Chem 1152 Lab Final
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
A polymer is _______________ made of ______________________, known as ________. Polymers can be natural, such as ________, or synthetic, such as ________.
a macromolecule;
many repeated subunits;
monomers;
proteins;
plastics
Match the definition to the type of polymer it describes.
1) A polymer formed as monomers link together without forming a byproduct.
2) A polymer formed as monomers link together, forming a small molecule as a byproduct.
1) Addition polymer
2) Condensation polymer
Identify the polymer based on each description.
1) A flexible polymer used in the manufacturing of grocery bags. The molecular structure is (C₂H₄)ₙ.
2) A polymer produced through a condensation reaction, with applications ranging from clothing to packaging.
3) A rigid, brittle polymer used in disposable food containers. The backbone of the polymer contains phenyl rings.
4) A rigid polymer used often in construction materials. The structure contains a halogen.
1) High-density polyethylene
2) Polyethylene terephthalate
3) Polystyrene
4) Polyvinyl chloride
Polypropylene is a polymer with a density of 0.89 g/mL.
Review the density table given and identify the expected observations if polypropylene is added to a beaker containing each liquid.
Liquid Density (g/mL)
water 1.00
methanol 0.79
ethanol 0.79
hexane 0.66
Select one or more:
- Polypropylene will float in methanol.
- Polypropylene will sink in ethanol.
- Polypropylene will float in hexane.
- Polypropylene will float in water.
- Polypropylene will sink in ethanol.
- Polypropylene will float in water.
In general, alcohols ________ when mixed with water because the _________ in alcohols can __________________ water.
dissolve;
O-H bonds;
hydrogen bond with
Which is NOT a good source of information about the hazards that affect waste disposal in a chemistry lab?
Your lab partner
When using organic chemicals, there are additional precautions and recommendations to work safely in lab.
Match each statement with the best corresponding lab practice or reason.
1) Do not use open flames, like Bunsen burners.
2) Rinse the glassware with organic solvents after the experiment.
3) Use glass containers, unless instructed to do otherwise.
4) Perform procedures in the fume hood, if possible.
1) Many organic chemicals are flammable.
2) Many organic chemicals do not dissolve in water.
3) Many organic chemicals dissolve plastics.
4) Many organic chemicals involve harmful vapors.
The synthesis of nylon requires solutions of 5% hexamethylenediamine and 5% adipoyl chloride. This polymer will form __________________________________. To remove the nylon, __________________________________.
in between layers of the solutions;
catch on the tip of a sharp object
In order to use a pipet, place a ____________ at the top of the pipet. Use this object to fill the pipet such that the ________ of the liquid is even with the volume line. Release the liquid, touching the tip of the pipet to the side of the container if necessary to release the last drop _______ the pipet tip.
bulb or pump;
meniscus;
outside
Identify effective techniques for accurate pipet use.
Select one or more:
- Do not let liquid enter the pipet bulb or pump.
- Leave any air bubbles in a pipet that occur after drawing up liquid.
- Use the pipet bulb to force the last drop out of the tip.
- Measure liquid by aligning the meniscus with the volume line.
- Do not let liquid enter the pipet bulb or pump.
- Measure liquid by aligning the meniscus with the volume line.
Match each titration term with its definition.
1) Process of slowly adding a solution to react with another solution and determine the concentration of one of the solutions based on the reaction between them
2) Glassware that allows a solution to be precisely and slowly added to another solution
3) Solution of known concentration that is slowly added to a solution of unknown concentration
4) A reagent added to the analyte solution that changes color when the reaction is complete
5) When the required amount of one solution has been added to the second solution to complete the reaction
6) Solution of an unknown concentration that has another solution slowly added to it
1) Titration
2) Buret
3) Titrant
4) Indicator
5) Endpoint
6) Analyte
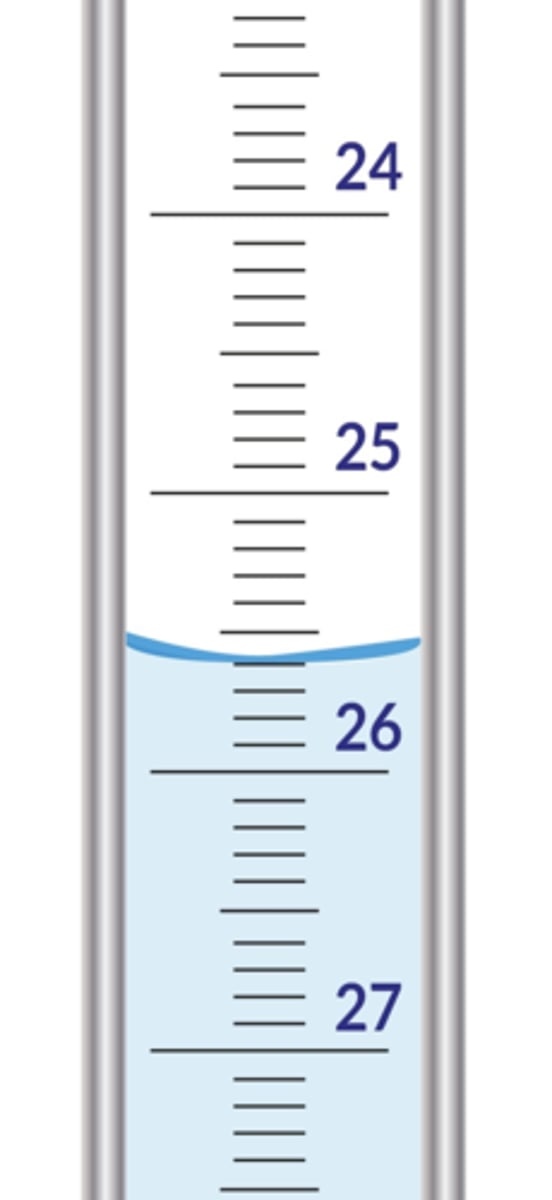
What is the correct reading of the volume in the pictured buret?
25.60 mL
Suppose you are performing a titration. At the beginning of the titration, you read the titrant volume as 2.71 mL. After running the titration and reaching the endpoint, you read the titrant volume as 23.43 mL.
What volume, in mL, of titrant was required for the titration?
20.72 mL
The titration of vitamin C with iodine proceeds according to the given equation.
C₆H₈O₆ + I₂ → C₆H₆O₆ + 2HI
In this reaction, vitamin C is ________ and iodine is _______.
oxidized;
reduced
The titration of vitamin C with iodine proceeds according to the given equation.
C₆H₈O₆ + I₂ → C₆H₆O₆ + 2HI
Suppose it takes 23.71 mL of 0.0053 M I₂ solution to reach the end point of the titration. How many moles of I₂ reacted?
.00013 moles of iodine
The titration of vitamin C with iodine proceeds according to the given equation.
C₆H₈O₆ + I₂ → C₆H₆O₆ + 2HI
Suppose it takes 14.92 mL of 0.0026 M I₂ solution to reach the end point of the titration. How many moles of vitamin C are present?
.000039 moles of vitamin C
Which functional group on the structure of p-aminophenol will react with acetic anhydride to produce acetaminophen?
amine
In a reaction, there are multiple ways to discuss the amount of compound produced. Identify the definition of each term related to the reaction yield.
1) The calculated amount of product under ideal conditions
2) The amount of product experimentally produced
3) The comparison of the experimental amount of product to the calculated amount
1) Theoretical yield
2) Actual yield
3) Percent yield
Fill in the words to complete the steps in the process of recrystallization.
1. Dissolve the substance in a _______ amount of hot solvent.
2. Allow the solvent to cool, precipitating the _________ while __________ remain in solution.
3. ______ the mixture to collect the pure substance.
minimal;
substance;
impurities;
filter
In order to dissolve a chemical sample in a recrystallization solvent, add the room-temperature solvent _______________________________ in an Erlenmeyer flask on a hot plate. Turn on the heat, starting at
______________________________________. Using a _____, add additional solvent from a second container on the heat source. Swirl the sample flask after each addition, and try to add
_____________________________ in order to dissolve the solid.
just until it covers the sample;
a low setting and increasing gradually;
pipet;
as little solvent as possible
If crystal growth does not start on its own after the solution in the flask returns to room temperature, identify the best ways to promote this process.
Select one or more:
- Scratch the bottom of the flask gently with a stirring rod.
- Place the flask on a hot plate to evaporate some solvent.
- Add ice cubes to the solution.
- Add a bit of solid as a seed crystal.
- Scratch the bottom of the flask gently with a stirring rod.
- Add a bit of solid as a seed crystal.
Why do you need to support a vacuum filtration apparatus with a clamp?
The filter funnel makes the apparatus top-heavy.
What are the reasons to determine the melting point of a sample in a melting point apparatus?
Select one or more:
- Identification of an unknown sample
- Removal of impurities from the sample
- Assessment of the sample's purity
- Conversion of the solid sample to liquid
- Identification of an unknown sample
- Assessment of the sample's purity
When performing a melting point determination, how should you report your findings?
As a range from the temperature when melting starts to the temperature when it ends
What elements make up a carbohydrate?
Select one or more:
- Hydrogen
- Nitrogen
- Carbon
- Oxygen
- Hydrogen
- Carbon
- Oxygen
Which substance is not a carbohydrate?
- Fiber
- Sugar
- Starch
- Lipid
- Lipid
Identify the type of sugar corresponding to each name.
1) Starch
2) Fructose
3) Sucrose
4) Glucose
5) Lactose
1) Polysaccharide
2) Monosaccharide
3) Disaccharide
4) Monosaccharide
5) Disaccharide
Fructose is an example of a ketohexose. The -hexose part of the name indicates that fructose is a ______________ that contains _ carbons.
The keto- part of the name indicates that fructose contains
________ functional group.
Fructose can combine with glucose to form sucrose. Therefore, sucrose is a ____________.
monosaccharide;
6;
a ketone;
disaccharide
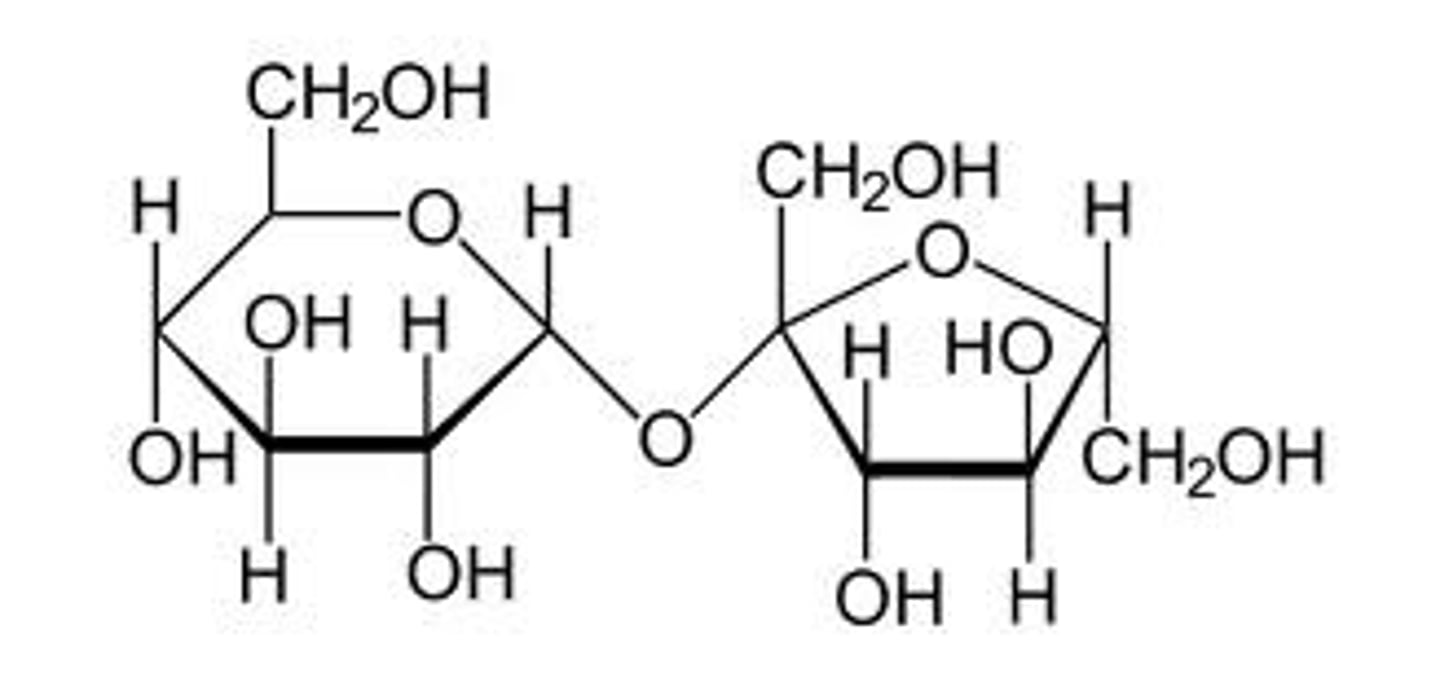
Consider the structure of the disaccharide, sucrose.
1) How many acetals are present in a sucrose molecule?
2) How many hemiacetals are present in a sucrose molecule?
1) 2
2) 0
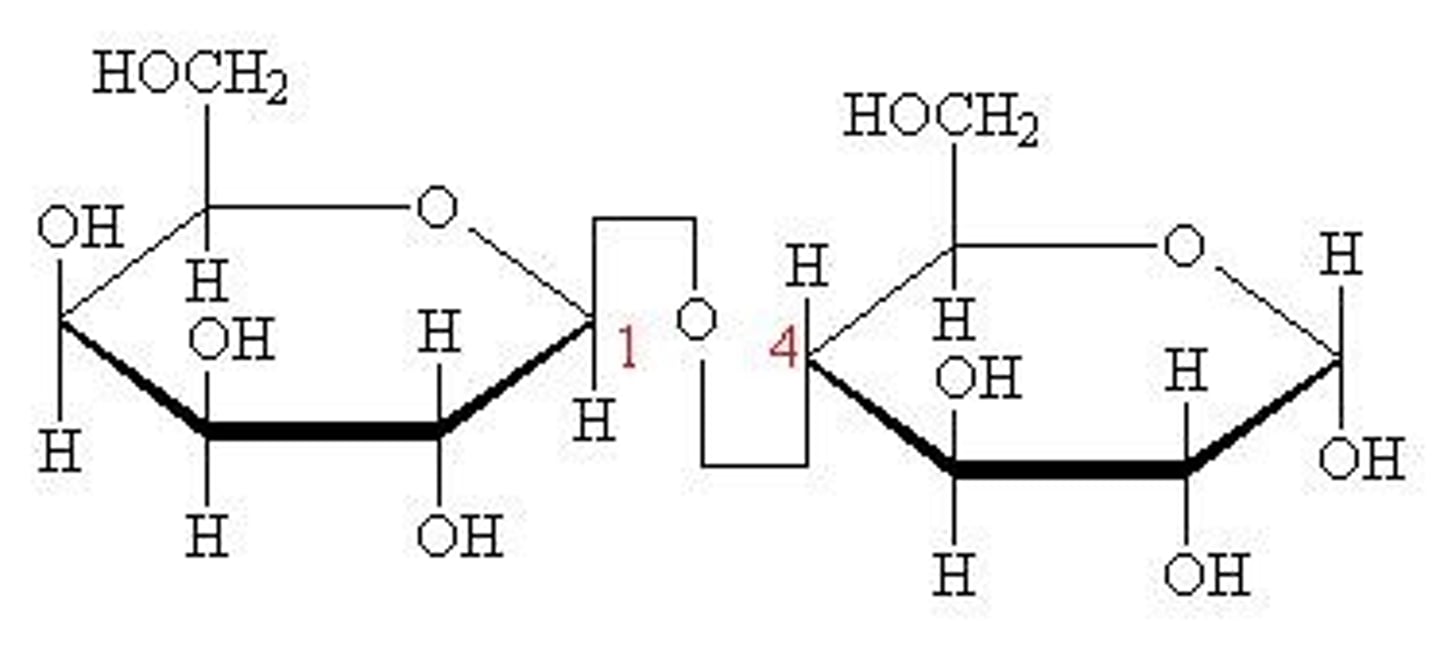
Consider also the structure of another disaccharide, lactose.
1) How many acetals are present in a lactose molecule?
2) How many hemiacetals are present in a lactose molecule?
1) 1
2) 1
Some carbohydrates are classified as reducing sugars due to their ability to reduce other reagents.
What features of a carbohydrate usually indicate that it is a reducing sugar?
Select one or more:
- The sugar is a disaccharide.
- There is a hemiacetal in the ring form.
- There is an aldehyde in the chain form.
- Only acetals are present in the sugar.
- There is a hemiacetal in the ring form
- There is an aldehyde in the chain form
An indicator is a substance added to a sample that has _________ change, such as a _____ change, in response to the ____________________ of the sample.
a visible;
color;
chemical composition
Multiple qualitative tests can be used to determine the properties of carbohydrate samples. Identify the test that provides the given information about carbohydrates.
1) Distinguish between ketoses and aldoses
2) Identify reducing sugars
3) Determine whether carbohydrates are present
4) Distinguish between monosaccharides and disaccharides
5) Distinguish between a pentose and a hexose
1) Seliwanoff's test
2) Benedict's test
3) Molisch test
4) Barfoed's test
5) Bial's test
Which metal is responsible for the color change in a Benedict's test?
Copper
Seliwanoff's test shows the presence of _______.
A positive Seliwanoff's test appears as ______________.
A negative Seliwanoff's test appears as _____________________.
ketoses;
a red solution;
a light pink solution
When testing the pH of a solution with pH or litmus paper, dip ______________ in the solution. Add a ____ of the solution to the paper. Compare the _____ of the pH paper to the scale that appears on the container.
a stirring rod;
drop;
color
Identify the term that applies to each definition.
1) A measurement of the amount of light taken in by a sample
2) A measurement of the amount of light that passes through a sample
3) A unit commonly used in spectrophotometry that is inversely proportional to energy and commonly measured in nanometers
4) A sample prepared using the solvent and any other chemicals in the sample solutions, but not the absorbing substance
5) A square-shaped container, typically made of quartz, designed to hold samples in a spectrophotometer
1) Absorbance
2) Transmittance
3) Wavelength
4) Blank
5) Cuvette
When heating liquids in a test tube, it is important that the test tube be positioned ___________, pointed _________ people, and _________.
at an angle;
away from;
half-full
What is a protease?
- An enzyme that breaks down a protein into individual amino acids
- A protein consisting of a chain of amino acids
- A component of foods such as fruit juices
Fill in the term to finish the description of each type of structural change of a protein.
1) When a protein is __________, the bonds between amino acids are cleaved and the protein is broken down into individual amino acids.
2) When a protein is _________, the protein loses its shape.
hydrolyzed;
denatured
For your data graph in the Proteases experiment, identify which variables will be plotted on each axis.
1) y-axis
2) x-axis
1) absorbance
2) time (sec)
The purpose of the best-fit line on an experimental scatterplot is to __________________________________________. The best-fit line allows us to ______________________________________________________.
identify any linear trend in scattered data;
predict behavior between measured data using its slope
Which of the following names identifies an enzyme?
dehydrogenase
Identify the enzyme terms described in each statement.
1) A compound that has a reaction an enzyme speeds up
2) A substance that limits or stops the activity of an enzyme
3) Specific arrangement maintained by intermolecular forces needed for an enzyme to work
4) A protein that is in no longer in the shape needed to function
1) Substrate
2) Inhibitor
3) Native structure
4) Denatured
Enzymes are biological catalysts that enhance the rate of a reaction by
decreasing the activation energy
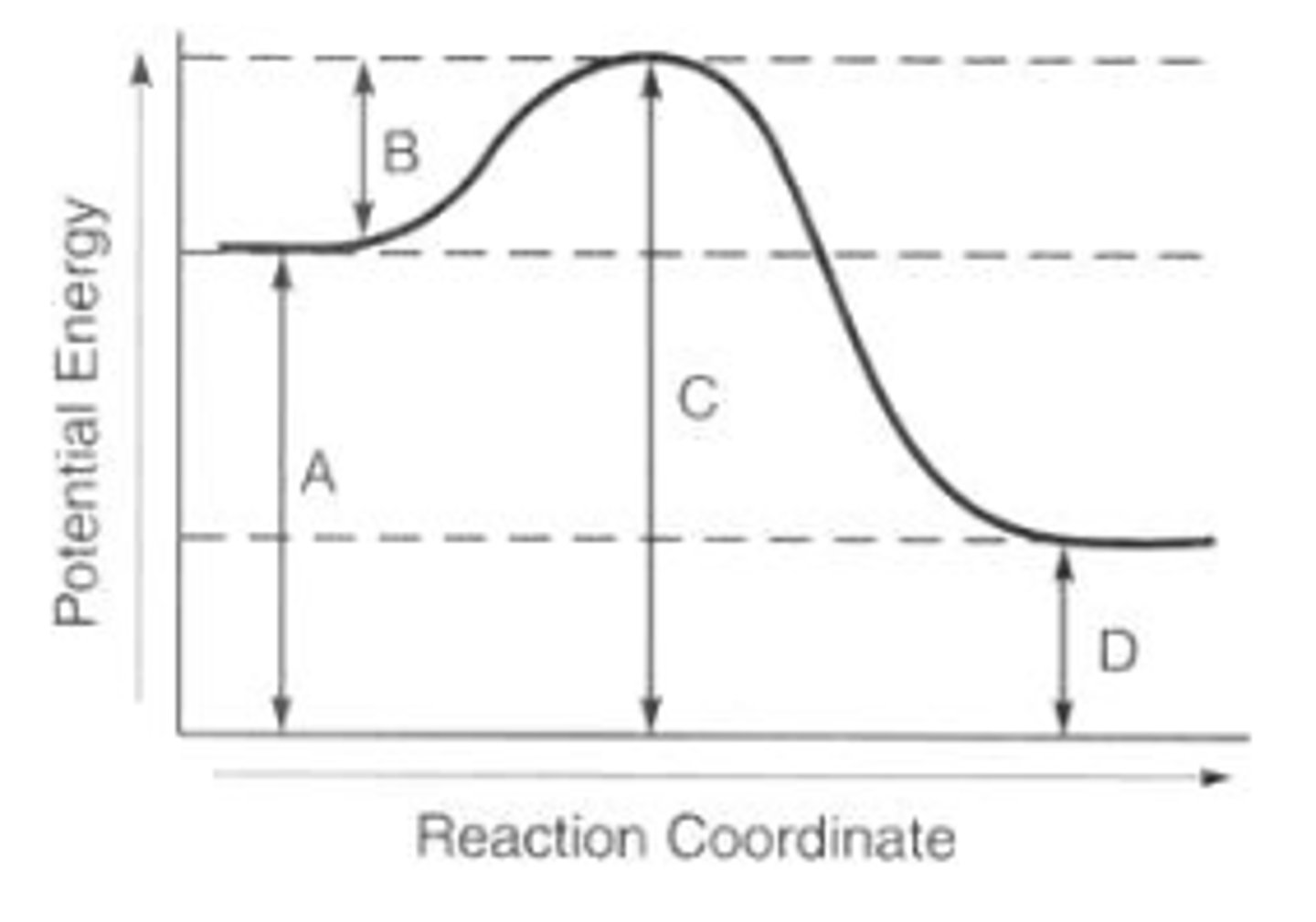
Consider the diagram of the potential energy over the course of a reaction. Which letter on the diagram represents the activated energy for the reaction?
B
What type of inhibition is occurring when the inhibitor may bind to either the enzyme or the enzyme-substrate complex?
noncompetitive
Identify the three types of reversible inhibitors.
1) A molecule that limits the effectiveness of the enzyme without binding to the active site.
2) A molecule that binds to the enzyme active site instead of the substrate.
3) A molecule that binds to the enzyme-substrate complex.
1) Noncompetitive
2) Competitive
3) Uncompetitive
Identify factors that impact the function of an enzyme.
Select one or more:
- Concentration of substrate
- pH
- Presence of inhibitor
- Temperature
- Concentration of enzyme
- Concentration of substrate
- pH
- Presence of inhibitor
- Temperature
- Concentration of enzyme
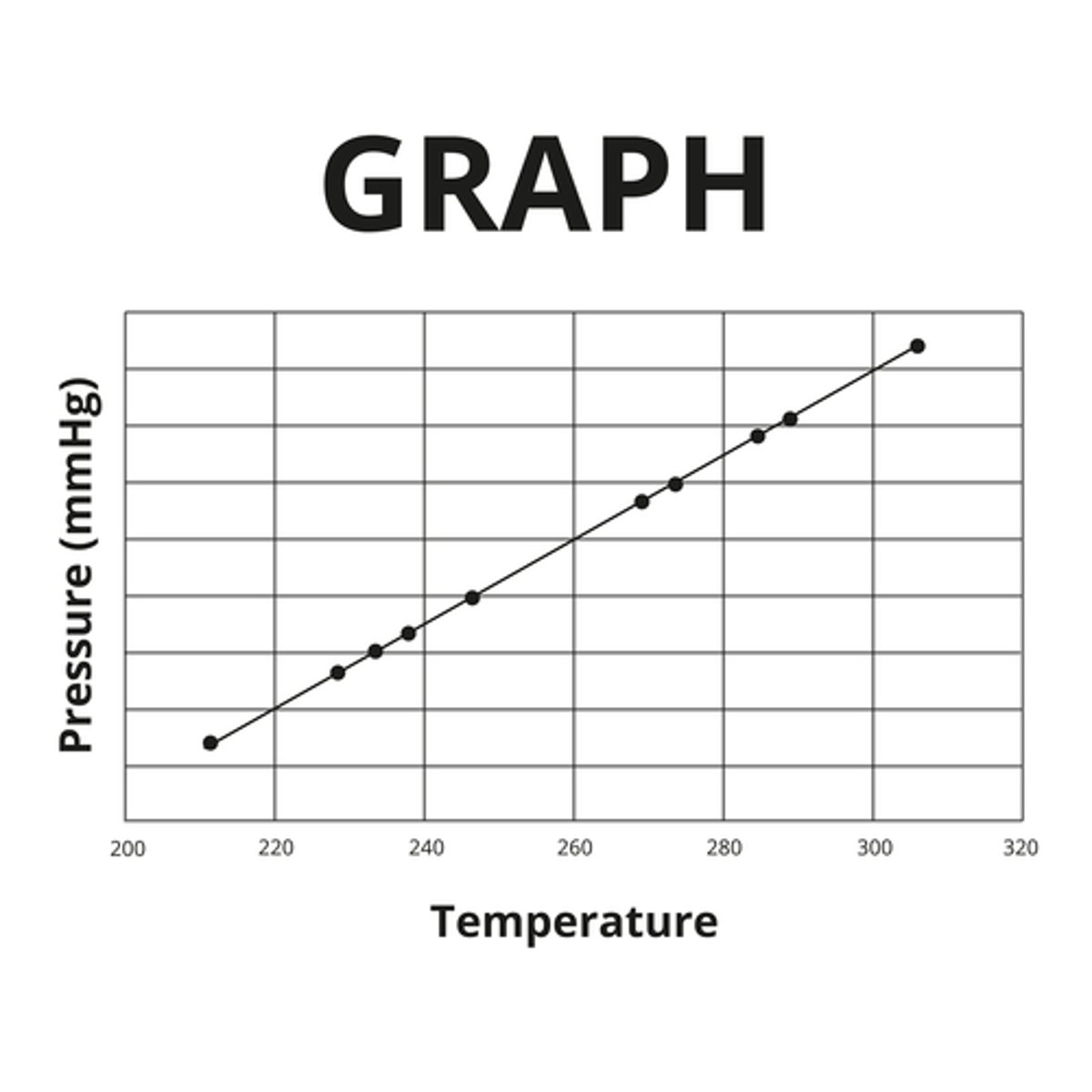
Identify the aspects of the pictured graph that are missing or contain errors.
Select one or more:
- x-axis numeric range
- Title
- y-axis numeric range
- x-axis label
- y-axis label
- Data points
- Title
- y-axis numeric range
- x-axis label
Fill in the palindromic sequence of the given DNA strand containing six bases.
5' GACGTC 3'
3' CTGCAG 5'
What effect do restriction enzymes have on DNA?
Restriction enzymes cleave DNA at specific sequences into fragments.
Which statement concerning the effectiveness of enzymes is NOT true?
- Enzymes are affected by salt concentration.
- The effectiveness of an enzyme is likely to vary over a range of temperatures.
- An enzyme may not function outside a certain pH range.
- Although the actions of different enzymes may vary, the effectiveness of each particular enzyme is constant.
- Although the actions of different enzymes may vary, the effectiveness of each particular enzyme is constant.
Gel electrophoresis is a method used to separate fragments of biomolecules such as ___. After loading a sample onto a gel, a _______ is applied. The sample is separated as the fragments _____________________.
DNA;
current;
travel across the gel
After an electrophoresis experiment, how are the lengths of the DNA fragments in each lane determined?
Comparing to a standard DNA ladder in one lane
What property is used to separate DNA fragments during a gel electrophoresis experiment?
size