Lectures 32-34 / Chapter 14
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Paul Ehrlich
Found compound 606 and killed Treponema pallidum (syphillis)
Alexander Fleming
Discovered penicillin, the first natural antibiotic
Klarer, Mietzch, and Domagk
Discovered prontosil, which killed streptococcal and staphylococcal infections
What is the active breakdown product of prontosil?
Sulfanilamide
What was the first synthetic antimicrobial?
Sulfanilamide
Dorothy Hodgkin
Discovered the structure of penicillin using x-ray. Scientists could now modify semisynthetic penicillins
Chemotherapeutic agent
Any drug used to treat infection
Antibiotic
Usually targets one part of the bacteria (specific)
Example: a key bacterial enzyme is blocked
Antimicrobial
A broad term but can often mean multiple targets (broad)
Selective toxicity
Harms microbes but not damaging to the host
Chemotherapeutic index
Maximum tolerable dose per Kg of body weight
Minimum dose per Kg of body weight which cures the disease
Narrow spectrum
Targets only specific subsets of bacterial pathogens
Broad spectrum
Targets a wide variety of bacterial pathogens, including gram-positive and gram-negative species
What are 2 broad spectrum antibiotics?
Streptomycin and tetracycline
Broad spectrum disadvantage
The formation of superinfections
Superinfection
A secondary infection in a patient who already had an infection, associated with broad spectrum antibiotics
How does a superinfection form?
When you take broad spectrum antibiotics, it kills off healthy natural flora that keep opportunistic pathogens in check.
Bacteriostatic graph
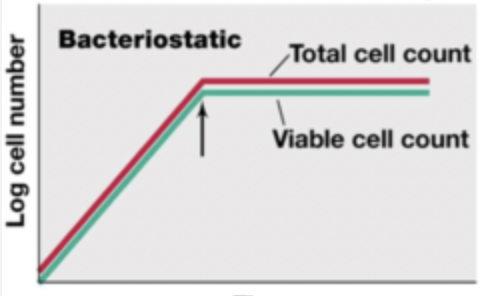
Bacteriocidal graph
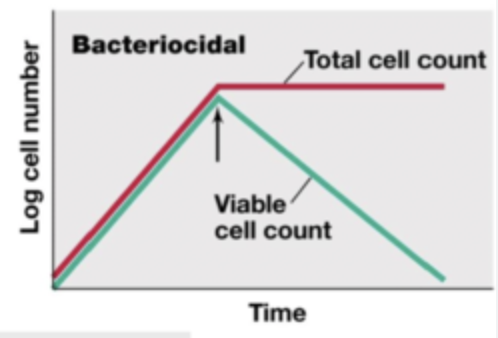
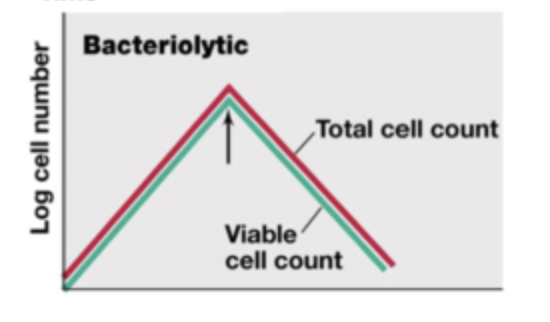
Bacteriolytic graph
Minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC)
The lowest concentration of the drug that will prevent the growth of an organism
Different tests for antiobioti activity
MIC test
Kirby-Bauer
E-test
Can the MIC test or the Kirby-Bauer test determine if a drug is bacteriocidal or bacteriostatic?
No
How to determine if a drug is bacteriocidal or bacteriostatic
Minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC)
Tube dilution test and removing the antibiotic
Minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC)
Tube dilution test and removing the antibiotic, if the cells grow in fresh medium without the antibiotic, the drug is… But if the cells do not grow, it is…
bacteriostatic
bactericidal
Attributes of an ideal antimicrobial
Solubility in body fluids
Selective toxicity
Toxicity not easily altered
Non-allergenic
Stability
Resistance by microorganisms not easily acquired
Long shelf-life
Reasonable cost
Dosage in children vs. adults
The amount of medication given during a certain time interval
In children: dosage is based upon the patients mass
In adults: standard dosage is used
Half-life of antibiotic
Rate at which 50% of a drug is eliminated from the plasma
Toxic dose
The maximum dose tolerated by the patient
Therapeutic dose
The minimum dose per kg of body weight that stops pathogen growth
The ratio of the therapeutic dose to the toxic dose is…
the chemotherapeutic index
Is the drug safe if it has a high or low chemotherapeutic index?
High
Which route of administration results in the highest amount of drug in the plasma?
IV (intravenous)
Synergistic drugs
Work poorly when they are given individually, but work very well when combined
Example: aminoglycoside and vancomycin
Antagonistic drugs
Mechanisms of action interfere with each other and diminish effectiveness
Example: penicillin and macrolides
Mechanisms of action for antibiotics: what can they target?
Cell wall synthesis
Cell membrane integrity
DNA synthesis
RNA synthesis
Metabolism
Antibiotics that target the cell wall
Beta-lactams
Penicillin
Cephalosporins
Polypeptides
Vancomycin
Bacitracin
Antimycobacterials
Isoniazid
Ethambutol
Penicillins
Penicillin binds to the enzymes that attach NAM and NAG
Without a cell wall, the growing cell bursts
Is penicillin bactericidal?
Yes
Is cephalosporin naturally occurring or synthetic?
Originally discovered in nature but has been modified, semisynthetic
Cephalosporin
Chemists have modified the basic structure of cephalosporin in ways that improve the drug’s effectiveness against penicillin resistant pathogens. New generations of the antibiotic
Polypeptide antibiotics that inhibit cell wall synthesis
Bacitracin and vancomycin
Bacitracin
Topical application
Against gram positives
Vancomycin
Glycopeptide
Important “last line” against antibiotic resistant S. aureus
Antimycobacterial antibiotics
Isoniazid and ethambutol
Isoniazid
Inhibits mycolic acid synthesis
Ethambutol
Inhibits incorporation of mycolic acid
How have microbes developed resistance to cell wall inhibiting antibiotics?
Bacteria with the enzyme beta-lactamase breaks a bond in the beta-lactam ring of penicillin to disable the molecule
Antibiotics that target the bacterial membrane
Polymycin
Tyrocidin
Platansimycin
Gramicidin
Polymycin B
Targets lipid A, which only gram-negative bacteria have. Therefore its narrow spectrum
Highly toxic
Gramicidin
Cyclic peptide
Inserts itself into the cytoplasmic membrane of gram-positive bacteria, disrupting the membrane and killing the cell
Antibiotics that affect DNA synthesis and integrity
Metronidazole
Sulfonamides
Quinolones
Metronidazole
Inactive until it enters anaerobic or microaerophilic bacterial cell
Ferredoxin reduces metronidazole into active form
Activates form binds to DNA and causes breaks
Sulfonamides
Prevent the synthesis of folic acid, therefore inhibiting the production of nucleic acids
Folic acid is the precursor to nucleic acid
Why don’t sulfonamides harm humans?
Mammals do not synthesize folic acid, we have to get it from diet or microbes
Quinolones
Inactivates DNA gyrase and topoisomerase
Blocks progression of DNA replication fork
Why don’t quinolones harm humans?
Bacterial DNA gyrases are structurally distinct from mammal DNA gyrase
RNA synthesis inhibitor
Rifampin
Rifampin
Selectively binds to bacterial RNA polymerase and prevents transcription
What does rifampin treat?
Tuberculosis and meningococcal meningitis
Antibiotics that inhibit protein synthesis
Aminoglycosides
Tetracyclines
Glycylcyclines
Chloramphenicol
Macrolides
Lincosamides
Oxazolidinones
Streptogramins
Drugs that affect the 30S ribosomal subunit
Aminoglycosides
Tetracyclines
Glycylcyclines
Aminoglyosides
Affects 30S ribosomal subunit*
Streptomycin, gentamicin, tobramycin
Causes misreading of mRNA
Tetracyclines
Affects 30S ribosomal subunit*
Doxycycline
Binds to 30S subunit and prevents tRNAs carrying amino acids from entering the A site
Glycylcyclines
Affects 30S ribosomal subunit*
Tigecycline FUNCTIONS IN TETRACYCLINE RESISTANT CELLS
Bind to 30S subunit and inhibit the entry of aminoacyl-tRNA into the A site.
Drugs that affect the 50S ribosomal subunit
Chloramphenicol
Macrolides
Lincosamides
Oxazolidinodes
Streptogramins
Chloramphenicol
Affects 50S ribosomal subunit*
Prevents peptide bond formation by inhibiting peptidyltransferase
Macrolides
Affects 50S ribosomal subunit*
Erythromycin, azithromycin, clarithromycin
Bind to 50S subunit and inhibit translocation of tRNA from A to P sites
Lincosamides
Affects 50S ribosomal subunit*
Clindamycin
Bind to peptidyltransferase and prevents peptide bond formation
Oxazolidizones
Affects 50S ribosomal subunit*
Bind to 50S subunit and prevent 70S assembly
Streptogramins
Affects 50S ribosomal subunit*
Quinupristin, dalfopristin
Bind to 50S subunit and block tRNA from entry into A site, while blocking the exit of growing protein from the ribosome
Mechanisms of antimicrobial drug resistance by bacteria
Drug modification or inactivation
Blocked penetration
Efflux pumps (altering porins in outer membrane)
Target modification
Target overproduction
Enzymatic bypass
Target mimicry
What does the influenza virus contain?
Hemagglutinin
Neuraminidase
Hemagglutinin function
Helps influenza virus bind to the host membrane receptors for entry by phagocytosis (helps virus get into cells)
Neuraminidase
Cleaves sialic acid to allow virus particles to escape from infected cells (helps virus exit cells to infect other cells)
Drugs that combat influenza
Amantadine
Oseltamivir (tamiflu)
Zanamivir (relenza)
Treatments that inhibit HIV
Protease inhibitors
Entry inhibitors
HIV treatment regimens
Protease inhibitors
Target the HIV protease enzyme
Entry inhibitors
Block the virus envelope protein from binding to the host receptor, so the virus never attaches
HIV treatment regimens
HAART (highly active antiretroviral therapy) involves administering combinations of three or more antiretroviral drugs
Antifugal agents
Polyenes
Azoles
Allylamines
Antiprotozoan agents
Metronidazole
Quinine
Chloroquinine
What drug is an antimalarial?
Chloroquinine
Antihelminthic drugs
Niclosamide
Praziquantel