NUR4355 Infants 1 month to 1 Year
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
What age is the "WHO" growth chart used for?
children from birth to 2 years old
What age is the "CDC" growth chart used for?
children from age 2 to 20 years old
What is the typical increase in weight for an infant in their first year
they double their weight by 6 months and triple their birth weight by 12 months (1 year)
What is the typical increase in height for an infant in their first year
1 inch per month until 6 months and 1/2 per month from 6 to 12 months
How many pounds increase for an infant in their first 6-12 months
- Infants gain 1 to 2 lbs by 6 months (doubling their weight)
- Infants then gain 1lbs every months until 12 (tripling their weight)
Define gross motor skills
involve the large muscle groups and form the basis for developmental skills, such as rolling over, sitting up, crawling, and walking.
Gross motor: expect in a 1 month infants
- turn head in a supine position
- Chin up in prone position

Gross motor: expect in a 2 month old infants
- when prone, holds the chest up
- Bobs the head when sitting
Gross motor: expect in a 3 month old infants
Begin to roll to the side
When prone, props up on forearms
Gross motor: expect in a 4 month old infants
Roll front to back
No head lag when pulled up
Sits with trunk support
Props up on the wrists
Gross motor: expect in a 5 month old infants
Rolls over from back to front
When falling, puts arms out to the front
Able to sit with pelvic support
Able to sit witth arms out in front, supporting upper body
Gross motor: expect in a 6 month old infants
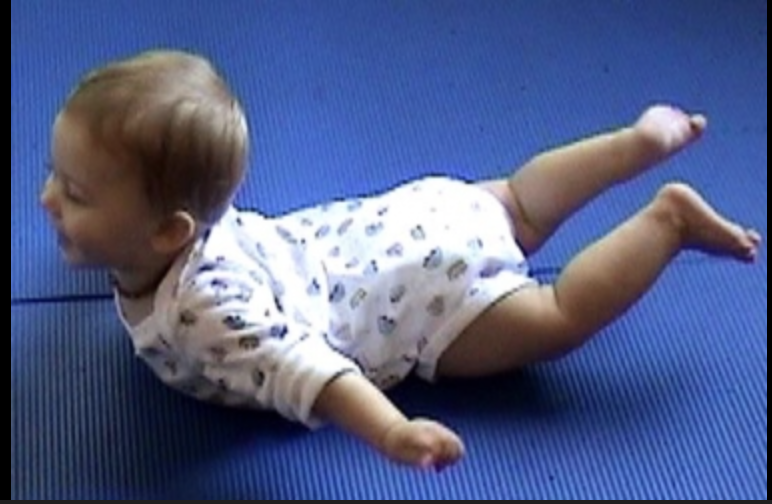
Think of pilot position:
Able to sit for a few moments propped (support) up on their hands
Bears weight on one hand in prone position
Pivots in prone position (lying on their tummy moving the arms in rotated and balancing leg up)

Gross motor: expect in a 7 month old infants
uses arms out to the sides to balance
Sits streadily without support
Bounces when held
Gross motor: expect in a 8 month old infants
Able to move into a sitting position
Crawls in a commando position
Able to pull to a sitting or kneeling position without assistance
Gross motor: expect in a 9 month old infants
Begins creeping
Pulls to stand
“stands” on feet and hands
Gross motor: expect in a 10 month old infants
Begin cruising (babies move sideways while holding onto furniture)
Able to stand of holding the hand of an adult
Able to walk if holding both hands of an adult
Gross motor: expect in a 11 month old infants
Able to move around furnitiure by holding on with one hand
Able to stand for a few seconds without support
Able to walk holding one hand of an adult
Pivot in sitting position
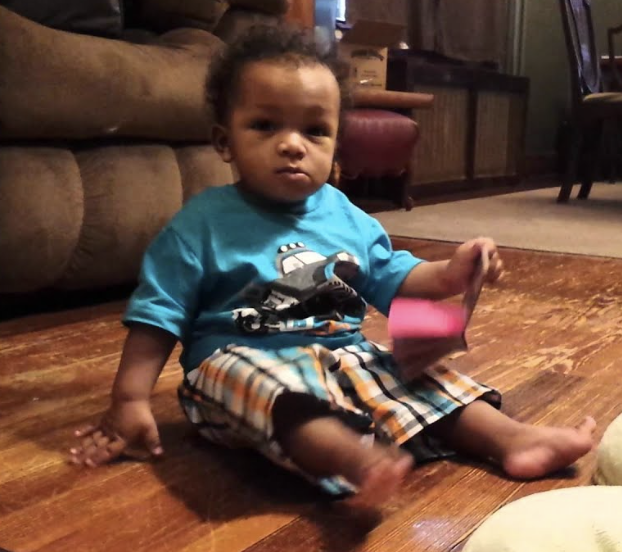

Gross motor: expect in a 12 month old infants
Able to stand up with arms upstretched and legs opened without falling
Able to walk indpendently without support
Define fine motor skills
involve small movements made by the hands and wrists, requiring coordination between the muscle groups and the brain
Fine motor: expect in a 1 month old infants
Hands in fist near face
Fine motor: expect in a 2 month old infants
50% of the time hands are open and unfisted
Able to hold a rattle if placed in the hand
Able to hold hands in the same spot together
Fine motor: expect in a 3 month old infants
Inspects fingers
Hits at objects close to body
Fine motor: expect in a 4 month old infants
Able to hold hands open most of the time
Grabs at objects close to the body, particularly clothes
Able to reach for objects tirelessly
Able to play with toys placed in hands
Fine motor: expect in a 5 month old infants
Grasps a cube with palm of hand (palmar grasp)
Transfers objects hand to mouth and then mouth to hand
Reaches/grasps things dangling in front of body

Fine motor: expect in a 6 month old infants
Transfers items from hand to hand
Can take a second object still holding on to a first
Reaches with one hand
Uses open and extended fingers to rake for things
Fine motor: expect in a 7 month old infants
Can hold an object between fingers and opposing thumb (radial palmar grasp)
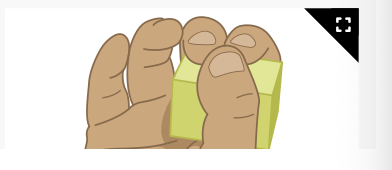
Fine motor: expect in a 8 month old infants
Hits objects with other objects after demonstration
Able to grasp things using all the fingers and the thumb (scissors grasp)
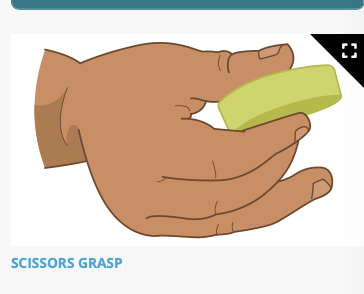
Fine motor: expect in a 9 month old infants
Bangs two cubes together
Able to grab things with the thumb and pointer or middle finger (pincer grasp)
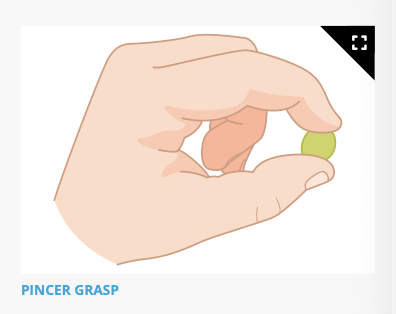
Fine motor: expect in a 10 month old infants
Isolates index finger and points at things
Can use the pincer grasp to pick up small items clumsily
Fine motor: expect in a 11 month old infants
Throws objects
Can stir something with a spoon
Fine motor: expect in a 12 month old infants
Scribbles after a demonstration
Can use the pincer grasp to pick up small things without difficulty
Holds a crayon
Attempts to put blocks on top of each other
Psychosocial motor: expect in a 1 month old infants
Can discriminate parent’s voice
Cries out in distress
Psychosocial motor: expect in a 2 month old infants
Smiles in return
Responds to adult’s voice and smile
Psychosocial motor: expect in a 3 month old infants
Follows movement in a room
Can express dislike to taste or sound
Psychosocial motor: expect in a 4 month old infants
Smiles as a result of a sight or sound
Stops crying when parent speaks
Psychosocial motor: expect in a 5 month old infants
Can recognize parent and Bonds to parent
Psychosocial motor: expect in a 6 month old infants
Stranger danger and anxiety develop
Psychosocial motor: expect in a 7 month old infants
Looks back and forth from a parent to an object when wanting help
Psychosocial motor: expect in a 8 month old infants
Able to communicate emotions
Follows the gaze of a parent to look the same way
Psychosocial motor: expect in a 9 month old infants
Separation anxiety
Able to follow a point
Visually recognizes people
Vocal/makes sounds to get attention
Psychosocial motor: expect in a 10 month old infants
Has fears
Responds to name
Psychosocial motor: expect in a 11 month old infants
Seeks out help from an adult for an object
Psychosocial motor: expect in a 12 month old infants
Seeks parent’s interest in objects
Proto-imperative pointing (Represents pointing to an object to communicate that it is desired or requested.)

Separation anxiety
The fear and anxiety an infant feels when they are separated from familiar caregivers and places.
When does Separation anxiety become pathological
If it interferes with feeding playing or sleeping
What are some interventions for soothing separation anxiety?
Giving infants stuffed animals or blankets they're familiar with to remain with them
Parents should leave infant for short period of time with a caregiver
slowly increasing intervals of separation (come back 15 minutes then 30 minutes later , then up to an hour)
remaining in a familiar environment (home)
Stranger anxiety
The fear and anxiety an infant experiences when encountering someone they are not familiar with.
By what month does stranger anxiety develop
6 months
By what month does separation anxiety develop
9 months
Typically stops at 3 years
What occurs in an infant's cognitive development from 1 month to 2 months
optical focal length is 10 inches (newborns 8 to 12 inches)
prefer contrasts of shapes, colors, and faces
develop preferences for people, objects, and high-pitched voices
What occurs in an infant's cognitive development from 2 months to 6 months
explore the environment with a sense of touch
stare at their hands and touch parts of their body
self-understandment
beginning to grasp cause and effect
achieve visual binocularity
What occurs in an infant's cognitive development from 6 months to 12 months
object performance develops:
reaching, inspecting, holding, putting objects in the mouth, and dropping objects becomes a part of sensory exploration
infant learns to manipulate the environment around them by using objects for a purpose.
Infants will begin to play games such as peek-a-boo
stranger and separation anxiety develop
first words at 11 months

Cognitive developement that parents are concern about
Disorder such as Down syndrome, fragile X syndrome, and fetal alcohol syndrome
Language motor: expect in a 1 month old infants
Reacts or startles to sounds and voices
Begins to make noises (such as cooing)
Language motor: expect in a 2 month old infants
Aware of voices and sounds
Smiles socially and makes noises that sound like vowels
Language motor: expect in a 3 month old infants
Regards someone speaking
Begins to laugh
Responds with sounds when someone talks to them
Language motor: expect in a 4 month old infants
Turns their head towards a voice when heard
Ceases crying when they hear a comforting voice
Begins to laugh out loud
Makes sounds even when alone
Language motor: expect in a 5 month old infants
Responds when name is said
Makes an “ah-goo” noise
Squeaks and squeals with excitement
Able to express anger using sounds other than crying
Makes raspberries with lips
Language motor: expect in a 6 month old infants
Stops for a minute when told no
Holds hands up when wanting to be picked up
Uses consonants when babbling
Stops to listen to someone and then vocalizes in response when they stop
Smiles and speaks to themselves in a mirror
Language motor: expect in a 7 month old infants
Looks toward a familiar object when named
Listens attentively to songs and music
Uses an increasing number of syllables when making noise
Language motor: expect in a 8 month old infants
Responds when called
Able to look for family members when asked
Says “dada” nonspecifically
Engages in echolalia (repetition of words just spoken by another person)
Shakes head for “no”
Language motor: expect in a 9 month old infants
Enjoys games with arm movements
Responds to name well
Begins to say “mama” without regards to who it is being said to
Babbles in a manner that cannot be copied
Repeats heard sounds
Language motor: expect in a 10 month old infants
Actively engages and enjoys playing games (such as peek-a-boo)
Begins to wave in response to someone else waving
Says dada to the person recognized as the father
Language motor: expect in a 11 month old infants
Stops doing something when told no
Dances to music
Begins to say first word
Makes noises or sings when listening to music
Language motor: expect in a 12 month old infants
Able to follow a simple one-step direction with hand/arm movements
Can differentiate objects when two or more objects are named
When desiring something, points in the direction of the desired object
Uses hand and arm motions (such as grabbing or reaching) with vocalizing
What is echolalia
The often pathological repetition of what is said by other people, as if echoing them.
starts at 8 months
What is the first sign of play in an infant
the social smile
appears at 4-6 weeks of age
By 3-6, the infant will look for others to interact or play with
Which milk is the most common that children exhibit allergic reactions to
protein in cows milk
How does early introduction of foods affect hypersensitivity
Research shows that early introduction decreases the development of hypersensitivity reactions
- should be introduced before 1 years
- foods such as eggs, peanuts
when should Iron drops be introdcued to infant
4 months
when should Vitamin D supplementation for breastfed infants be introduced
2 months
Risks for sudden unknown infant death
maternal age of 20 or younger
maternal smoking
lack of prenatal care
secondhand smoke
low premature birth weight
infant of male sex
overheating
At what month does the palmar grasp occur
5 months
baby closes their finger around in the palm of their hand
At what month does the radial palmar grasp occur
7 months
holds the object between all of the fingers and the opposing thumb
At what month does the scissor grasp occur
8 months
Objects are held between the thumb and the side the of index finger
At what month does the pincer grasp occur
9 months, becomes "fine at 12 months"
grabs things with the thumb and the pointer or middle finger
At what month can the toddler scribble after the demonstration
12 months
At what month does the head lag stop?
4 months
infant is able to hold their head up without flopping around or lagging behind upper body
At what month does creeping movement begin
9 months
crawling movement with the stomach elevated off the floor
also starts pulling up to stand
At what month does cruising begin
10 months
able to cruise or move around furniture by holding on with both hands
When is the infant able to roll to the side versus the back to the front, and get into sitting position
3 months: roll over onto the side
4 months: rolls from front to back
5 months: roll from back to front
8 months: sitting position
When can the infant discriminate parents' voices
1 month
what is Proto-imperative pointing
represents infant pointing at an object to communicate desire or request of it
occured at 12 months
Breastfeeding decreases the risk of
Ear infection
Respiratory infections
Asthma
Development of SUID
Formula fed increases the risk of
Chronic disorders such as
Asthma
Diabetes mellitus
Respiratory
Ear infection
Preterm infant should be fed using what
both colostrum and breast milk
Educate mother based on feeding with bottle
- Position bottle at angle to prevent aspiration and choking when feeding
- Never prop the bottle UP this will increase risk for ear infection, tooth decays, and choking
- Never place infant in bed with bottle or leave it when sleeping
- Leftover formula after feeding should be discarded (increased risk for bacterial growth)
How does breastfeeding prevent infection
provides IgA
Until what age should cows milk be avoided
do not introduce until after 12 months
infant is unable to digest properly
Until when should bottles continously be sterilized
until after 4 months of age
when is the first meal used to introduce solid foods in what month?
After 6 months, Iron fortified cereal mixed with breast or formula milk
Add new food every 3 to 5 days
Introduce vegetable, fruit, then meat
Solid food once a day then progress to two/three times daily
What kind of food is unsafe for the infant
HONEY 🍯 🐝 (source of bacteria clostridium botulinum)
What should be introduced first, fruits or veggies?
veggies first before fruits (introduce taste for veggies rather than sweet tooth)
What kind of mothers shouldn’t breastfeed their infants?
Mothers with
HIV and AIDS due to because virus can be passed down to the infant through breast milk
untreated tuberculosis
severe malnutrition
active herpes sores on breast/nipples
(alcohol substances and certain medication can also be passed down to infant)
What foods are known to cause food hypersensitivity commonly
peanuts
soy
milk
wheat
Why Infant is at risk for iron deficiency anemia?
Breastmilk contain a very small amount of iron in them. This is why Iron drops are recommended at 4 months of age
What month that AAP recommends these infants to receive vitamin D
Within the first 2 months of life
What vitamin suppment mother are require to take if they are vegan
vitamin-B12 deficient mothers require supplementation of vitamin B12
Sleep issues
Infants 3 months and younger get 16 to 17 hours of sleep
Infants 4 months to one year should get 13 to 14 hours of sleep per day
Encourage parents to establish sleep schedule for infant to calm down and sleep
What is Failure to thrive
Inability to convert calories to energy or not properly intaking calories
weight for age that Less than 5th PERCENTILE on CDC growth chart
Neglect and lack of parent education can result in lack of feeding and failure to thrive
(think you fail your baby)