Microscopic Anatomy and Organization of Skeletal Muscle
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Muscle refers to….
A tissue, an organ, a fiber
Muscle Tissue
skeletal, cardiac, or smooth
Muscle organ
bicep brachii
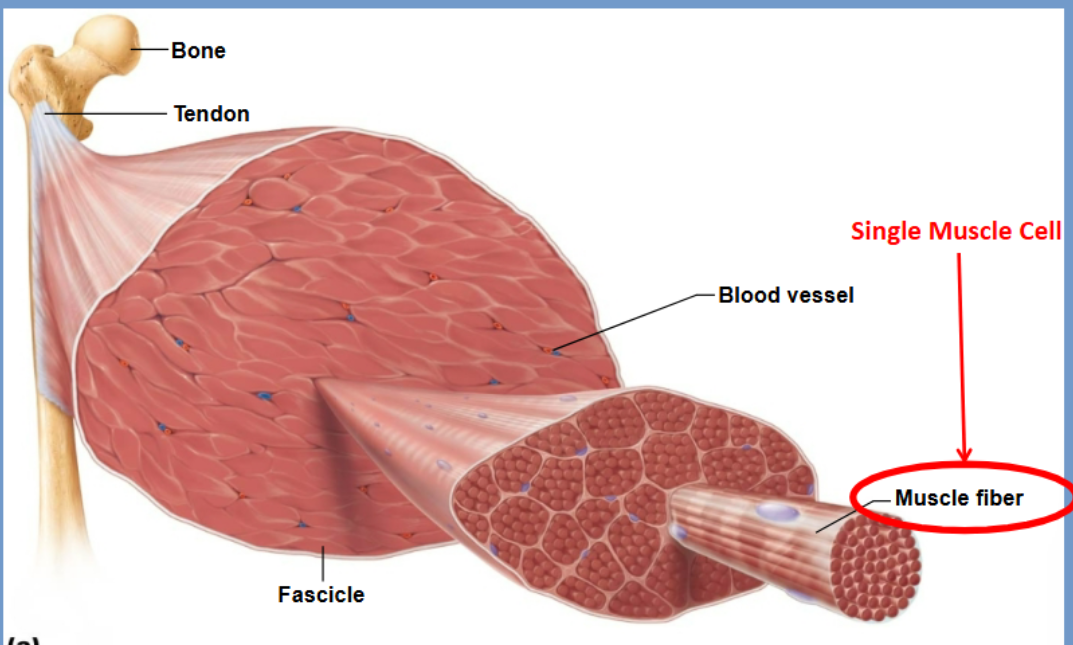
A muscle fiber
a single cell of muscle tissue
Epimysium
Dense CT covering the entire muscle
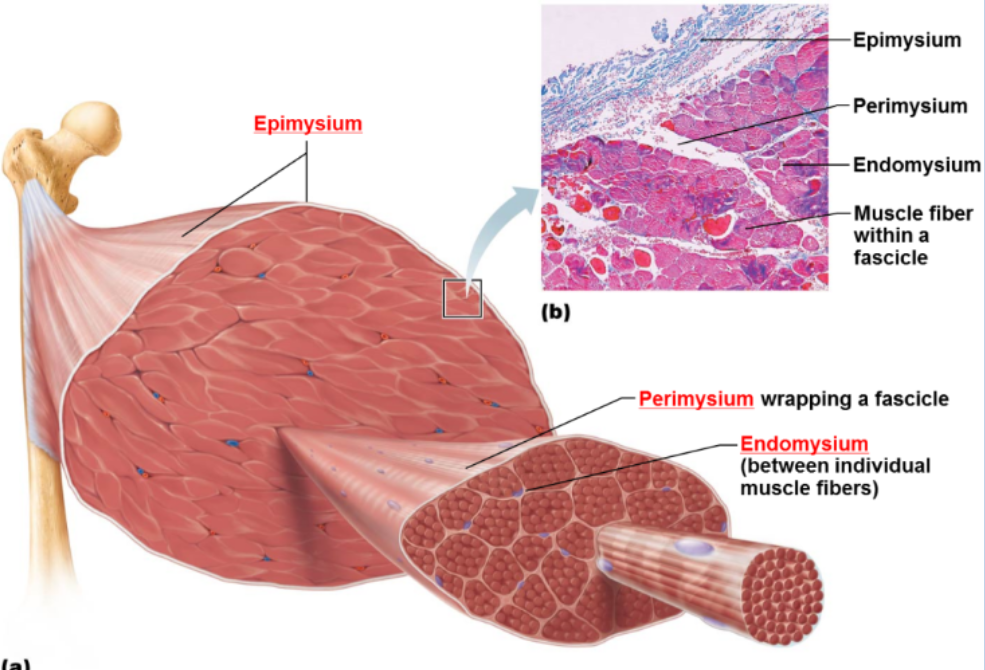
Perimysium
CT surrounding each muscle fascicle
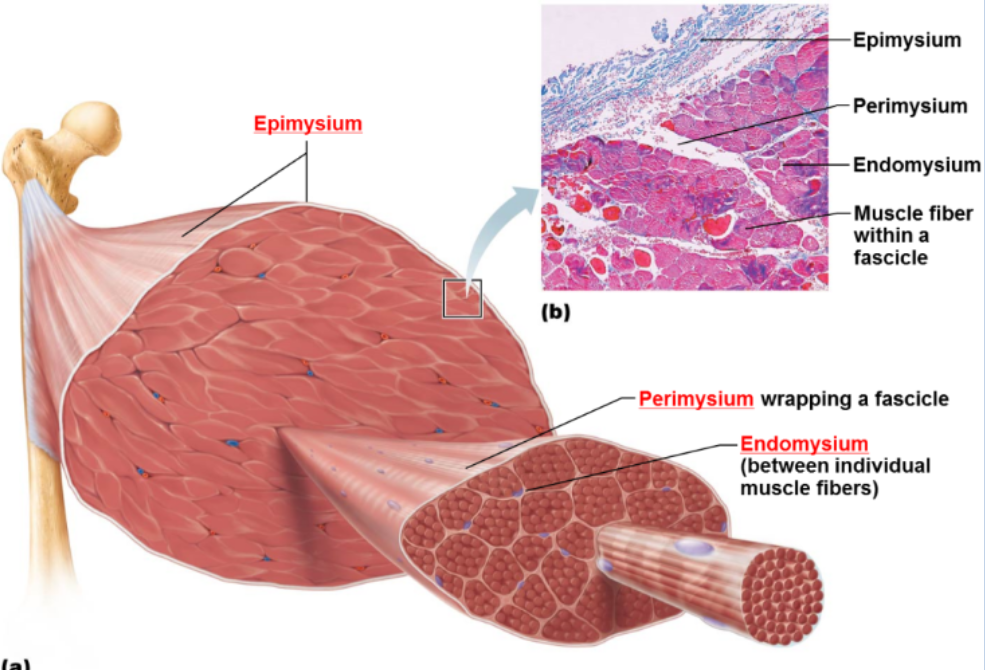
Endomysium
Surrounds each muscle fiber, sub diving the fascicles
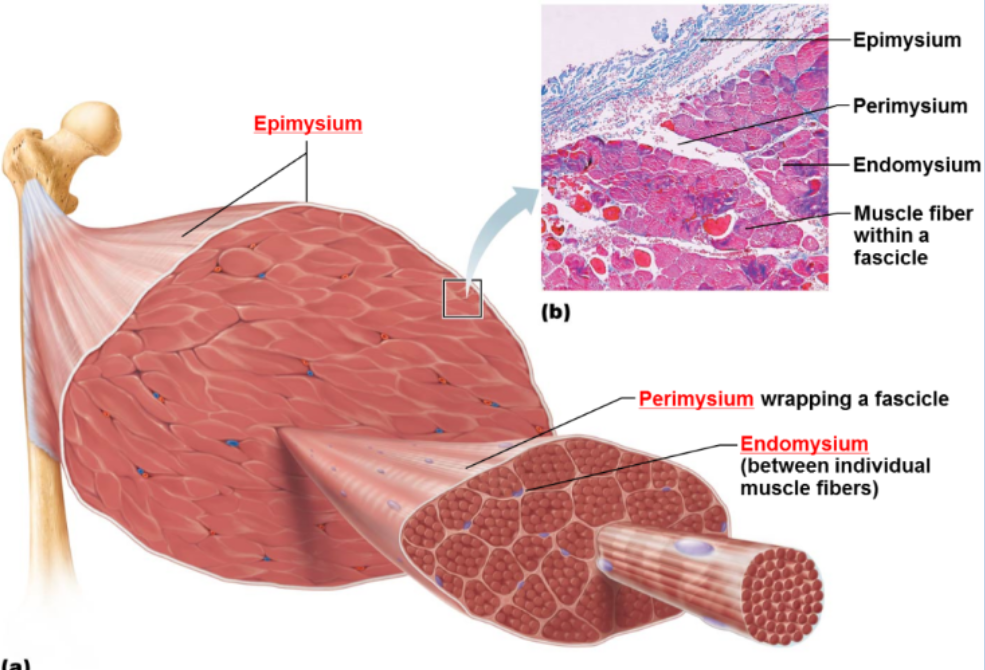
Functions of these connective tissue
provide strength, insulation and connection to tendons. Transmits contraction force to bone.
Connective tissue layer are
continuous with tendons
What composes muscle fiber
many myofibrils
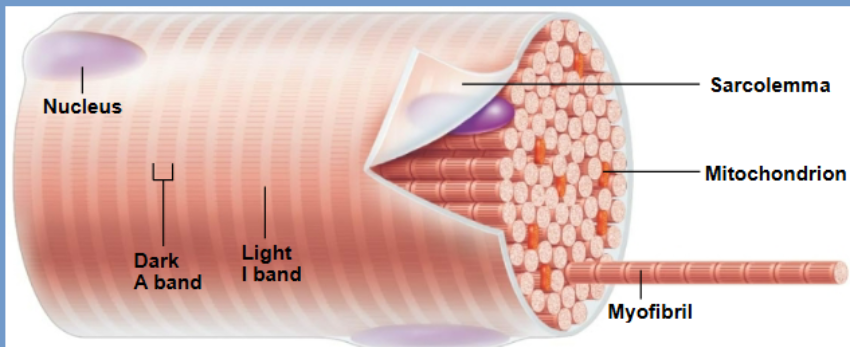
Myofibrils
Cylindrical bundles inside each muscle fiber.
Contain sarcomeres arranged end-to-end → responsible for striations and contraction.
Sarcolemma
The muscle cell membrane; conducts electrical impulses from the neuron into the muscle cell.
Important for initiating contraction through depolarization.
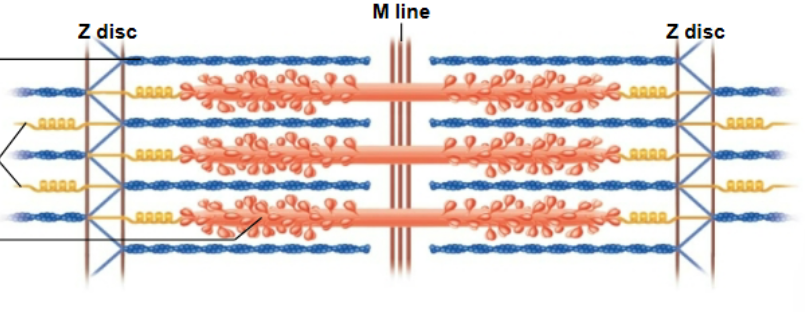
Sarcomere
Smallest component capable of contraction
Shortens during contraction
sarcomere
What proteins make up a sarcomere
actin, tropomyosin and troponin (also known as microfilaments)
Myosin; motor protein
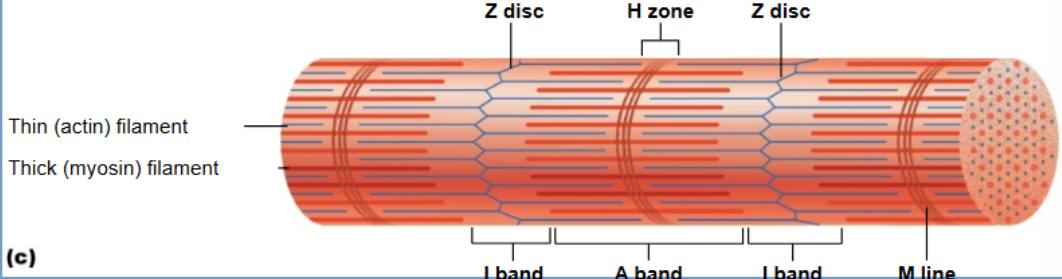
Z disc
Define sarcomere boundaries and anchor actin filaments
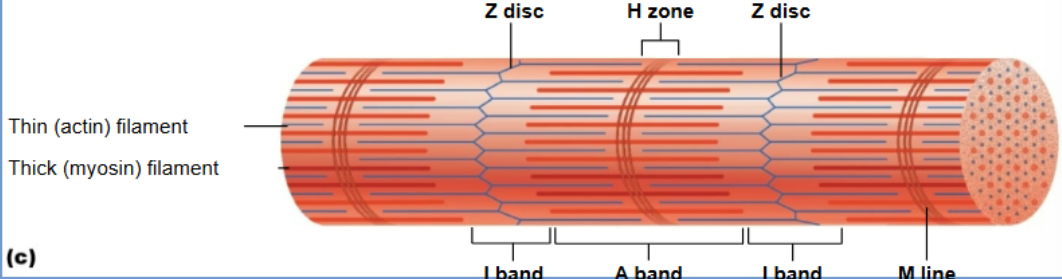
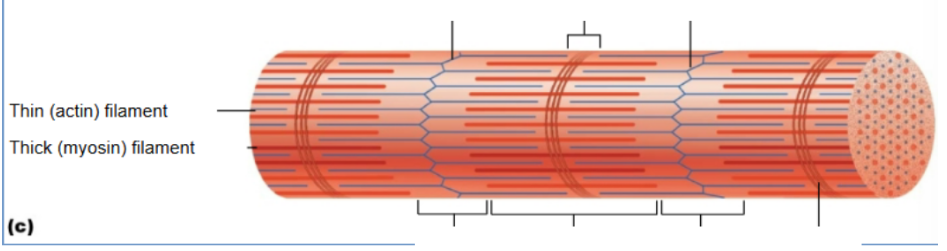
H zone
Only myosin; disappears when fully contracted
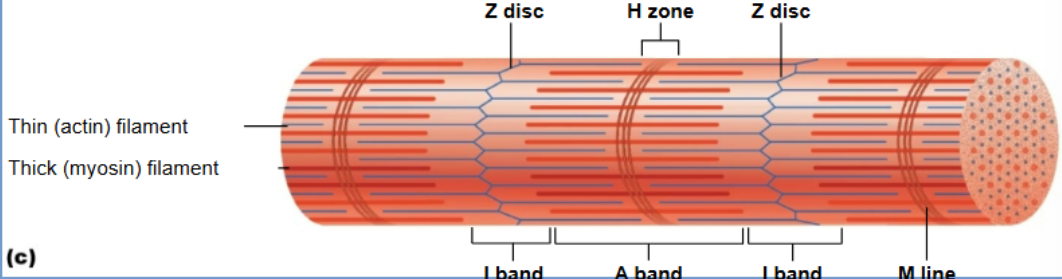
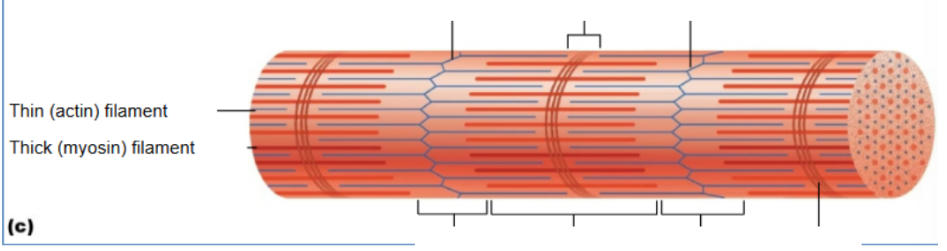
I band
Thin actin filaments; shortens during contraction
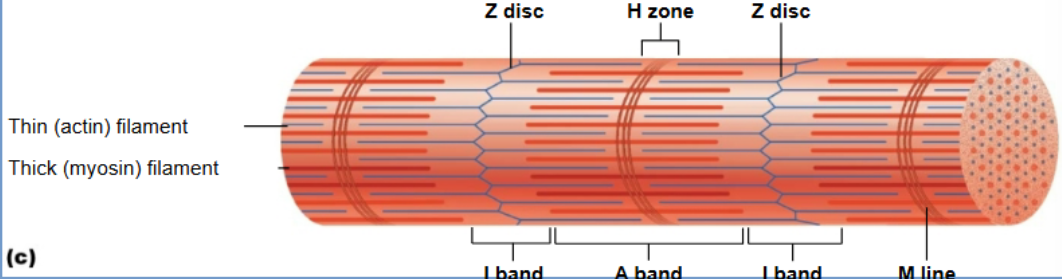
A - band
thick myosin filament; stays same length
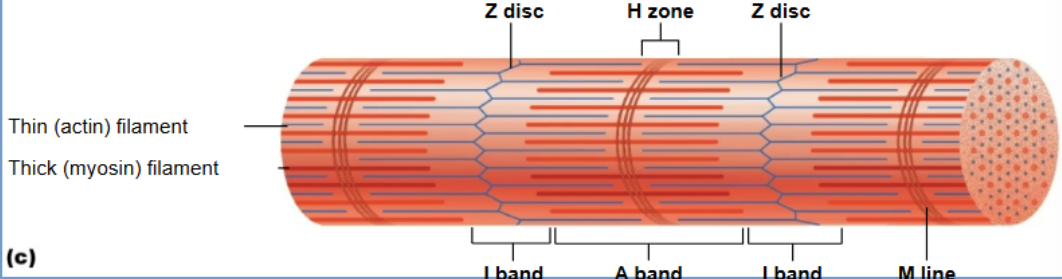
M line
Actin (thin filament)
Contains binding sites for myosin; moves during contraction.
Myosin (thick filament)
Motor protein with heads that attach to actin and perform the power stroke.
Hierarchy (small → large) of muscle
Myofibril — muscle fiber — fascicle — whole muscle
Tropomyosin
when resting blocks the myosin binding site on the actin protein
Troponin
reacts to Calcium and moves tropomyosin
Activation of tropomyosin example
Nerve impulse → ACh released → binds to receptors on motor end plate.
Action potential spreads through sarcolemma & T-tubules.
Ca²⁺ released from SR via RyR channels.
Ca²⁺ binds to troponin, moving tropomyosin off actin’s binding sites.
Cross-bridge cycle:
Myosin binds actin → power stroke (actin pulled toward M-line).
ADP + Pi released → new ATP binds → myosin detaches and resets.
Cycle repeats as long as Ca²⁺ and ATP are available
Relaxation of tropomyosin
Ca²⁺ pumped back into SR; tropomyosin re-blocks actin sites.
T tubules
Invaginations of sarcolemma that carry the action potential deep into the fiber.
Work closely with sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR).
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum (SR):
Modified smooth ER that stores and releases Ca²⁺ for contraction.
Terminal cisterns form part of a triad with a T-tubule.