5.2 What factors affect cycle with drainage basin
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
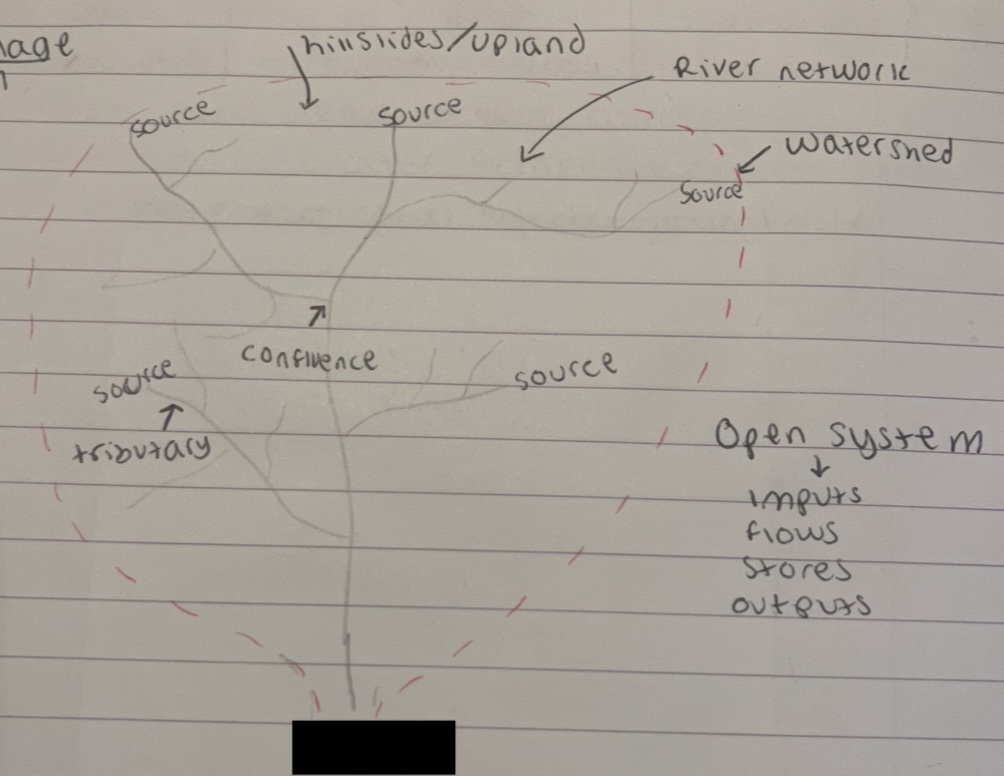
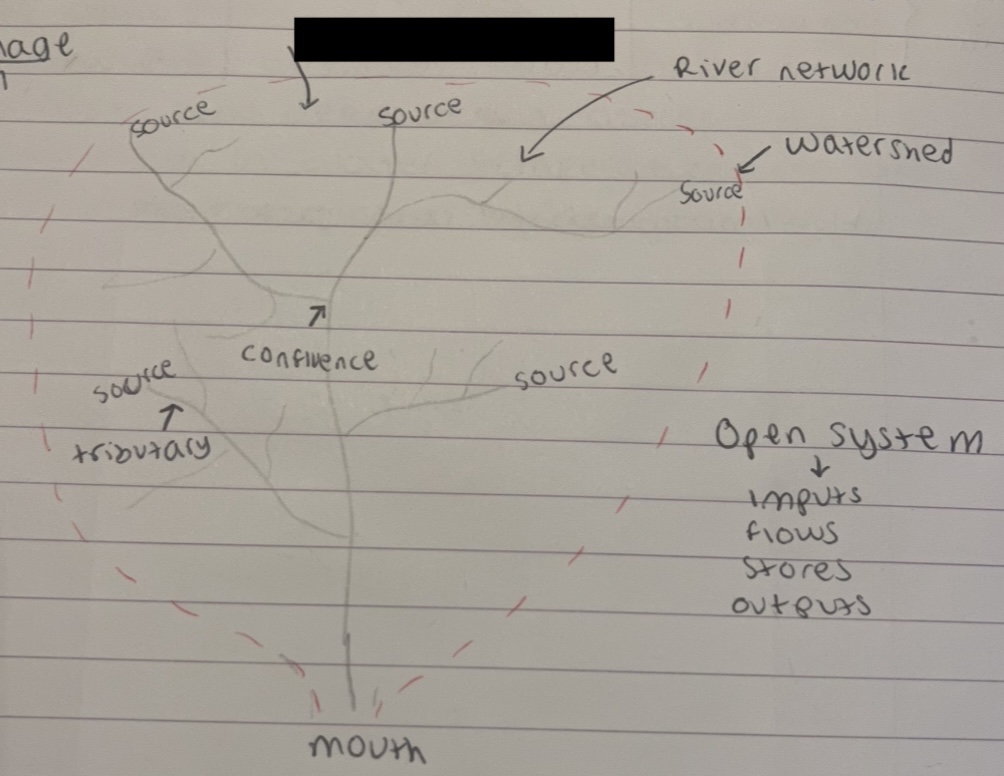
what is this part of the drainage basin
mouth
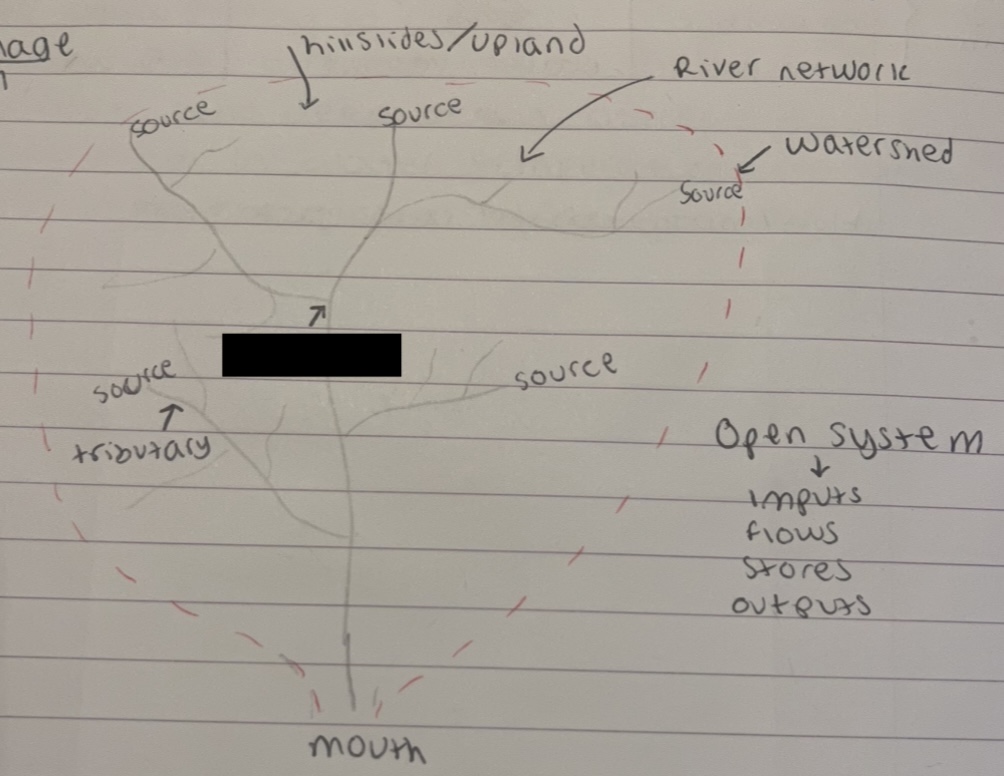
what is this part where the tributaries meet
confluence
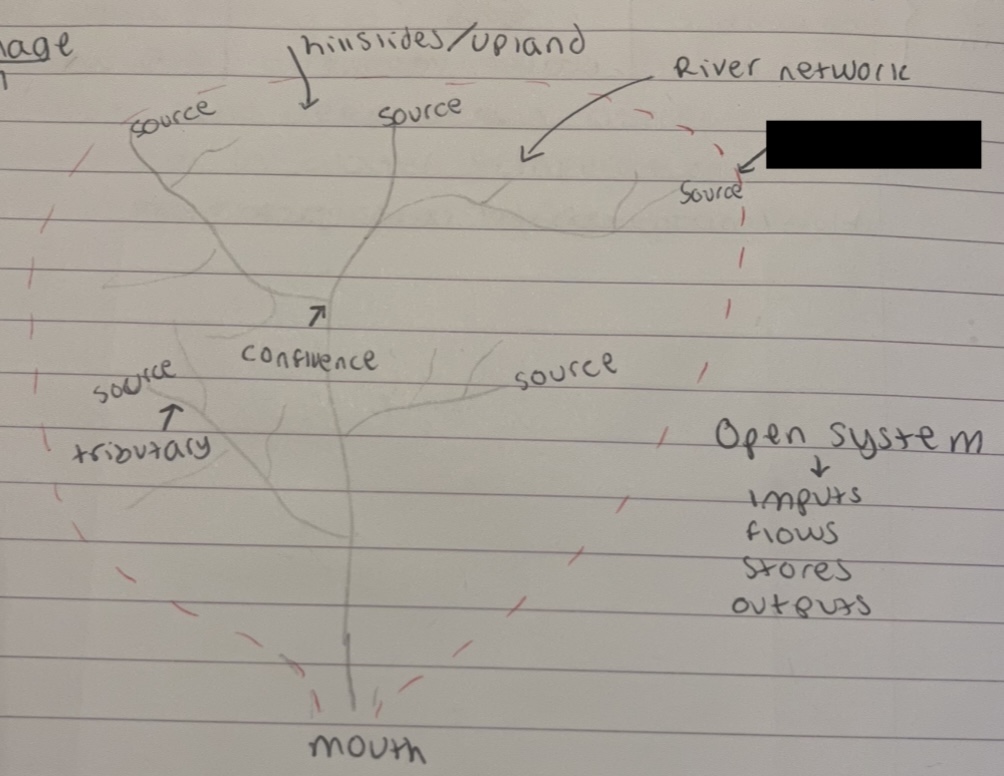
what is the dotted red line
watershed
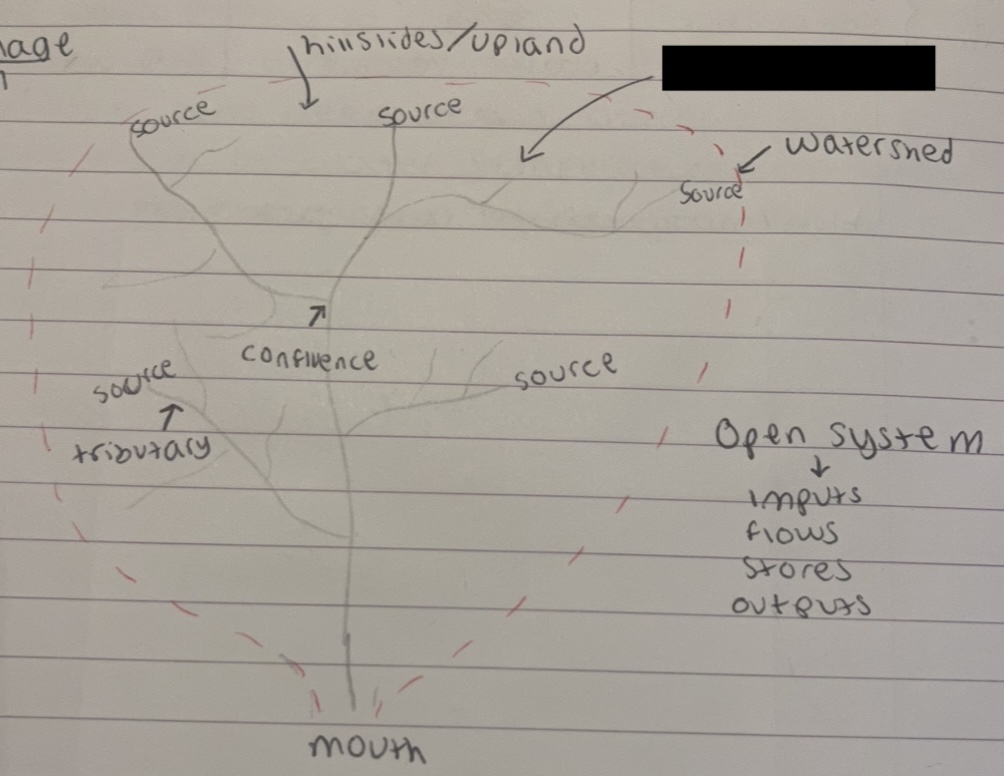
what is the whole river called
river network
what is the drainage basin on
hillslides and uplands
what are the starts of all rivers called
source
what is this part of the river called
tributary
what system is the drainage basin
open system - inputs, flows, stores, outputs

what does the black represent
flow

what does the red represent
store

what does the purple represent
input

what is this part
into lake or sea

what is this part
evaporation

what is this part
groundwater flow (through rock) (slowest)

what is this part
throughflow

what is this part
surface runoff (fastest)

what is this part
percolation

what is this part
infiltrate

what is this part
stem flow

what is this part
evaporate

what is this part
stored on leaves

what is this part
stored within plants. veg store

what is this part
precipiation

what does the green represent
output

what is this part
intercaption
what physical factors might affect the drainage basin
relief-shape of land, geology-rock type(permability), climate-amoutn of precipitate, vegetation, soil type
what human factors might affect the drainage basin
river management, landuse-urbanisation, deforestation, agriculture, create reservoirs, rehmove water-domestic industrial and irrigation
how does cloud seeding affect the hydrological cycle
increases precipitation - silver iodine released into atmosphere and acts as hygroscopie nuclei that is required for precipitations. demand for water increase so hoped to help
how does deforestation affect the hydrological cycle
leads to more flooding - weakens soil and reduces drainage
how does flood management affect the hydrological cycle
increase water storage and interception and infiltration
how does urbanisation affect the hydrological cycle
leads to loss of wetland - causes more flooding, more intense rainfall as warming climate
how does afforestation affect the hydrological cycle
increases flooding and reduces infiltration - trees dont have deep enough roots, dont decompose properly
how does dam building affect the hydrological cycle
increases or reduces a rivers discharge - increases evaporation, increase riverbank erosion
how does climate change affect the hydrological cycle
causes more extreme rainstorms and droughts - evaporation increase so more intense storm events
what physical facts affect the hydrological cycle
climate, geology, soils, relief, vegetation
how does climate affect the hydrological cycle
hotter means more evaporation and transpiration, wet climate has more precipitation than dry climate, dry area mean more surface runoff as ground is solid dry
how does geology affect the hydrological cycle
impermeable rock means more surface runoff as soil is saturated faster, permeable rock means more water percolate and stored as ground water
how does soils affect the hydrological cycle
some more permeable than others e.g. sand than clay, different sized particles, bigger is more permeable as they cant be squashed together
how does relief affect the hydrological cycle
steeper means more runoff as more gravitational potential energy, takes time to infiltrate, snow and ice in high up mountains
how does vegetation affect the hydrological cycle
more water stored in plant and more transpiration so evaporation, slowed cycle in forest as water is held in trees longer than grass, more vegetation means more infiltration
what is the case study for cloud seeding
idaho USA, 2017 NCAR has been collecting and analysing data from a could seeding experiment and many local farmers rely on melting snow as water supply
what is the case study for deforestation
freetown, sierra leone, 2017 after rainy season 1141 died from massive mudslide and made flooding worse, highland overlooking city was deforested
what is the case study for flood management
pickering, uk, used 4 techniques to to reduce flooding ‘slowing the flow’, constructing low level soil embankment, planting more trees, restoring woody debris dams in small streams, restoring wetlands
what is the case study for urbanisation
houston, texas, population doubled leading to loss of 100000 hectares of wetland and 7000 houses built on flood plains, when hurricane harvey struck there was extreme flooding due to loss of wetland
what is the case study for afforestation
ireland, planted trees to cover from 1%-11% targeted 18% but sitka spruce which captures carbon but have needles that dont decompose and only shallow roots
what is the case study for dam building
grand ethiopian renaissance, 2011 dam built in ethiopia to slow process of filling reservoir, all hydroelectricity generated is fed into national grid hoped to supply 65million ethiopians