Ch. 2 Female Bodies Social Psych Notes
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
Vulva
The female external genitalia, including the mons, labia, vaginal opening, and clitoris.
Erogenous Zone
A region of the body whose stimulation causes sexual arousal.
Vasocongestion
Tissue swelling caused by the increased filling of local blood vessels.
Labiaplasty
Surgical modification of the inner labia.
Bartholin's Glands
Two mucus-secreting glands that help lubricate the vaginal opening.
Glans
The terminal knob of the clitoris or penis.
Frenulum (of the clitoris)
An erotically sensitive fold of tissue that connects the labia to the underside of the clitoris.
Corpus Spongiosum
A single midline erectile structure that fills the glans; in males, it surrounds the urethra.
Erectile Tissue
Tissue that stiffens an organ by filling with blood.
Smegma
A whitish, greasy secretion that can build up under the hood of the clitoris or the foreskin of the penis.
Menstruation
The breakdown of the endometrium at approximately monthly intervals with consequent loss of tissue and blood through the vagina.
Endometriosis
The growth of endometrial tissue at abnormal locations such as the oviducts.
Oviducts
Either of two bilateral tubes that lead from the uterus toward the ovaries; the usual site of fertilization.
Fimbria
The fringe at the end of the oviduct composed of finger-like extensions.
Menstrual Toxic Shock Syndrome
A rare but life-threatening illness caused by a staphylococcal infection and associated with tampon use.
Dysmenorrhea
Menstrual pain severe enough to interfere with a woman's activities.
Amenorrhea
Absence of menstruation.
Hormone Therapy
Drugs that block the action of estrogen.
Mastectomy
Surgical removal of the breast.
Breast Cancer
Cancer that can affect the female reproductive system, specifically the tissues of the breast.
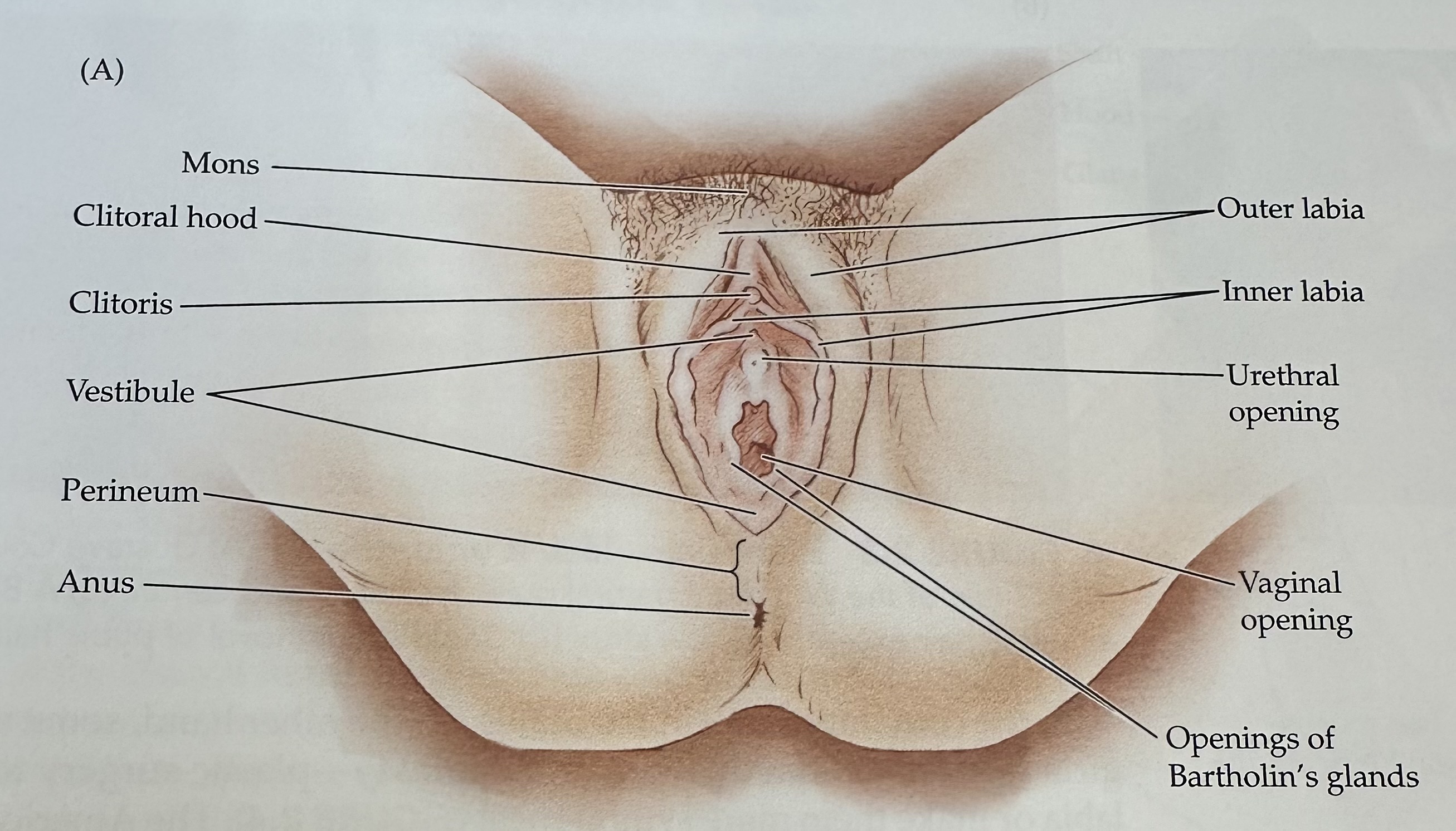
Mons
The rounded mass of fatty tissue located above the pubic bone, covered with pubic hair after puberty.
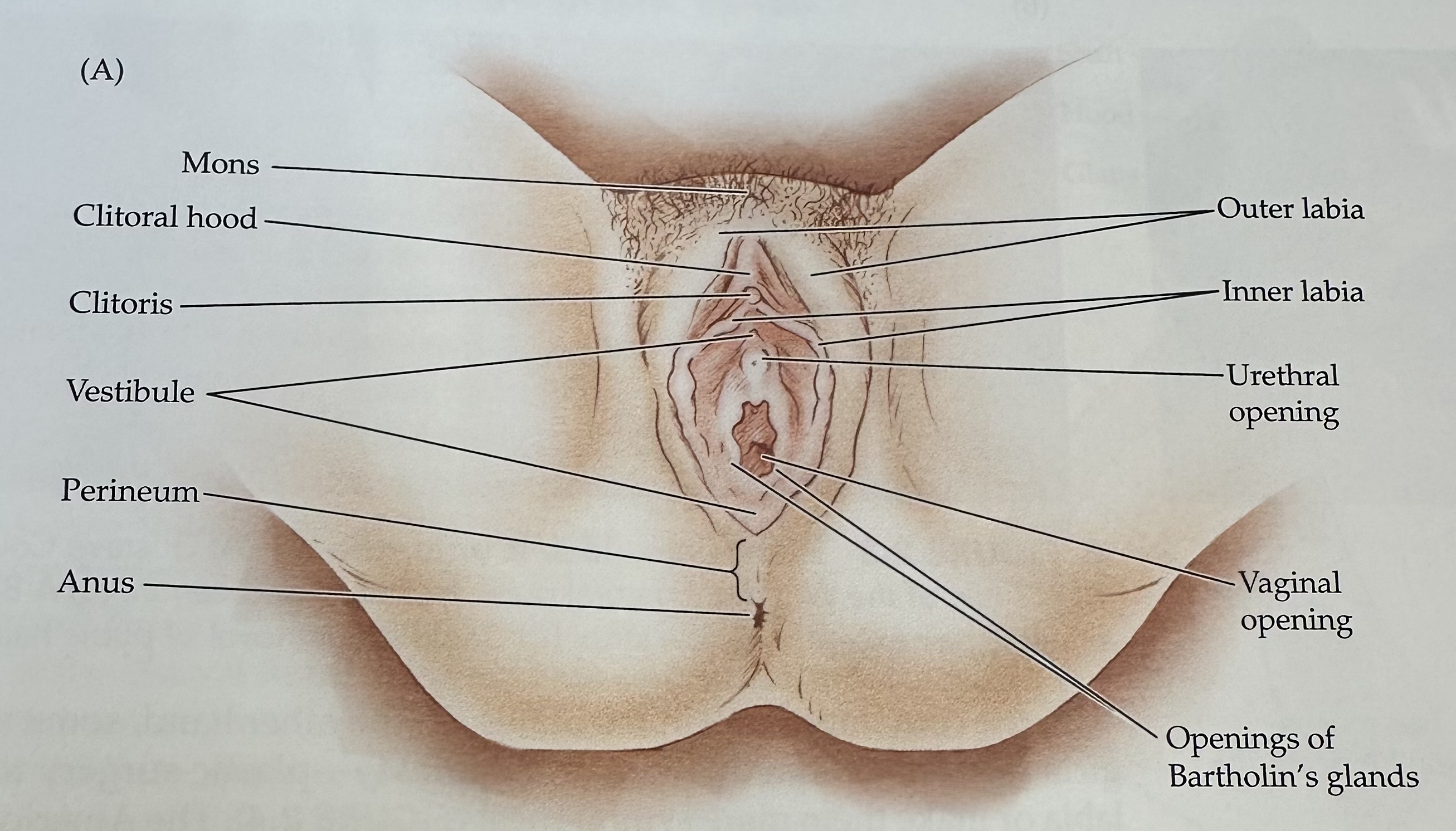
Labia
The folds of skin surrounding the vaginal opening, consisting of the labia majora and labia minora.
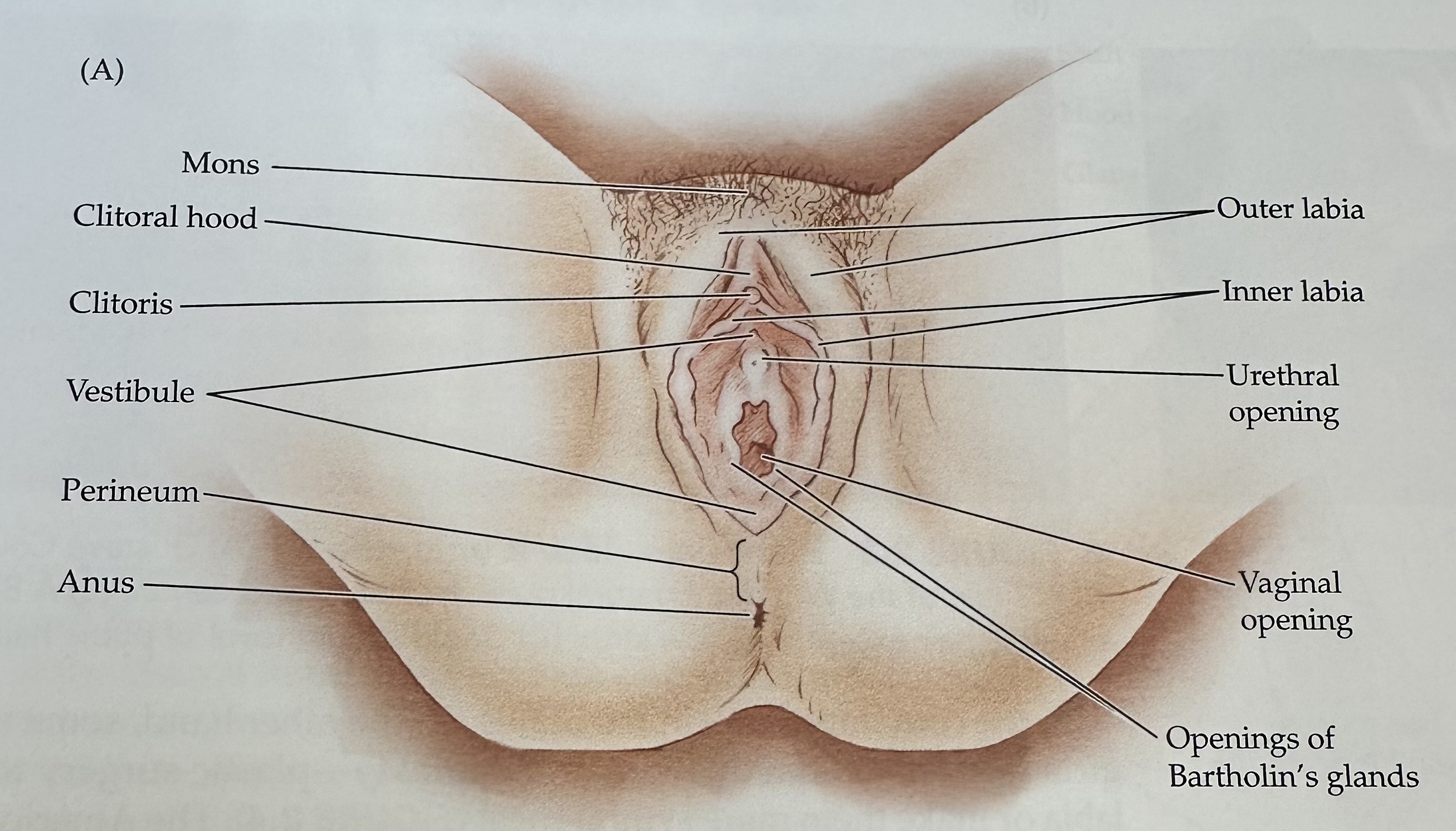
Outer Labia
The outer folds of skin surrounding the vaginal opening, providing protection and containing sebaceous glands.
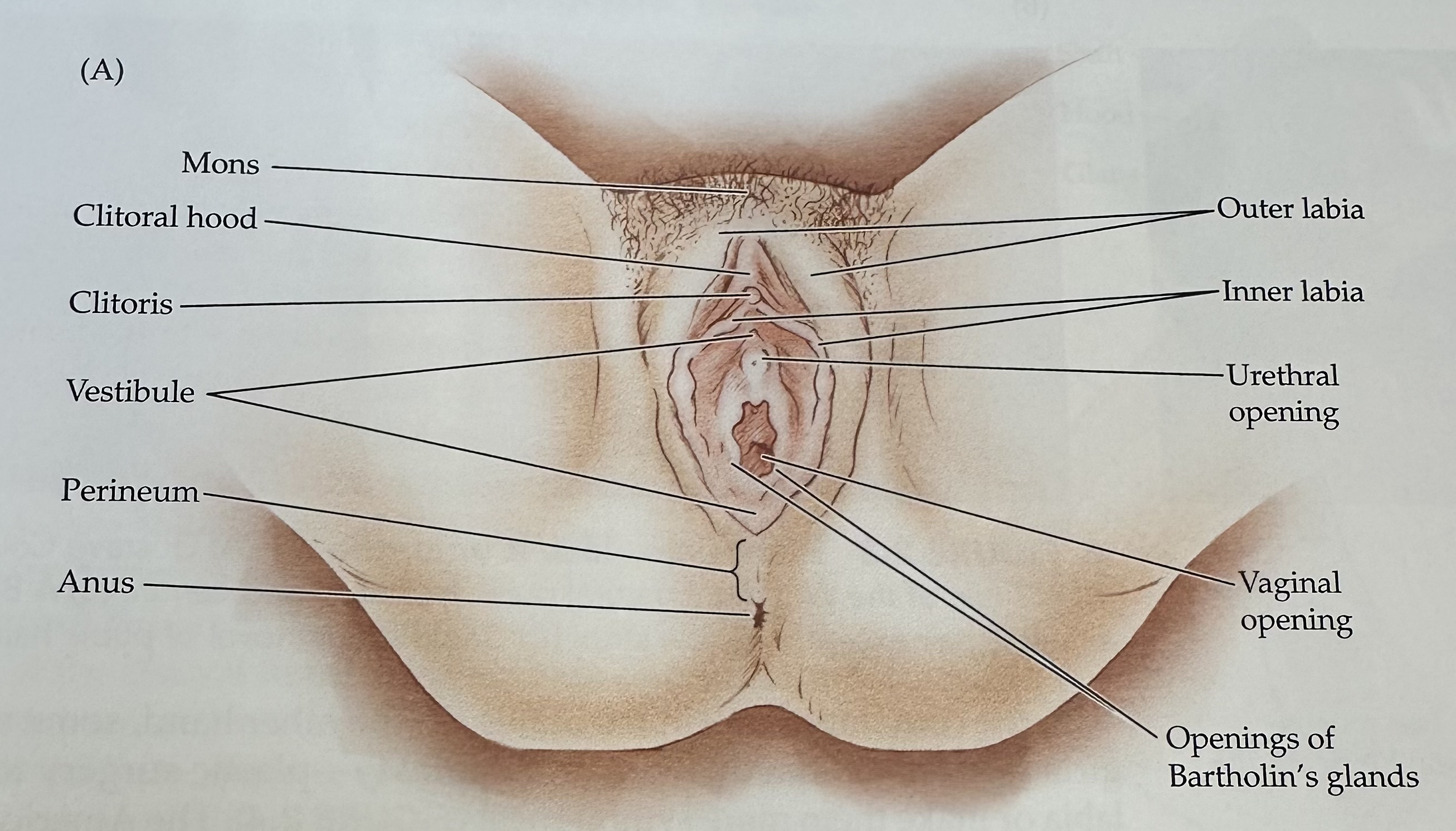
Inner Labia
The inner folds of skin surrounding the vaginal opening, which are more delicate than the outer labia and rich in blood vessels and nerve endings.
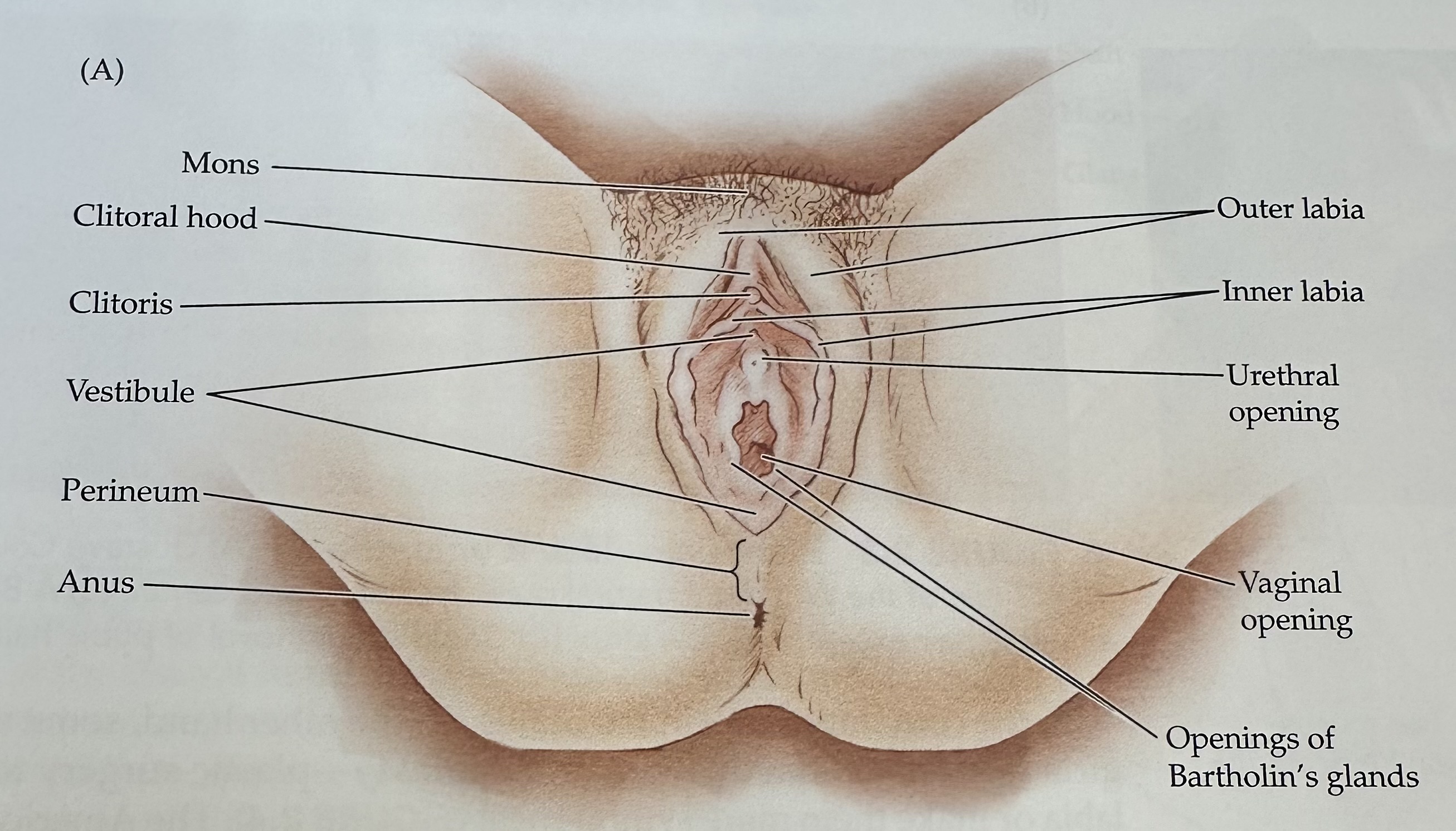
glans
The sensitive, bulbous tip of the clitoris, which is covered by the clitoral hood and plays a crucial role in sexual arousal.
Vestibular Bulbs
Two erectile tissue structures located on either side of the vaginal opening, involved in sexual arousal and pleasure.
Urethra
The tube through which urine exits the body, located above the vaginal opening in females.
Birth Canal
The passage through which a baby travels during childbirth, consisting of the cervix and vagina.
Follicular Phase
The first part of the menstrual cycle, where follicles in the ovaries mature in response to hormonal signals, leading to ovulation.
Luteal Phase
The second part of the menstrual cycle following ovulation, during which the corpus luteum forms and secretes hormones to prepare the uterus for potential pregnancy.
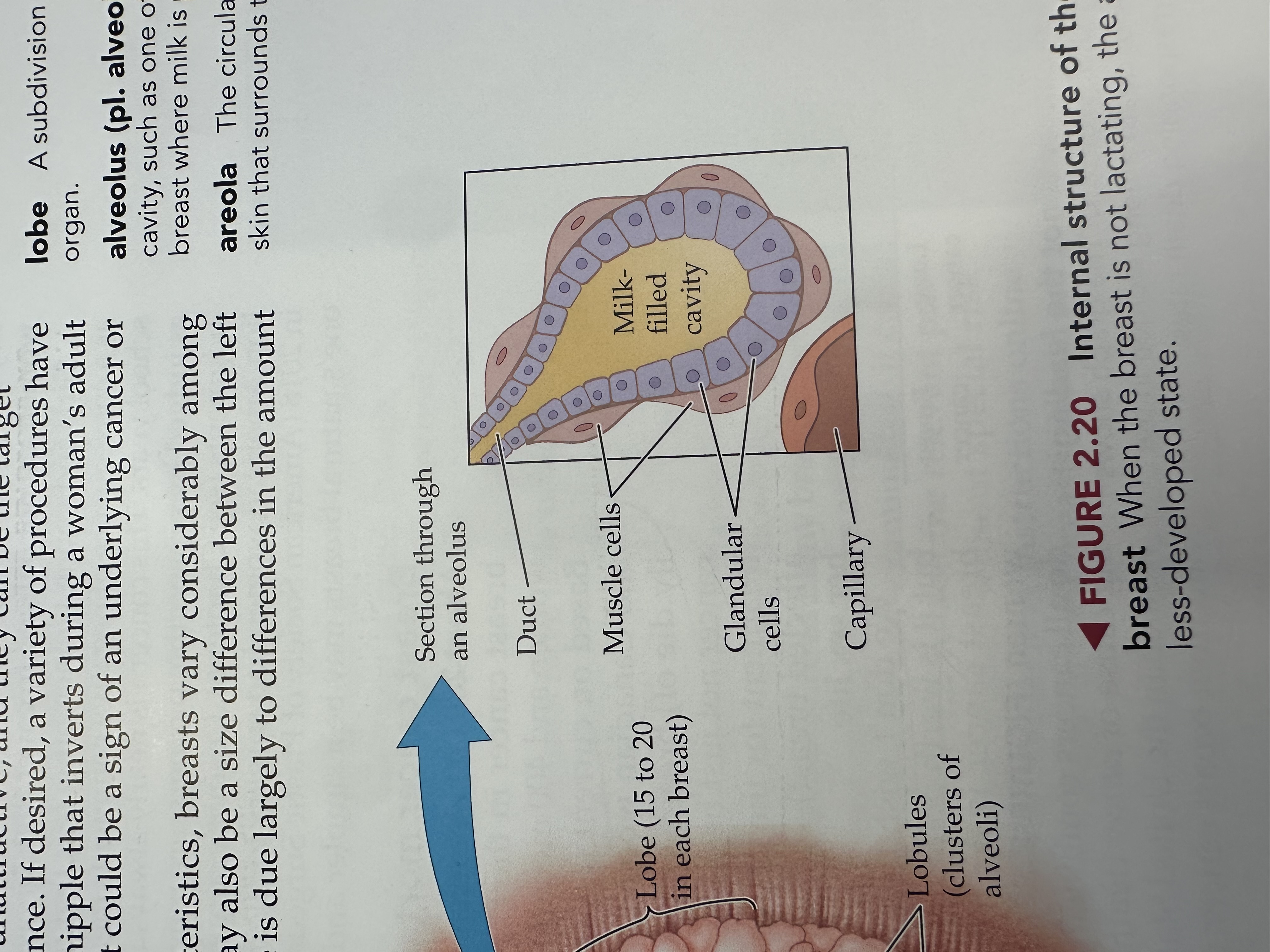
Alveoli
a microscopic cavity such as one of those in the breasts where milk is produced
Areola
The pigmented area surrounding the nipple, containing glands that help lubricate the nipple during breastfeeding.
Vaginal Opening
The external orifice of the vagina, serving as the entry point for intercourse and the exit for menstrual fluid and childbirth.
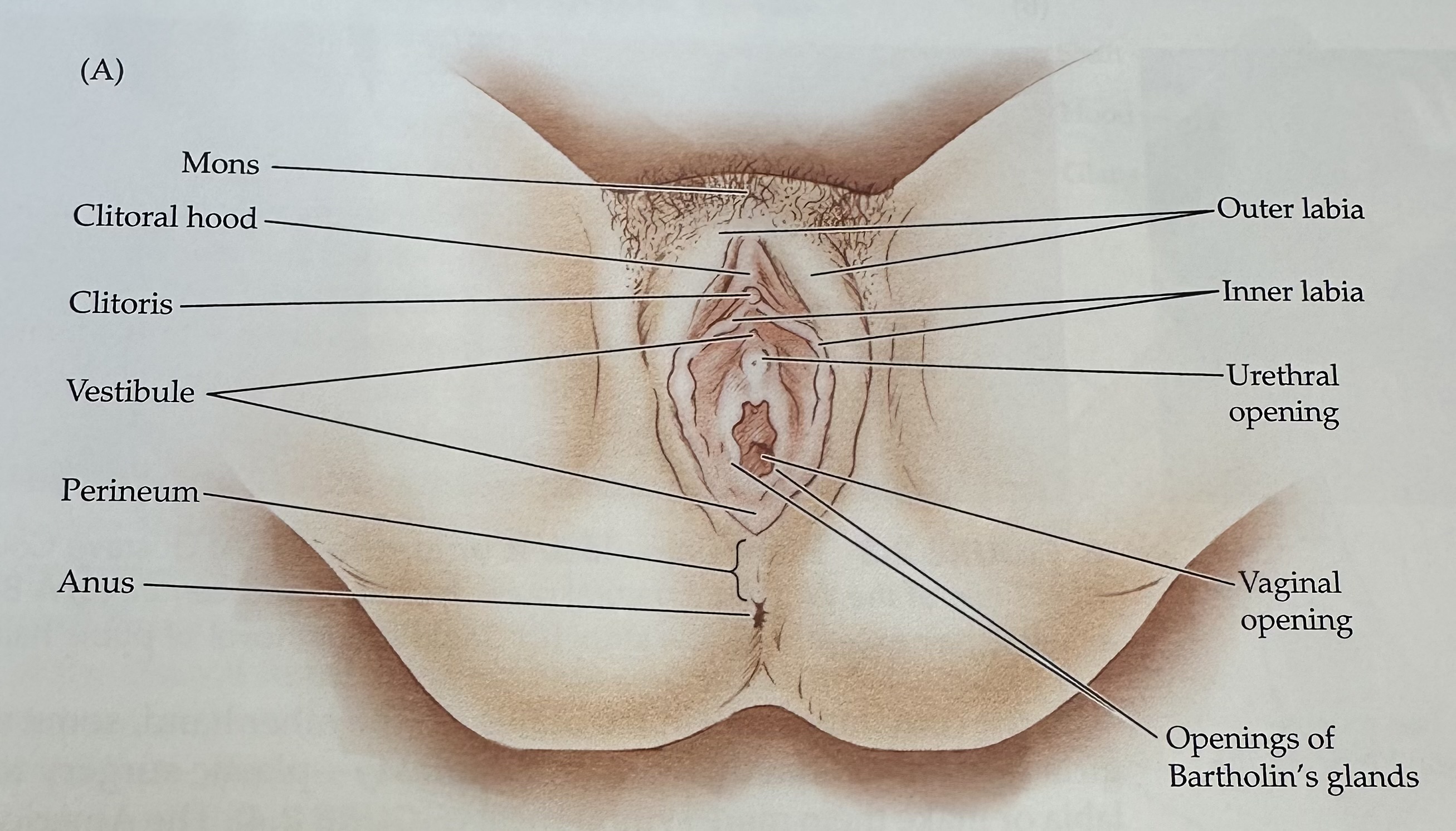
Clitoris
External portion located at the junction of the inner labia just in front of the vestibule
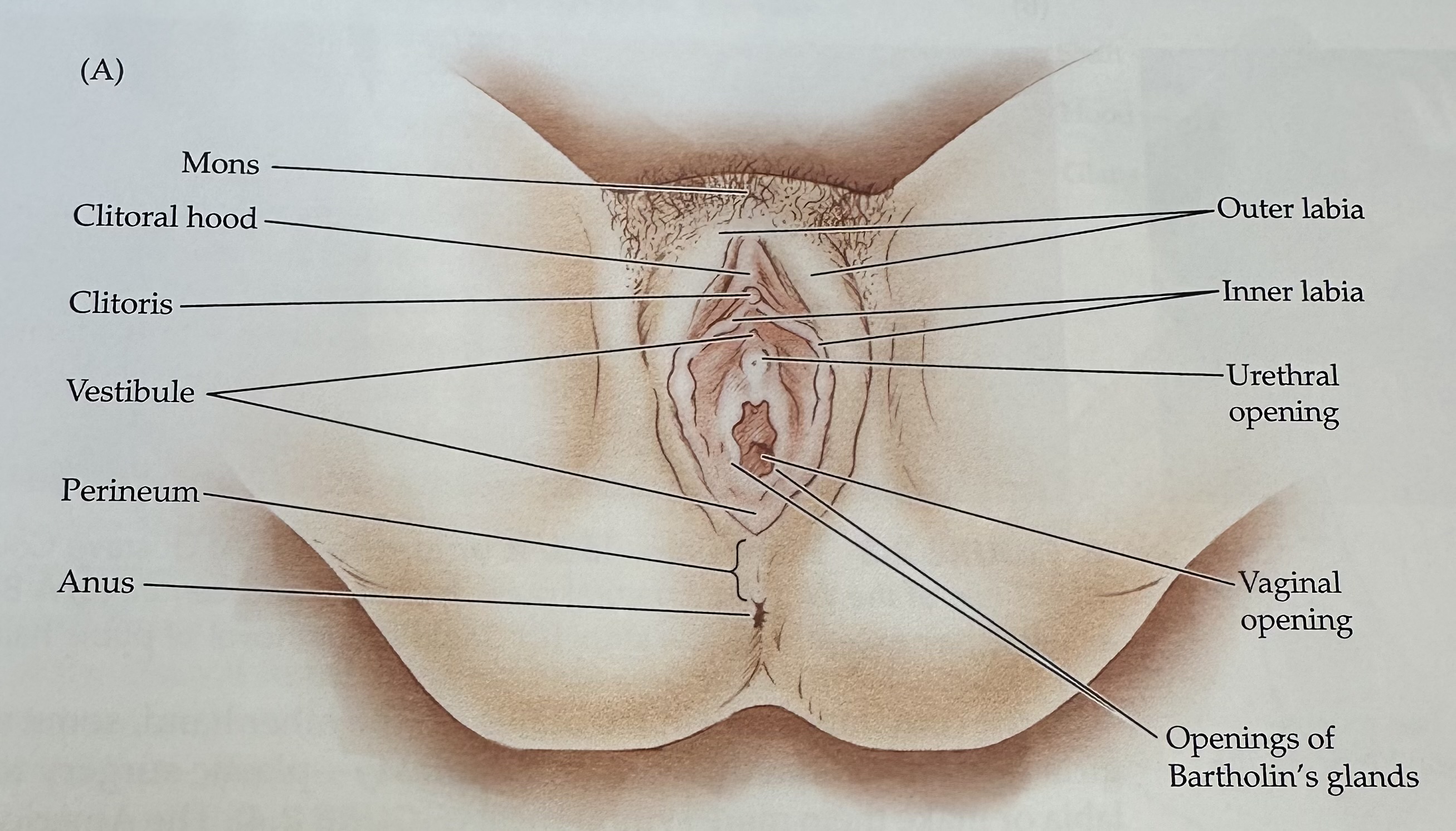
Vestibule
The recess or space in the female genitalia located between the labia minora, containing the vaginal opening and the urethra.
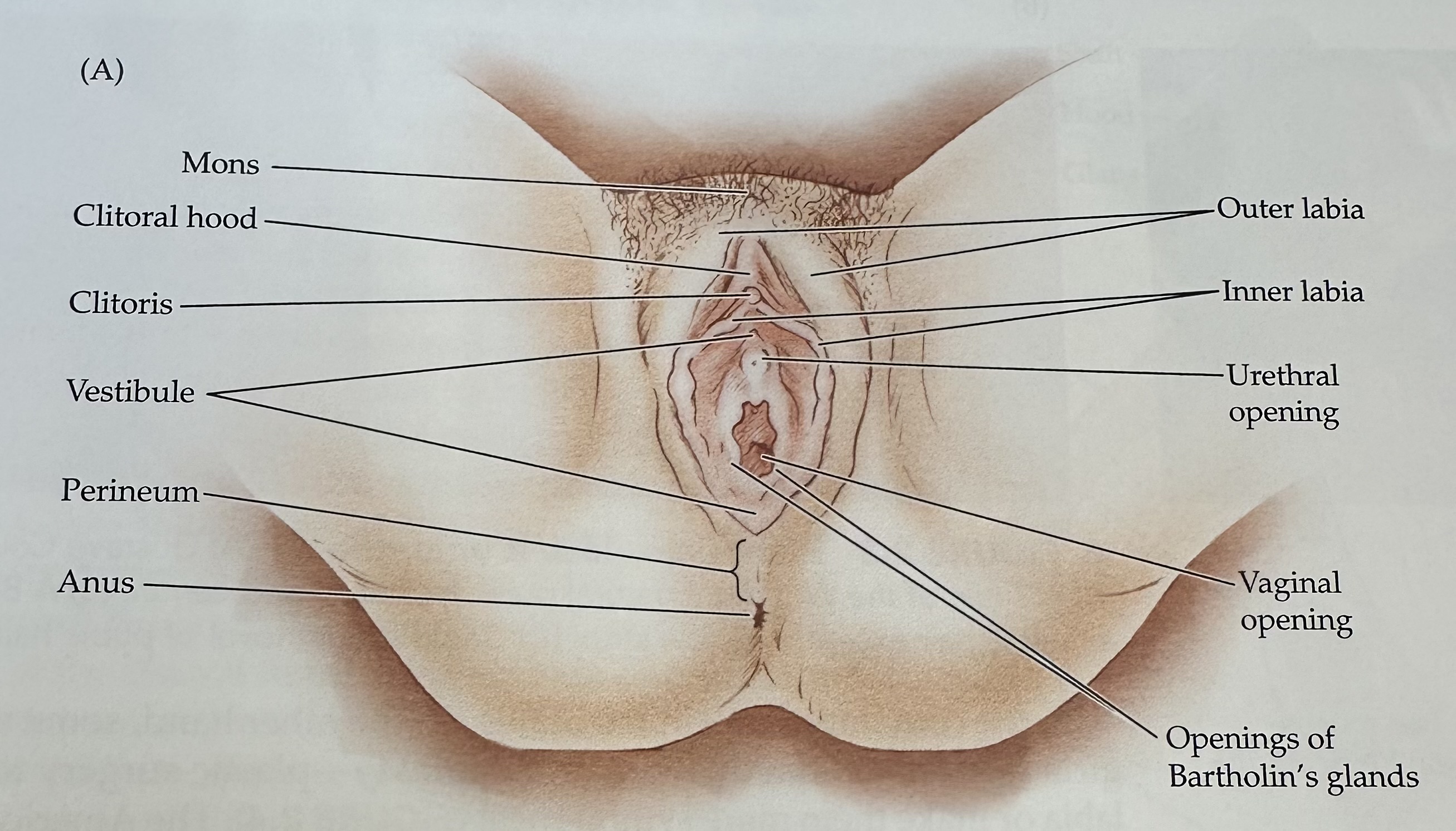
Perineum
The region of the body between the anus and the genitals; it plays a role in both the urinary and reproductive systems.
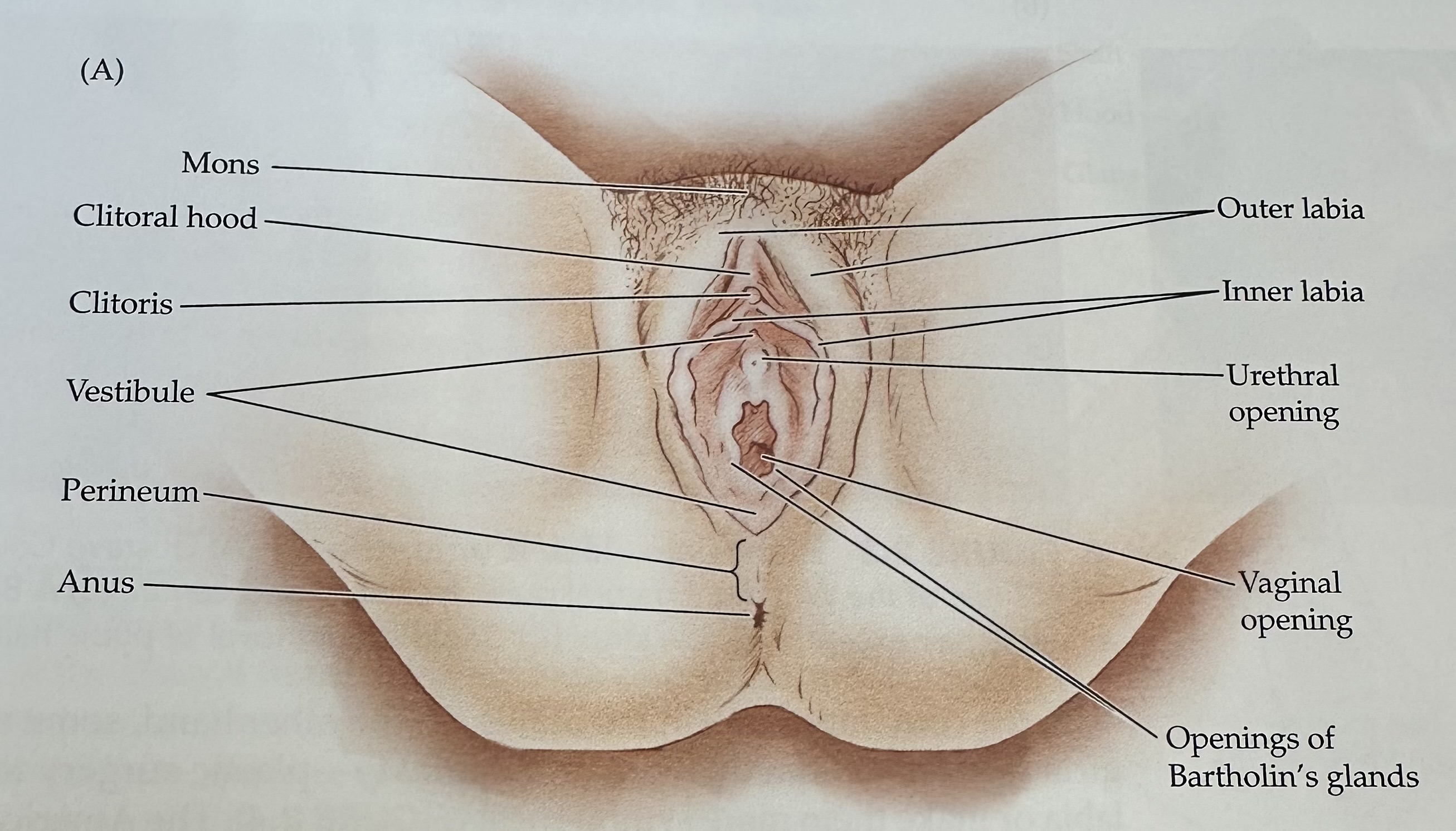
Urethral Opening
The external orifice of the urethra, through which urine exits the body, located above the vaginal opening in females.
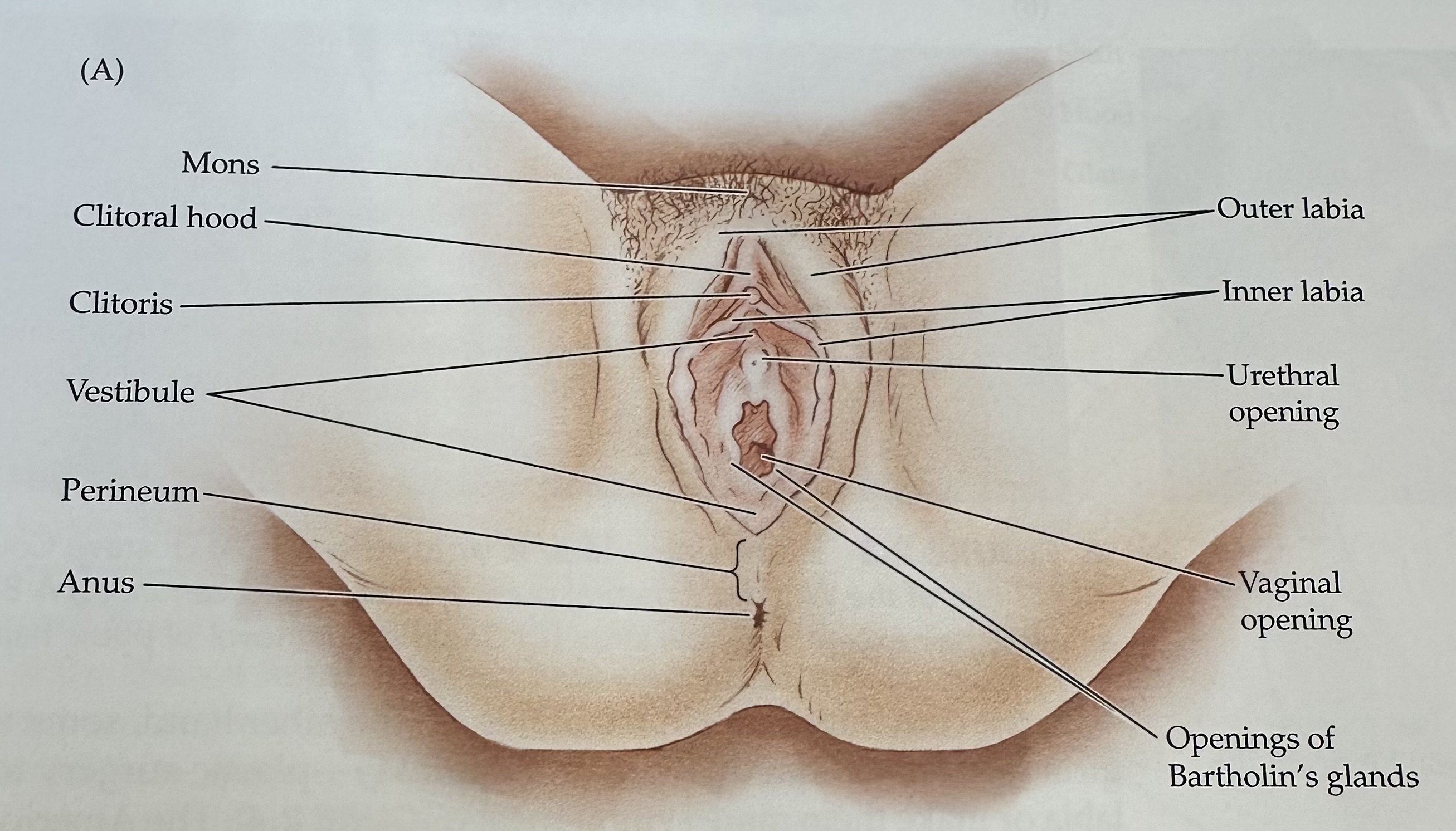
Opening of Bartholin's Glands
The openings of two mucus-secreting glands located bilaterally at the vaginal opening, which help lubricate the vagina during sexual arousal.
Shaft of the Clitoris
The elongated portion of the clitoris that extends from the glans and contains erectile tissue, playing a role in sexual arousal.
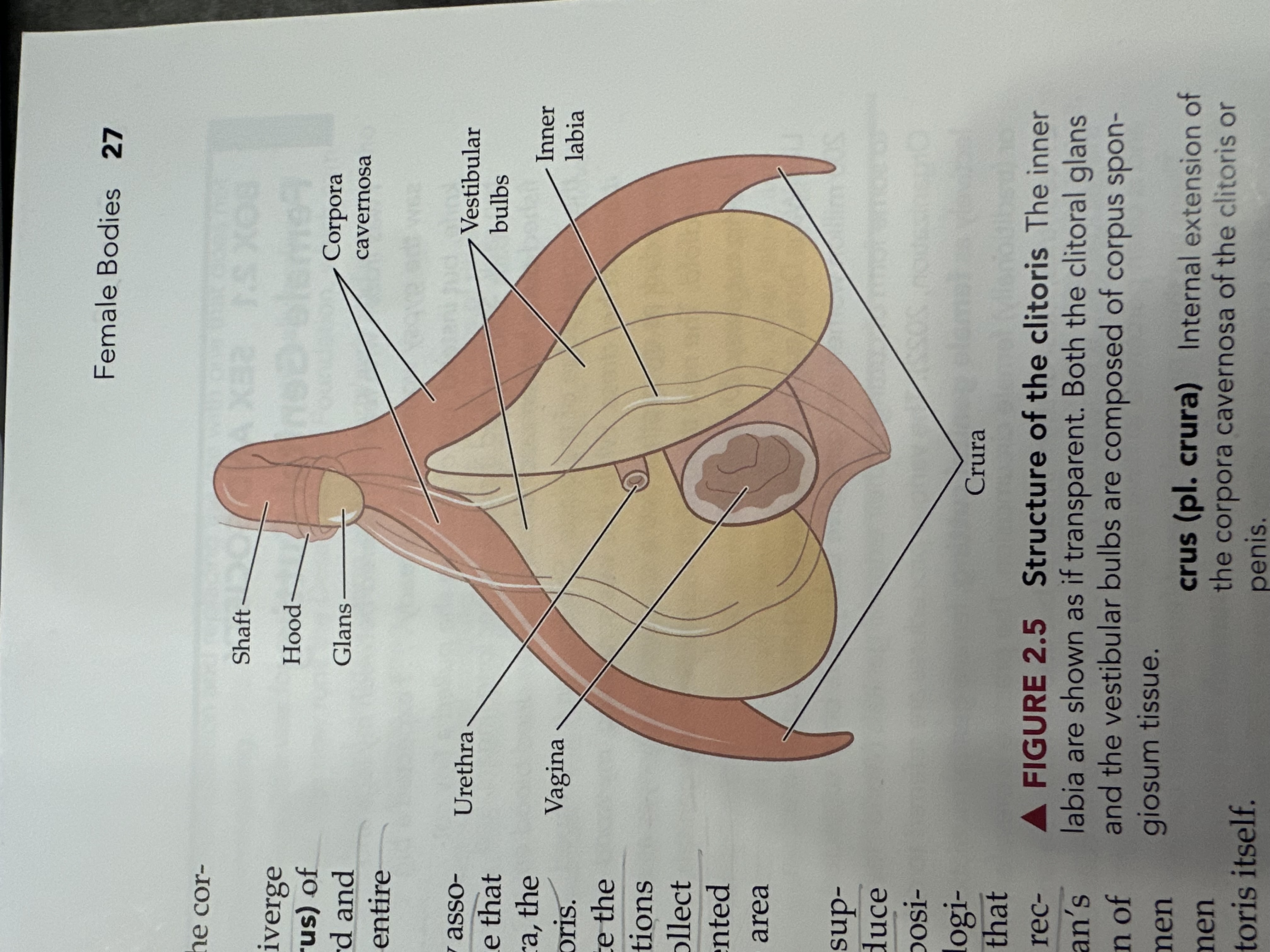
Hood (of the clitoris)
The fold of skin that covers and protects the glans of the clitoris, contributing to sensitivity and arousal.
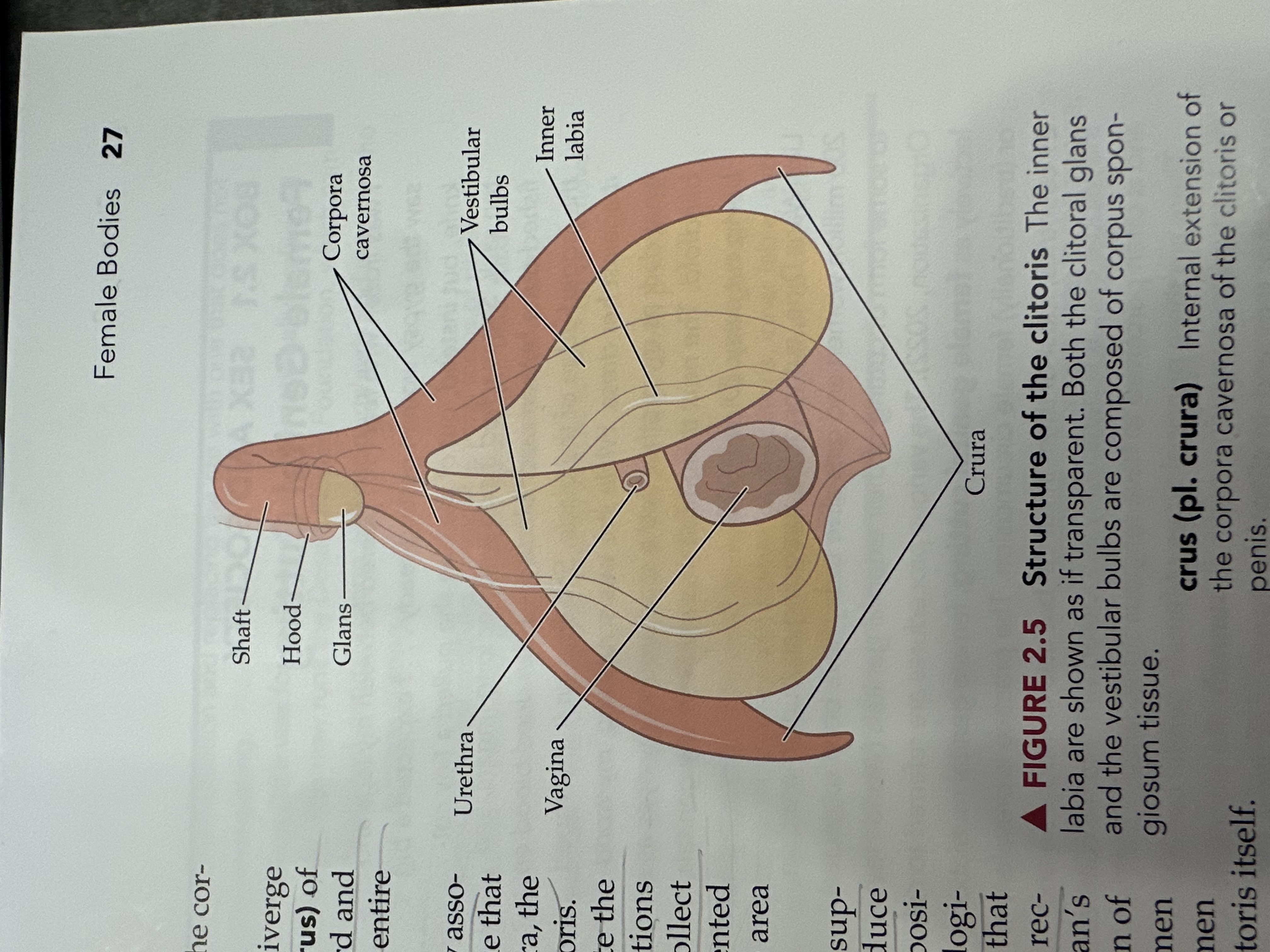
Glans
The sensitive, bulbous tip of the clitoris, which is covered by the clitoral hood and plays a crucial role in sexual arousal.
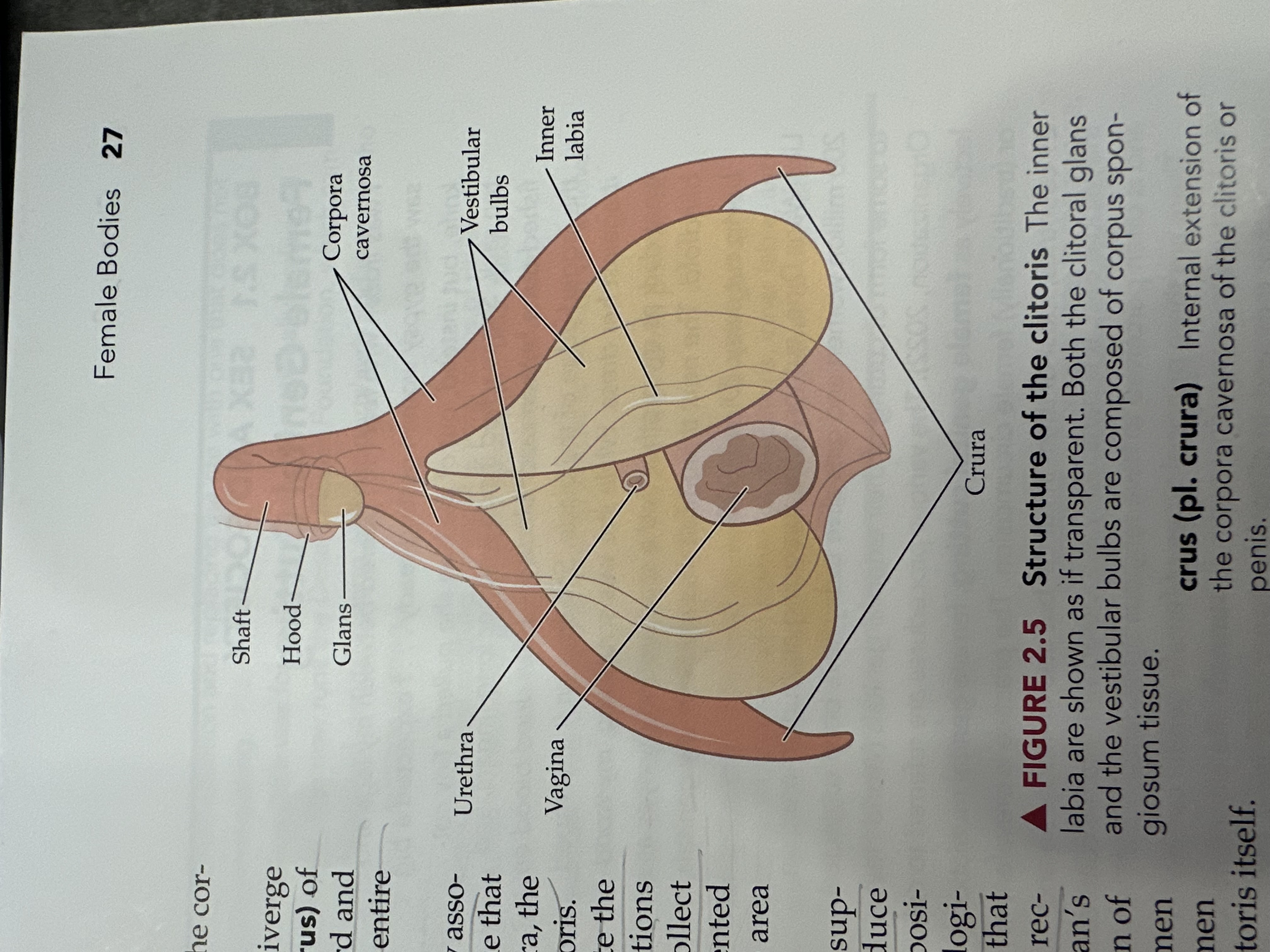
Corpora Cavernosa (of the vagina)
Erectile tissue that fills with blood during sexual arousal, contributing to vaginal lubrication and engorgement.
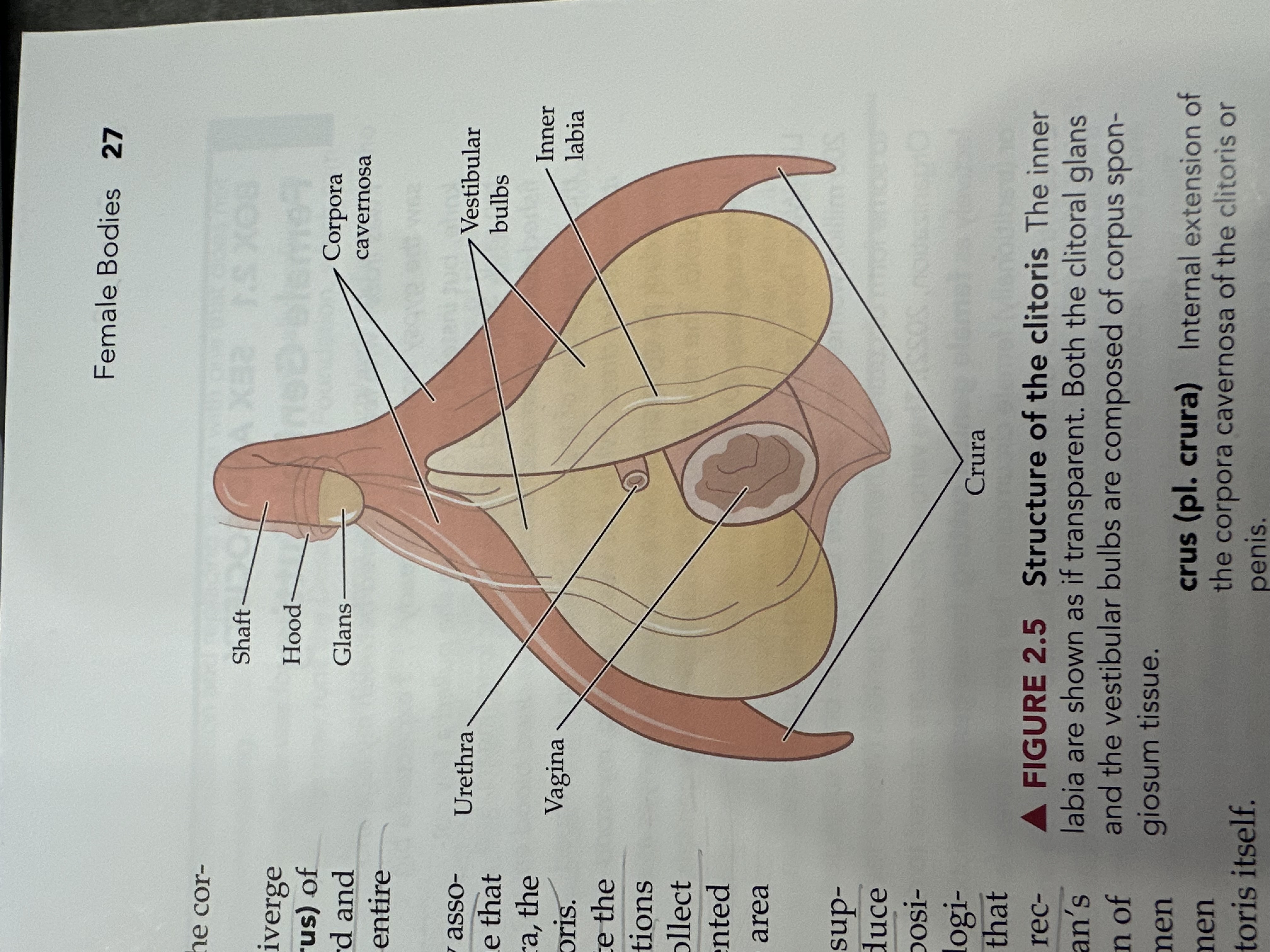
Vestibular Tubes
Two bilateral tubes that lead from the uterus to the ovaries, also known as oviducts; the usual site of fertilization.
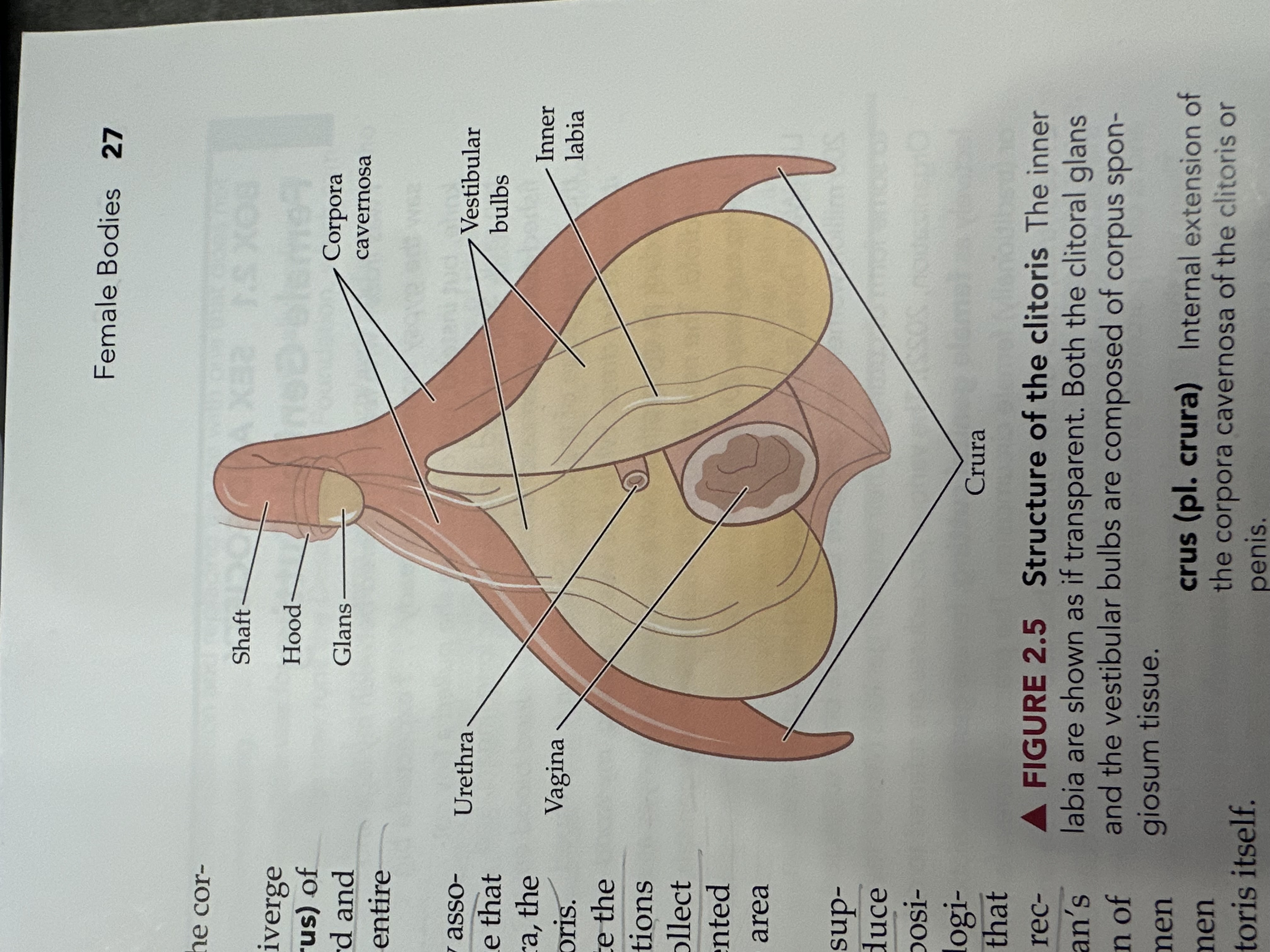
Inner Labia
The inner folds of skin surrounding the vaginal opening, which are more delicate than the outer labia and rich in blood vessels and nerve endings.
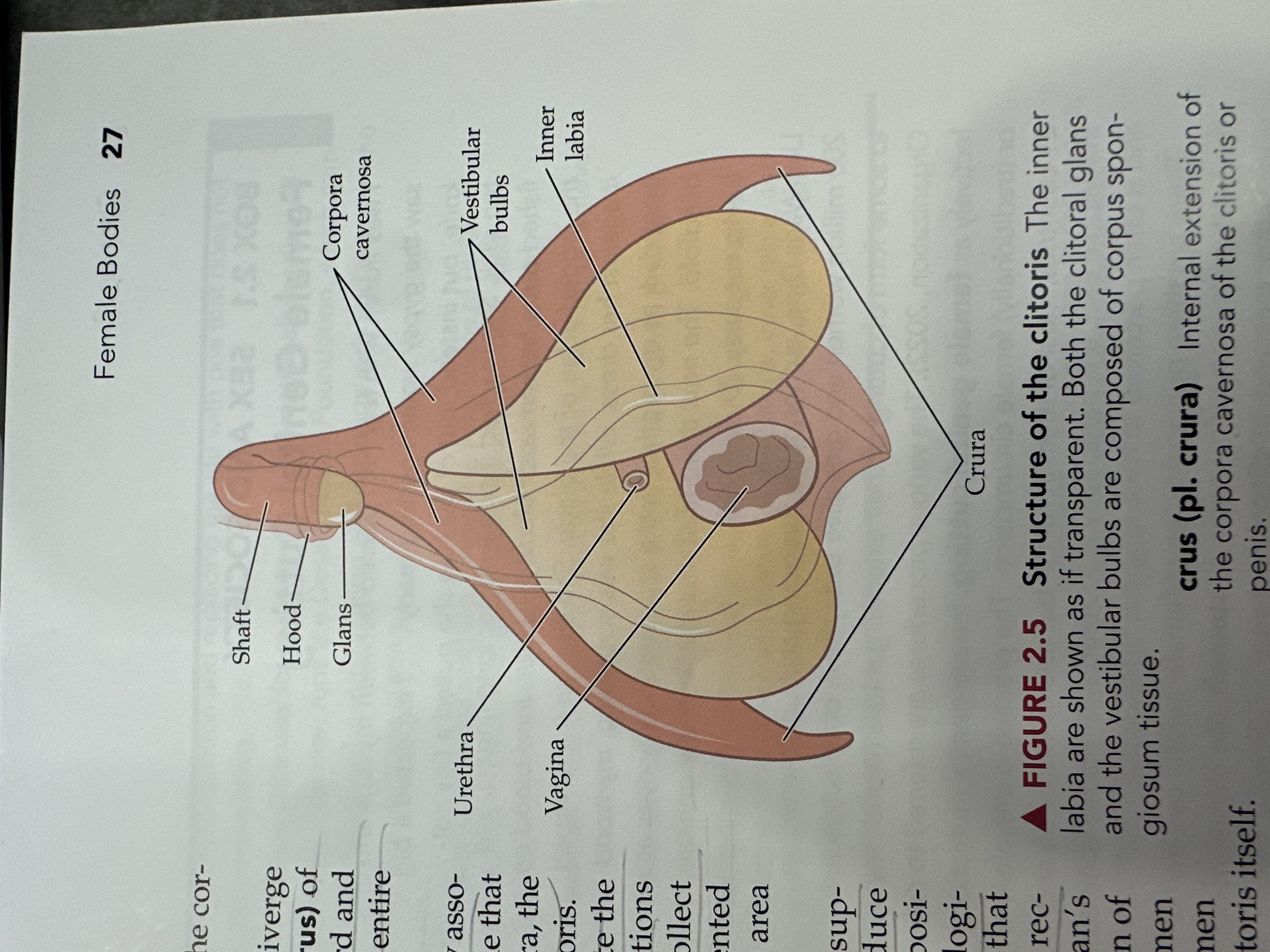
Urethra
The tube through which urine exits the body, located above the vaginal opening in females.
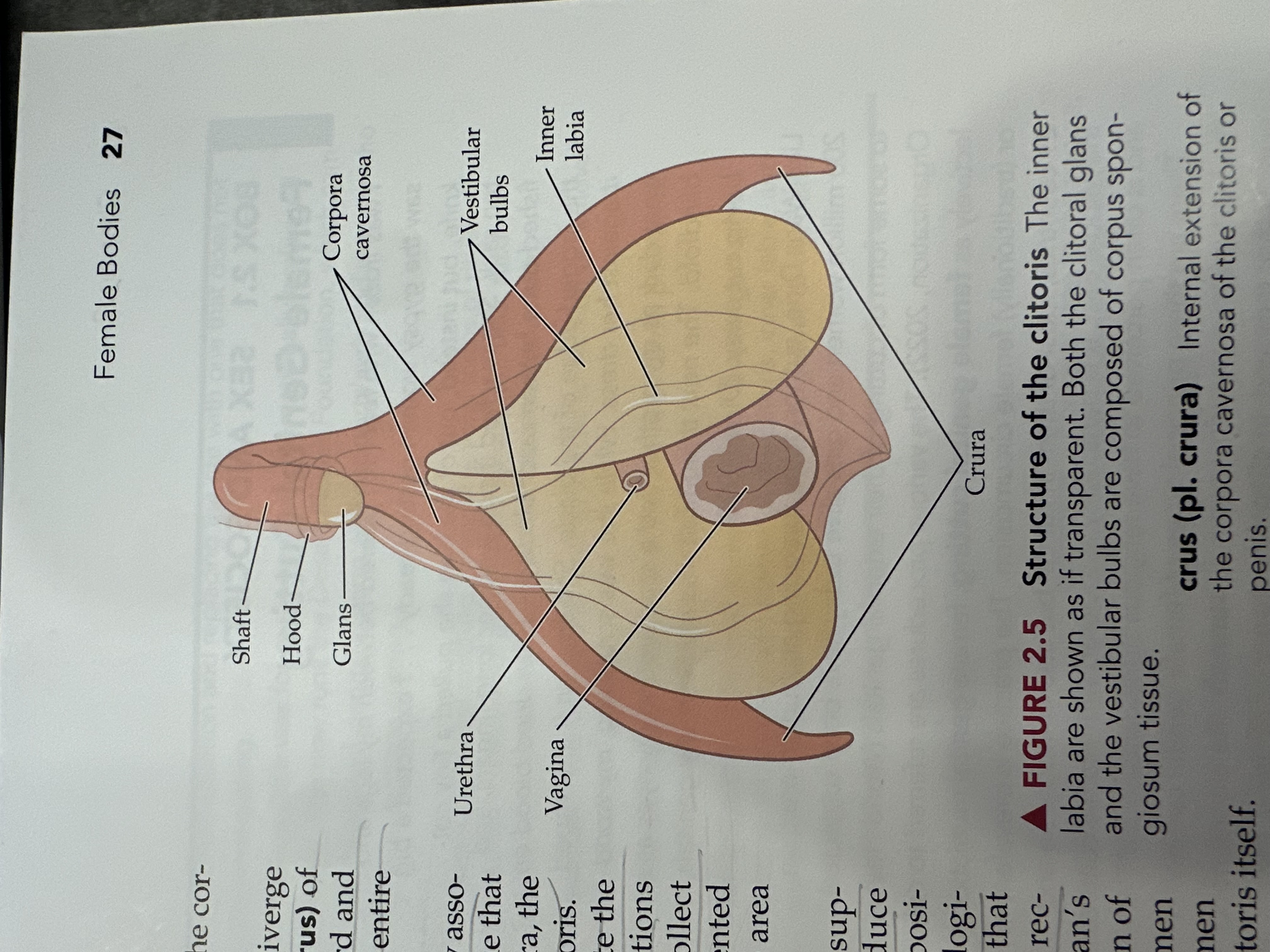
Vagina
The muscular tube that connects the external genitals to the uterus, serving as the birth canal and passage for menstrual fluid.
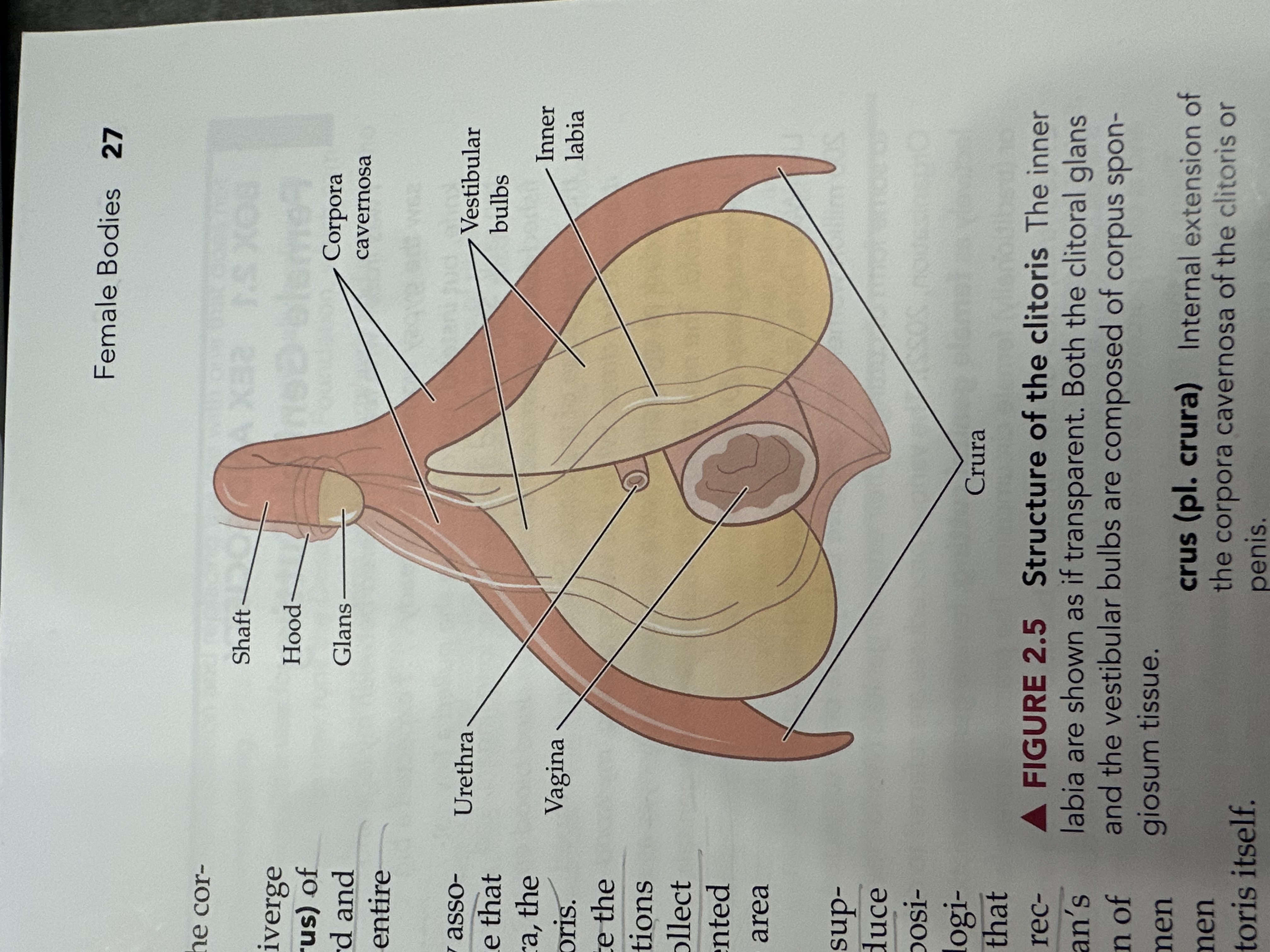
Crura
The two elongated erectile tissues that extend from the clitoris along the pubic bone, playing a key role in sexual arousal by increasing blood flow.
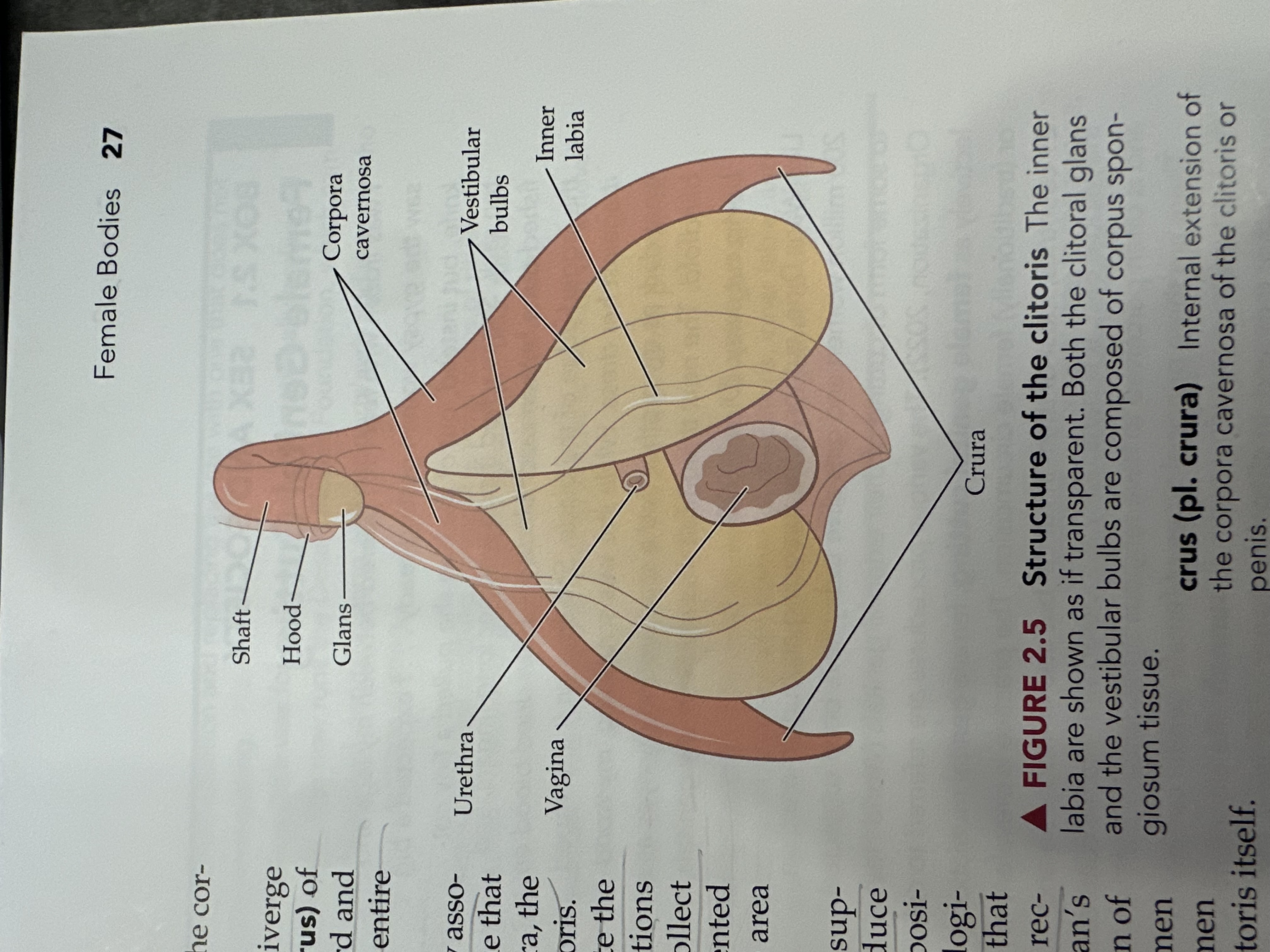
Hymen
A membrane that covers the vaginal opening
Oviducts
Either of two bilateral tubes that lead from the uterus toward the ovaries; the usual site of fertilization.
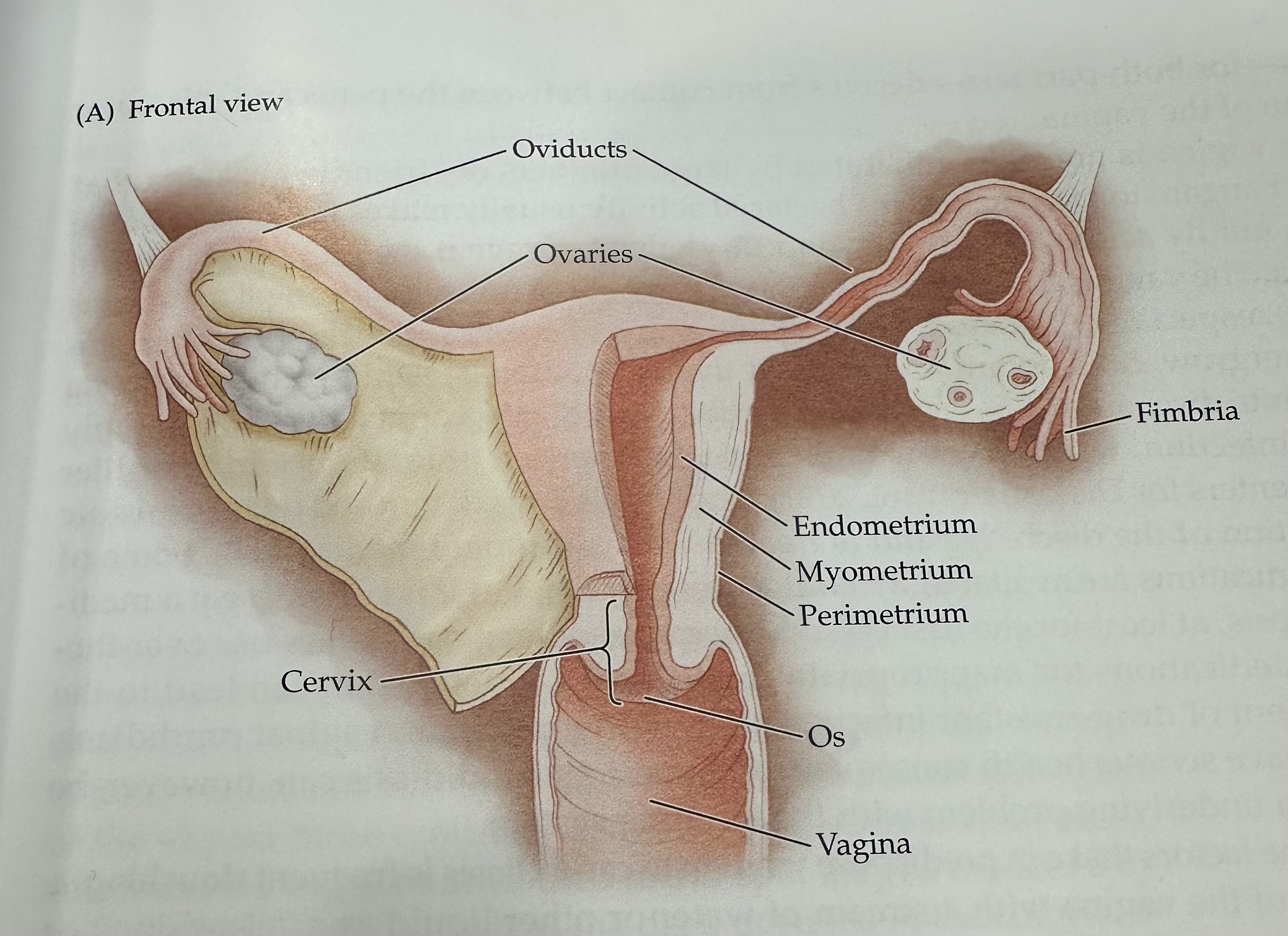
Ovaries
The female reproductive organs that produce ova (eggs) and secrete hormones such as estrogen and progesterone.
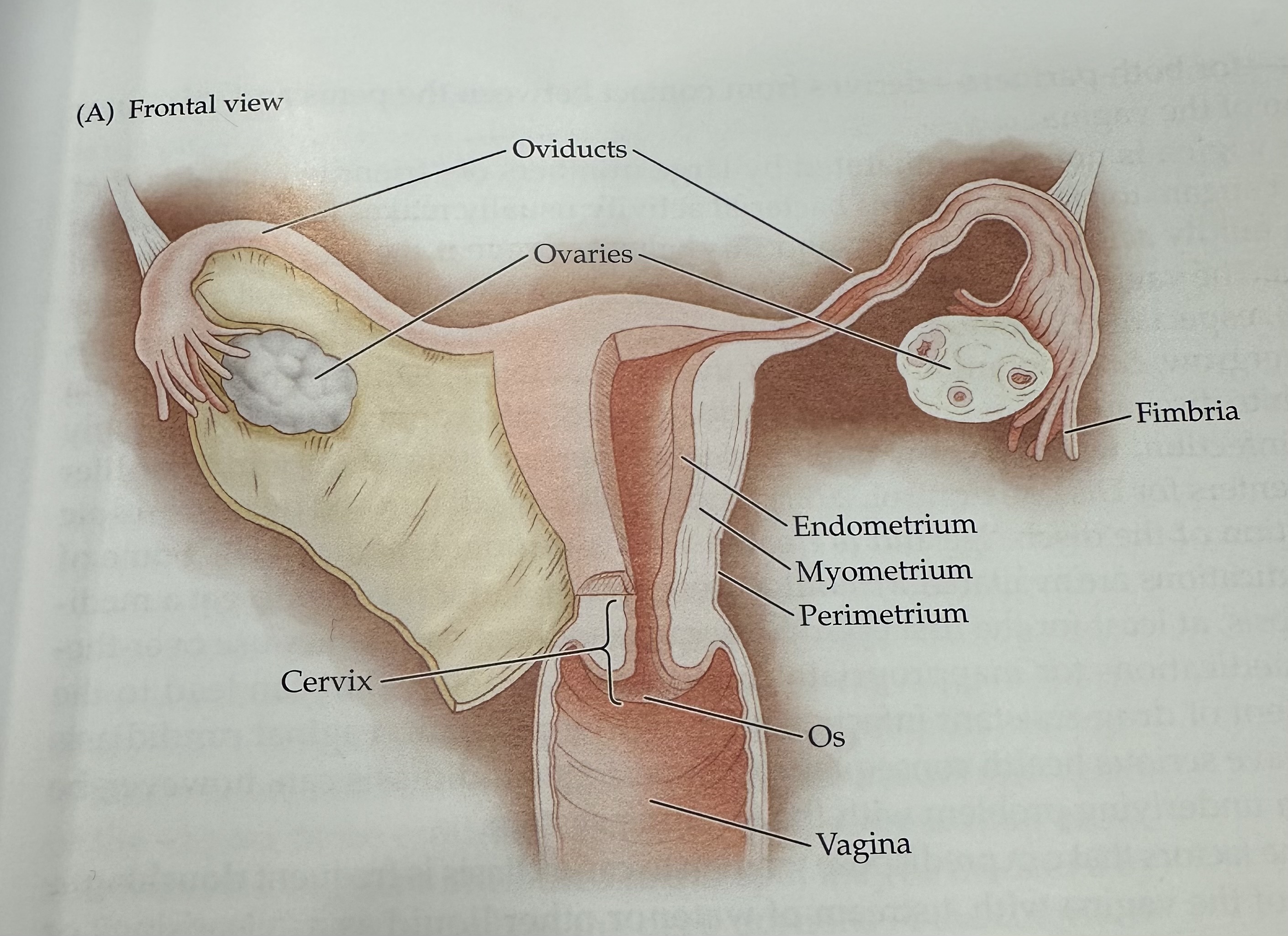
Fimbria
The fringe at the end of the oviduct composed of finger-like extensions.
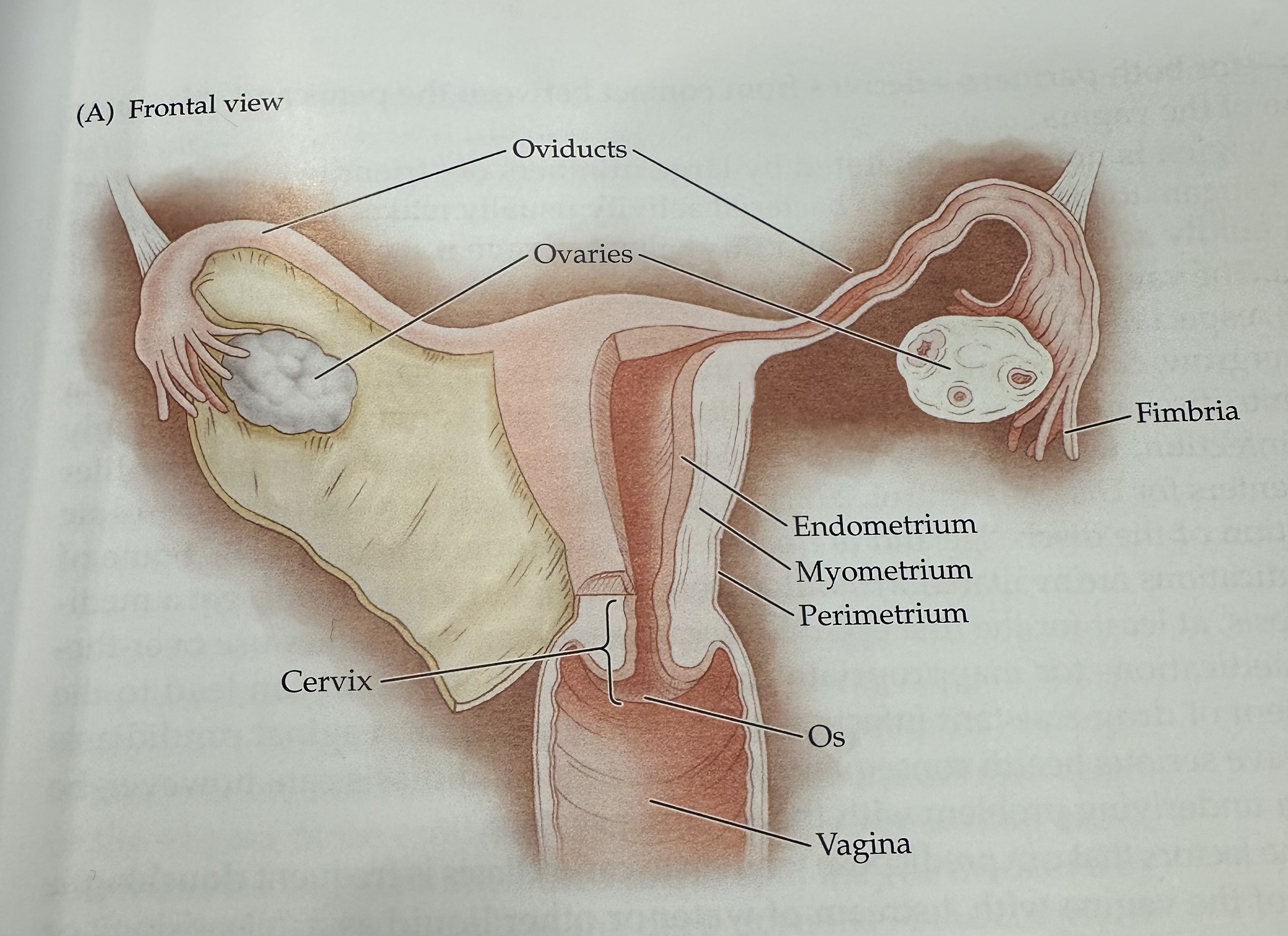
Endometrium
The inner lining of the uterus, which thickens during the menstrual cycle to prepare for potential implantation of a fertilized egg.
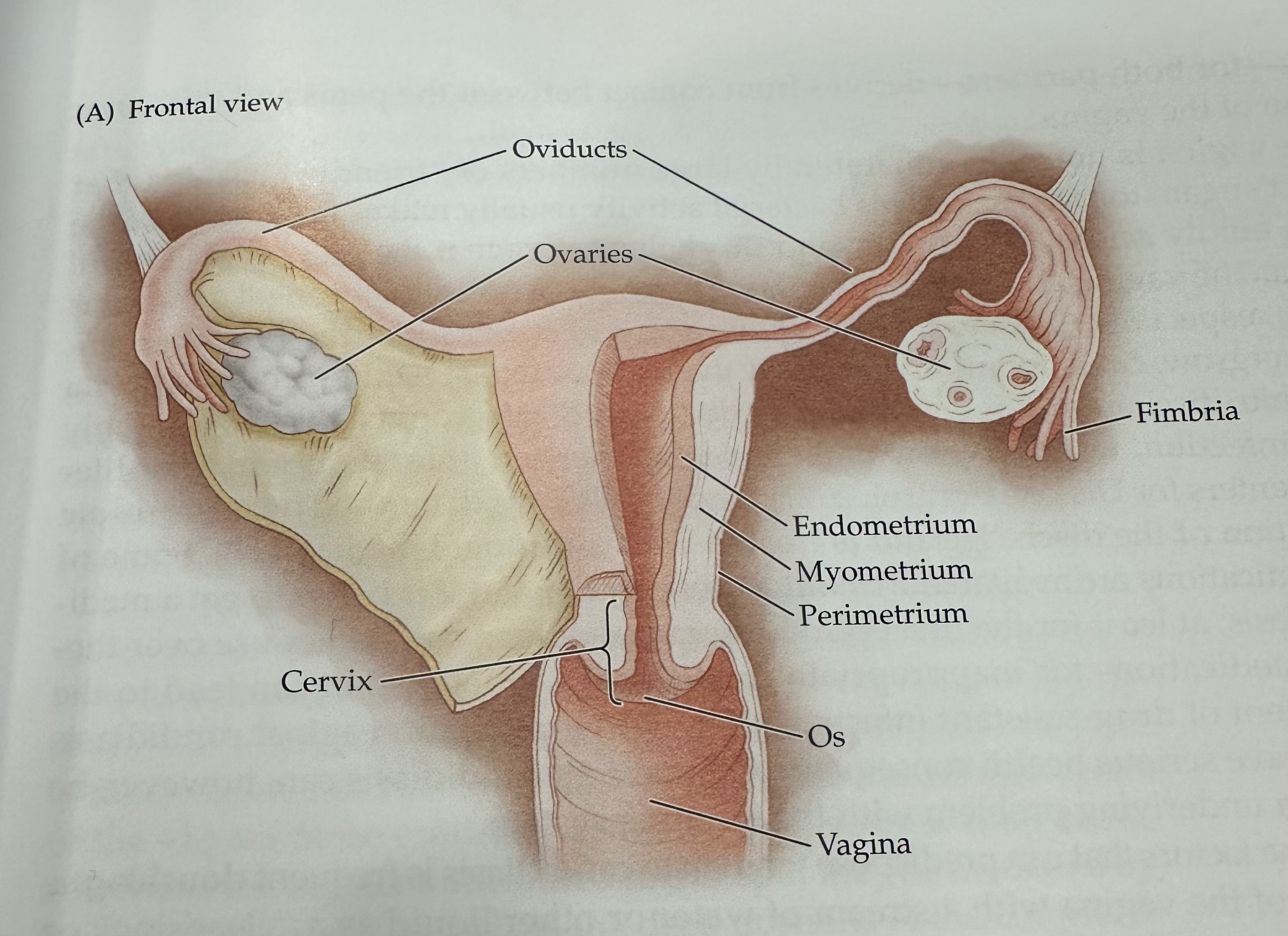
Myometrium
The middle layer of the uterus, consisting of smooth muscle, responsible for uterine contractions during childbirth.
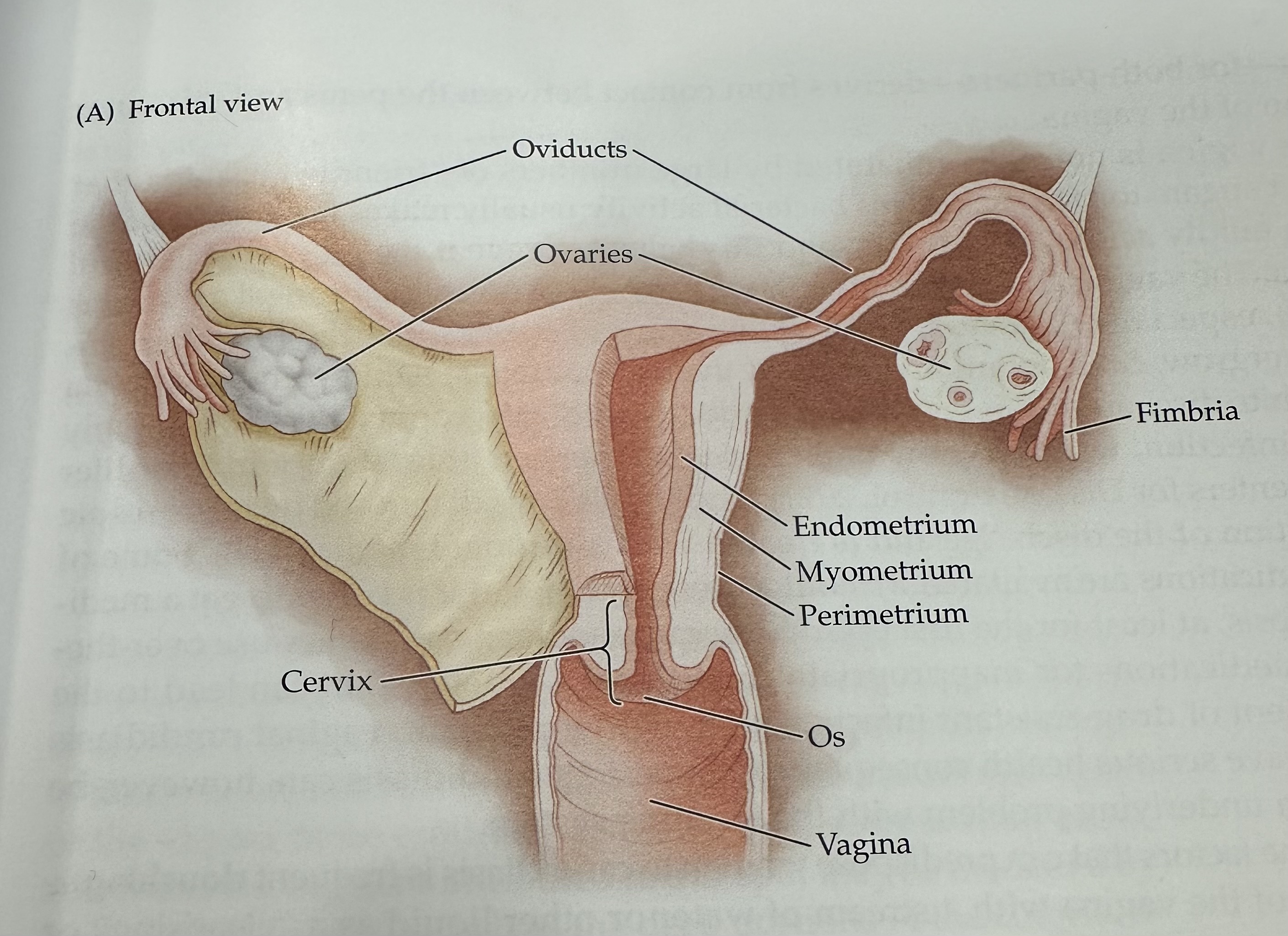
Perimetrium
The outermost layer of the uterus, consisting of a thin layer of tissue that covers the outside of the uterus.
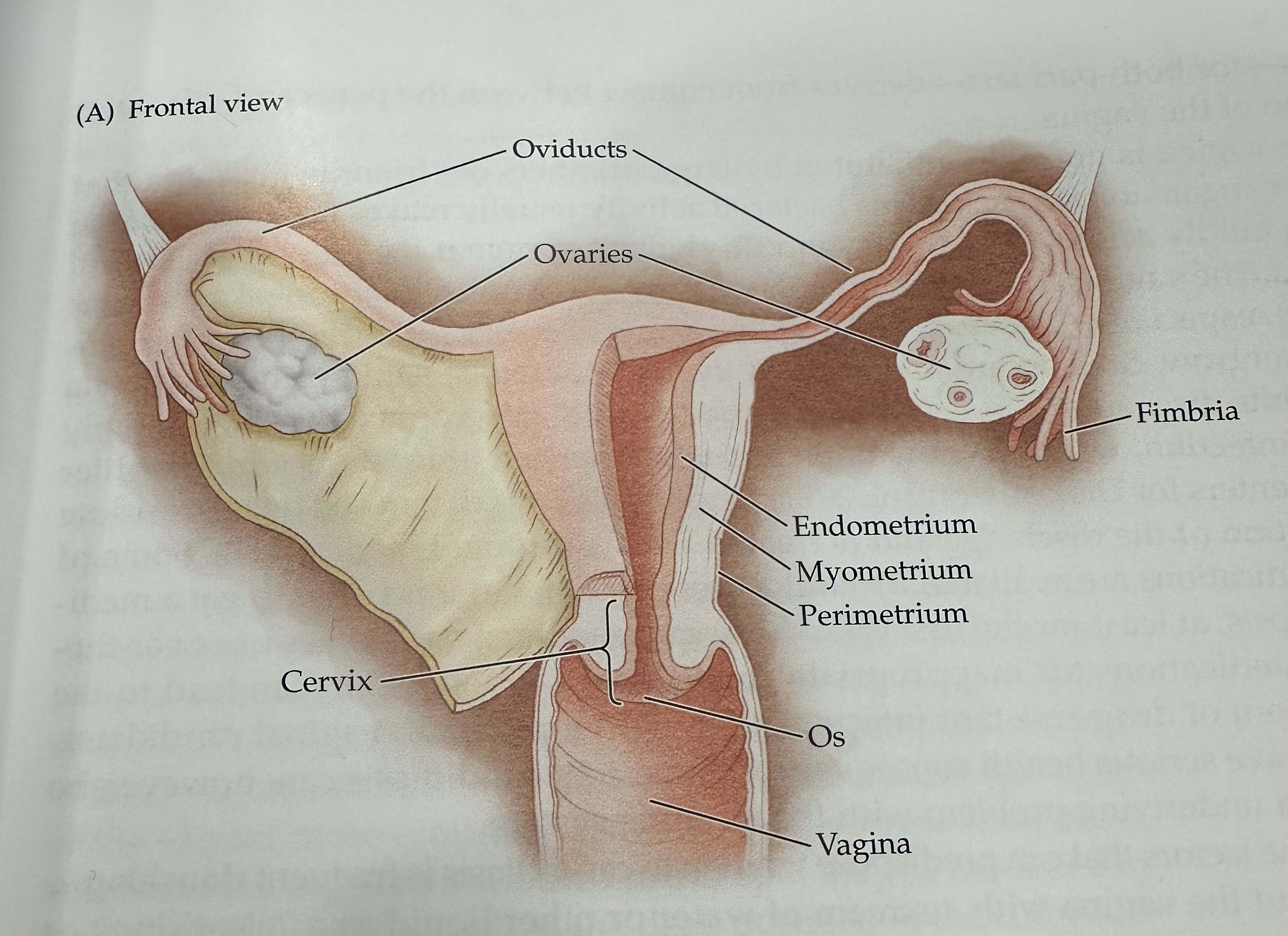
Os (vagina)
The opening of the cervix into the vagina, which allows menstrual fluid to exit and sperm to enter.
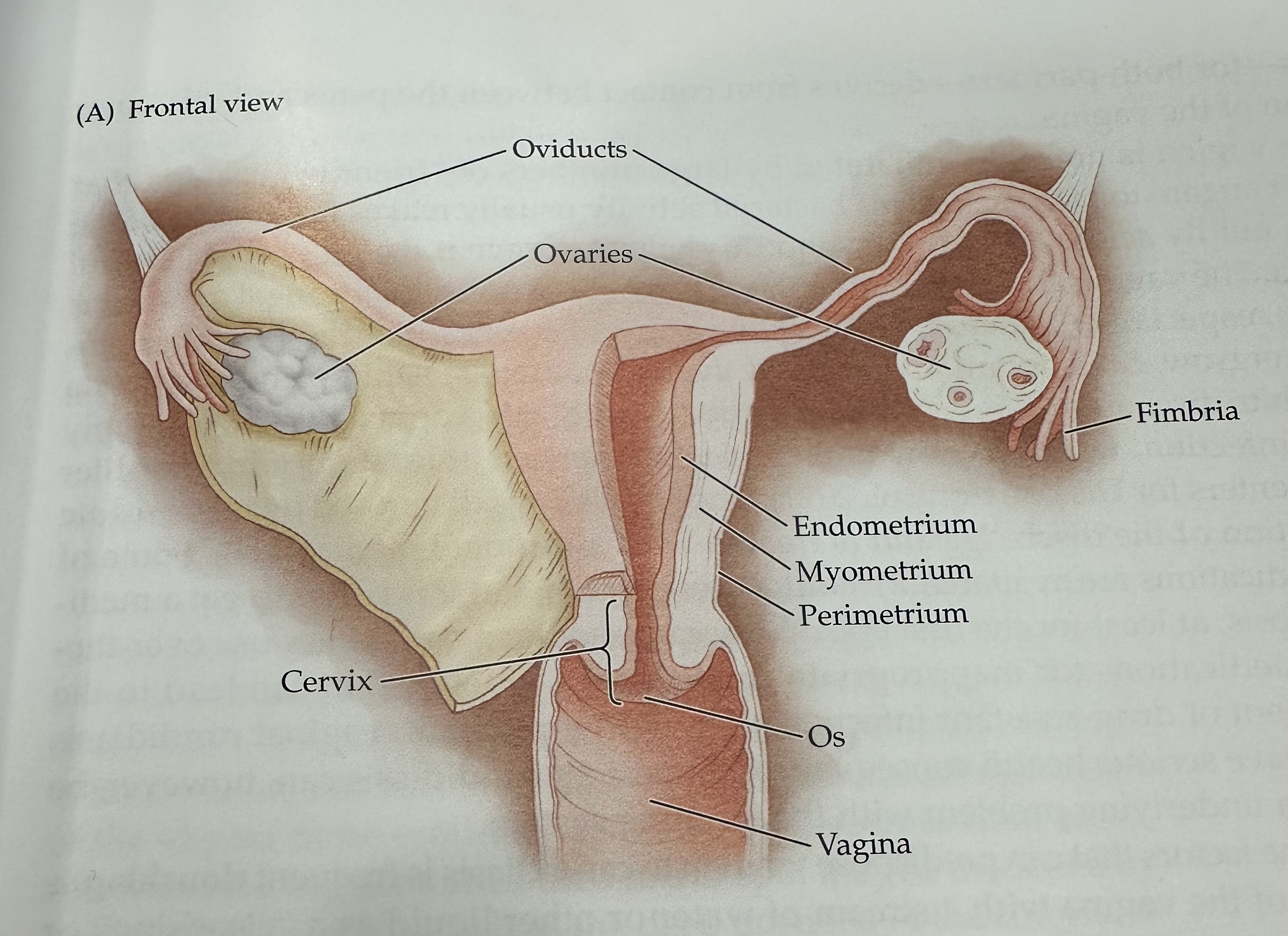
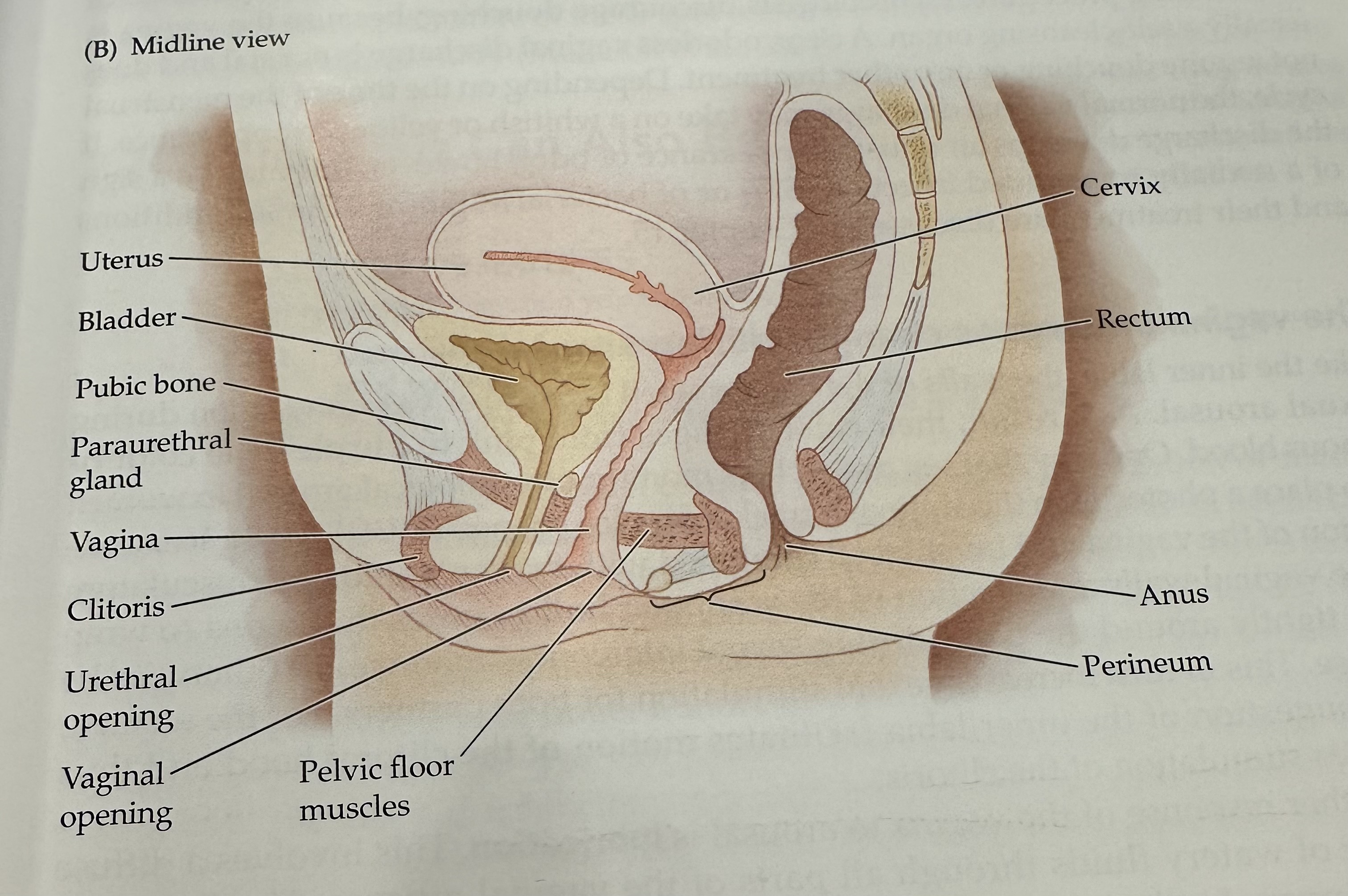
Cervix
The narrow, lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina; it allows menstrual fluid to exit and sperm to enter.
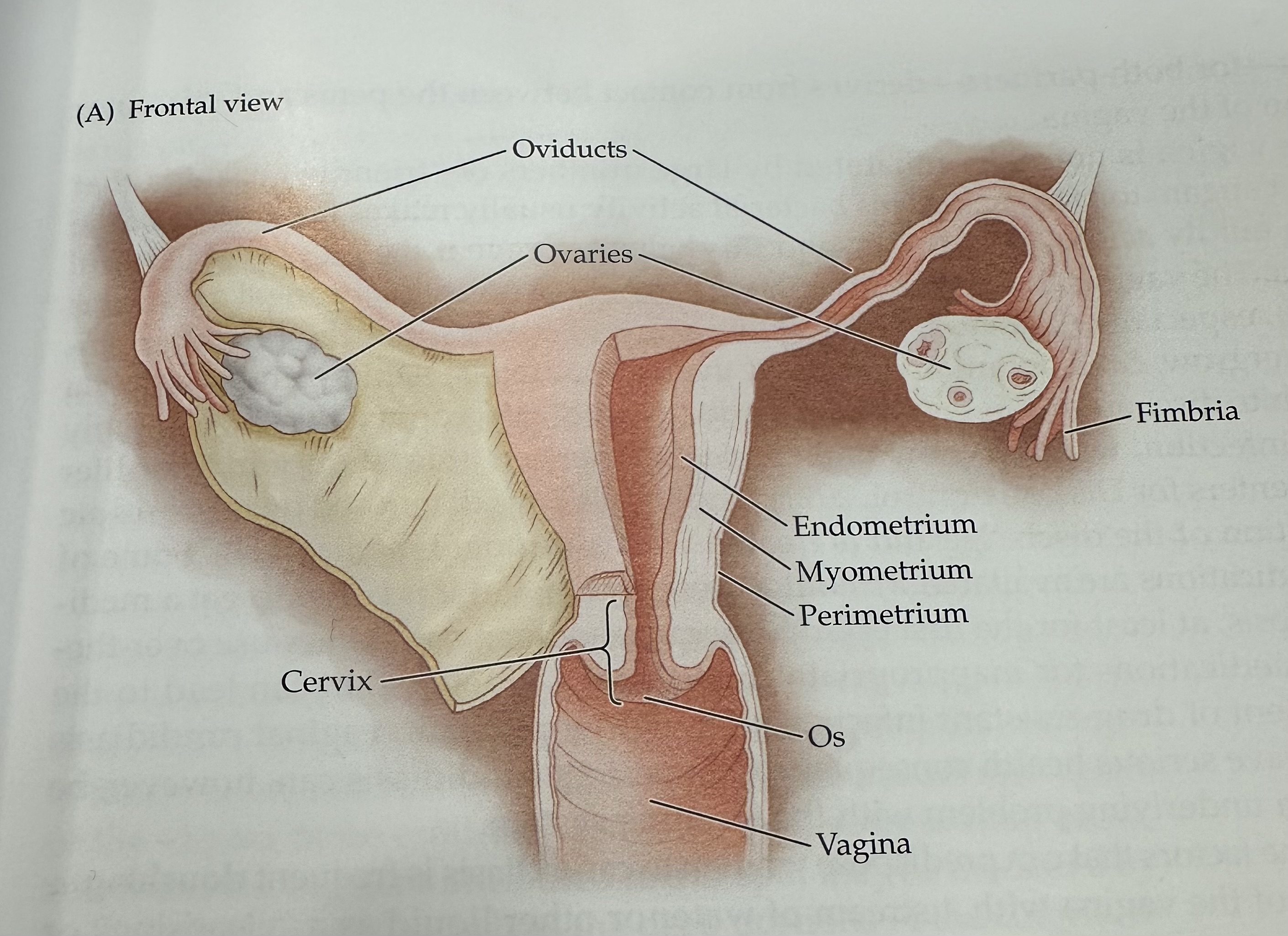
Uterus
The hollow muscular organ in a female's pelvis where a fertilized egg implants and a fetus develops during pregnancy.
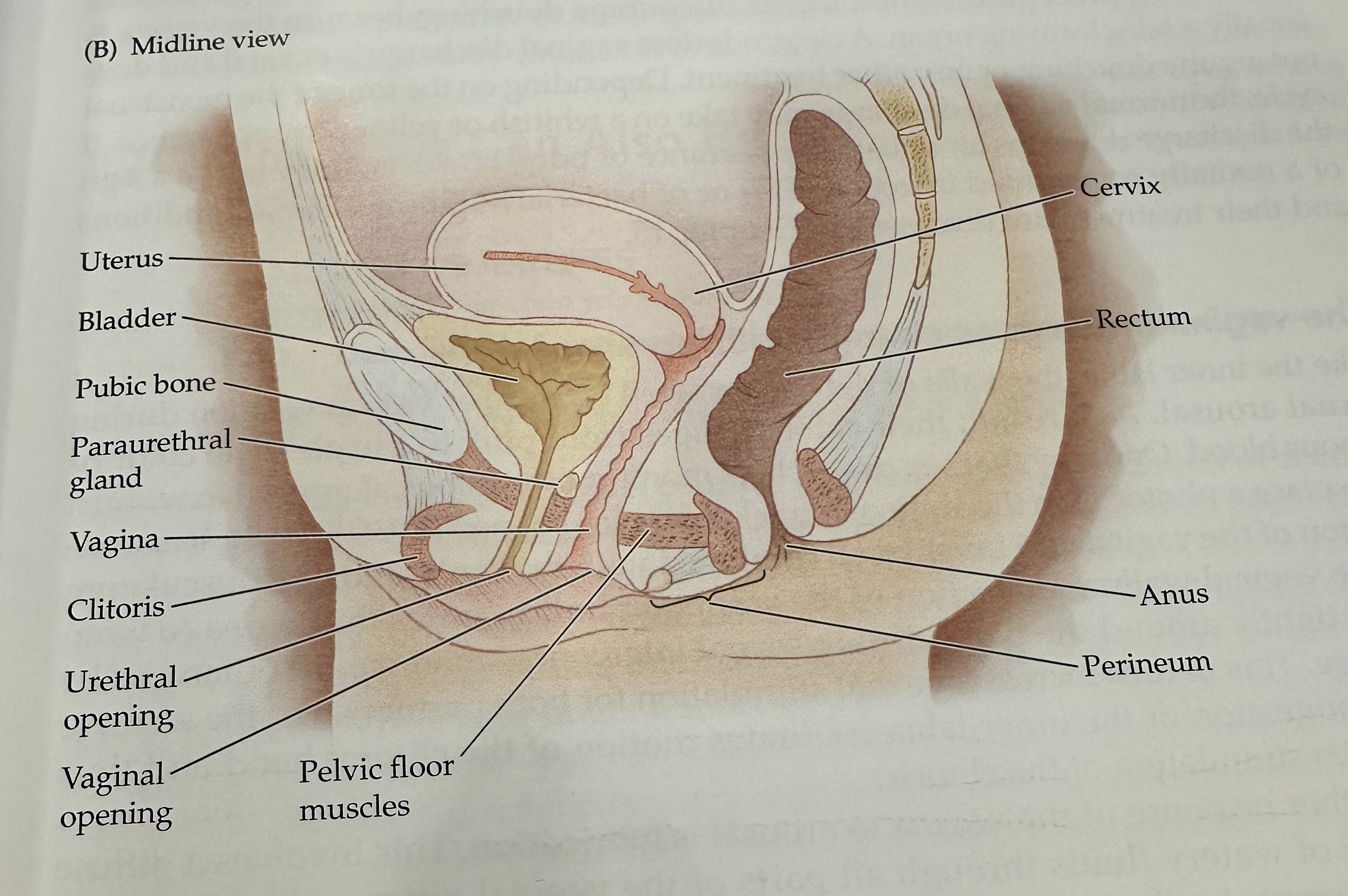
Cervix
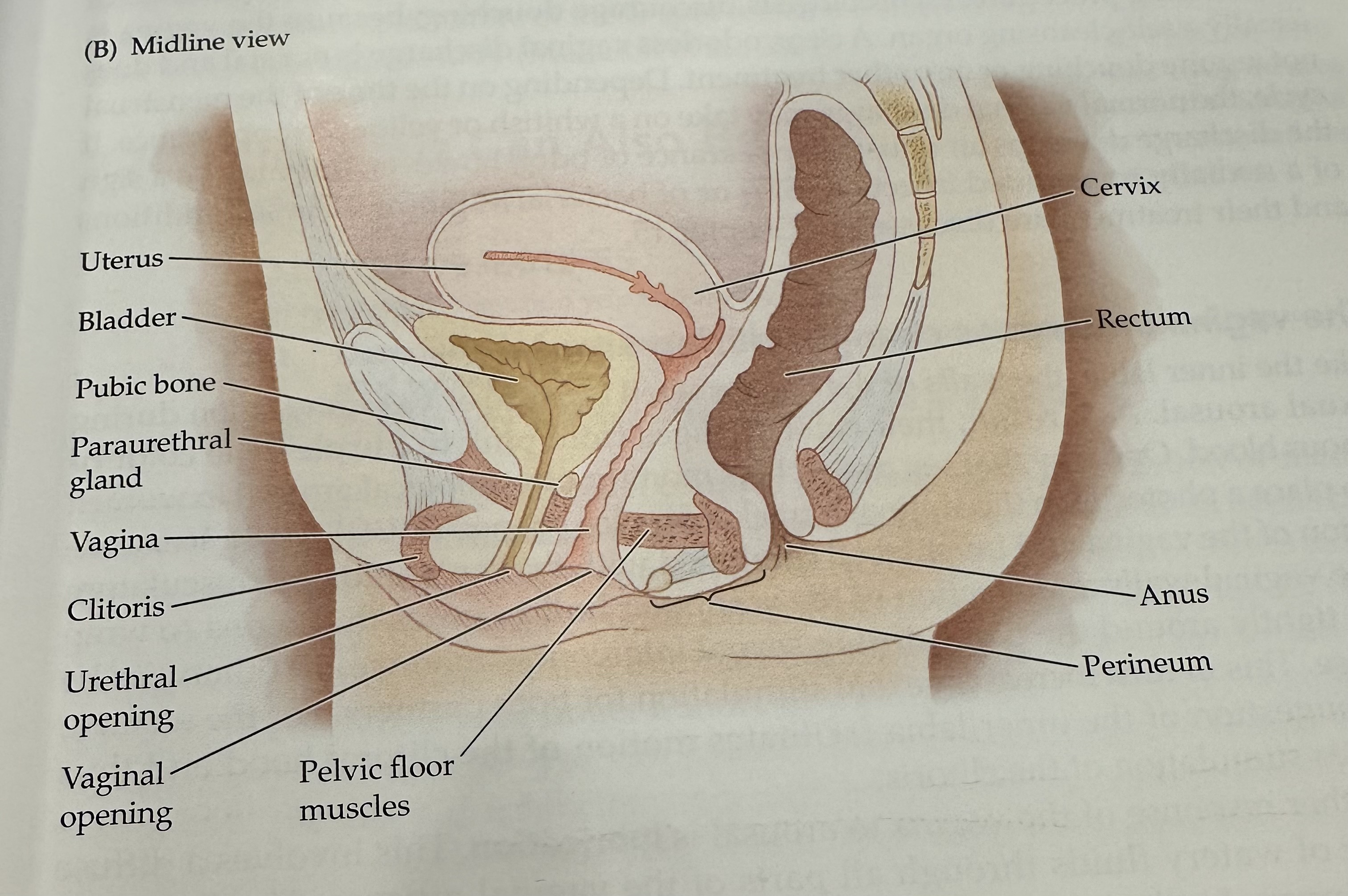
Rectum
The final section of the large intestine, leading to the anus, where waste is stored prior to elimination.
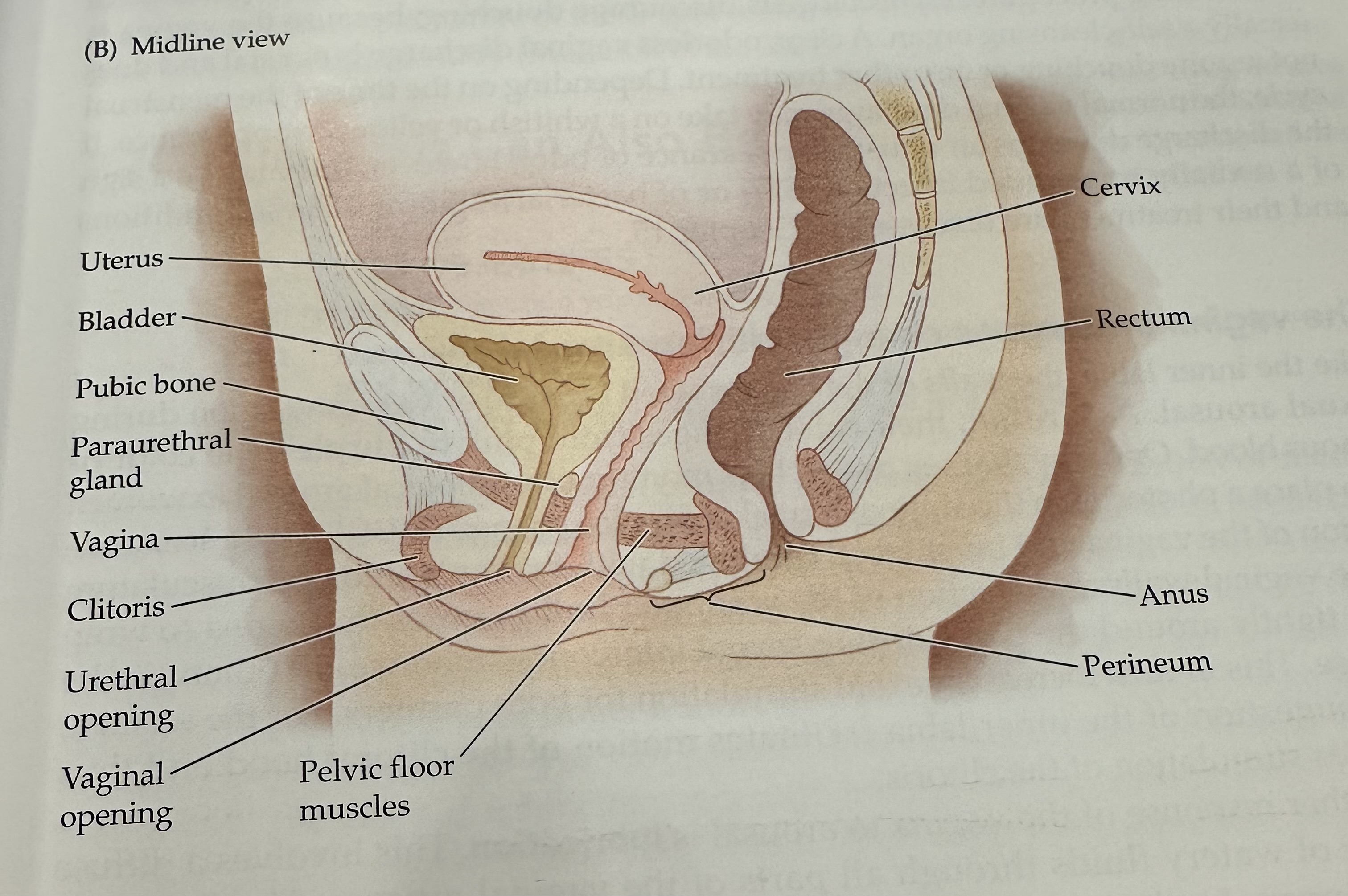
Anus
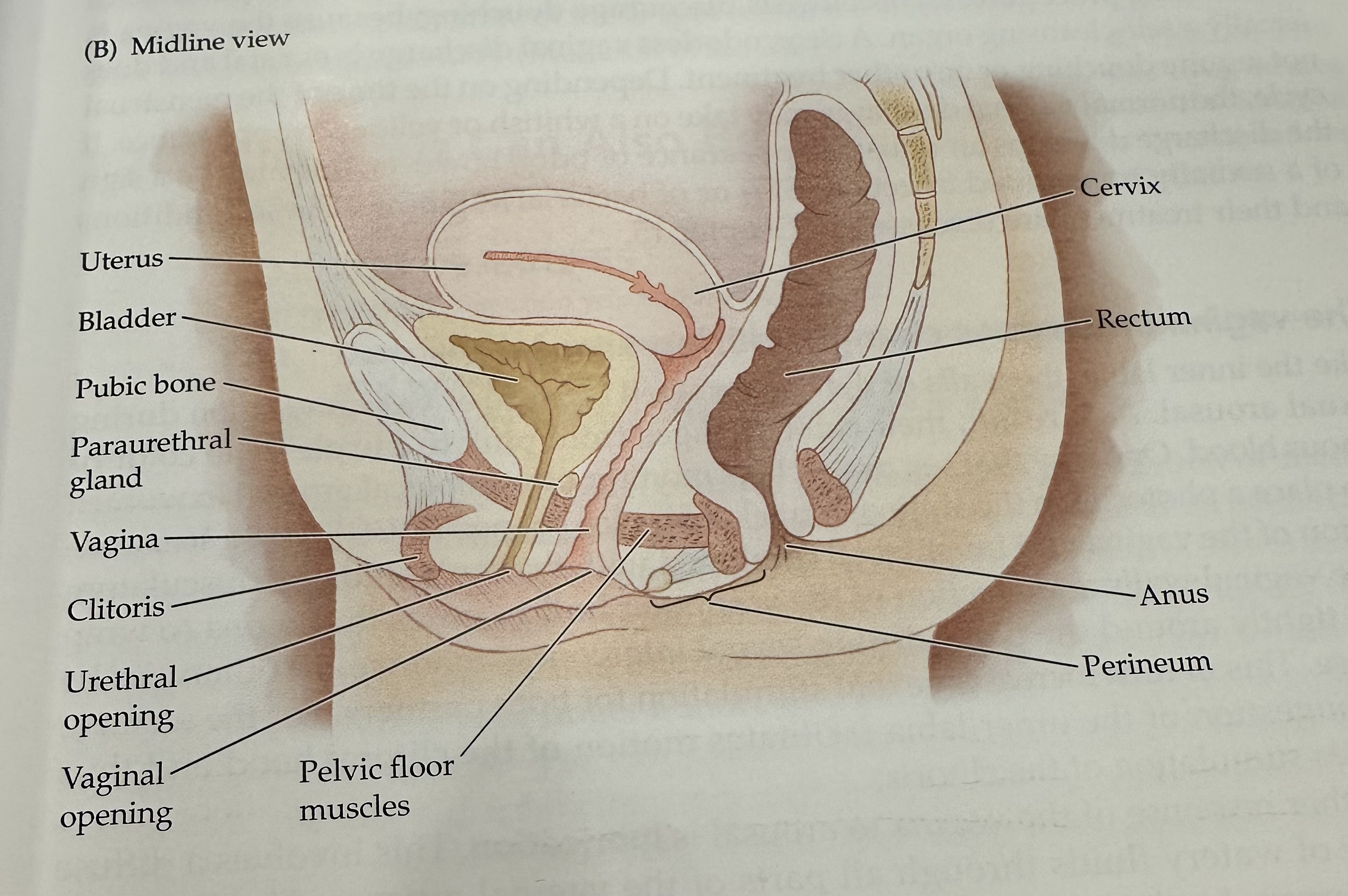
Perineum
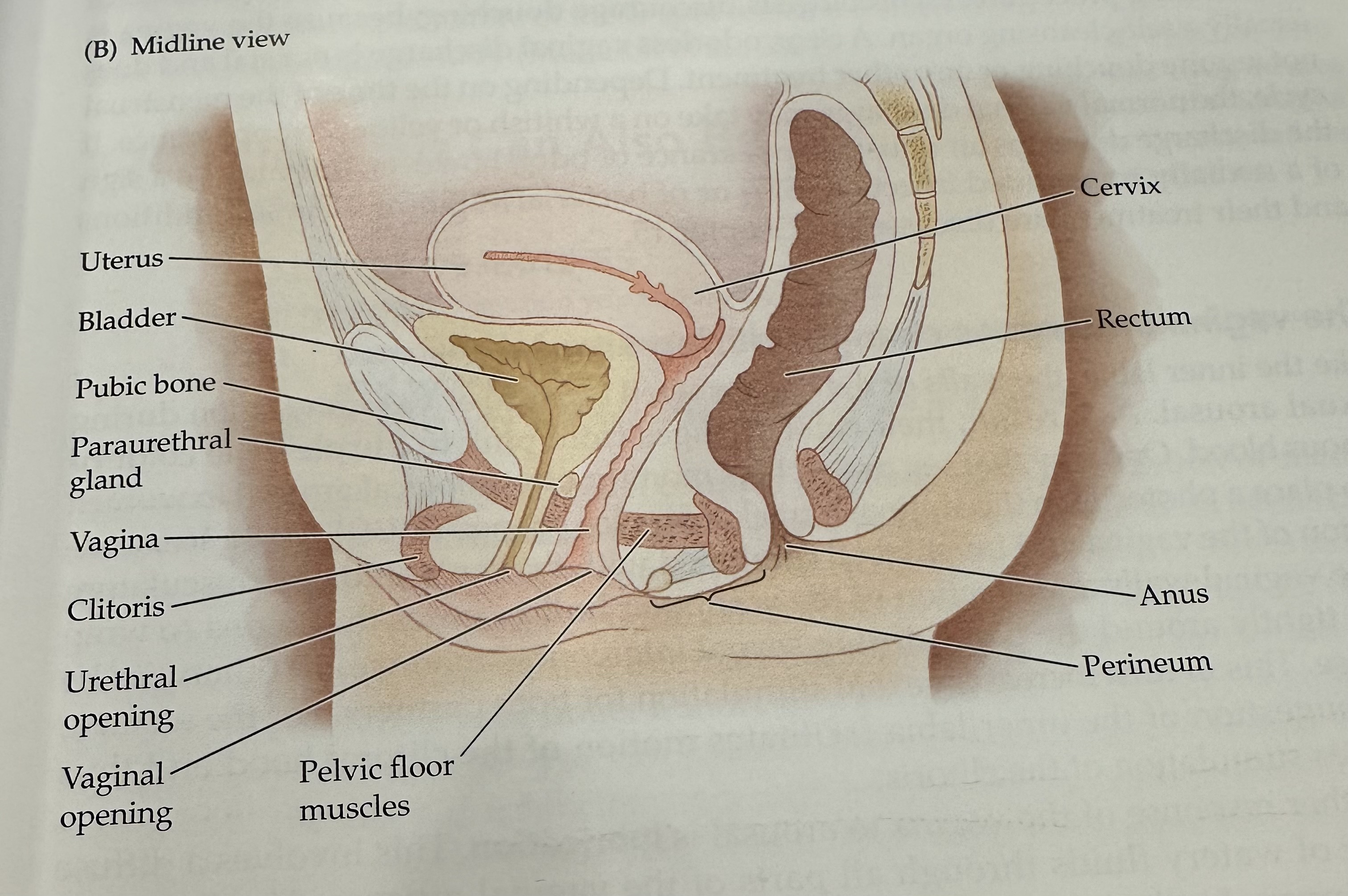
Pelvic Floor Muscles
Muscles that support the pelvic organs (bladder, intestines, uterus) and play a key role in urinary and reproductive health.
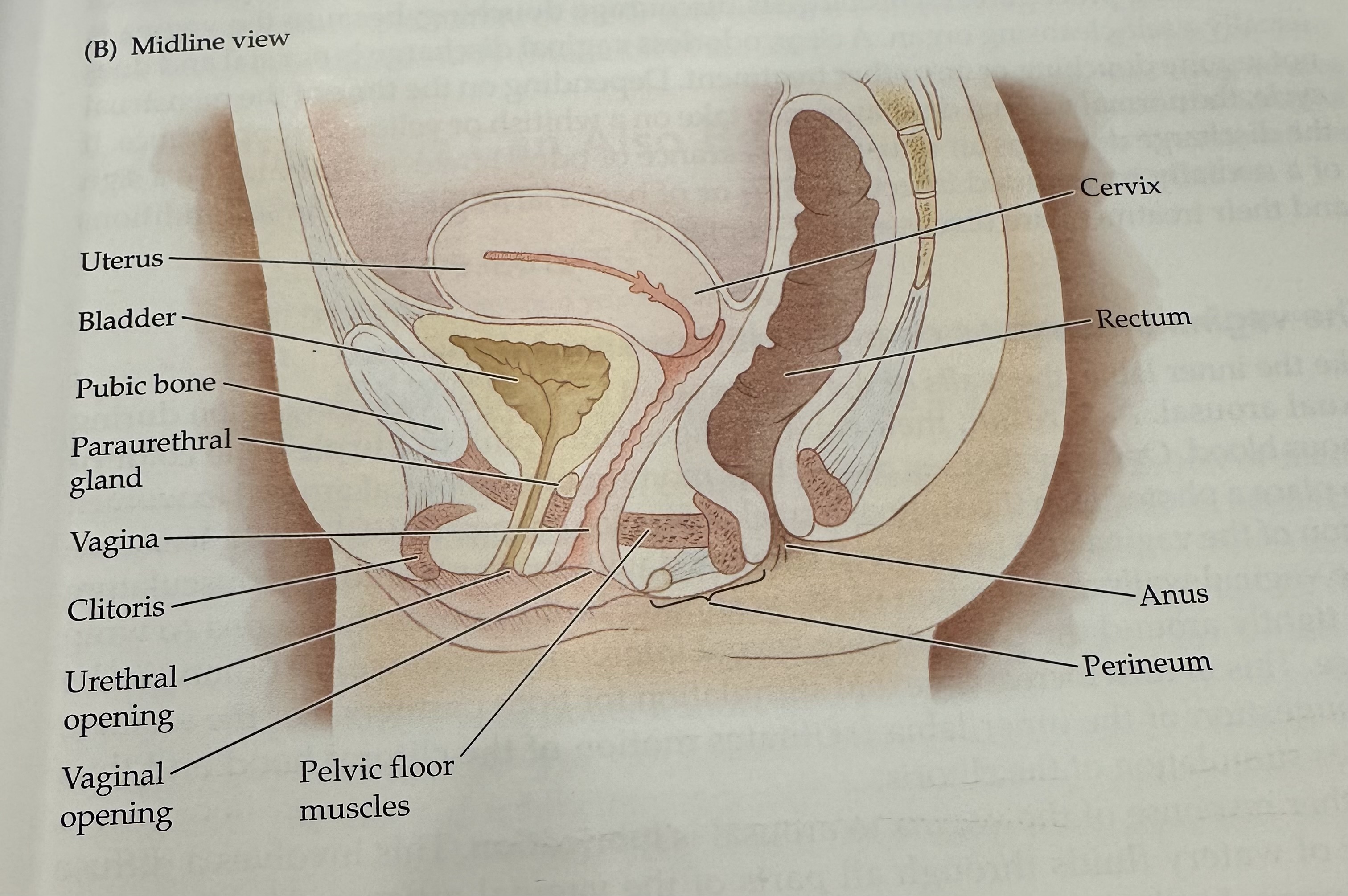
Vaginal opening
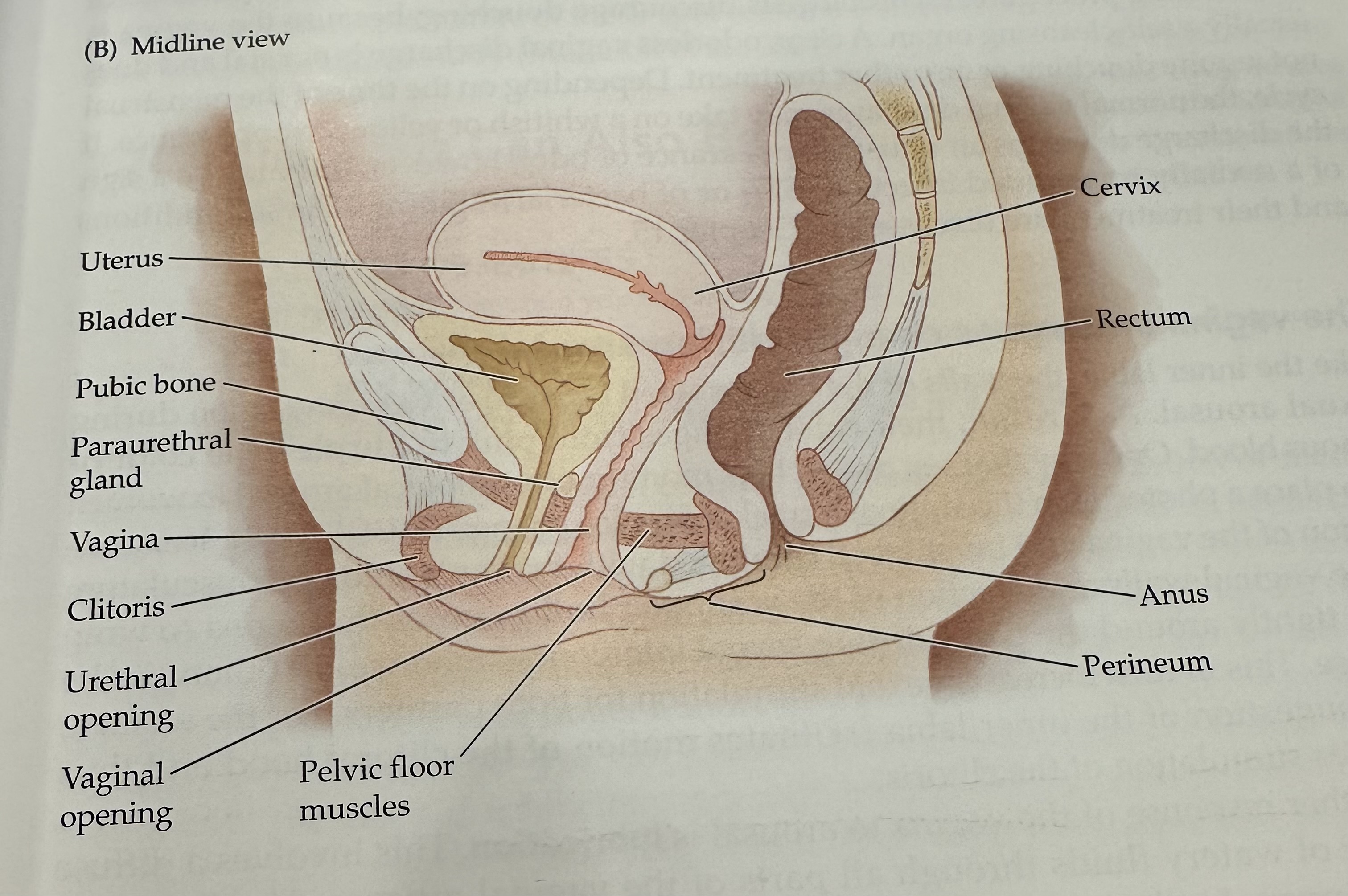
Urethral opening
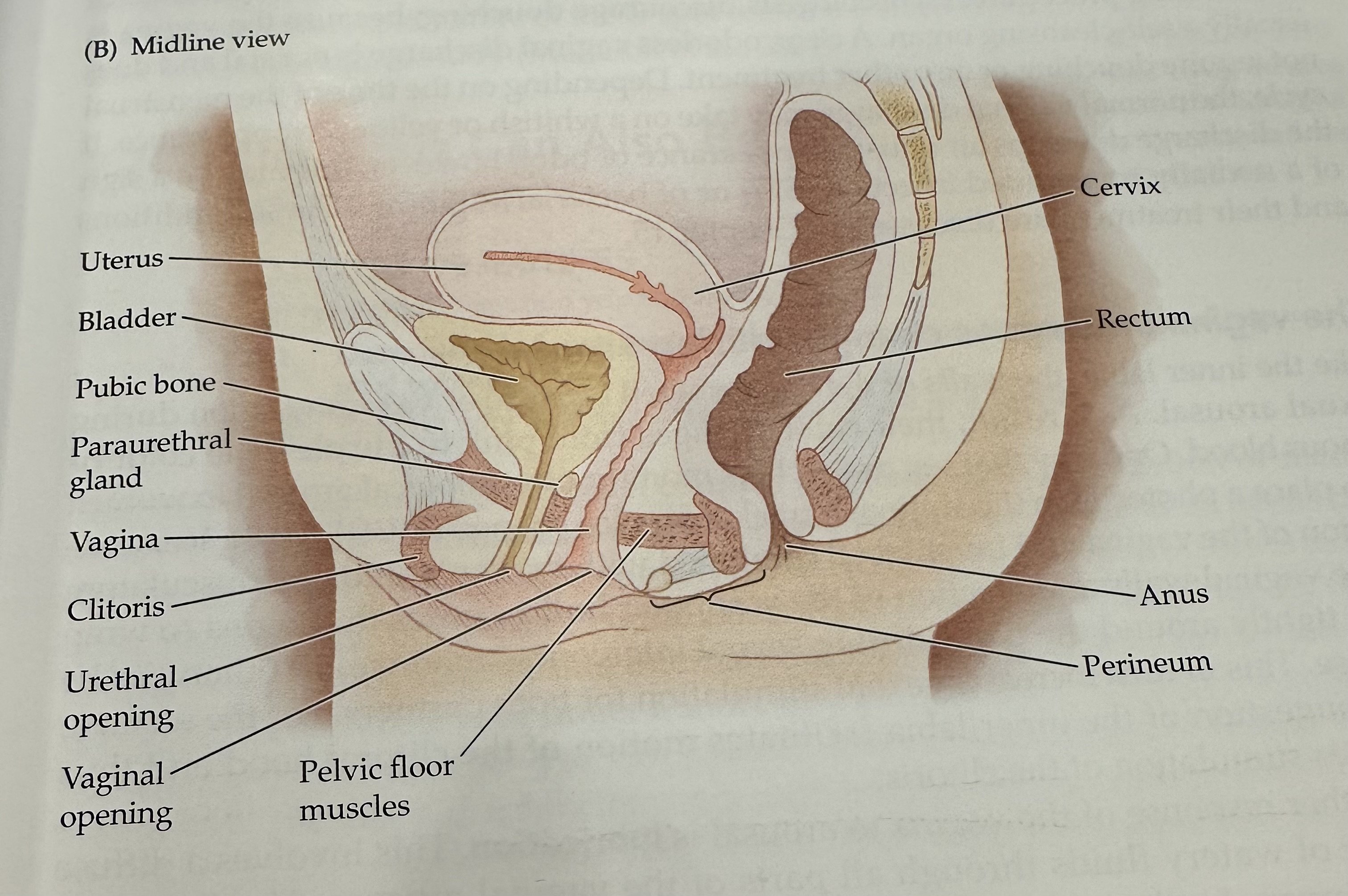
Cltoris
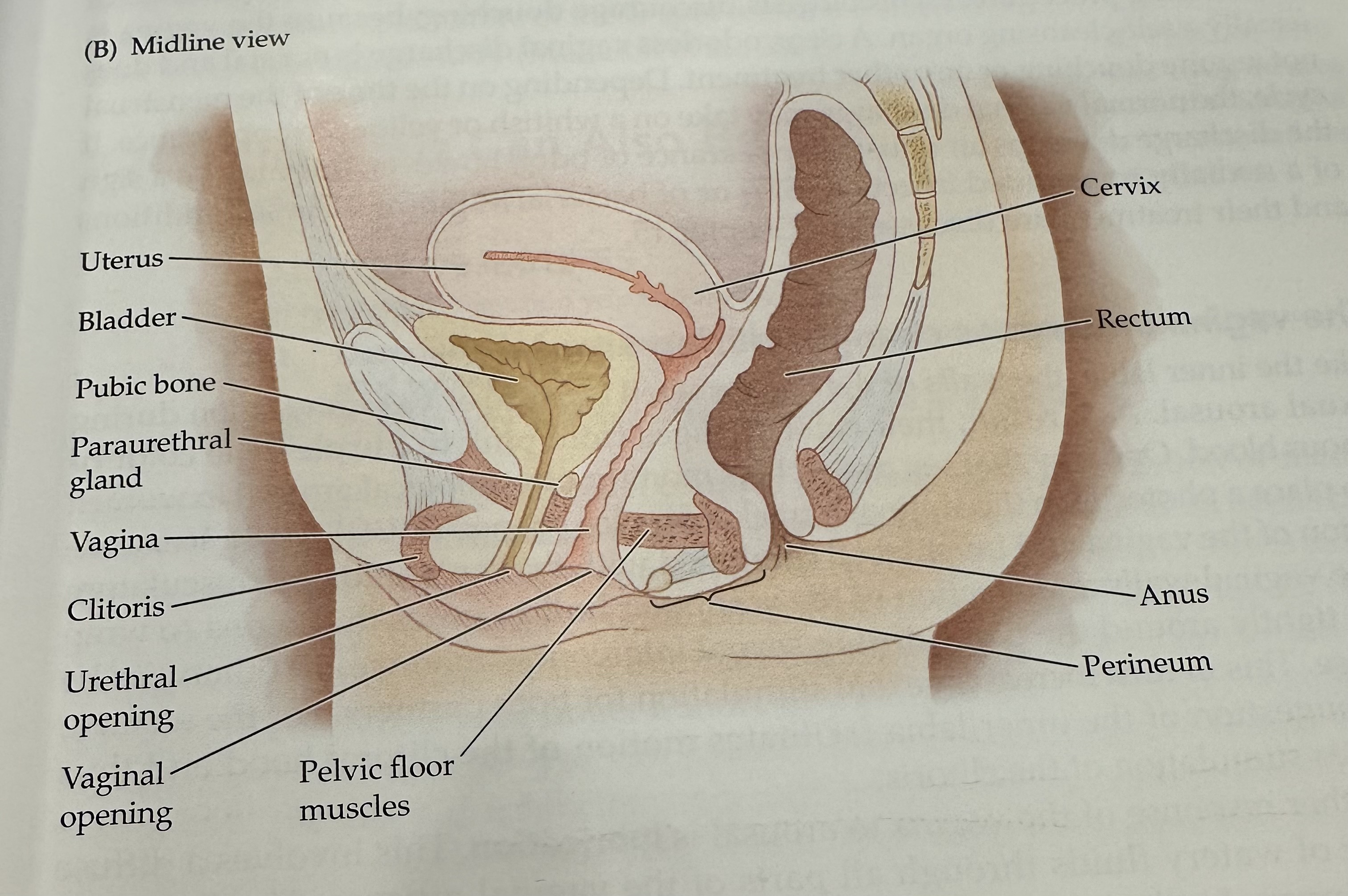
Vagina
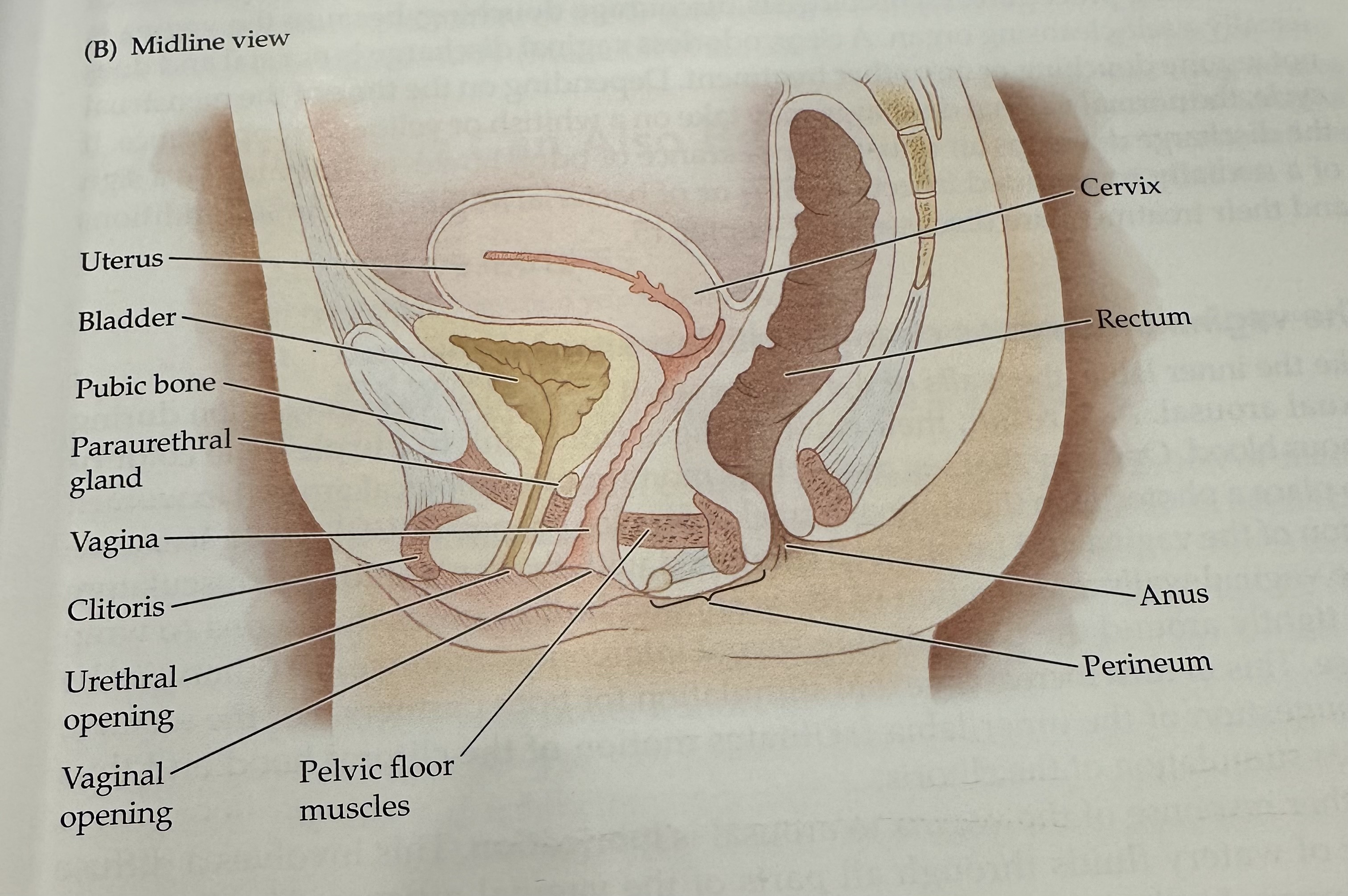
Parauretheral Gland
A gland located near the urethra that secretes fluid to help lubricate the urethral opening.
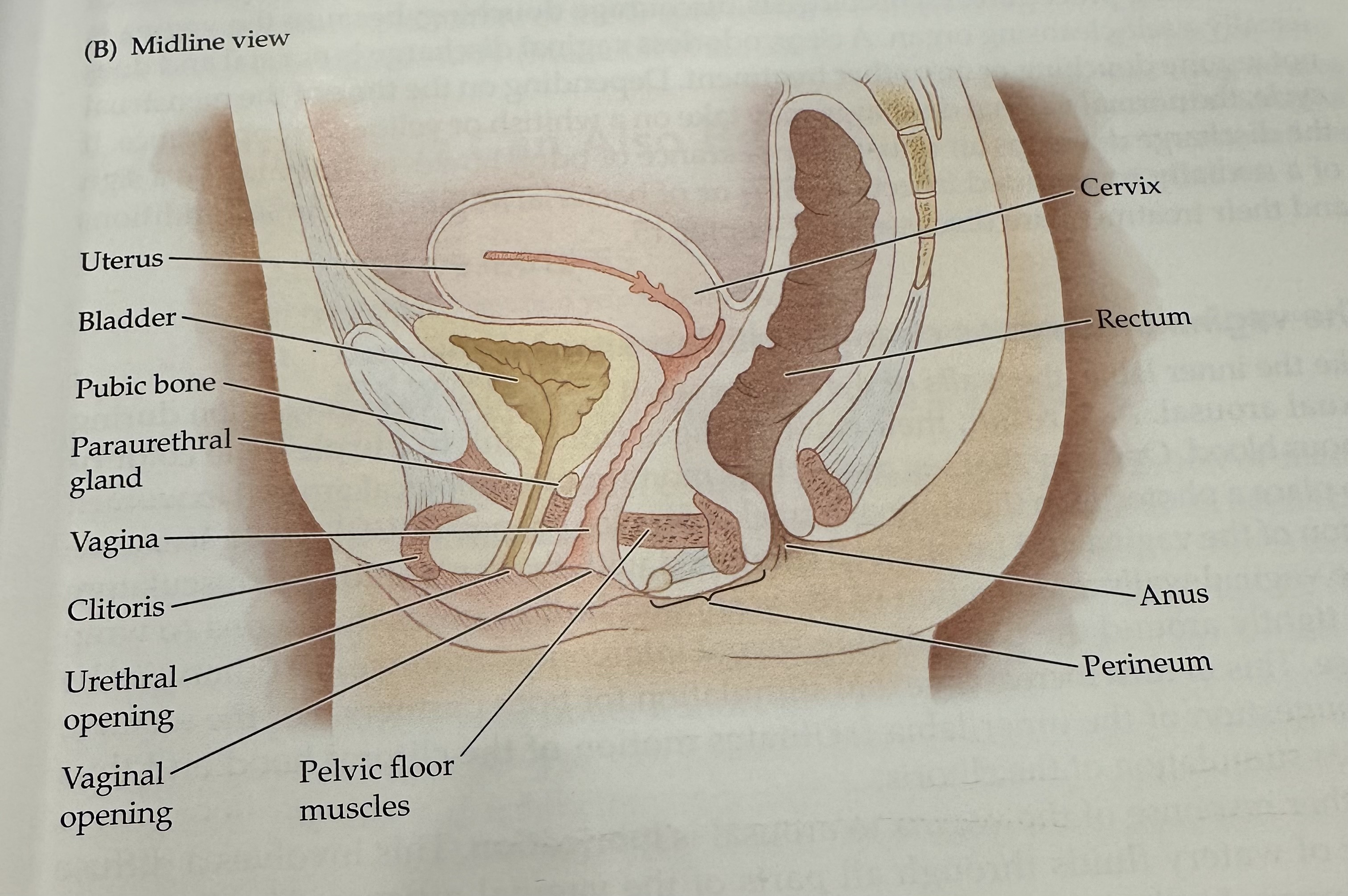
Pubic Bone
The anterior part of the pelvic bone, which supports the structure and protects the reproductive organs.
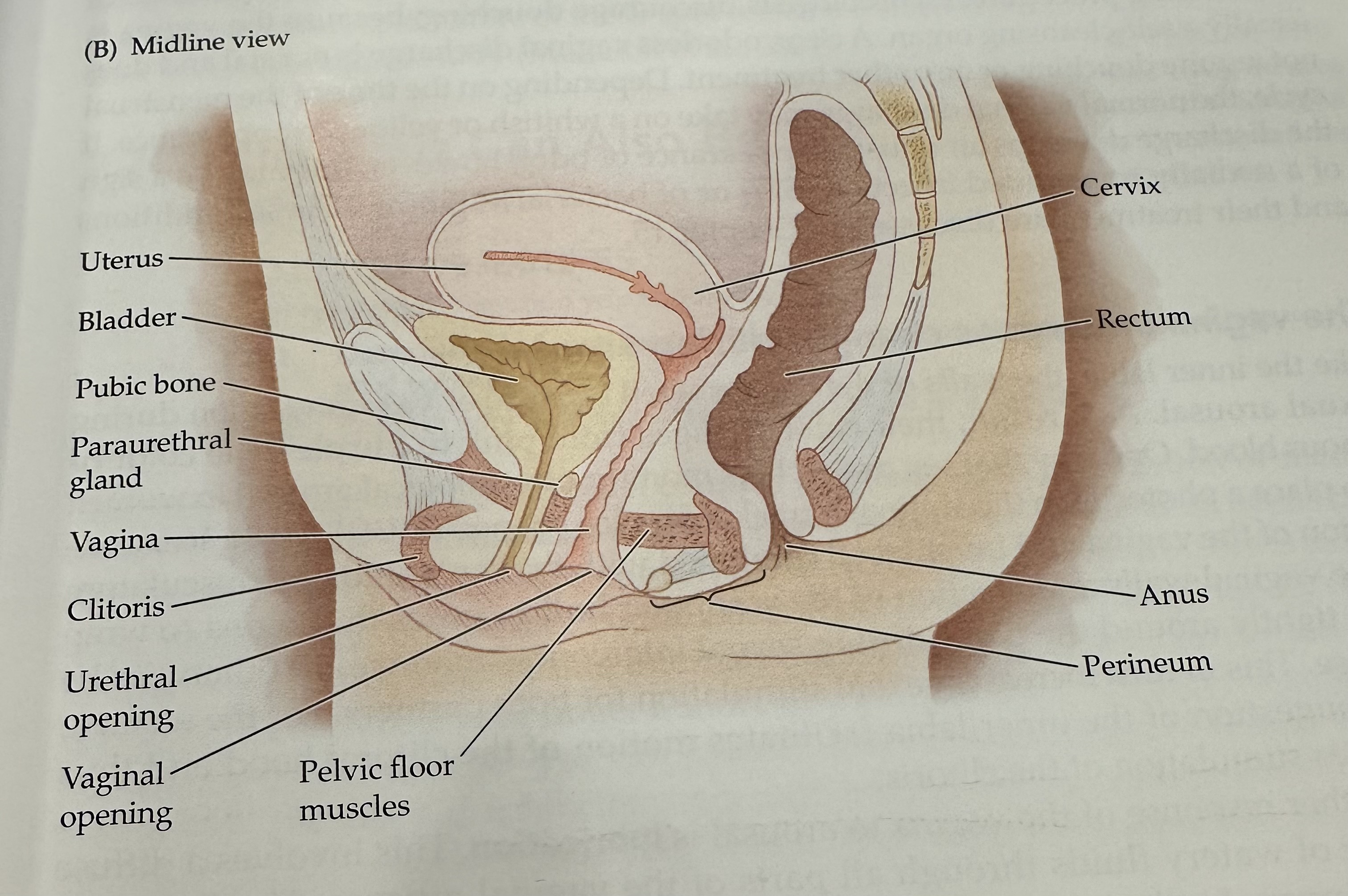
Bladder
A muscular sac in the pelvis that stores urine from the kidneys before it is expelled from the body.
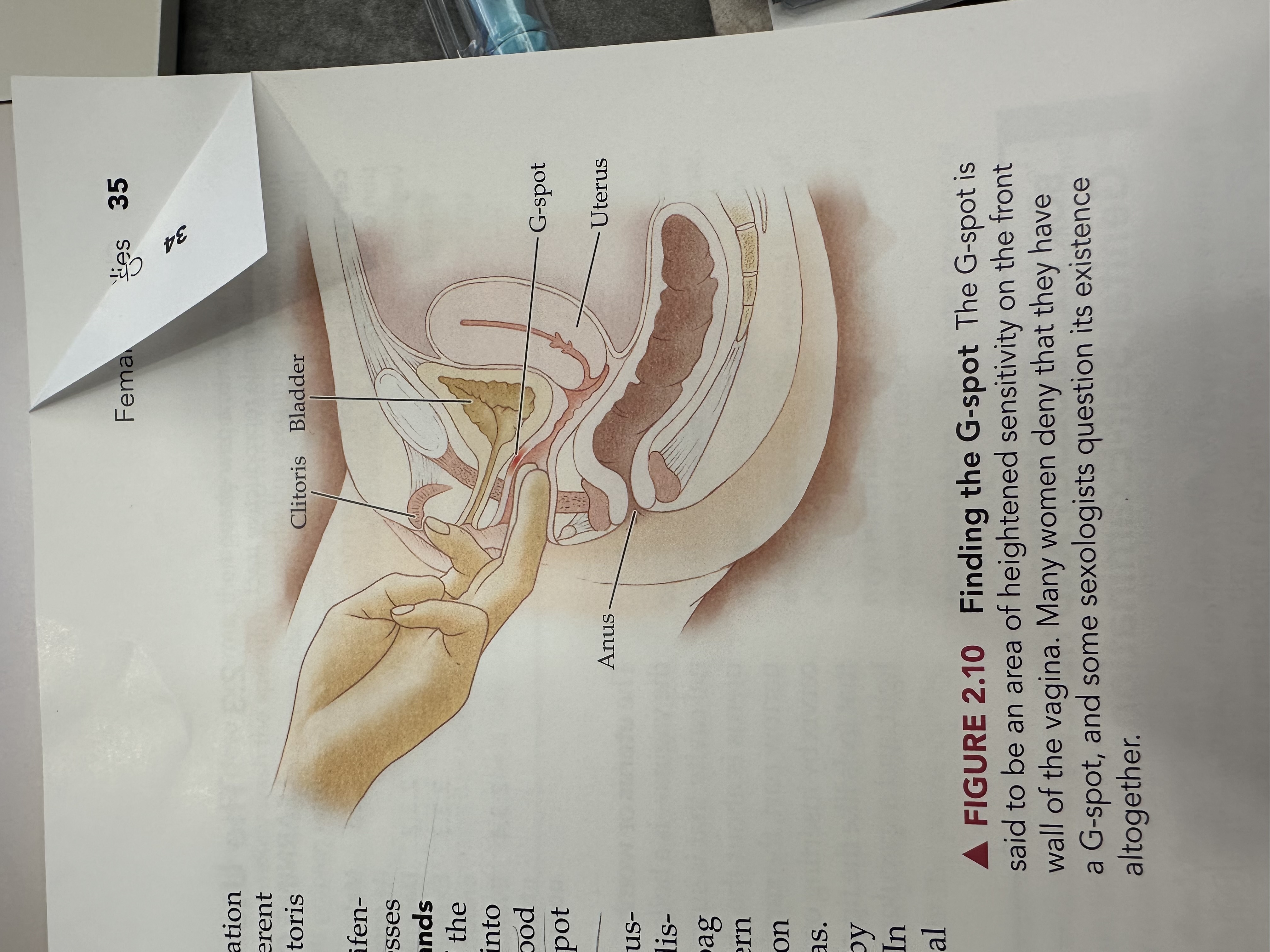
G Spot
An area located on the anterior wall of the vagina, often associated with heightened sexual arousal and orgasm when stimulated.
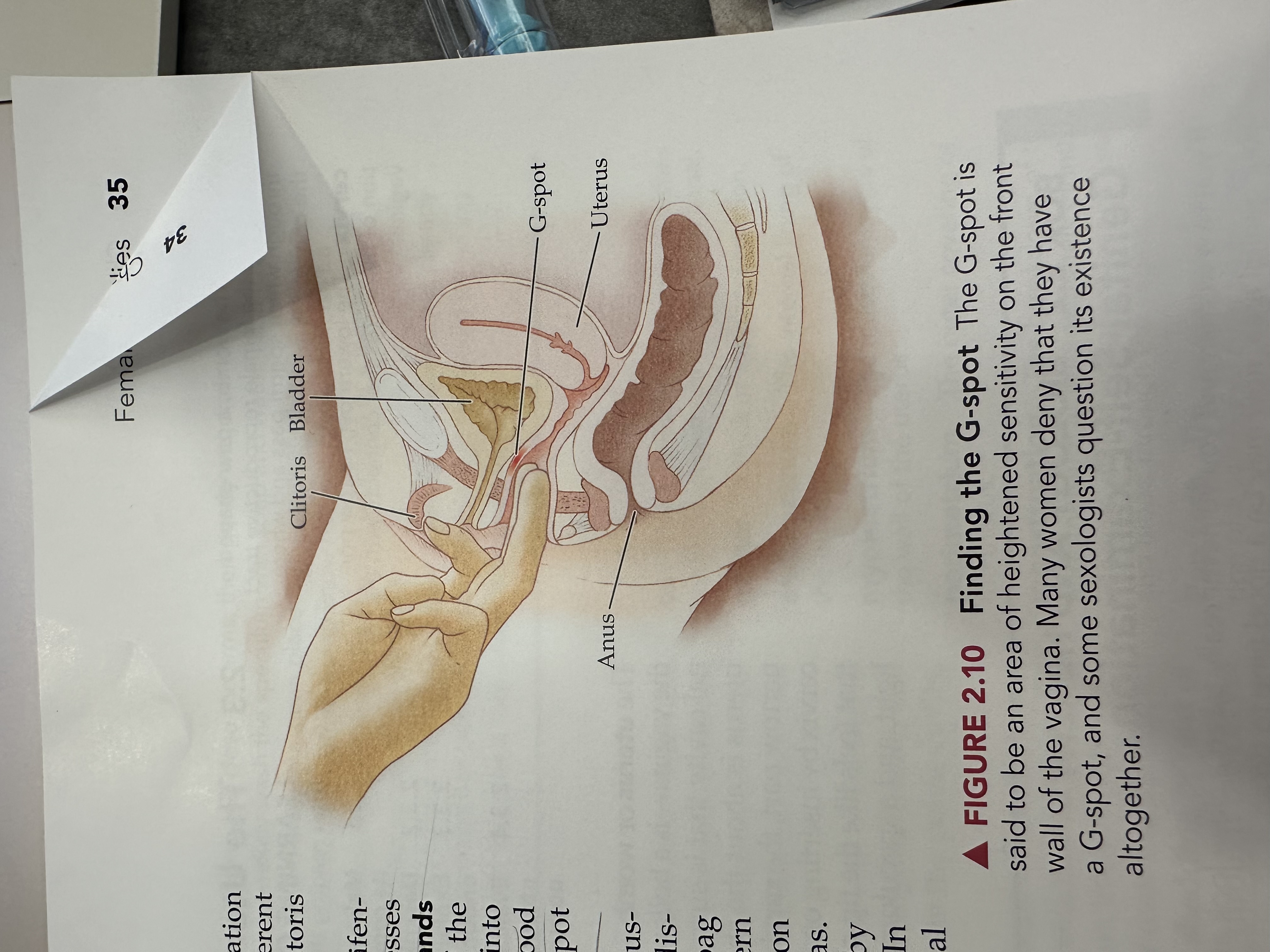
Clitoris
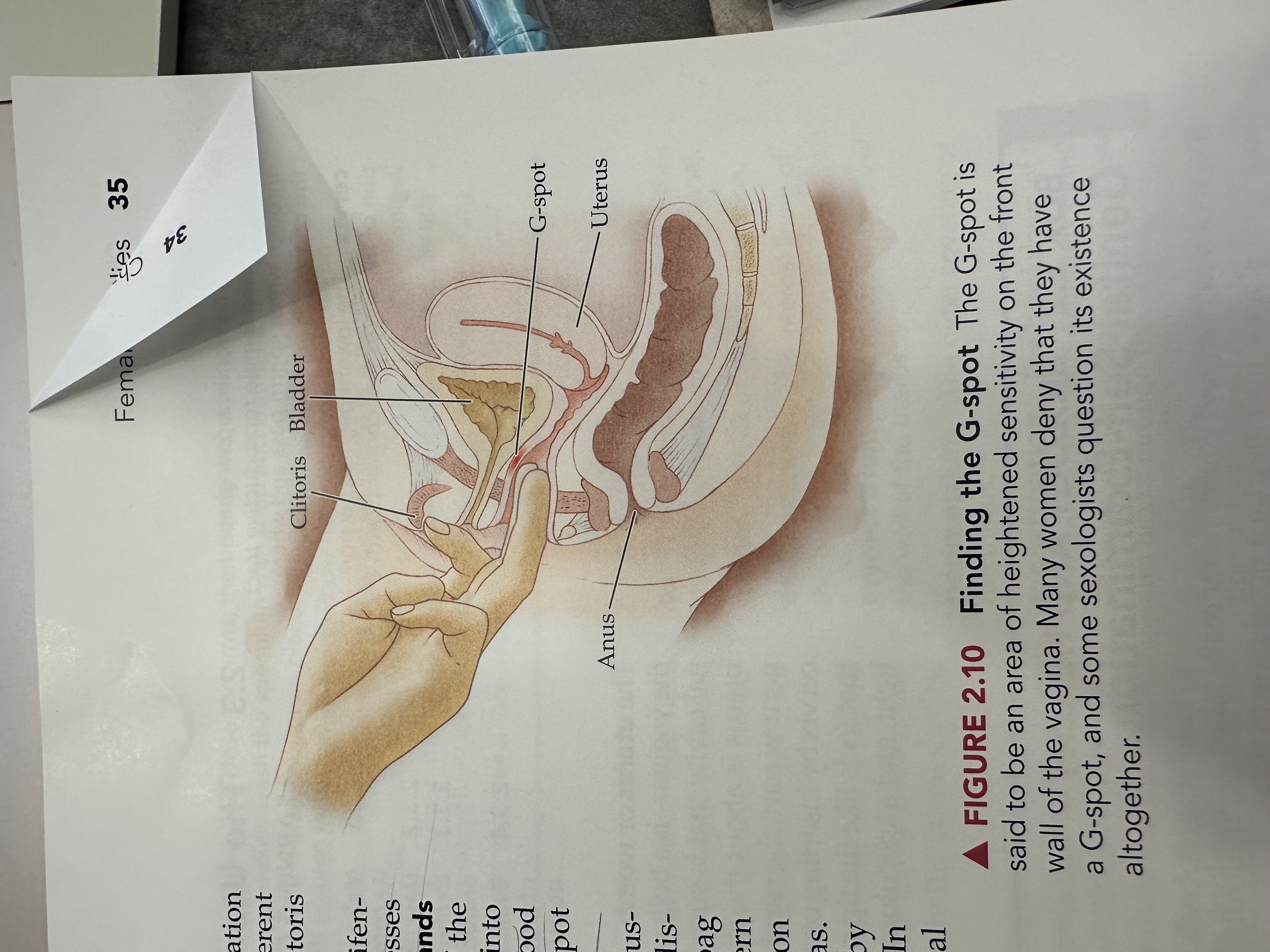
Bladder
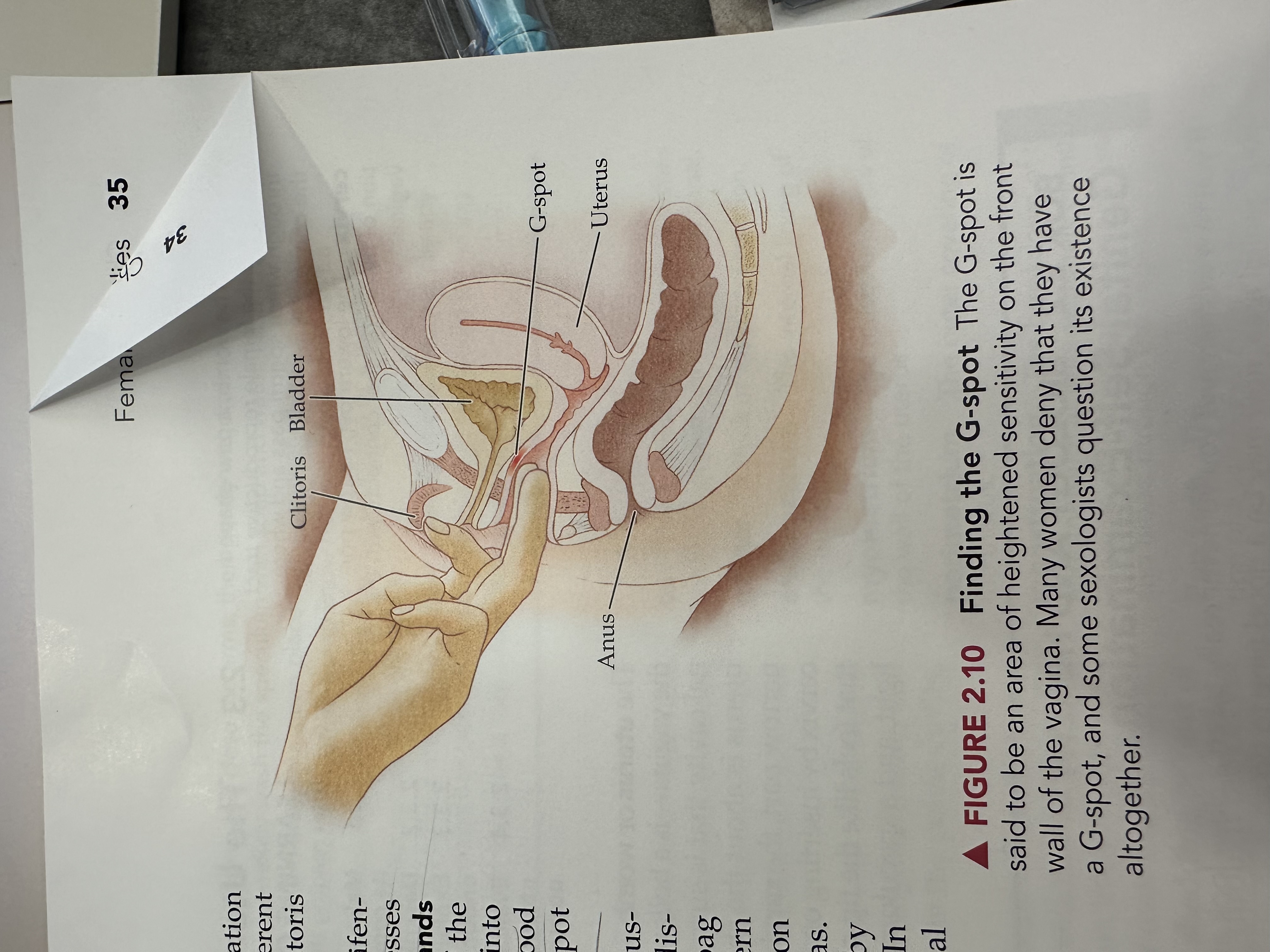
Uterus
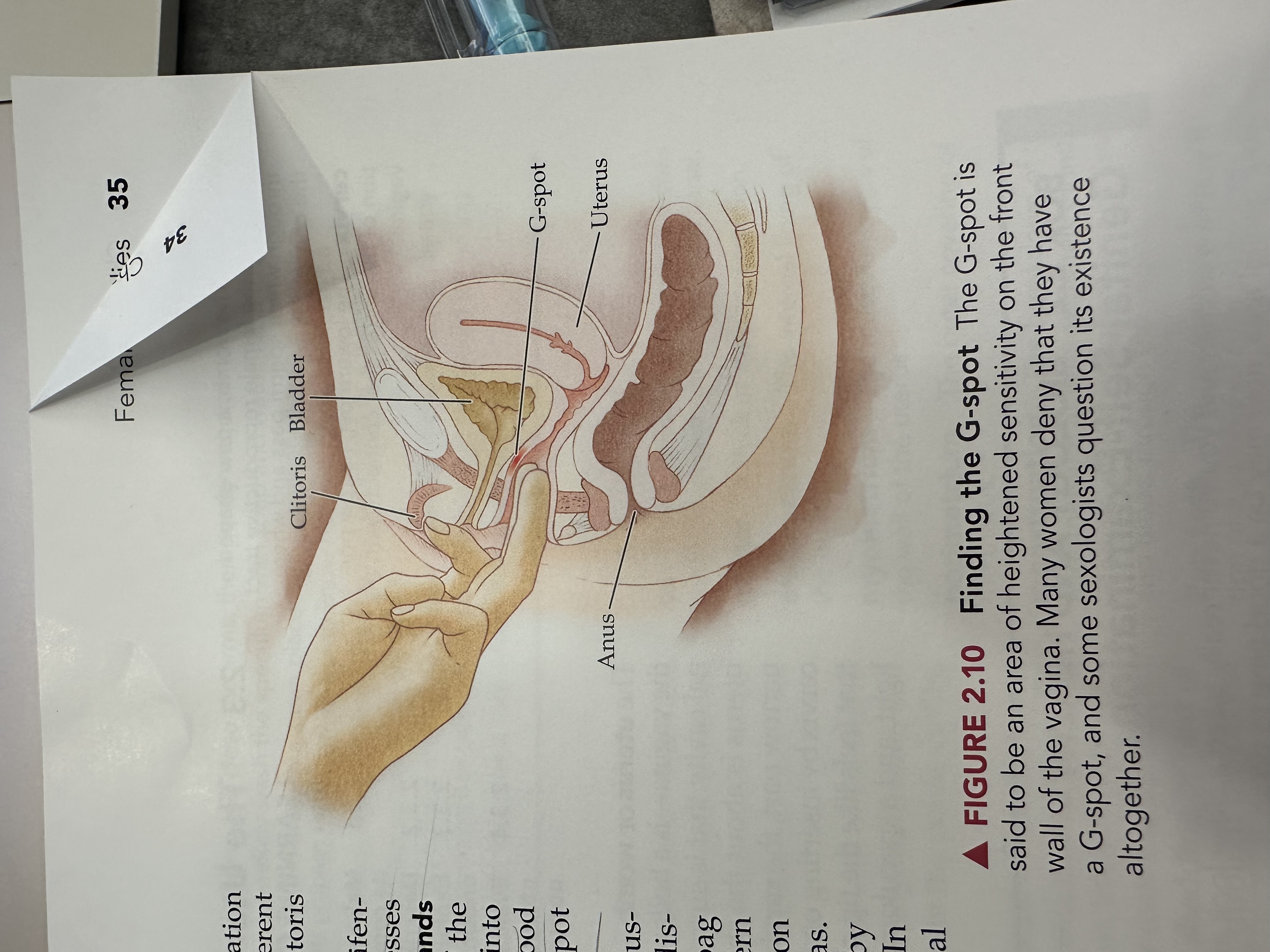
Anus
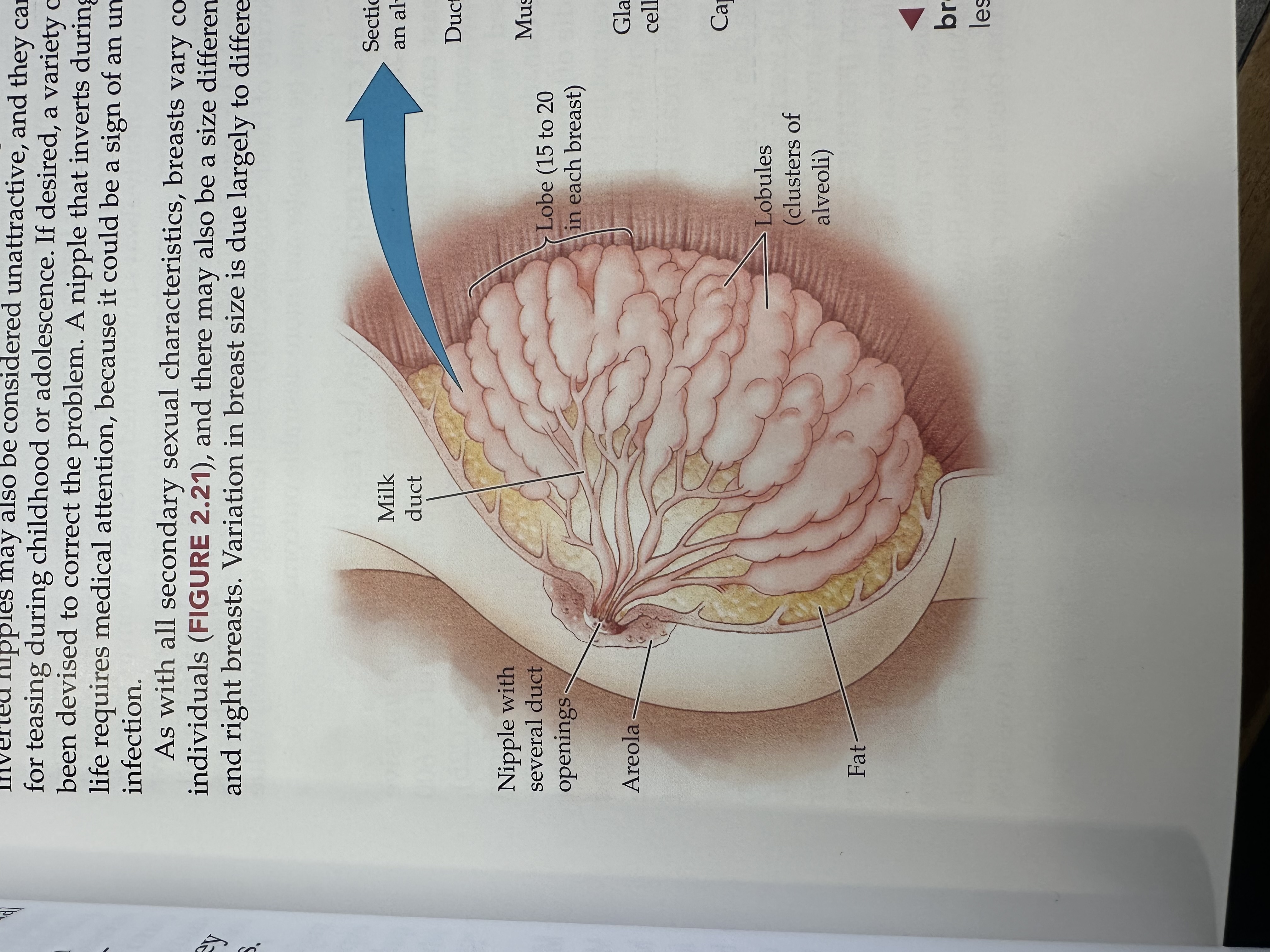
Milk duct
Tubes that carry milk from the lobules of the breast to the nipple.
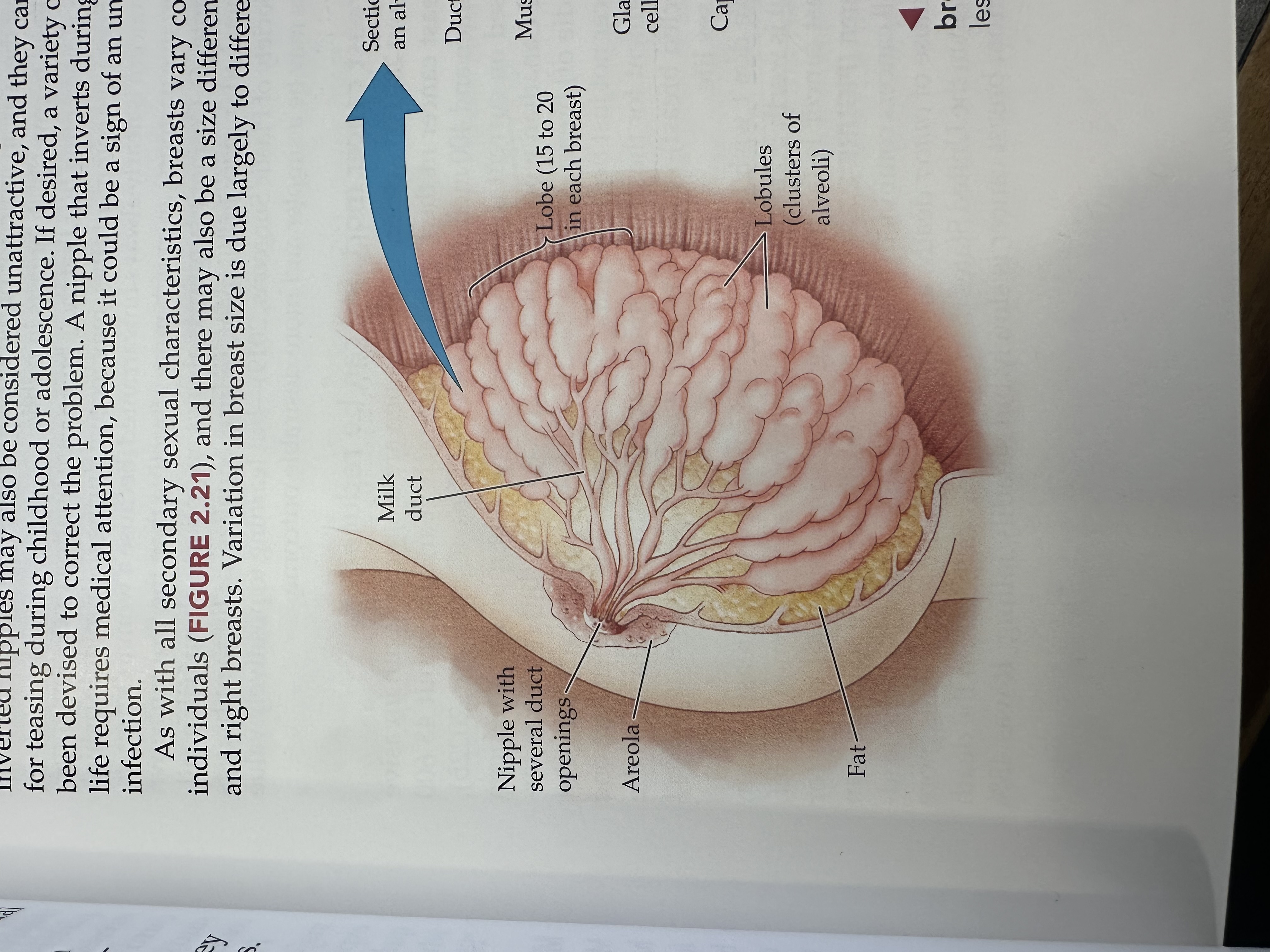
Nipple
The external structure of the breast that contains multiple duct openings, allowing for the passage of milk during breastfeeding.
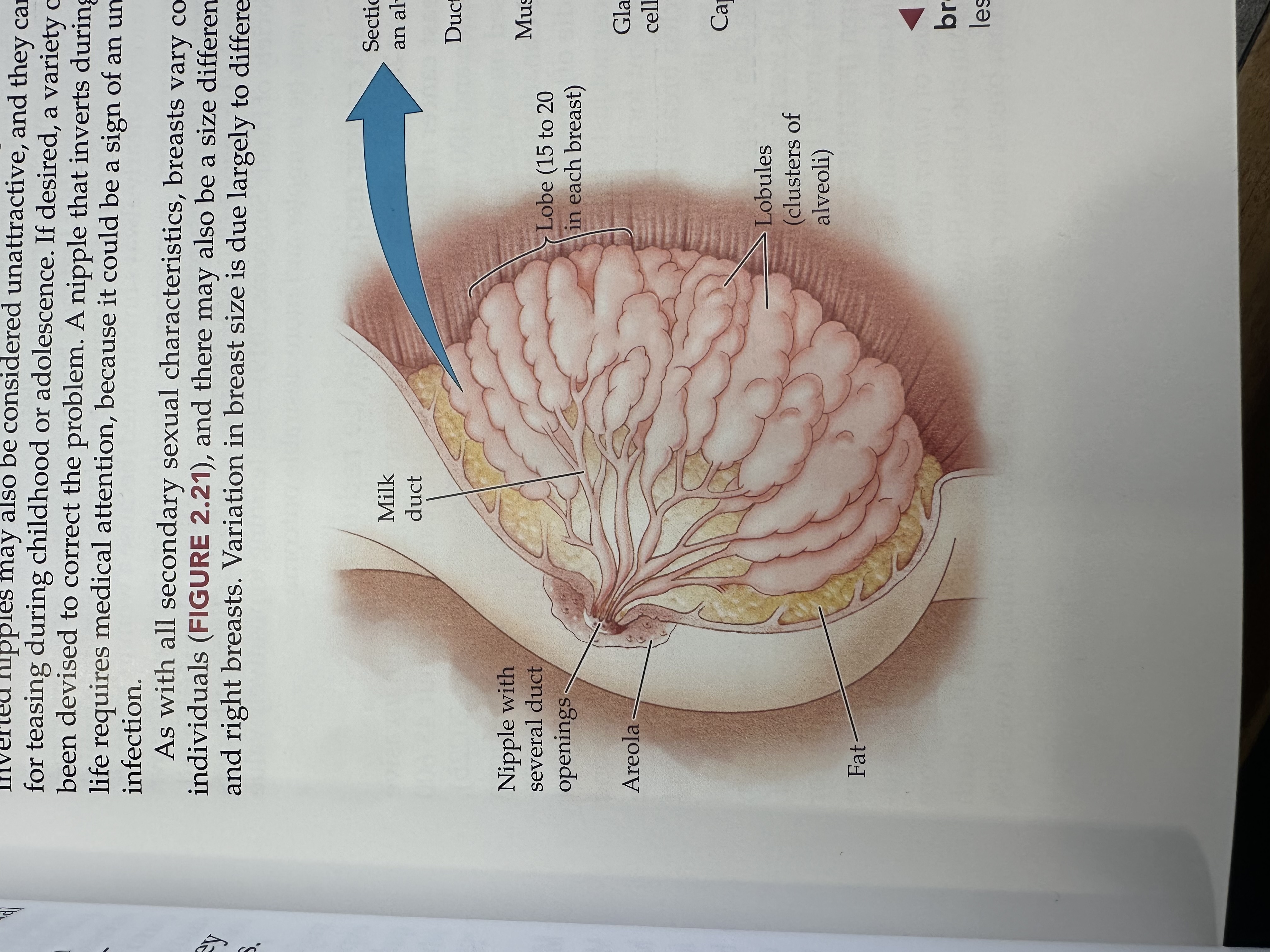
Areola
The pigmented area surrounding the nipple, containing glands that help lubricate the nipple during breastfeeding.
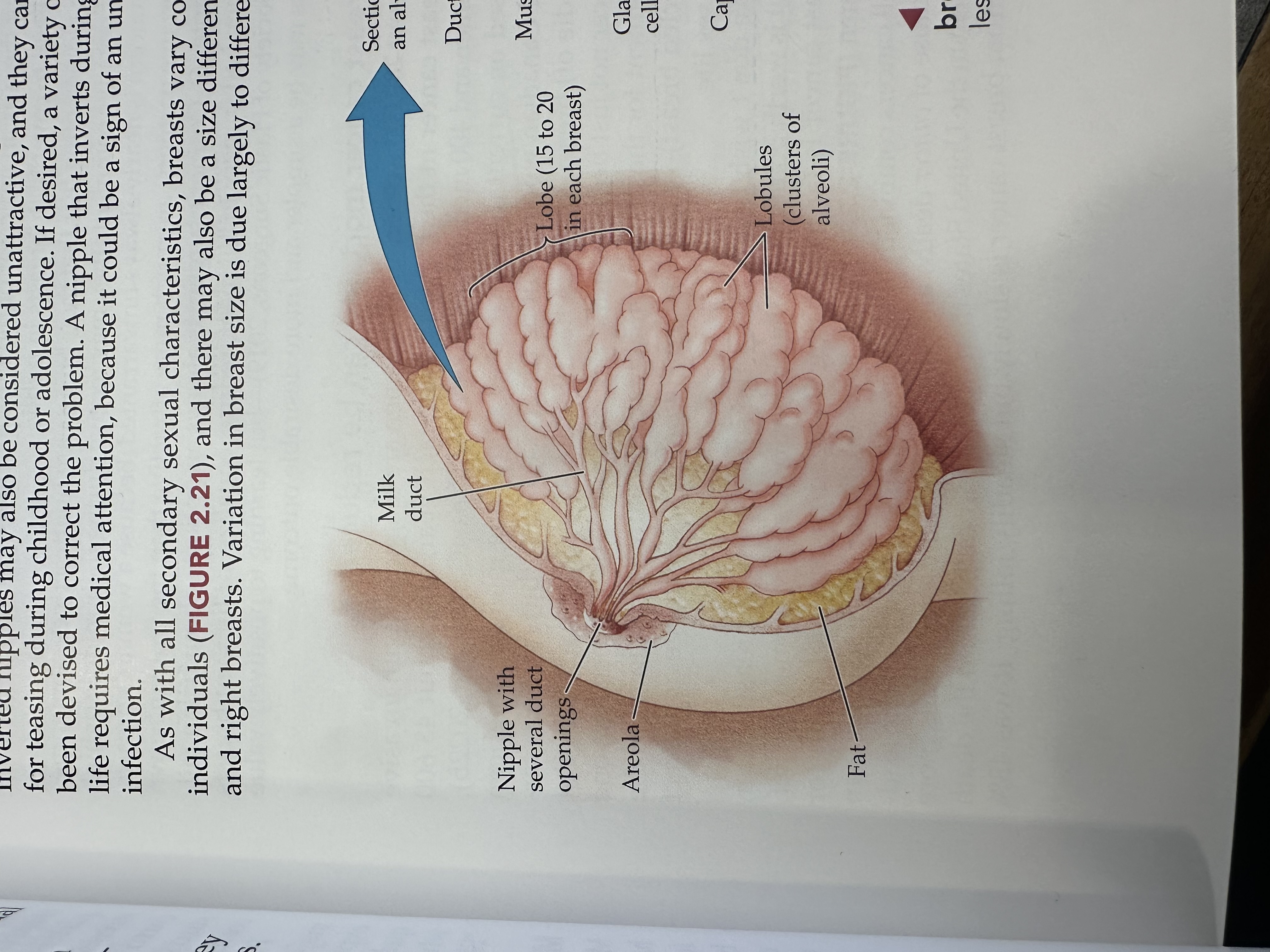
Lobe of the breast
The structural units of the breast, each containing lobules that produce milk and ducts that carry it to the nipple.
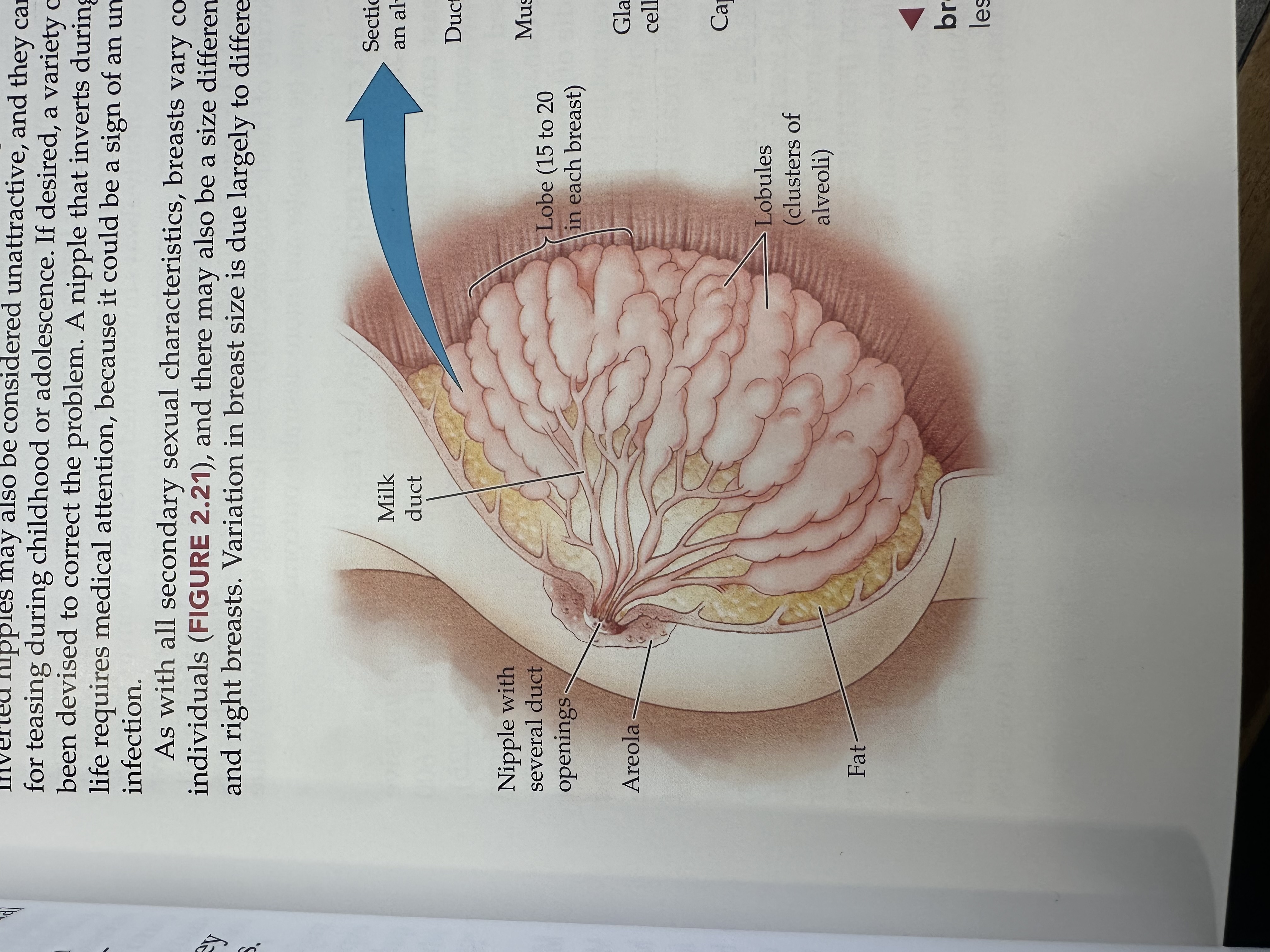
Lobules
Small spherical structures in the breast that produce milk and are connected to the milk ducts, allowing milk to flow to the nipple.
Duct of a Lobule
A small tube within the breast lobule that channels milk produced in the lobules to the milk ducts leading to the nipple.
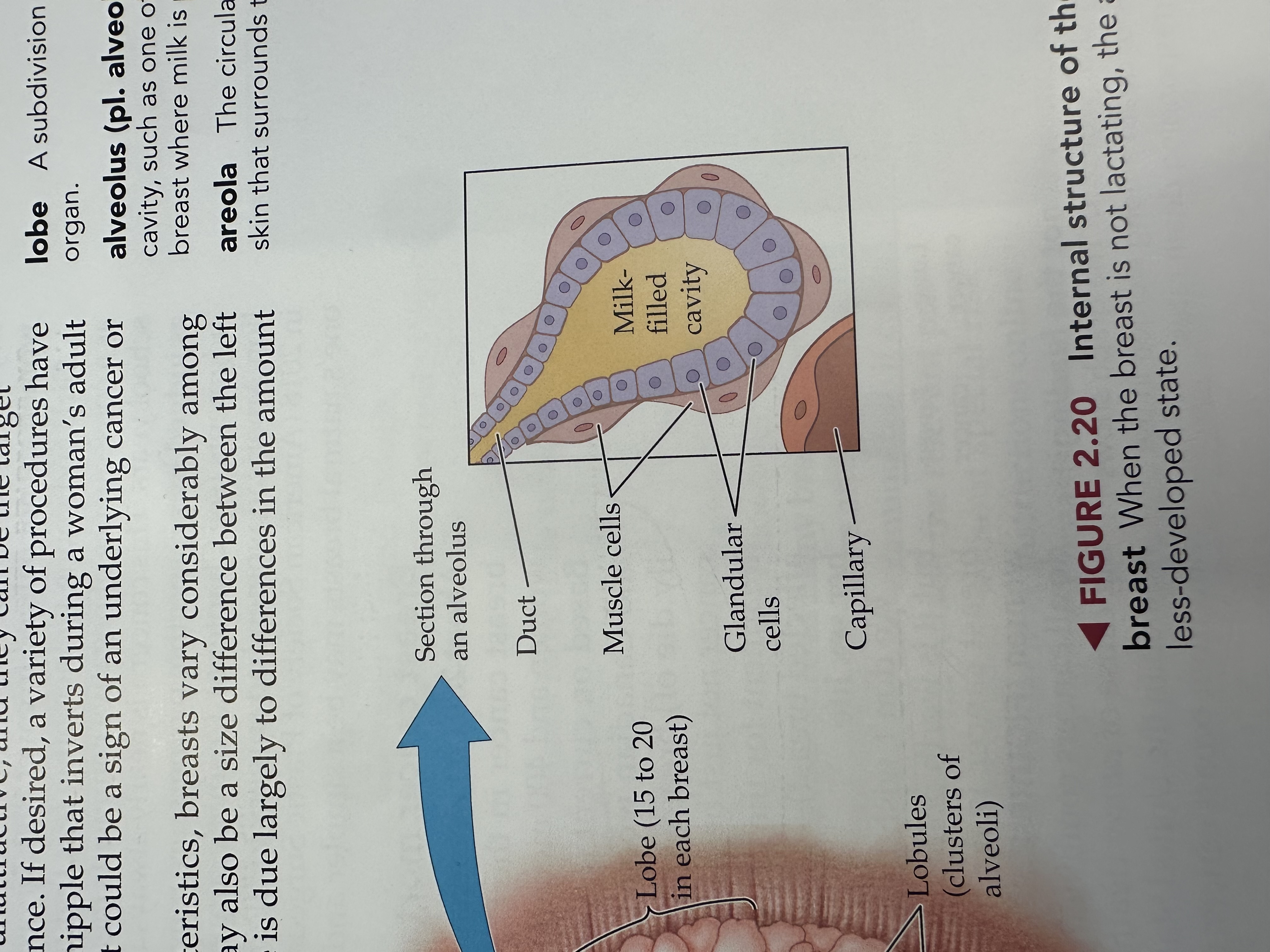
Muscle Cells of a Lobule
Specialized cells in the breast lobules that contract to help push milk into the ducts during breastfeeding.
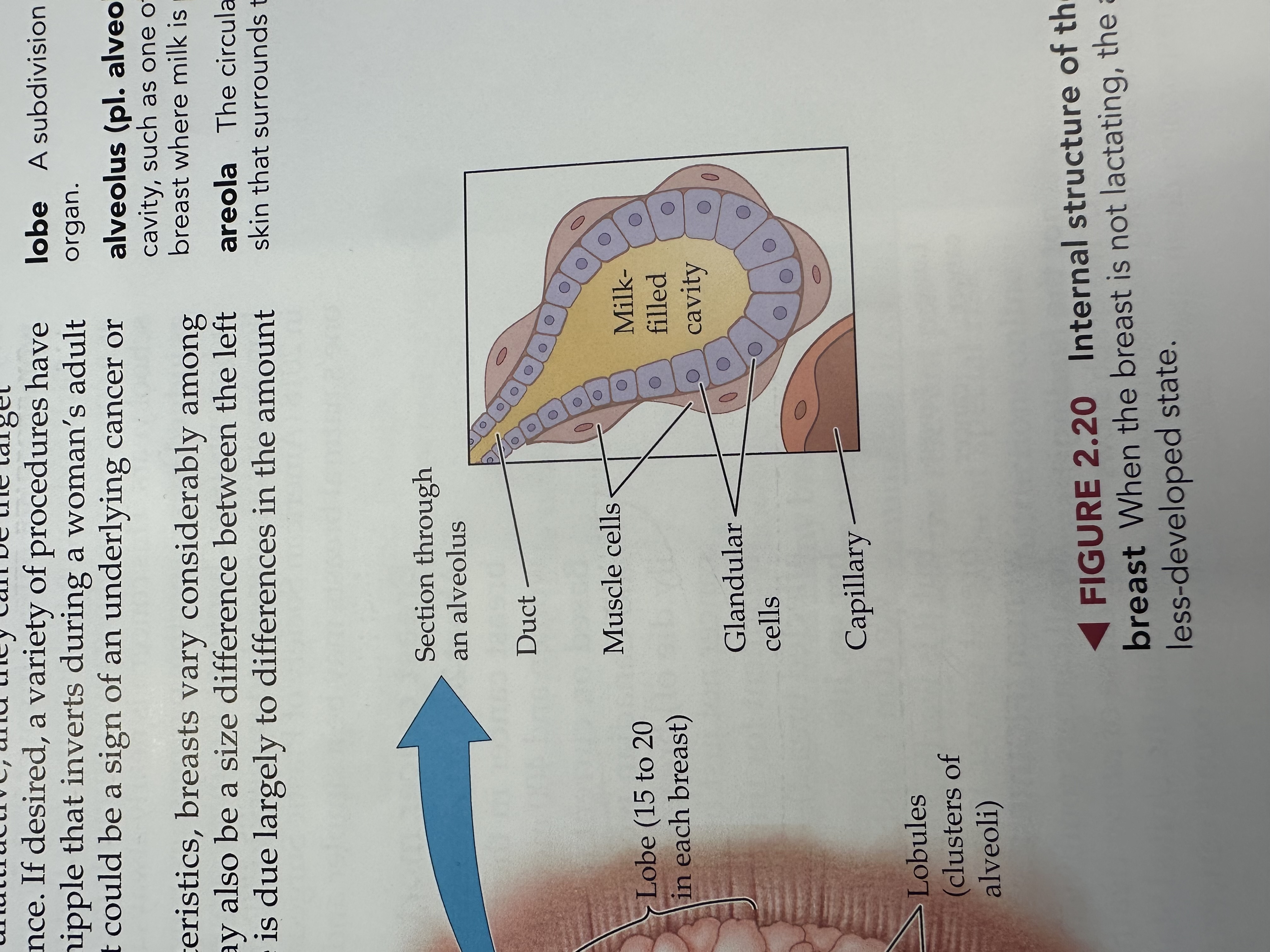
Glandular Cells
Cells in the breast lobules responsible for milk production, playing a key role in lactation.
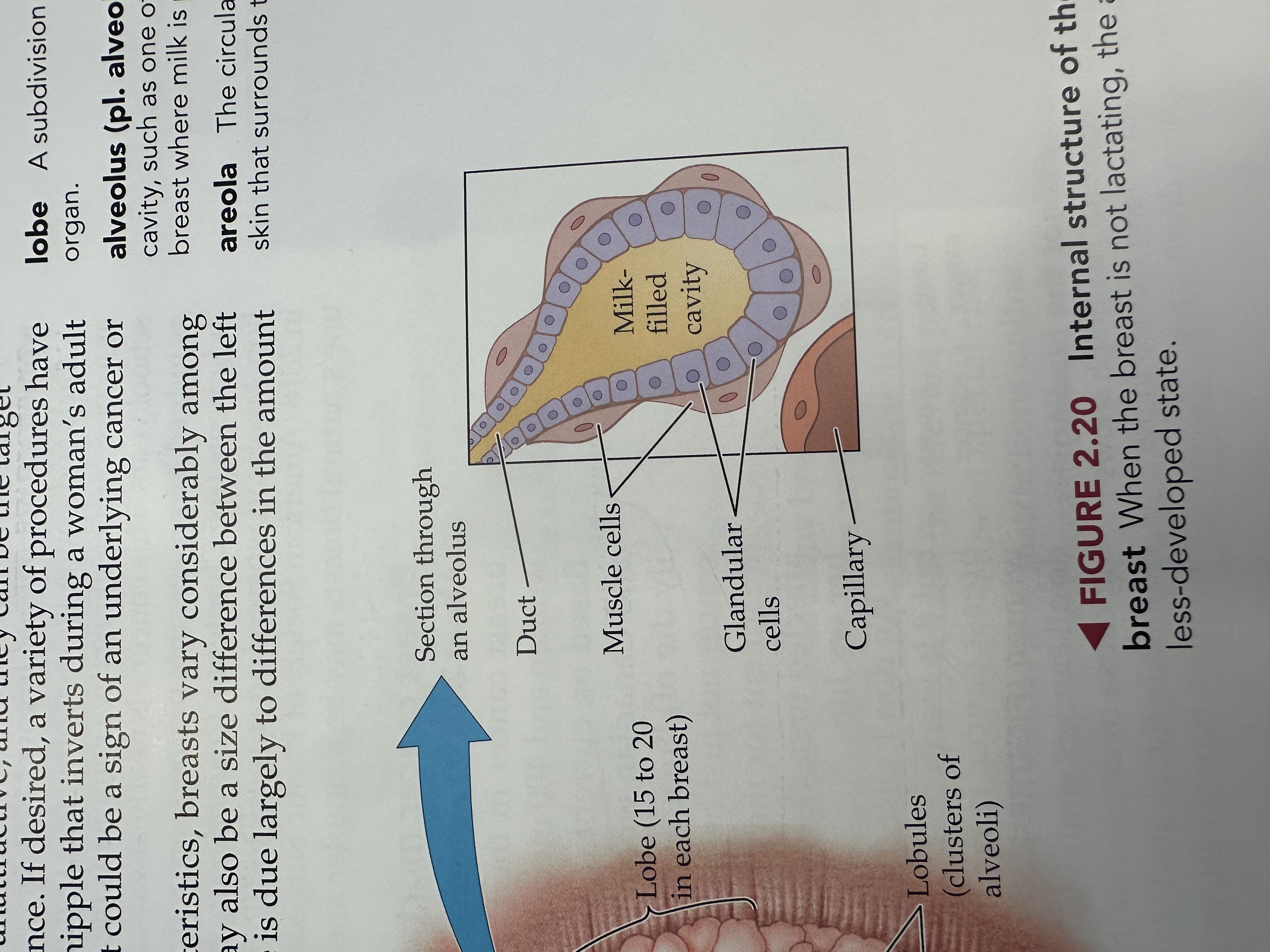
Capillary of the Lobule
Small blood vessels in the breast lobules that supply nutrients and oxygen to the glandular cells and facilitate the flow of milk.