PSYC 132: Chapter 12
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Learning and Memory
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Learning
An adaptive change in behavior that results from experience
Associative learning (AKA conditioning)
Association between two stimuli is established
Affected by hormones
Nonassociative learning
Change in the strength of response to a stimulus after repeated exposures
Affected by hormones
Associative Learning: Types
Classical
e.g. Pavlov’s dog
More reflexive behavior
Operant
Punishment/reward
Appetitive
Reinforcement via a positive outcome
Avoidance/aversive
Change in behavior to avoid a noxious outcome
Active avoidance
Individual must perform an action to avoid noxious situation
* Negative reinforcement: Taking an Advil to get rid of an advil
Passive avoidance
Individual must suppress some behavior that would otherwise be exhibited
Nonassociative Learning: Types
Sensitization
Progressive amplification of a response after repeated administrations of a stimulus
Increase of NT release
Habituation
Decrease in response after repeated exposures
Decrease in NT release
Memory
The encoding, storage, and retrieval of information about past experience
Sensory memory
Immediate (e.g. echoic memory)
Short-term memory (spatial and nonspatial)
Long-term memory (spatial and nonspatial)
Working memory
Part of short-term memory involved with immediate conscious perceptual and linguistic processing
Long-Term Memory
Can be divided
Declarative (AKA Explicit)
Memory for facts or events
Procedural (AKA Implicit)
Memory that stores long-term information about how to perform procedures
e.g. walking, swimming, how to ride a bike
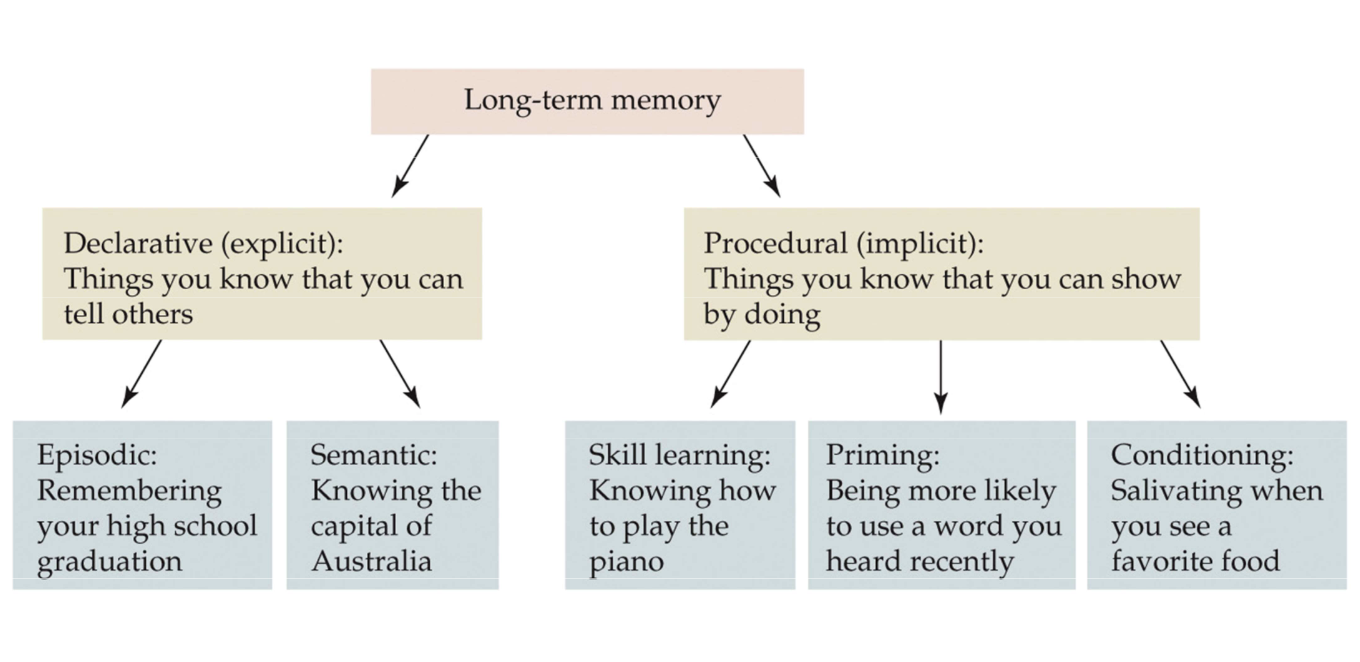
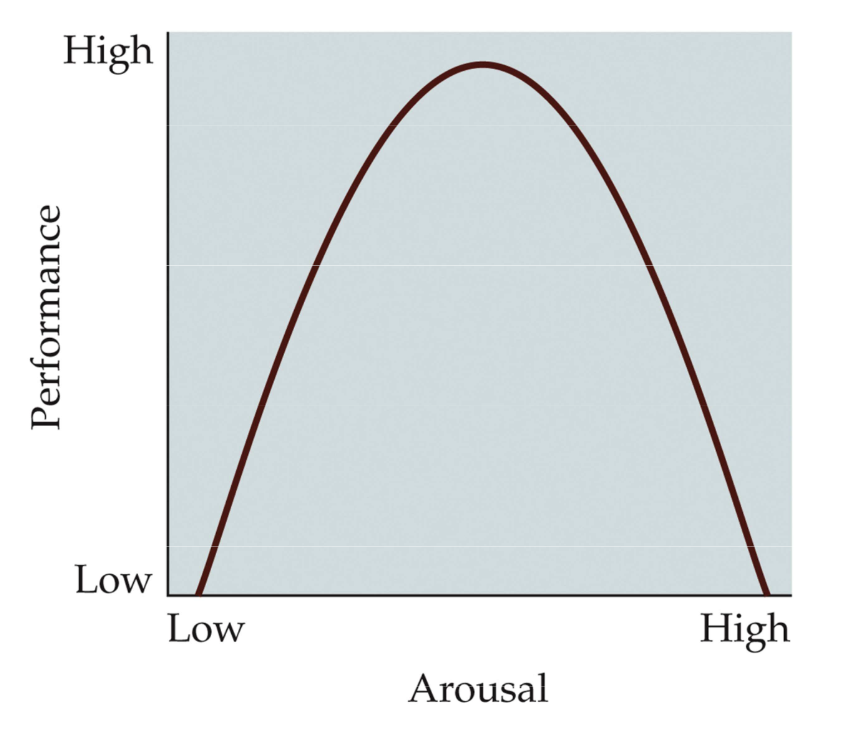
Fig. 12. 2 Arousal and learning
Optimal performance on learning occurs at moderate levels of arousal
Also influenced by hormones
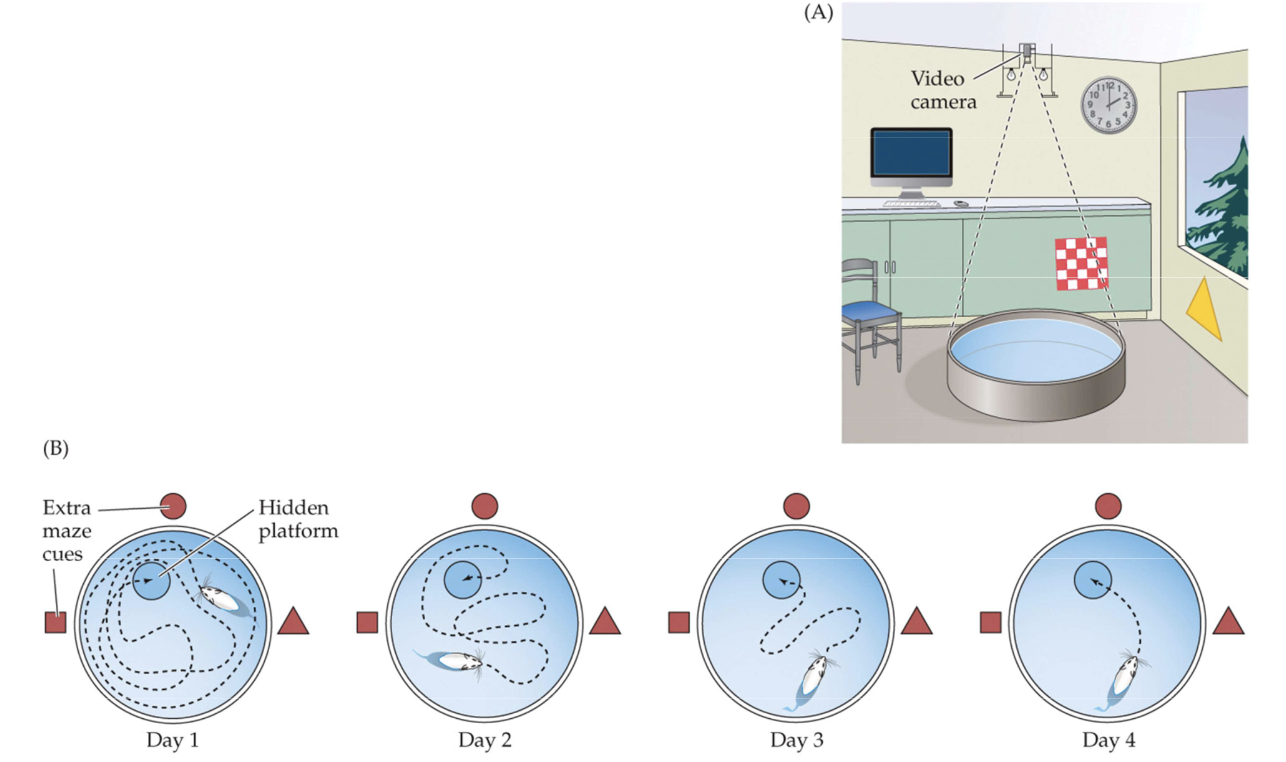
Fig. 12.16: Morris water maze
A) Rats must swim to find a submerged platform hidden below the surface of milky water
Requires relational learning (use cues around the tank)
* More explicit learning
B) Healthy rats will learn to navigate directly to the platform
If the hippocampus is lesioned, rats swim aimlessly until it finds the platform
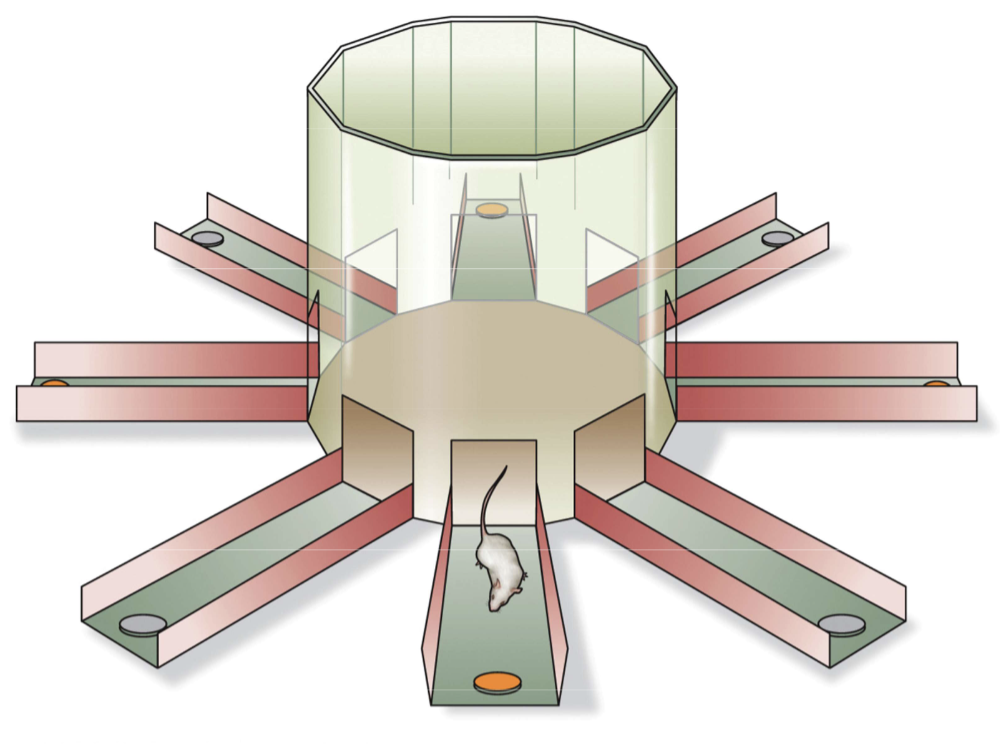
Fig. 12.20 Radial arm maze
Popularized by David Olton
Open-top maze with 8, 12, 36, etc. arms depending on difficulty
During training
Subject learns that only some arms are rewarded
Must learn to get reward on the first try
Requires LTM (reference) and STM (working; remembering which they went down already)
Memory: Epinephrine
(In general) Enhances memory but it’s dose- and time-dependent
High and low blood levels of E impair memory
Theory:
E increases blood glucose → movement of glucose into neurons → release of more ACh into synapses
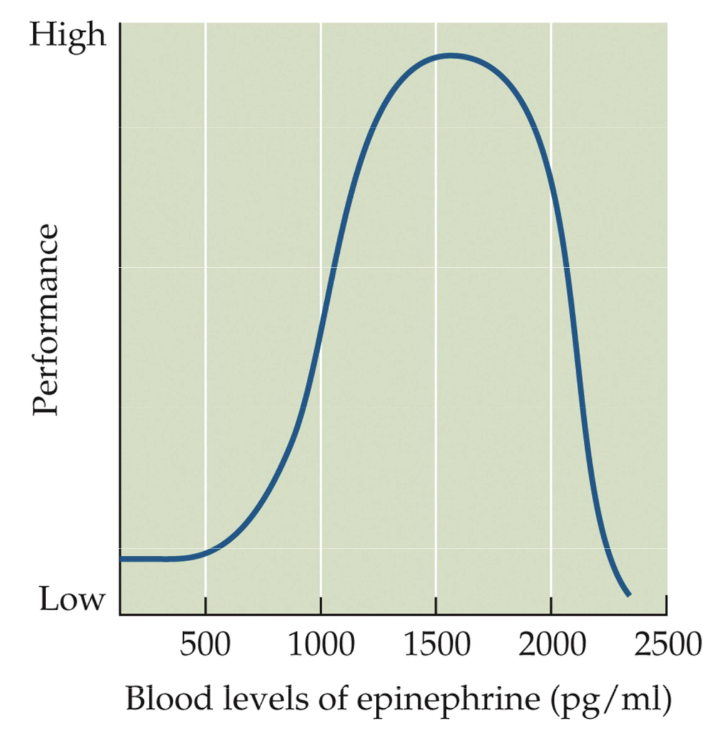
Dose effect: Fig. 12.8 Effects of epinephrine on performance
Optimal dose in rats is about 0.1 mg/kg (1500 pg/ml)
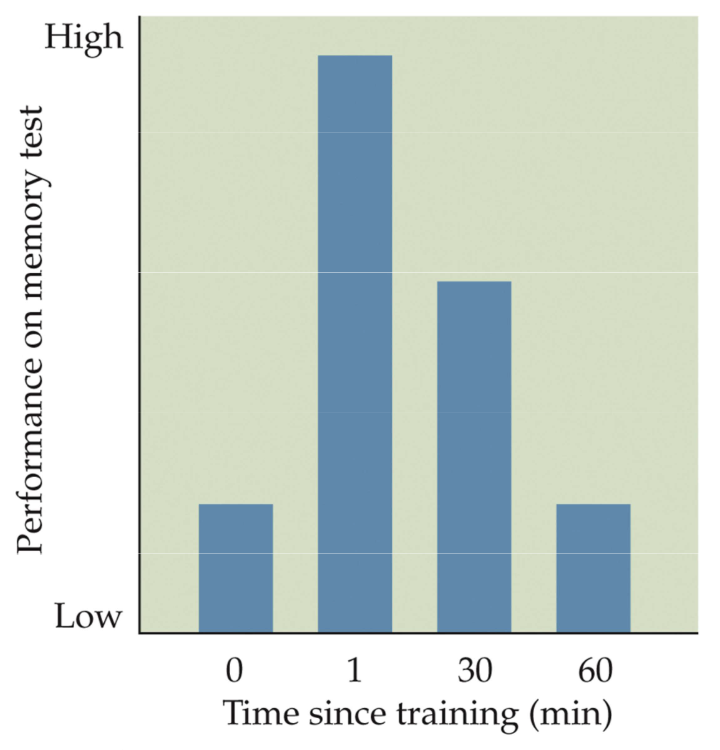
Fig. 12.9 Effects of epinephrine on memory are time-dependent
Injections (1 mg/kg) are most effective in enhancing memory if given 1 minute after training.
Effects diminish 60 mins after training
Glucocorticoids
Acutely high levels of corticoids (acute stress) enhance memory, chronically high (or low) levels impair
Glucocorticoids seem to have effects by influencing the structure or function in the hippocampus and amygdala
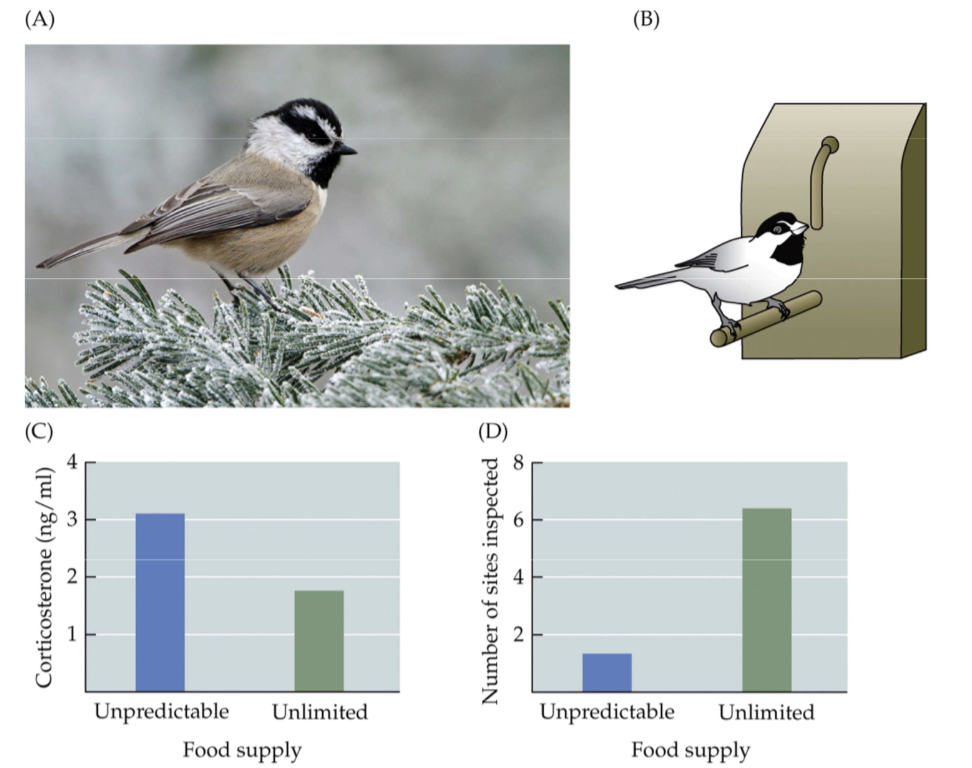
Fig. 12.23: Food-changing mountain chickadees
Corticosterone (stress) is elevated in birds receiving limited and unpredictable food as compared to birds receiving ad libitum food
Birds with unpredictable food visited fewer sites (indicating better memory performance)
Sex Differences in learning and memory
Male rodents perform better at spatial learning tasks than female rodents
likely mediated by hormones
Estrogens
Estradiol enhances memory, especially spatial memory in human and non-human animals
Depends on:
Which cognitive processes are being studied
The timing of hormone administration
Gonadal state of individual
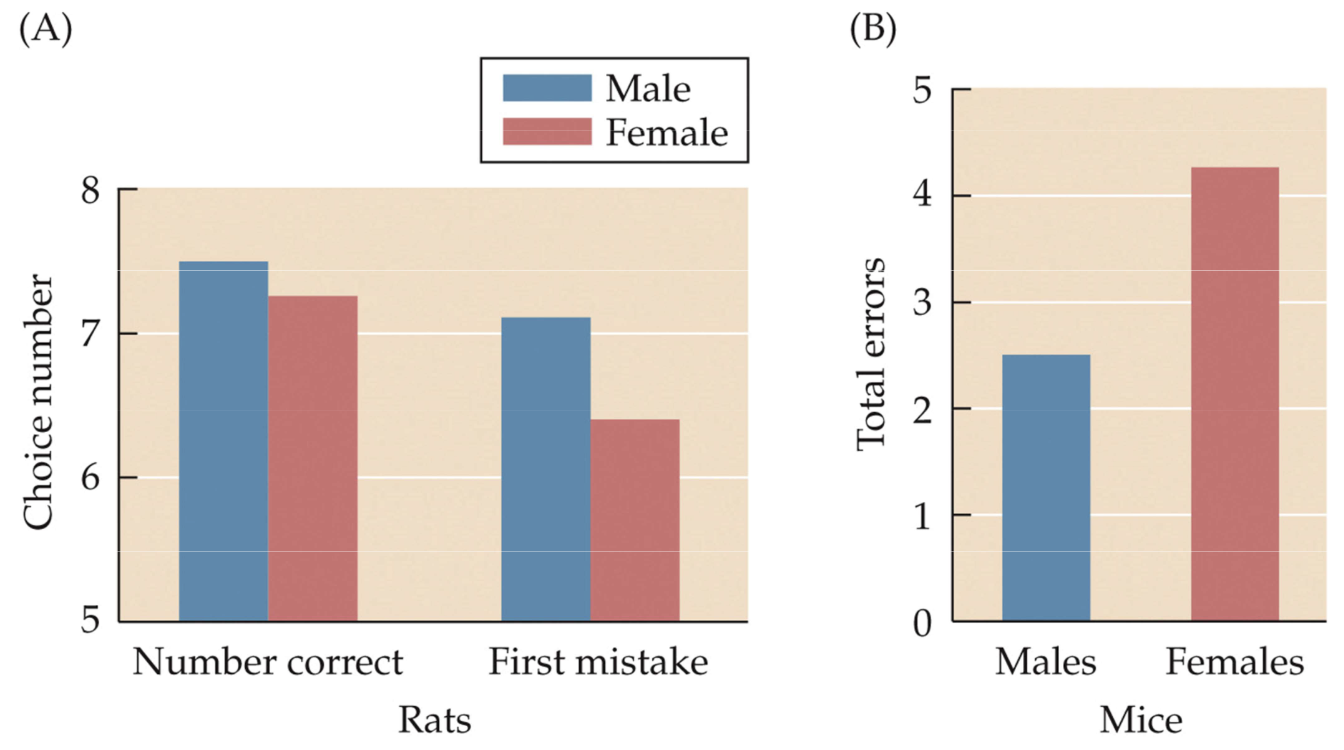
Fig. 12.26 Male rats and mice perform better on radial arm mazes than females
A) Male rats make more correct choices and make mistakes later in their tests
B) Males make fewer errors
Androgens
Do not have major effects on learning and memory in rats
e.g. Castrated and intact male rats learned mazes equally well
Organizational effect
However, learning/ memory effects have been reported during the breeding season in some species, when androgens are higher
Activational effect
Peptides (5)
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
Enhances memory
Oxytocin
Inconsistent results
Vasopressin
Enhances memory but dose and time dependent
Endogenous opioids
Usually have amnestic (decreased memory) properties
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
Enhances learning and memory
* These 5 peptides (+ E) have been noted to acted centrally (i.e. in the CNS) in affecting memory
Acting as NT rather than hormones
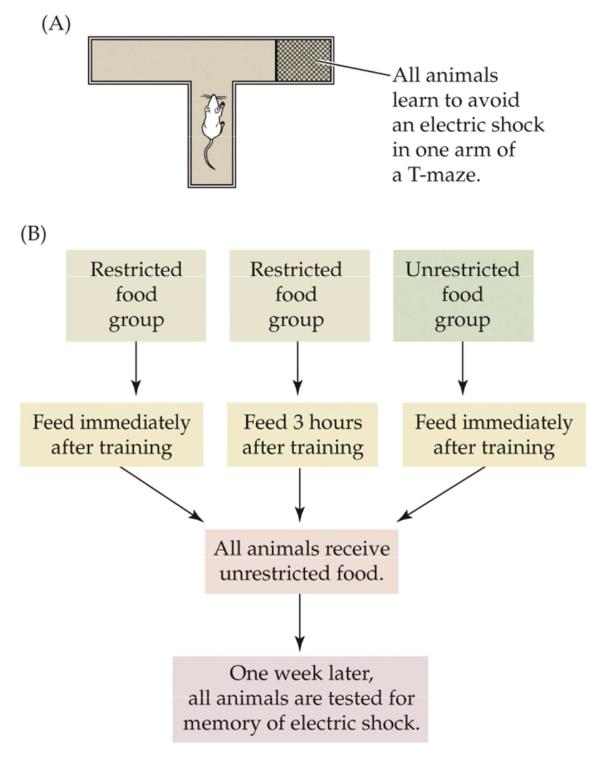
Fig. 12.36: CCK enhances memory in mice
Mice learn to avoid an electric shock in one arm of a T-maze
3 groups:
1) Food restricted mice fed immediately after training
2) Food restricted mice fed 3 hours after training
3) Freely fed mice fed immediately after training
Food restricted that were fed immediately (1) performed the best
The food likely caused the hungry mice to secrete cholecystokinin (CCK) shortly after training