resp/urinary anatomy exam
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
respiration
ventilation of the lungs (breathing) that is accomplished by the respiratory system, which rhythmically takes in air and expels it from the body
respiratory system functions
gas exchange: O2 and CO2 exchanged between blood and air
communication: speech, laughing, crying
olfaction: sense of smell
acid-base balance: influences pH of body fluids by eliminating CO2
BP regulation: by synthesis of angiotensin II
blood and lymph flow: breathing creates pressure gradients
platelet production: more than half of platelets are made by megakarocytes in lungs
expulsion of abdominal contents: breath-holding assists in urination, defecation, and childbirth
nose
functions to warm, cleanse, and humidify air; also detect odor
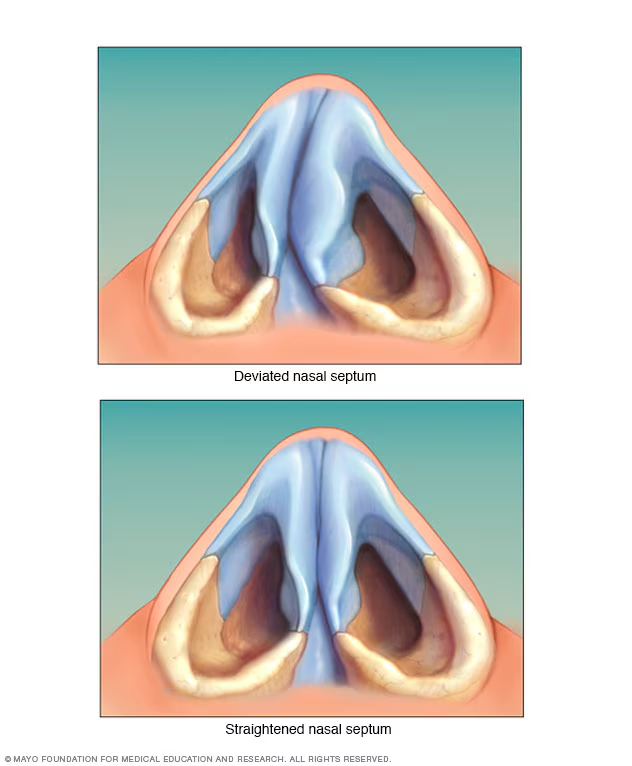
nasal septum
vertical wall that divides nasal cavity
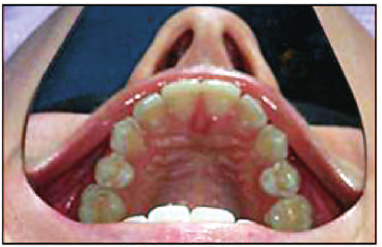
hard palate
forms floor and separates nasal cavity from oral cavity and allows you to breath while you chew food
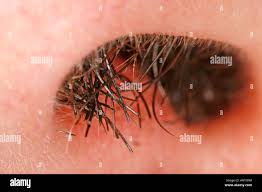
vibrissae
stiff guard hairs that block insects and debris from entering nose
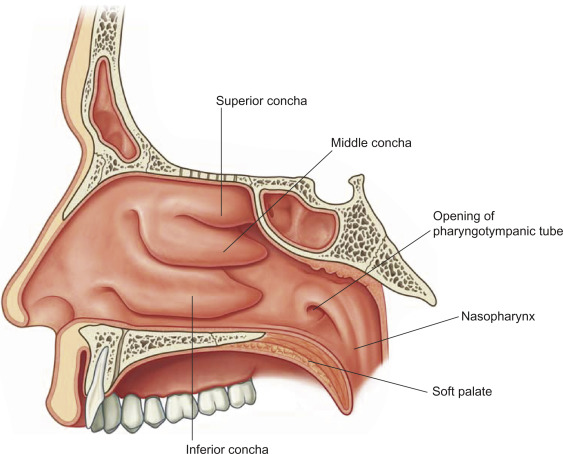
superior, middles, and inferior nasal conchae
project from lateral walls toward septum, creating a narrow chamber and subsequent air turbulence (ensures most air contacts mucous membranes to clean, warm, and moisten air)
respiratory epithelium
consists of:
ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium
nested in epithelial cells are goblet cells that produce mucous
mucous traps inhaled debris; mobile cilia propel debris-ridden mucous posteriorly toward pharynx where its swallowed or spit out
the pharynx
muscular funnel extending from oral/nasal cavity to the larynx
three pharynx regions
nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx
nasopharynx
superior to soft palate receives auditory tubes and contains pharyngeal tonsils
oropharynx
space between soft palate and epiglottis, and contains palatine tonsils
laryngopharynx
epiglottis to cricoid cartilage, where esophagus begins
larynx
cartillaginous chambers (4cm long)
responsible for phonation, aka voice box
guarded by epiglottis
primary function to keep food/drink out of airway
epiglottis
at rest stands almost vertically
during swallowing, extrinsic muscles pull larynx upward
tongue pushes ______ down to meet larynx
closes airway and directs food to esophagus behind it
3 large larynx cartilages
epiglottic cartilage: spoon-shapes supportive palate in epiglottis
thyroid cartilage: shield like w/ midline laryngeal prominence (adams apple)
cricoid cartilage: ring-like; connects larynx to trachea
3 small larynx cartilages
arytenoid cartilage - posterior to thyroid cartilage
comiculate cartilage: attatched to arytenoid cargilage like a pair of horns
cuneiform cartilages: sit atop arytenoids and support soft tissue between arytenoids and epiglottis
3 fibrous larynx ligaments
thyrohyoid ligament: suspends larynx from hyoid
cricothyroid ligament: susepends cricoid from thyroid cartilage
location of incision made in tracheotomy
cricotracheal ligament: suspends trachea from cricoid cartilage
collectively caleld the extrinsic laryngeal ligaments! bc they link larynx to other organs
superior vestibular folds
no role in speech
close larynx during swallowing
inferior vocal cords
produce sound when air passes between them
contains vocal ligaments
stratified squamous epithelium
glottis is the opening between the cords
how vocal cords produce sound
intrinsic laryngeal muscles control the vocal cords by pulling on the corniculate and arytenoid cartilages, causing them to pivot. when they pivot, they cause the vocal cords to adduct and abducts, when air passes through them they vibrate and produce sound
ADDUCT: high pitch, taunt
ABDUCT: low pitch, slack
the trachea
rigid tube, anterior to esophagus
16-20 c-shaped rings of hyaline cartilage
hyaline rings of trachea
act to reinforce trachea and prevent collapse during inhalation
opening in c rings faces posteriorly toward esophagus
allow esophagus to expand as food passes by
trachealis muscle spars opening in rings; contracts or relaxes to adjust airflow
the tracheal wall
lined by pseudostratified columnar epithelium
mucous-secreting goblet cells, ciliated cells, and stem cells
mucociliary escalator, a mechanism for debris removal
middle tracheal layer
ct beneath tracheal epithelium
contains lymphatic nodules, muscous and serous glands, and the tracheal cartilages
costal surface
pressed against ribs
mediastinal surface
faces medially; toward heart
right lung
3 lobes
inferior, middle, superior
horizontal and oblique fissure
left lung
2 lobes
superior and inferior
oblique fissure
cardiac impression
hilium
slit where lung recieves main bronchus, bv, lymphatics and nerves
bronchial tree
branching system of air tubes in each lung
right main bronchi
gives off three lobar bronchi
aspirated foreign objects lodge more in _______ than left, because its wider and more vertical
left main bronchi
gives off to lobar (secondary) bronchi
in both lungs, lobar bronchi divide into 8-10 segmental (tertiary) bronchi
histology of bronchial tree
epithelium - ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium
mucous glands and lymphocytes nodules act to intercept pathogens
elastic ct acts in recoil that expels air during expiration
bronchioles
continuations of airways that lack cartilage and have ciliated cuboidal epithelium
well-developed layer of smooth muscle
each one divides in to 50-80 terminal ______
terminal bronchioles
no muscous glands/goblet cells
have cilia that move muscous draining into them back by muscociliary escalator
gives off 2+ respiratory ______
these divide into 2-10 alveolar ducts
trachea, main bronchi, secondary bronchi, tertiary bronchi, smaller branches, bronchioles, terminal bronchioles, respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveoli
flow of air
squamous type 1
cell that is directly involved in gas exchange
great type 2
repair alveolar epithelium, secrete pulmonary surfactant, preventing collapse with exhalation
alveolar macrophage
dust cells that keep alveoli free from debris by phagocytizing dust particles
visceral pleura
forms lung inner surface
parietal pleura
adheres to mediastinum, inner surface of rib cage, and superior diaphragm
pleural cavity
potential space between plurae
pleura function
reduction of friction
creates pressure gradient between atmosphere and lungs
creates compartment that prevents spread of infection from one organ in mediastinum to other
respiratory muscles
change lung volume and create differences in pressure in relation to the atmosphere
diaphragm
prime mover of respiration accounts for 2/3 of airflow
internal and external intercostal muscles
synergists to diaphragm
ventral respiratory group
primary generator of the respiratory rhythm of 8-12 breaths per minute
dorsal respiratory group
modifies the basic respiratory rhythm after recieving info from chemo and stretch receptors
pontine respiratory group
recieves input from HBCs and sends input to both VRG and DRG, adapting breathing to special circumstances such as sleep, exercise, vocalization and emotional responses
intrapulmonary pressure
that within alveoli
intrapleural pressure
slightly negative pressure that exists between the out parietal and inner visceral pleural layers, within the pleural cavity, filled w/ pleural fluid
equal
at rest, the intrapulmonary pressures are ____, and there is no airflow
steps to inspiration
when the ribs swing upward and outward during inspiration, the parietal pleura follows them
the visceral pleura clings to it by the cohesion of water and it follows the parietal pleura
alveoli within the lungs are stretched
so, the entire lung expands along the thoracic cage
as lung increases in volume, its internal pressure drops below ambient atmospheric pressure, and air flows in
warming of inhaled air also contributes to expansion
two factors that determine airway resistance
diameter of bronchioles, pulmonary compliance
bronchodialation
increase in diameter
epinephrine and sympathetic stimulation increase airflow
bronchoconstriction
decrease in diameter
histamine, parasympathetic nerves, cold air, and chemical irritants decrease airflow
pulmonary compliance
ease of which the lungs can expand, reduced in diseases in which the lungs are stiffened by scar tissue
compliance is limited by the surface tension of the water film inside alveoli, increasing stickiness of alveolar walls too much
SOLUTION: pulmonary surfactant. it reduces surface tension and improves compliance
take home idea: PULMONARY COMPLIANCE IS PROPORTIONAL TO FLOW
anatomical dead space
the volume of air within the respiratory system's conducting airways (nose, mouth, trachea, bronchioles) that does not participate in gas exchange
spirometry
clinical measurement of pulmonary ventilation
partial pressure
if a contained is filled with more than one gas, each exerts its own pressure. that pressure is this
o2 transport
98.5% bound to hemoglobin
1.5% dissolved in plasma
when o2 bound to hemoglobin = oxyhemoglobin
when 100% saturated - 4 o2 - 1 hgb
75% - 3o2 - 1 hgb
co2 transport
90% is hydrated to form carbonic acid
5% bound to proteins
5% dissolved as gas in plasma
kidney functions
filter blood and excrete toxic metabolic wastes
reg blood volume, pressure, and osmolarity
reg electrolytes and acid-base balance
secrete EPO, which stims the prod of RBC
help reg ca+ lvls through calcitrol synthesis
clear hormones from blood
in starvation, they synthesize glucose from aa
metabolic waste
waste substances produced by the body
major sources:
50% urea
uric acid
creatine
BUN measures lvl of nitrogenous waste in blood
excretion
separating wastes from body fluids and eliminating them
respiratory
integumentary
digestive
urinary
kidney position, size, and shape
position: posterior abdominal wall T-12 to L3, right lower than left
size: bar of bath soap
shape: convex lateral surface; convex medial surface w/ hilium that gets bvs, lymphatics, and ureter
enclosed in fascia, fat and fibrous capsule
renal columns
extensions of cortex that project inward toward sinus
renal pyramids
6 to 10 conical structures with broad base facing cortex and renal papilla facing sinus
lobe of kidney
one pyramid and its overlying cortex
minor calyx
cup that nestles the papilla of each pyramid; collects its urine
major calyces
formed by convergence of 2 or 3 minor calyces
renal pelvis
formed by convergence of 2 or 3 major calyces
ureter
a tubular continuation of the pelvis that drains urine down to the urinary bladder
renal a, segmental a, interlobar a, arcuate a, interlobular (cortical radiate) a, afferent arterioles, glomerulus, efferent arteriola, pertitubular capillaries, interlobular v, arcuate v, interlobar, renal v
renal blood circulation (RSIAIAGEPIAIR)
vasa recta
in the medulla, the efferent arterioles give rise to this. its the capillary bed supplying the nephron loop
peritubular capillaries
branch off the efferent arterioles supplying the tissue near the glomerulus
nephron
functional unit of the kidney
two principal parts
renal corpuscle: filers blood plasma
renal tubule: converts filtrate to urine
renal corpuscle
glomerulus
glomerular capsule: encloses glomerulus
parietal outer layer: ss epithelium
visceral inner layer: podocytes
renal tubule
duct leading away from glomerular capsule
four regions
pct
nephron loop ayyyy *descending/ascending limb)
dct
glomerular capsule, pct, nephron loop, dct, collecting duct, papillary duct, minor calyx, major calyx, renal pelvis, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra
flow of fluid from the point where the glomerular filtrate is formed in the renal tubule to the point where it leaves body (GPNDCPMMRUUU)
renal plexus
nerves and ganglia wrapped around each renal artery
sympathetic stim —> reduces glom blood flow and urine prod
additional role to respond to falling bp by stim kidneys to secrete RENIN
four stages of urine conversion (from blood plasma)
glomerular filtration
tubular reabsorption
tubular secretion
water conservation
glomerular filtrate
the fluid in the capsular space; like blood plasma except it has no protein
tubular fluid
fluid from the pct through the dct; substances have been removed or added by tubular cells
urine
fluid that enters the collecting duct; undergoes little alteration beyond this point except for changes in water content
glomerular filtration (step 1)
process by which water/solutes in blood plasma pass from glomerular capillaries into capsular space of nephron
podocytes
spider-like blood capillaries that from the visceral layer of the glomerular capsule (has ARMS and FOOT PROCESSES, and FILTRATION SLITS dafuggg??? bro dis a monster)
filtration membrane three barriers
fenestrated epithelium of capillary pores
basement membrane
filtration slits of FOOT PROCESSES (aka monster)
three pressures through gfm
blood hydrostatic pressure
colloid osmotic pressure
capsular hydrostatic pressure
glomerular filtration rate
amount of filtrate produced
99% of filtrate is reabsorbed (wahhhh????)
gfr too high = dehydration/electrolyte depletion
too low = wastes are reabsorbed
chronic = kidney disease
gfr regulation
renal autoregulation
myogenic
tubuloglomerular
sympathetic
hormonal
renin
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone mechanism
drop in bp - baroreceptors alter symp ns
sympathetic fibers release renin —> results in angiotensin that raises bp
constriction of art bv stimulates aldosterone release, which increases nacl and h20 retention in nephron
tubular reabsorption and secretion (step 2)
occurs through pct to dct
tubular fluid is modified
OCCURS ALONG ENTIRE RENAL TUBULE
renal tubule extracts waste chemicals from blood and secretes them in
pct reabsorption
this reabsorbs 65% of glomerular filtrate
na+, glc, k+, cl-, h2o, urea, uric acid
na+ creates steep gradient that drives reabsorption
transcellular and paracellular
salinity gradient
generated by nephron loop
enables collecting duct to concentrate the urine and conserve water
needed bc tubular fluid is still dilute in dct
concurrent multiplier
feedback mechanism
this is how nephron loop maintains osmotic gradient
descending loop - h2o only, not nacl
ascending loop - na, k, cl only, not h2o
h2o conservation in collecting duct
collecting duct reabsorbs water which concentrates urine x4!! (crazy girl!)
tissue fluid osmolarity 4x higher in medullary cd than in cortex
medullary portion of cd more permeable to water than solutes
adh role
acts upon permeability of medullar collecting duct epithelial cells to water by upregulating aquaporins
dont drink water —> adh increase
drink lots —> adh decrease
normal urine volume
1-2 liters per day
polyuria
urine output in excess of 2L per day
body can’t maintain safe, low concentration of water in plasma
leads to AZOTEMIA - elevated nitrogenous waste in blood