The Humanistic Approach
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What does the humanistic approach believe?
Emphasises importance of individual experience rather than general laws
Free will - we decide our behaviour - we are affected by internal/external influences but we are active agents
Reject scientific model that establish general principles of human behaviour
What is Maslow’s hierarchy of needs?
To reach self-actualisation, we must meet basic needs and progress through the hierarchy
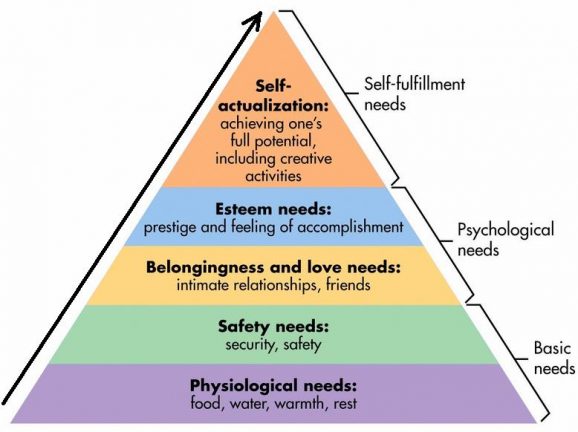
What is self-actualisation?
We have an innate desire to achieve our full potential — we need self-actualisation to do this
Human psychologists see personal growth as an essential part of being human
Can we all self-actualise?
Psychological barriers may stop someone from reaching their potential
How did Rogers believe personal growth can be achieve?
An individual’s concept of the self must be in congruence with their ideal self
What is a state of incongruence?
When there is a large gap between one’s concept of the self and ideal self and they have negative feelings of self-worth - will not be able to achieve self-actualisation
What is Rogerian therapy?
Client-centred
Effective therapists provide a warm, supportive and non-judgemental environment for the client
Improves client’s feelings of self-worth, reduce level of incongruence and helps them fully function
Why did Rogers create a new kind of therapy?
Many issues we experience as adults had roots in childhood and conditioned love - he wanted to provide unconditional positive regard for clients who didn’t have it as children
How did Rogerian therapy influence psychotherapy?
Led to development of counselling
Best applied to ‘mild’ psychological conditions
What are the strengths of the humanistic approach?
Not reductionist
Positive approach
What are the limitations of the humanistic approach?
Not scientific
Culturally-biased
Limited application
Why is rejecting reductionism a strength?
More validity than other approaches as it considers the whole person’s subjective experience
Other approaches reduce behaviour to certain things
How is a positive approach a strength?
Promotes positive image of the human condition (compared to psychodynamic approach that sees everyone as prisoners of the past, living between ‘common unhappiness and absolute despair’)
Sees all people as good, free to work towards achieving their full potential and control over their lives
How is the humanistic approach not being scientific a limit?
Few concepts can be broken down into a single variable and measured
Lacks empirical evidence to support its claims
How is the humanistic approach culturally biased?
Emphasises individual freedom and personal growth - associated with individualist cultures
In collectivist cultures, there is an emphasis on the needs of the group
In these cultures, the approach may not be important
Cannot be applied universally
How can the humanistic approach have limited application?
Critics argue it has little application as the approach is not a comprehensive theory, but an abstract set of ideas