UNLV KIN 223 EXAM 2! corrected, KIN223 Exam 2, KIN 223 Exam 2 Review, KIN 223 Exam 2
1/341
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
342 Terms
During transcription
a protein is formed as a DNA sequence is read.
an RNA molecule is formed as a DNA sequence is read.
a protein is formed as a RNA sequence is read.
an amino acid is transferred to a ribosome as a DNA sequence is read.
a DNA sequence is formed as a RNA sequence is read.
an RNA molecule is formed as a DNA sequence is read.
Apoptosis is best described as
the process of immune cells recognizing an infected cell as "foreign".
the process of an aging cell becoming cancerous.
the destruction of a cell through mechanical damage.
a process where cells destroy themselves.
a process where cells destroy themselves.
The _______ is responsible for forming the outer, limiting barrier of a cell.
mitochondrion
ribosome
peroxisome
centrosome
plasma membrane
plasma membrane
The building blocks that form the DNA double helix are called
nitrogenous acids.
steroid bases.
nucleotides.
nucleoli.
nuclear pores.
nucleotides.
When a cell surrounds a large particle with pseudopodia and then engulfs it, the process is called
phagocytosis.
exocytosis.
secondary active transport.
pinocytosis.
receptor-mediated endopinocytosis.
phagocytosis.
Pinocytosis is the process in which the cell
internalizes ("eats") a large solid particle.
pumps small solutes against their concentration gradient and out of the cell.
internalizes ("drinks") a droplet of interstitial fluid.
splits ("pinches") off a small part of itself to secrete into the extracellular space.
internalizes ("drinks") a droplet of interstitial fluid.
!The function of the nucleolus is to make!
the secretions that will be packaged by the Golgi apparatus.
histones.
DNA molecules.
the deoxyribose sugar.
the subunits of ribosomes.
the subunits of ribosomes.
!When a cell is placed in a solution with a very low solute concentration, water diffuses into the cell. Such a solution is called a(n) _________ solution.!
isotonic
endergonic
hypertonic
hypotonic
hypotonic
Proteins that are embedded within, and extend across, the phospholipid bilayer are called _____ proteins.
catalytic
integral
peripheral
cytoskeleton
integral
The phase of mitosis that begins as spindle fibers pull sister chromatids apart at the centromere is
anaphase.
metaphase.
telophase.
prophase.
interphase.
anaphase.
Channel-mediated diffusion is a subtype of
simple diffusion.
facilitated diffusion.
active transport.
carrier-mediated diffusion.
endocytosis.
facilitated diffusion.
Which of the following is not a component of the cytoplasm?
Organelles
Chromatin
Cytosol
Inclusions
Chromatin
Movement of a substance from an area of higher concentration to one where it is less concentrated is known as
facilitation.
equilibrium.
active transport.
selective transport.
diffusion.
diffusion.
Which of the following serve to increase the surface area of a cell for absorption and secretion?
Cilia and microvilli
Cilia
Flagella
Cilia and flagella
Microvilli
Microvilli
Forms the outer barrier of the cell
cytoplasm
plasma membrane
nucleus
plasma membrane
Contains the cytosol, inclusions, and organelles
cytoplasm
plasma membrane
nucleus
cytoplasm
The cell's control center
cytoplasm
plasma membrane
nucleus
nucleus
Movement of fluids through a selectively permeable membrane caused by hydrostatic pressure is referred to as _____.
osmosis
hydrostatic pressure
filtration
carrier-mediated diffusion
concentration gradient
simple diffusion
filtration
The pressure exerted by a fluid on the inside wall of its container (or vessel, in the case of the human body), is called ____.
osmosis
hydrostatic pressure
filtration
carrier-mediated diffusion
concentration gradient
simple diffusion
hydrostatic pressure
The movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration describes ___.
osmosis
hydrostatic pressure
filtration
carrier-mediated diffusion
concentration gradient
simple diffusion
simple diffusion
Movement away from high solvent concentration or towards high solute concentration describes
osmosis
hydrostatic pressure
filtration
carrier-mediated diffusion
concentration gradient
simple diffusion
osmosis
The movement of small, polar molecules across the plasma membrane by a carrier protein is called.
osmosis
hydrostatic pressure
filtration
carrier-mediated diffusion
concentration gradient
simple diffusion
carrier-mediated diffusion
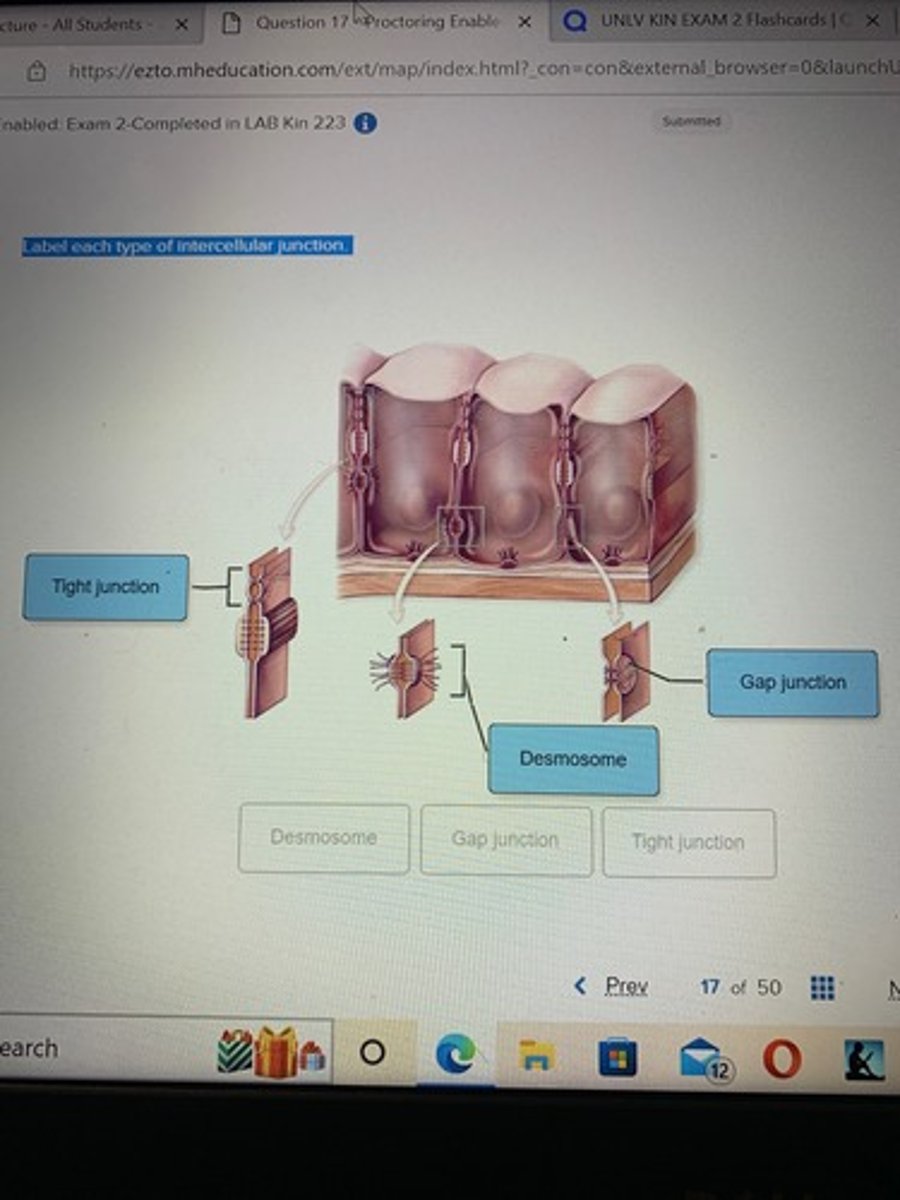
Label each type of intercellular junction.
Which type of epithelium is composed of multiple layers, including an apical layer containing tall, slender cells?
Simple columnar
Stratified squamous
Pseudostratified squamous
Simple squamous
Stratified columnar
Stratified columnar
Endocrine glands
lack ducts and secrete their products into the bloodstream or into interstitial fluid.
lack ducts and secrete their products onto the skin surface.
possess short ducts and secrete their products directly onto the skin surface.
possess ducts to secrete their products into the bloodstream or into interstitial fluid.
secrete mucus directly into a body cavity.
lack ducts and secrete their products into the bloodstream or into interstitial fluid.
Ligaments are very strong but resistant to stretch. Which protein fiber probably predominates?
Collagen
Reticular
Adipose
Elastic
Collagen
Plasma is
platelets and a watery ground substance.
a dissolved ground matrix and a lining of epithelial cells.
a liquid ground substance containing dissolved proteins.
platelets, red blood cells, and white blood cells.
a liquefied ground substance that includes several dissolved cells.
a liquid ground substance containing dissolved proteins.
Which tissue type covers body surfaces and lines the inside of organs and body cavities?
Muscle
Connective
Epithelial
Nervous
None of the choices is correct.
Epithelial
The primary role of epithelial tissue in the stomach is
regulation of contraction.
housing blood vessels and nerves.Incorrect
secretion of substances for chemical digestion.
mixing and propulsion of foodstuffs.
secretion of substances for chemical digestion.
Connective tissue proper is divided into two broad categories: loose connective tissue and dense connective tissue. This classification is based upon the
size of the cells present.
origin of the tissue type.
number of different cells types and their respective arrangement.
relative proportions of cells, fibers, and ground substance present.
location of the tissue.
relative proportions of cells, fibers, and ground substance present.
Suppose that you were involved in an automobile accident and suffered a back injury. When examined by your physician you are told that you have a slipped disc in the lower back. What type of tissue is involved?
Bone
Fibrocartilage
Elastic cartilage
Adipose tissue
Dense regular connective tissue
Fibrocartilage
Endocrine glands secrete
sweat.
hormones.
saliva.
digestive enzymes.
All of the choices are correct.
hormones.
The type of muscle that is found in blood vessel walls is __________ muscle.
cardiac
skeletal
smooth
smooth
Groups of similar cells and extracellular products that carry out a common function are called
organs.
organ systems.
matrices.
tissues.
tissues.
The type of epithelium that lines the urinary bladder and may include some binucleated cells is called ____________ epithelium.
simple squamous
stratified squamous nonkeratinized
stratified squamous keratinized
pseudostratified
transitional
transitional
The heart is confined within a double-walled serous membrane sac. The part of the membrane that is in contact with the heart is the _____ layer.
visceral
serous
synovial
parietal
mesothelial
visceral
The two types of cells that make up the nervous system are
neurons and mast cells.
neurons and chondrocytes.
macrophages and mast cells.
neurons and glial cells.
mast cells and fibrocytes.
neurons and glial cells.
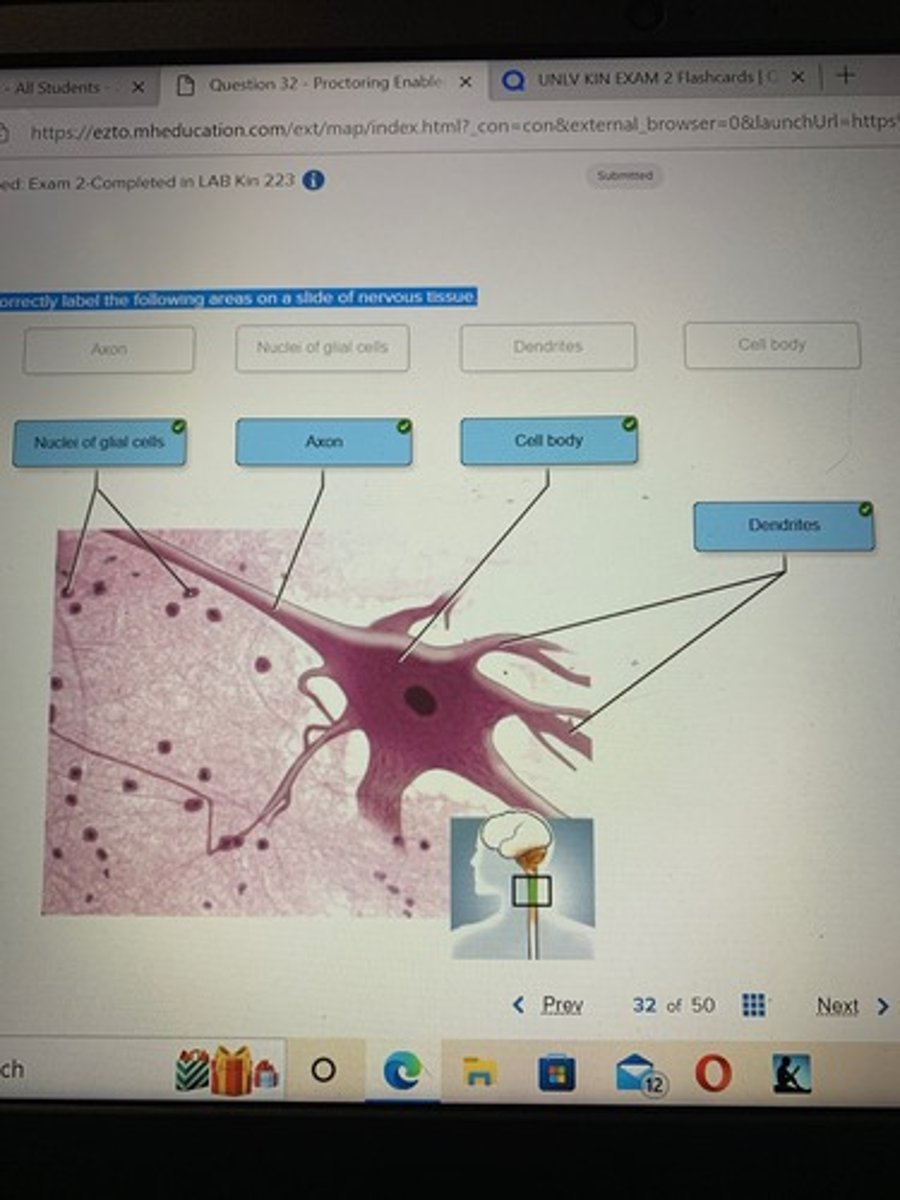
Correctly label the following areas on a slide of nervous tissue.
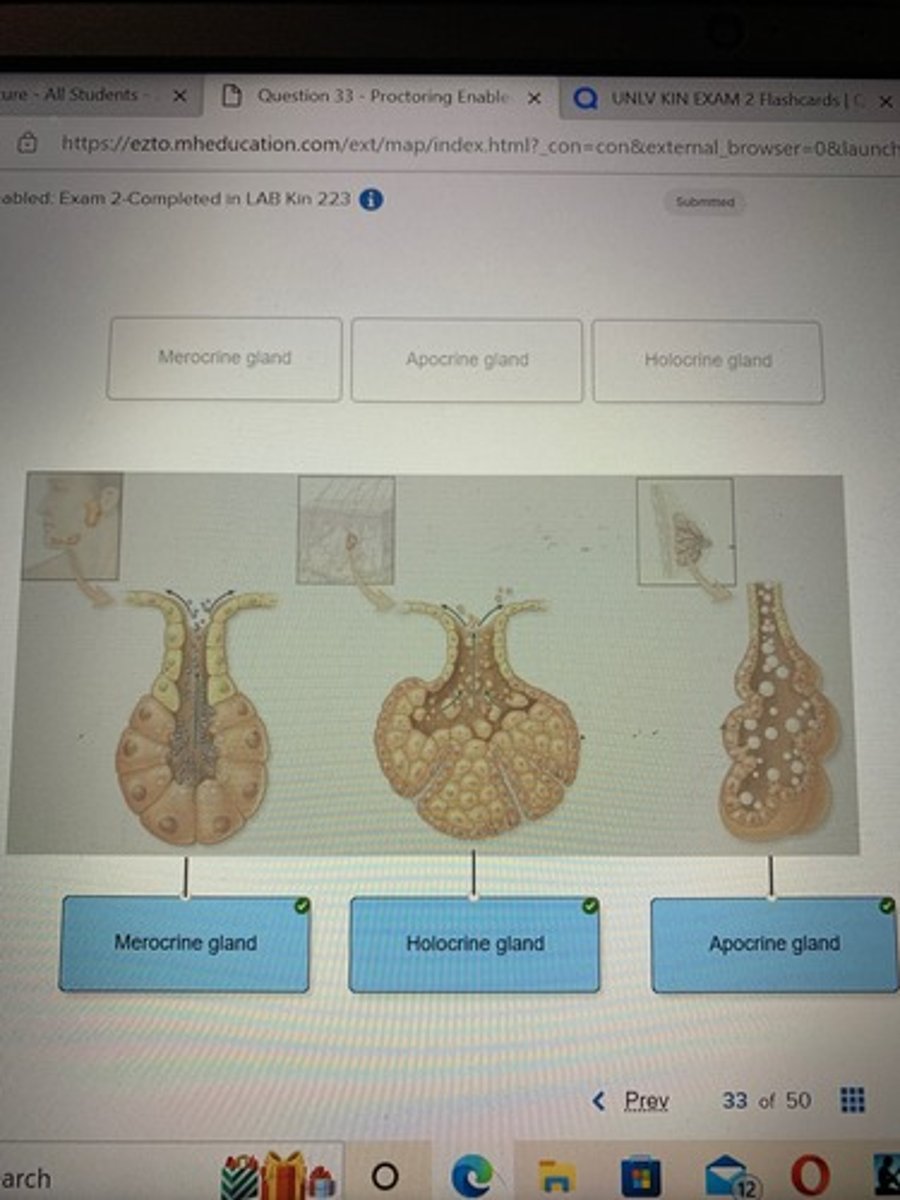
Classify the exocrine glands based on their mode of secretion.
The structure responsible for pulling on the follicle and causing "goose bumps" is the
epithelial root sheath.
internal root sheath.
papilla.
arrector pili muscle.
external root sheath.
arrector pili muscle.
Normally, skin color results from a combination of
a: melanin
b: hemoglobin
c: bilirubin
d: carotene
a, d
a, c, d
b, c, d
a, b, c
a, b, d
The integument consists of the epidermis, which is composed of _____________, and the dermis, which is composed primarily of ____________ connective tissue.
simple columnar epithelium; stratified
simple squamous epithelium; dense regular
dense irregular connective tissue; dense regular and dense irregular
stratified squamous epithelium; dense irregular
stratified squamous epithelium; dense irregular
Protects against abrasion; contains melanin, which absorbs damaging UV light
skin
hair
glands
nails
skin
Protects against abrasion; acts as a heat insulator, protects the eyes against foreign objects
skin
hair
glands
nails
hair
Produce secretions that create an environment unsuitable for some microorganisms
skin
hair
glands
nails
glands
Protect the ends of the fingers and toes from damage; can be used in defense
skin
hair
glands
nails
nails
Why might someone pale when they are exposed to a cold temperature?
Constriction of the dermal collagen and elastic fibers
Dehydration of the stratum corneum
Vasoconstriction has occurred
Purely psychological
Vasodilation has occurred
Vasoconstriction has occurred
The hypodermis is rich in adipose, and thus its functions include
frequent regeneration, structural support, and defense against infection.
maintenance of boundaries and sensation of stimuli.
water regulation and vitamin synthesis.
organ protection, energy storage, and thermal insulation.
organ protection, energy storage, and thermal insulation.
Of the following factors, which one does not contribute to skin aging?
Beginning in middle age, reduced stem cell activity in the epidermis results in thinner skin that is less likely to protect against abrasive, mechanical trauma.
Chronic overexposure to UV rays can damage the DNA in epidermal cells and accelerate aging as well as increase the risk of skin cancer.
As individuals get older, collagen fibers in the dermis decrease in number and organization, and elastic fibers lose elasticity.
The skin increases the number and efficiency of epidermal dendritic cells, causing an increase in immune responsiveness.
The skin increases the number and efficiency of epidermal dendritic cells, causing an increase in immune responsiveness.
Which are applicable to the stratum corneum?
a: Most superficial stratum
b: Consists of about 3-5 cell layers
c: Cells are dead
d: Interlocking keratinized cells
e: Cells are anucleate
a, c, e
a, c, d, e
a, b, c, d, e
a, c, d
a, b, d
a, c, d, e
Which is not a function of the integument?
Water loss prevention
Synthesis of cholecalciferol (vitamin D precursor)
No exceptions; all are functions of the integument
Protection
Temperature regulation
No exceptions; all are functions of the integument
From deep to superficial, the order of the strata of the epidermis is
Corneum - lucidum - granulosum - spinosum - basale
Basale - granulosum - spinosum - lucidum - corneum
Spinosum - granulosum - basale - lucidum - corneum
Basale - spinosum - granulosum - lucidum - corneum
Corneum - granulosum - lucidum - spinosum - basale
Basale - spinosum - granulosum - lucidum - corneum
What type of epithelium is found in the epidermis?
Keratinized stratified cuboidal
Nonkeratinized stratified squamous
Transitional
Nonkeratinized stratitified cuboidal
Keratinized stratified squamous
Keratinized stratified squamous
Which of these are functions of hair?
a: Sensory reception
b: Heat retention
c: Immune function
d: Protection
e: Formation of Vitamin D3
a, d, e
a, b, d, e
a, b, d
a, b, c, d, e
a, b, d
Which of the following is not found in thick skin?
Sweat glands
Hair follicles
Stratum lucidum
Stratum corneum
Hair follicles
Structures found in the dermis include
a: sweat glands
b: hair follicles
c: collagen fibers
d: sensory nerve endings
e: arrector pili muscles
a, c, d
a, b, c, e
a, b, d
a, b, c, d, e
a, b, d, e
a, b, c, d, e
Nails are a scalelike modification of the stratum corneum layer of the ___.
epidermis
stratum corneum
dermis
dorsal
ventral
do
do not
epidermis
Nails form on the ___ edges of the fingers and the toes.
epidermis
stratum corneum
dermis
dorsal
ventral
do
do not
dorsal
Fingernails ___ protect the digits from damage.
epidermis
stratum corneum
dermis
dorsal
ventral
do
do not
do
Going outside on a cold day
Vasoconstriction
Vasodilation
Vasoconstriction
Jumping into a cold pool
Vasoconstriction
Vasodilation
Vasoconstriction
Sitting in the sun on a warm day
Vasoconstriction
Vasodilation
Vasodilation
Running on the treadmill at the gym
Vasoconstriction
Vasodilation
Vasodilation
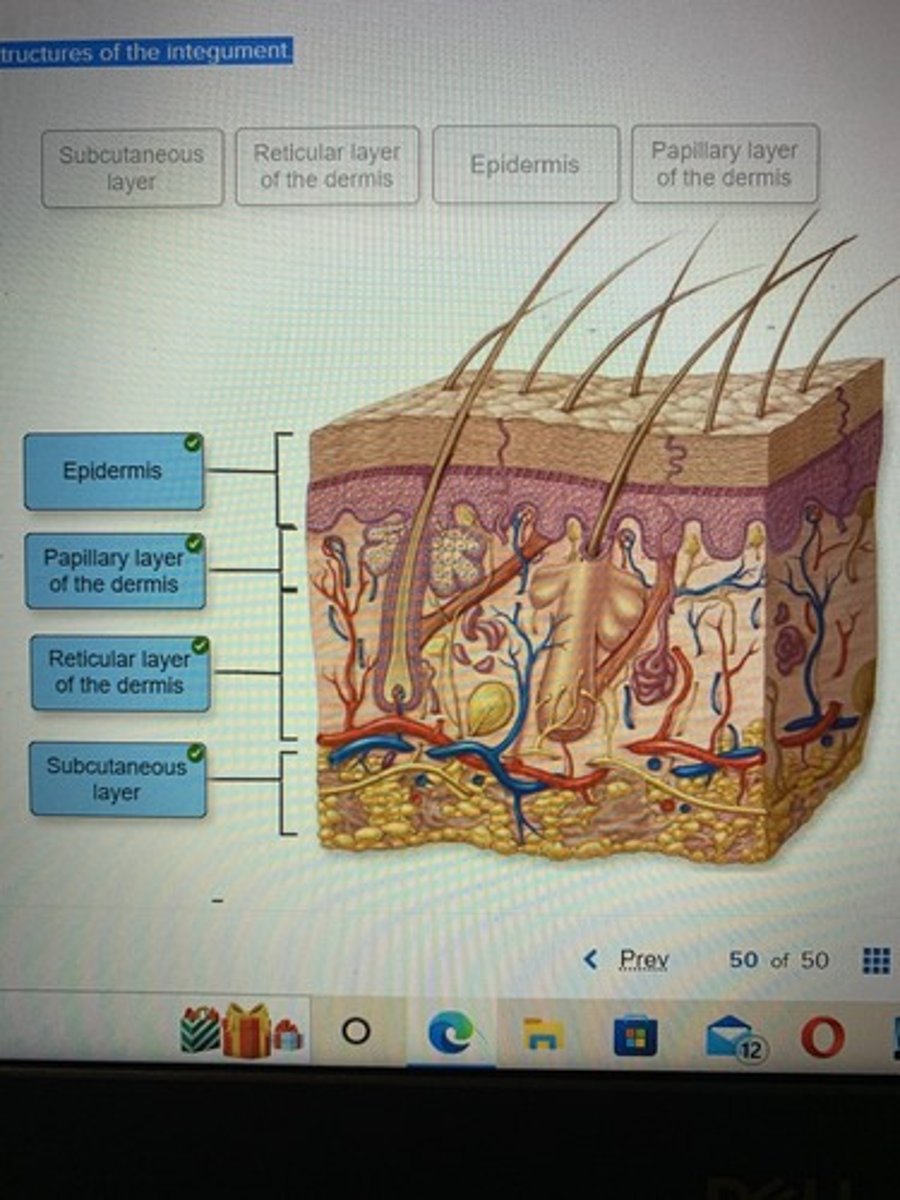
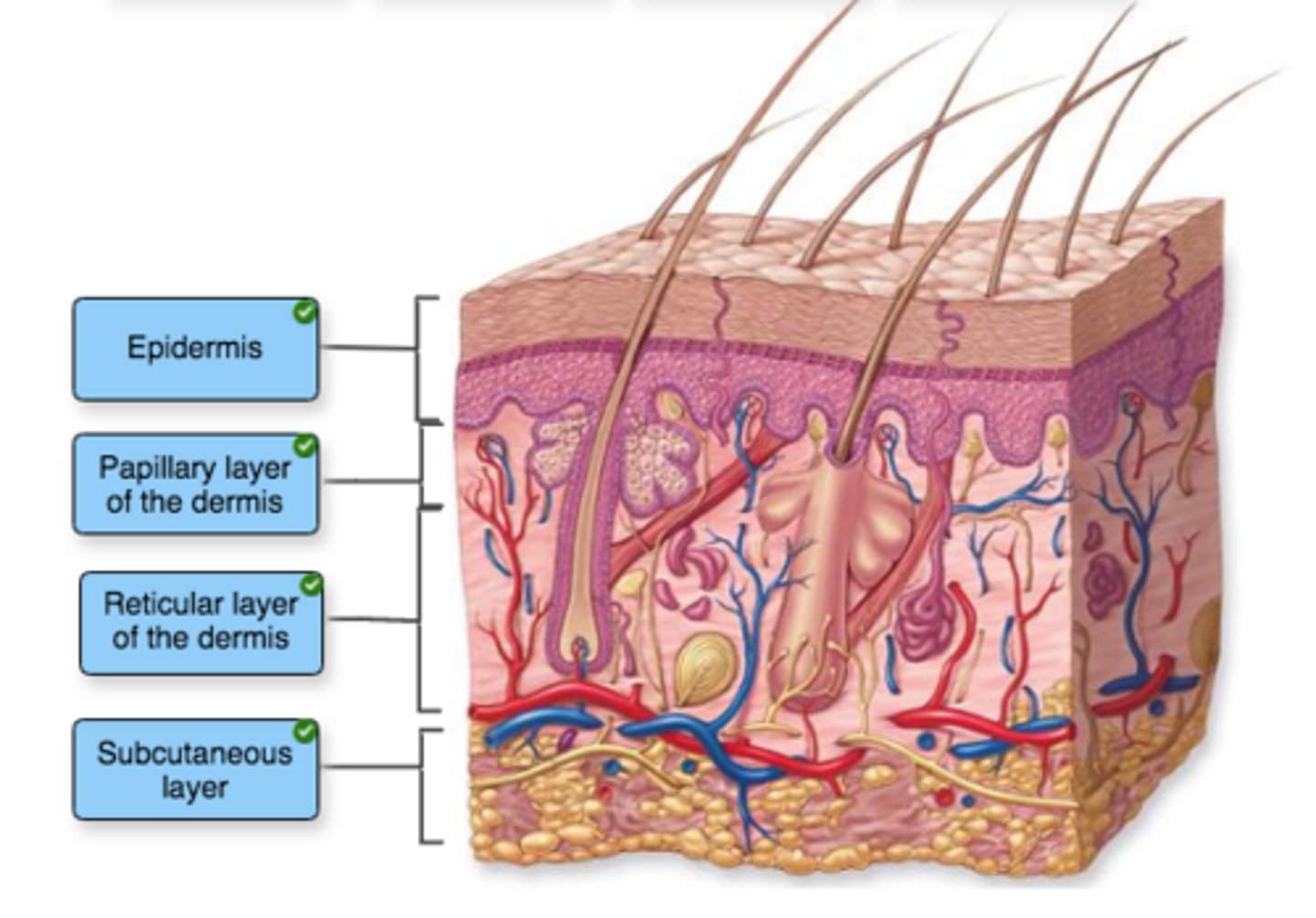
Label the structures of the integument.
Active transport requires
a. an open channel on the surface of the cell
b. a carrier protein on the surface of the cell
c. a receptor within the cell
d. an enzyme within the cell
b. a carrier protein on the surface of the cell
Translation is terminated when a stop codon is presented at the ___ site
a. a
b. p
c. e
d. b
a. a
Translation is the synthesis of
a. mRNA from DNA
b. mRNA from proteins
c. proteins from DNA
d. proteins from mRNA
e. proteins from tRNA
d. proteins from mRNA
When sugar is mixed with water, equilibrium is reached when
a. molecules of sugar stop moving
b. water and sugar molecules are moving at the same speed.
c. the dissolved sugar molecules are evenly distributed throughout the solution
d. there are the same number of water molecules as dissolved sugar molecules
e. two tablespoons of coffee are added
c. the dissolved sugar molecules are evenly distributed throughout the solution
The rate of diffusion is affected by which of the following?
a. temperature
b. size of molecules
c. steepness of the concentration gradient
d. temperature, size of molecules, and steepness of the concentration gradient
e. temperature and size of the molecules only
d. temperature, size of molecules, and steepness of the concentration gradient
Which of the following will pass through a cell membrane most easily?
a. small polar molecules
b. small nonpolar molecules
c. large polar molecules
d. large nonpolar molecules
e. large neutral molecules
b. small nonpolar molecules
Microscopic membrane extensions that extend from the plasma membrane are called
a. cilia
b. microvilli
c. flagella
d. mucus
e. desmosomes
b. microvilli
The lysosome contains ____ enzymes
a. photosynthetic
b. anabolic
c. hydrolytic
d. melancholic
e. alcoholic
c. hydrolytic
The type of epithelium that would best allow for rapid diffusion, osmosis or filtration is ____ epithelium
a. pseudostratified columnar
b. transitional
c. stratified squamous
d. simple squamous
d. simple squamous
A thin extracellular layer upon which an epithelium rests is called a(n)
a. basement membrane
b. apical surface
c. intercellular junction
d. stroma
a. basement membrane
Complete the following multiple-choice questions that describe different connective tissue types:
a. What type of tissue supports epithelium?
b. Which of the following tissues has cells residing in lacunae?
c. Osteocytes are residents of ________ tissue.
d. Tendons and ligaments are primarily made of
e. The structure of the spleen and lymph nodes are composed mainly of
a. loose connective tissue
b. hyaline cartilage
c. bone
d. dense regular connective tissue
e. reticular connective tissue
during childhood, an example of ___ occurs when the liver increases in size as the hepatocytes undergo cell division
a. hyperplasia
b. hypertrophy
c. neoplasia
d. hepatoplasia
a. hyperplasia
From which primary germ layer is the epidermis of the skin derived?
a. endoderm
b. mesoderm
c. ectoderm
d. mesenchyme
e. the epidermis is derived from all three primary germ layers
c. ectoderm
Which feature of a holocrine gland will distinguish it from merocrine and apocrine glands?
a. secretes its product into a duct
b. secretes its product to the outside of an epithelium
d. secretions are released by exocytosis
e. secretions are released by rupture of whole cells
e. secretions are released by rupture of whole cells
Which nerve cell process receives incoming signals and transmits them to the cell body?
a. dendrite
b. axon
a. dendrite
the type of epithelial tissue that is only one cel-layer tech is called ____; the type of epithelial tissue that is two or more cell-layers thick is called ____
a. stratified; columnar
b. pseudostratified; cuboidal
c. simple; stratified
d. squamous; transitional
c. simple; stratified
Correctly label the following structure of a nail
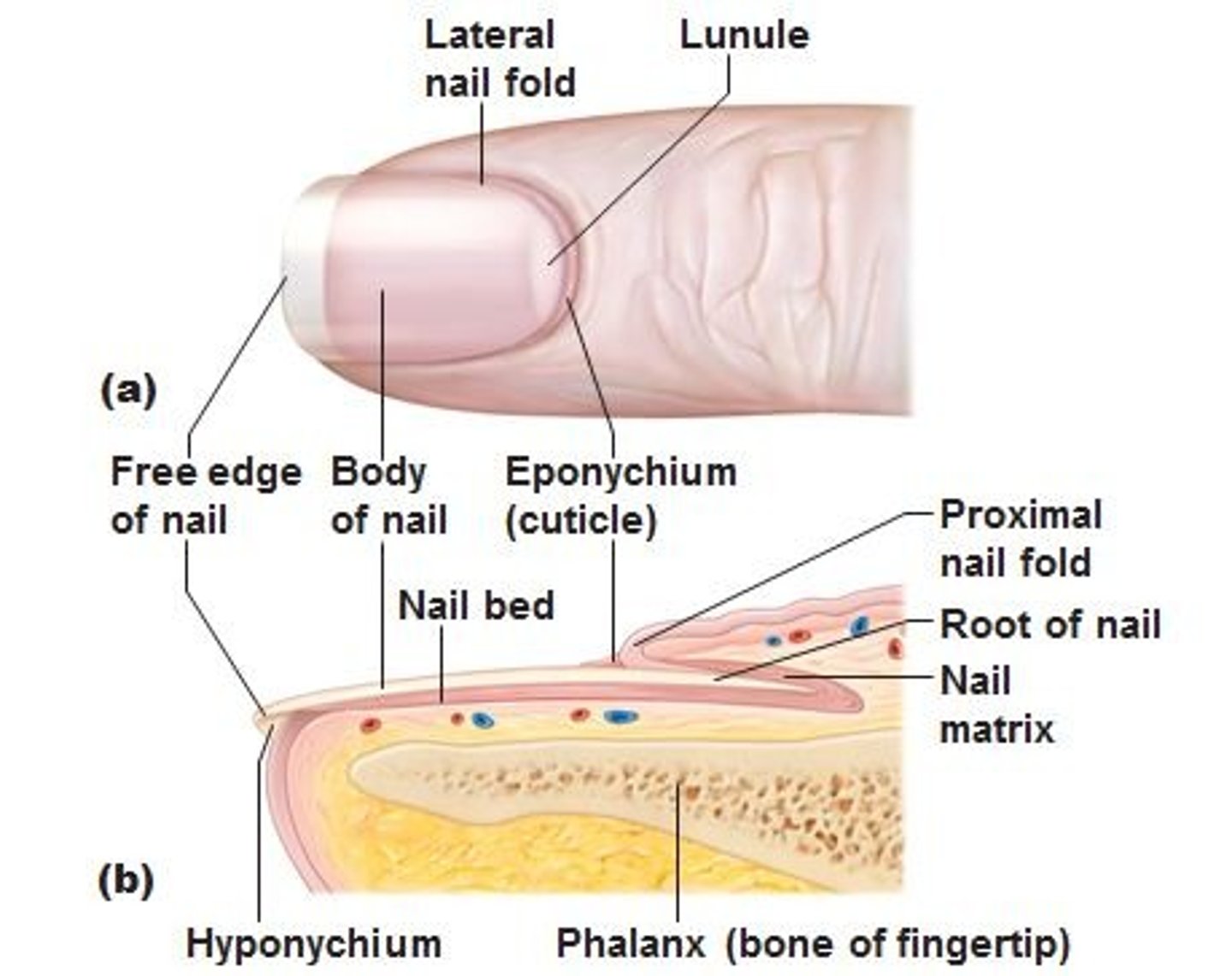
label structures of the integument
Classify the descriptions based on whether they pertain to thin or thick skin
1. found on the palm of the hands,
2. soles of feet
3. do not contain hair follicles
4. contain all 5 epidermal strata
5. contains sebaceous glands
6. does not include the stratum lucidum
7. contains hair follicles
8. found over most of the body
Thick skin: found on palm of the hands, soles of feet, do not contain hair follicles , and contain all 5 epidermal strata
Thin skin: contains sebaceous glands, does not include the stratum lucidum, contains hair follicles, found over most of the body
place the events that occur during wound healing into the correct order, using the images as a guide
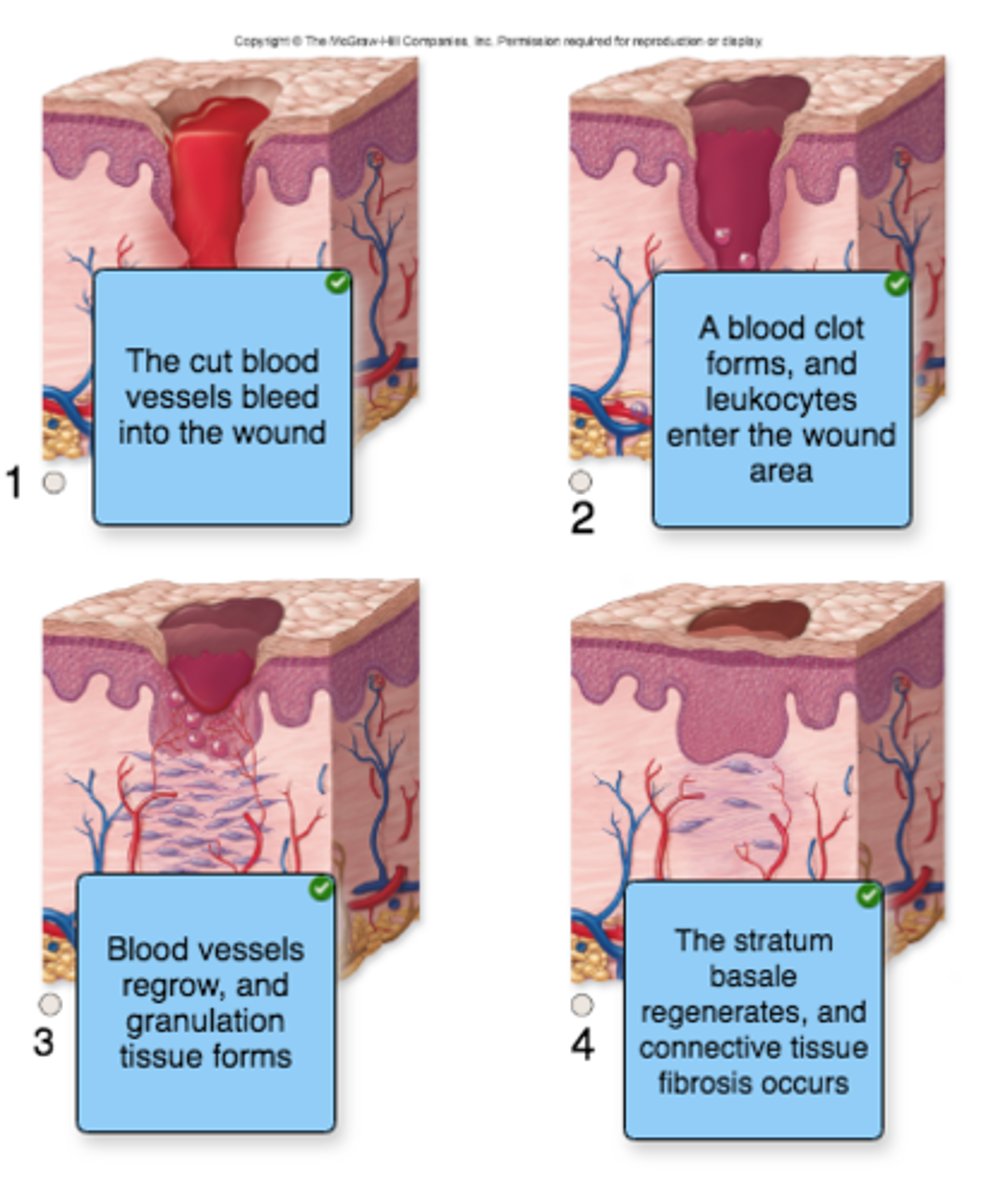
immune cells found in the epidermis are called
a. epidermal dendritic cells
b. keratinocytes
c. melanocytes
d. adipocytes
a. epidermal dendritic cells
Which of the following are functions of the skin? Check all that apply.
a. Absorption of oils or lipid-soluble chemicals or drugs, such as estrogen or nicotine, through transdermal patches
b. Excretion of sebum that lubricates the skin surface and hair
c. Secretion of the waste product urea during sweating
d. secretion of water and salt during sweating, which plays a role in electrolyte homeostasis
ALL OF THE ABOVE
Which of the following is a true statement regarding sebaceous glands? Check all that apply.
A. Sebaceous glands are a form of sudoriferous gland.
B. Sebaceous glands secrete an oily substance called sebum.
C. Sebaceous glands are modified mammary glands.
D. Sebaceous glands are responsible for the oil that coats the hair on your scalp.
A, B , D
another name for the intracellular fluid is
a. intercellular matrix
b. cisternae
c. cytoplasm
d. cytosol
e. interstitial fluid
d. cytosol
In nutrient glycogen is found stored inside a cell, it is considered a(n)
a. membrane-bound organelle
b. non-membrane-bound organelle
c. inclusion
d. pigment
c. inclusion
Glycolipids are found on the:
a. outer layer of the cell membrane, and they help make the sticky sugar coating on its surface.
b. inside of the cell, where they are a source of high-energy nutrition to power mitochondria
c. middle layer of the cell membrane and they function to transmit solutes through the membrane
d. the inner layer of the cell membrane, and they provide scaffold support to the cell membrane.
a. outer layer of the cell membrane, and they help make the sticky sugar coating on its surface.
proteins that assist the movement of a substance across the membrane are called ____ proteins
a. catalytic
b. cytoskeleton
c. identification
d. intercellular attachment
e. transport
e. transport
Cell shrinking, also known as crenation, occurs when a cell is placed into a(n) _________ solution.
a. exergonic
b. isotonic
c. hypotonic
d. hypertonic
d. hypertonic
Which is a passive transport process?
a. ion pump
b. osmosis
c. receptor-medicated endocytosis
d. pinocytosis
e. phagocytosis
b. osmosis
What is an active transport process?
a. osmosis
b. simple diffusion
c. bulk filtration
d. ion pump
e. facilitated diffusion
d. ion pump
During osmosis, water moves toward the solution with the _________ solute concentration.
a. lesser
b. greater
b. greater
the sodium-potassium pump moves both potassium and sodium down their concentration gradients, from higher to lower concentration.
a. true
b. false
b. false
To maintain a resting membrane
potential, the sodium-potassium pump
a. passively transports 3 sodium ions out of the cell and 2 potassium ions into the cell.
b. actively transports 3 potassium ions out of the cell and 2 sodium ions into the cell.
c. actively transports 3 sodium ions out of the cell and 2 potassium ions into the cell.
d. passively transports 3 potassium ions out of the cell and 2 sodium ions into the cell.
c. actively transports 3 sodium ions out of the cell and 2 potassium ions into the cell.
Removal of old organelles is via a process called
a. filtration
b. autophagy
c. autolysis
d. pinocytosis
e. vascularization
b. autophagy
which of the following serve to increase the surface area of a cell for absorption and secretion?
a.microvilli
b. flagella
c. cilia
d. cilia and microvilli
e. cilia and flagella
a. microvilli
Which are the smallest components of the cytoskeleton?
a. centrosomes
b. microfilaments
c. centrioles
d. microtubules
e. intermediate filaments
b. microfilaments