which type of cell division is occurring in the image?
The DNA is being exchanged by the cell to the chromosomes.
18
New cards
When does crossing-over (exchange of DNA) in homologous pairs occur?
Prophase I of MEiosis
19
New cards
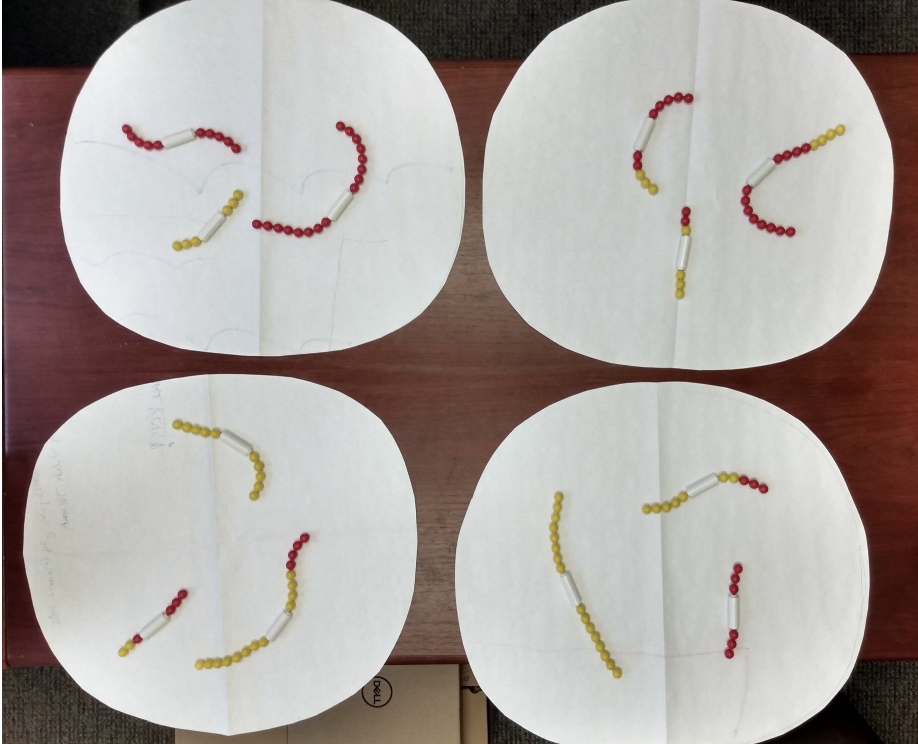

These are the daughter cells that have been produced after meiosis and cytokinesis are complete. How many total chromosomes did the parent cell have?
6
20
New cards
Does the “crossing over” of genetic information during meiosis occur in sister chromatids or non-sister chromatids?
non-sister chromatids
21
New cards
If an allele is expressed only when the dominant allele is NOT present, it is called the (BLANK) allele
recessive
22
New cards
According to the exercises we performed in lab, a corn plant that produces all yellow corn kernels can have which of the following genotype(s)?
Homozygous recessive (pp)
23
New cards
The classic Mendelian phenotypic ratio that results from a cross of two heterozygous parents (Pp x Pp) is
3:1
24
New cards
You have a corn plant that grew from a purple kernel. BOTH of its parents were homozygous dominant for purple kernels. Knowing that, what is your plant’s GENOTYPE (ANSWER 1). When your plant produces gametes, what allele will the gametes have for kernel color? (ANSWER 2)
PP, dominant
25
New cards
An individual with a heterozygous genotype for a given trait will express which of the two alleles it inherited? In other words, it’s phenotype will be (BLANK)
dominant
26
New cards
What is the “Central Dogma” of biology?
The Central Dogma of Biology is the fundamental principle that explains how genetic information flows within a biological system. It states that DNA is transcribed into RNA, which is then translated into proteins. This principle is essential to understanding the molecular basis of life.
27
New cards
In a DNA molecule, the “backbone” is comprised of a (BLANK) group and a (BLANK) molecule, which is bonded to one of the following four nitrogenous bases (BLANK), (BLANK), (BLANK), (BLANK), or (BLANK)
Phosphate, deoxyribose, adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine
28
New cards
When DNA is replicated nucleotides are added in the (BLANK)’ to (BLANK)’ direction
5, 3
29
New cards
REPLICATE the following nucleotide sequence: 5’-ATGTCTCACGGGAATATGAAATGA3’
3'-TACAGAGTGCCCTTATACATTTACT-5'
30
New cards
What kind of molecule is the above nucleotide sequence?
DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid)
31
New cards
TRANSCRIBE the nucleotide sequence: ATGTCTCACGGGAATATGAAATGA
AUGUCUCACGGGAAUAUGAAAUGA
32
New cards
Show the CODONS of your transcribed sequence “AUGUCUCACGGGAAUAUGAAAUGA”
AUG-UCU-CAC-GGG-AAU-AUG-AAA-UGA
33
New cards
TRANSLATE the nucleotide sequence from “AUG-UCU-CAC-GGG-AAU-AUG-AAA-UGA”
M/START-S-H-G-A-M-L-Stop
34
New cards
What kind of organic molecule is the sequence in your answer to: M/START-S-H-G-A-M-L-Stop
protein
35
New cards
Where does DNA replication occur?
Inside the nucleus
36
New cards
Where does Transcription occur?
Inside the nucleus
37
New cards
Where does Translation occure?
Outside the nucleus