Klein Chapter 8 - Doppler and Hemodynamics
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is the equation for MV area using the PHT method?
MVA = 220/PHT
stroke volume equation
SV = area (cm2) x VTI (cm)
example: SV across MV = MVA x MV VTI
FYI Cardiac output = SV x HR
Pressure half time calculation
PHT (ms) = 0.29 x DT
Cardiac output equation
CO (L/min) = SV (mL) x HR (bpm)

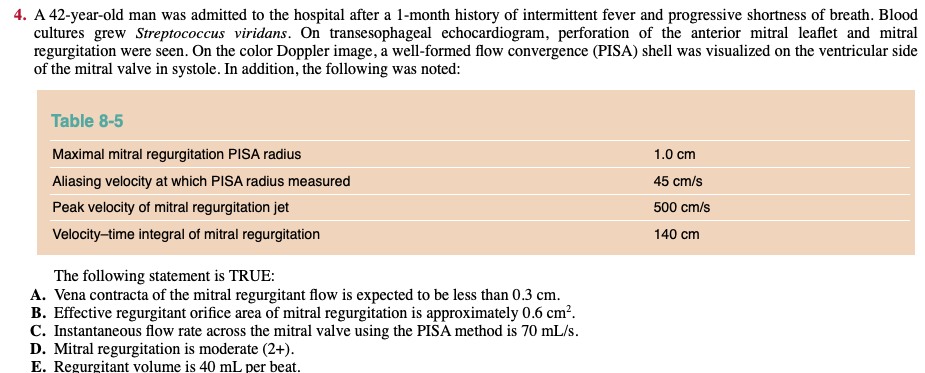
A 32-year-old woman is referred for evaluation of rheumatic mitral valve stenosis. No mitral regurgitation was noted. The following values were obtained by Doppler echocardiography. Which of the following statements is TRUE:
A) Mitral valve area can be calculated by dividing 220 into deceleration time.
B) Stroke volume across the mitral valve is 72 mL per beat.
C) Pressure half-time is 355 ms.
D) Mitral valve area is 0.8 cm2.
E) During exertion, her mean gradient is expected to decrease.
D) MVA is 0.8 cm2

What does “Qs” mean?
systemic blood flow
What does the Qp:Qs ratio mean?
ratio of pulmonic to systemic blood flow
if someone has a patent ductus arteriousus (PDA), what communication does this result in?
communication between the descending thoracic aorta (DTA) and the proximal left pulmonary artery
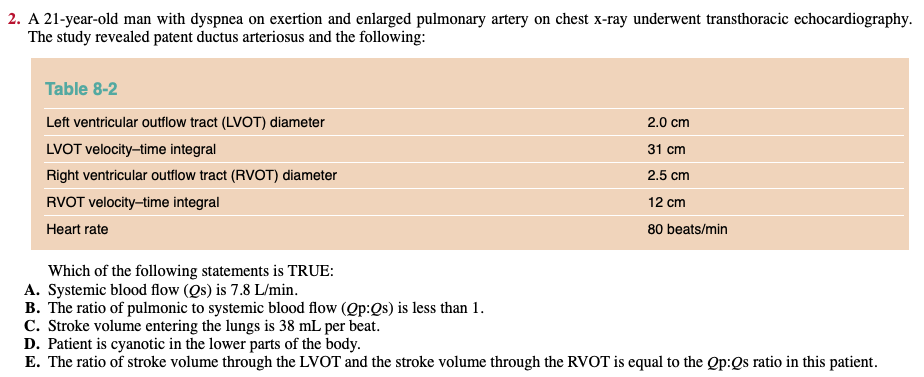
Qp:Qs in a patient with PDA
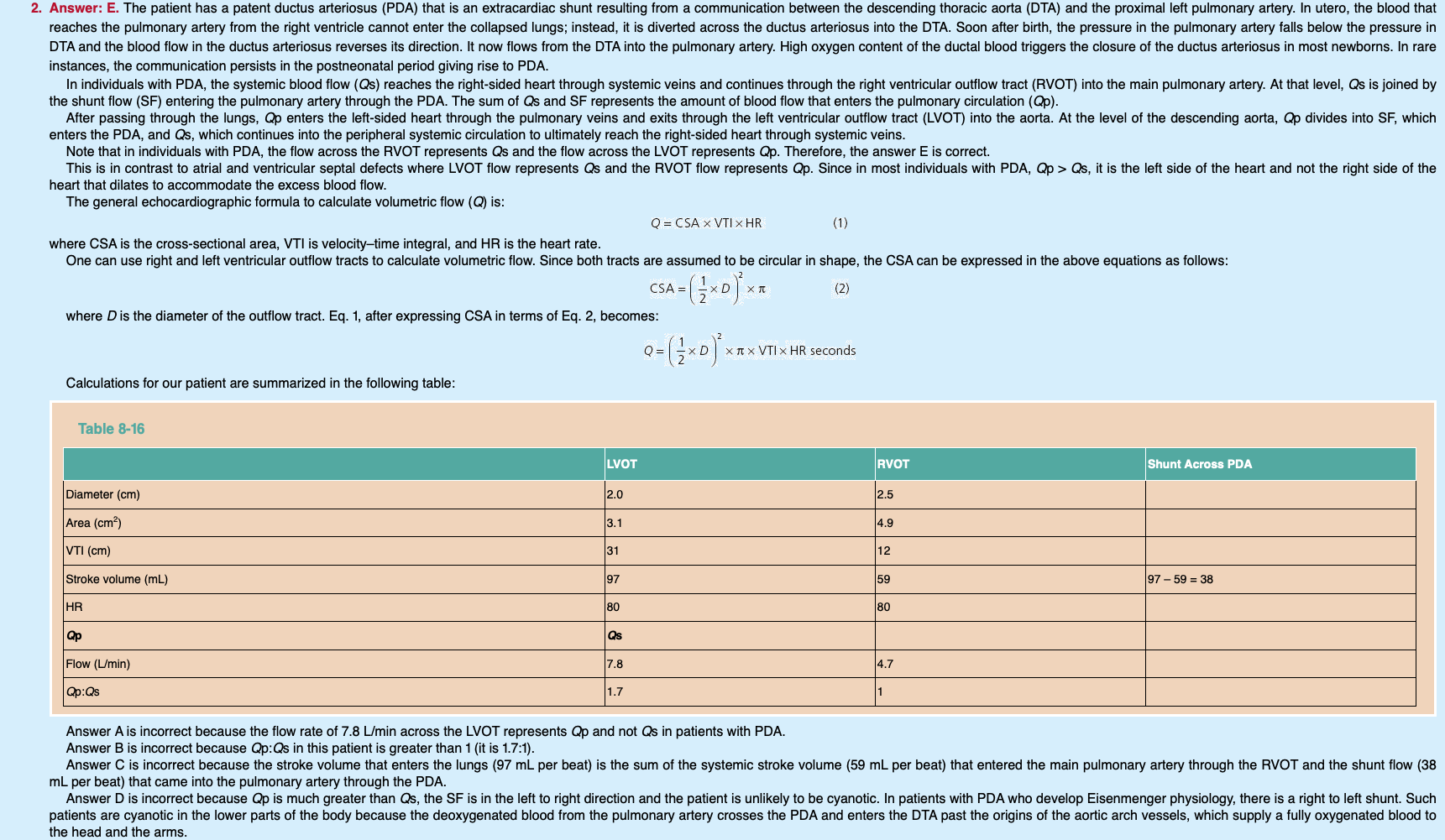
Most individuals with a PDA, Qp will be [greater/less] than Qs
Qp > Qs
FYI it is the left side of the heart and not the right side of the heart that dilates to accommodate the excess blood flow
Qp:Qs formula
= (RVOT area x RVOT VTI) / (LVOT area x LVOT VTI)
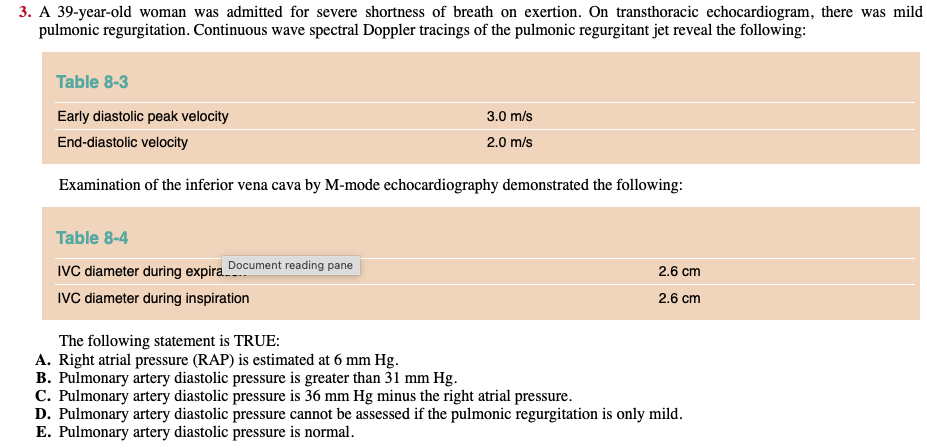
Calculating RVSP or PASP
Answer B
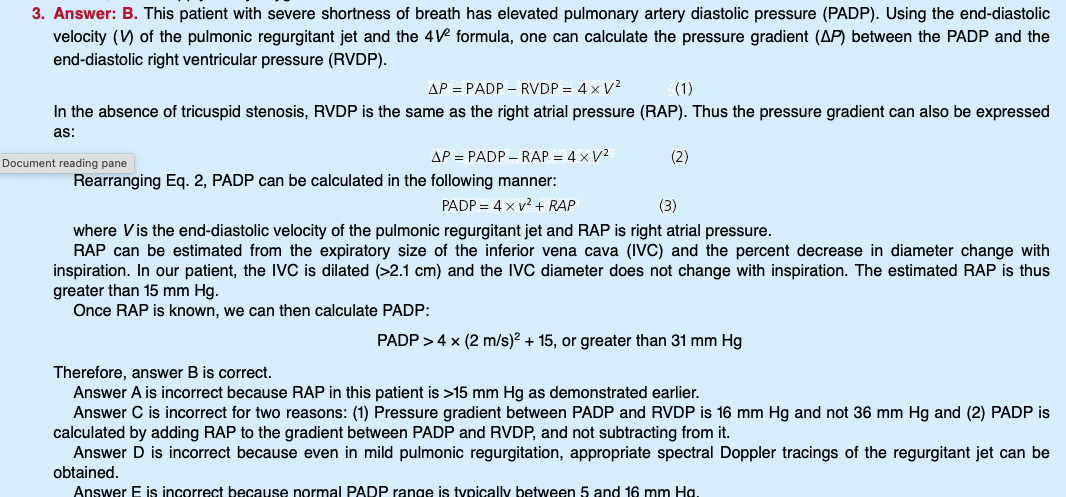
IVC greater than _____ cm is considered dilated?
>2.1 cm
FYI if < 50% collapse then RAP estimated > 15 mmHg

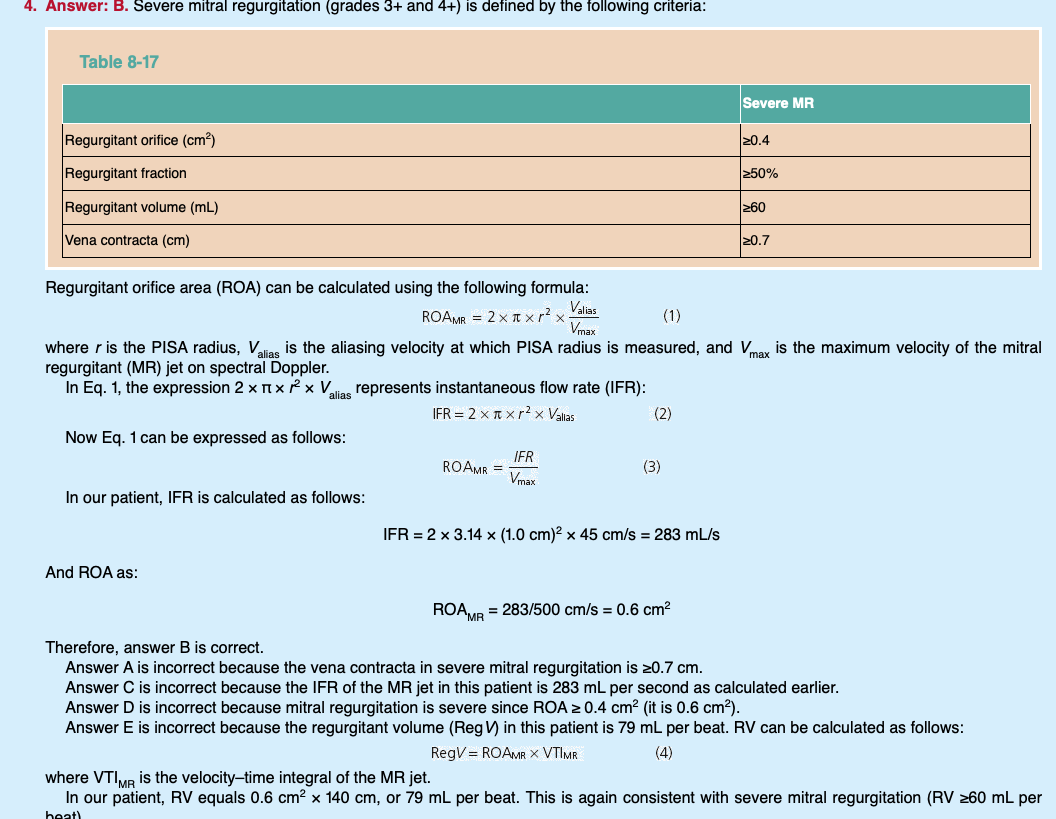
How is severe MR (grade 3+ and 4+) defined —
What is the regurgitant orifice (cm2) greater than or equal to?
What is the regurgitant fraction greater than or equal to?
What is the regurgitant volume (mL) greater than or equal to?
What is the vena contracta (cm) greater than or equal to?


Equation for regurgitant orifice area (ROA)
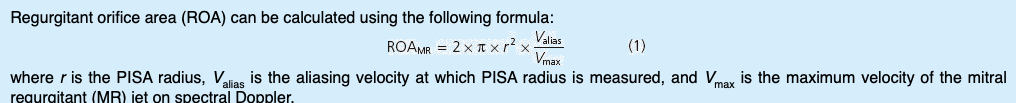
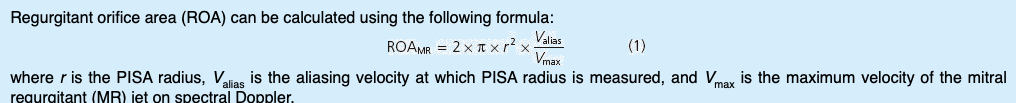
Equation for regurgitant volume
RV = EROA x VTI