Rickets Pathology
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering important concepts, causes, symptoms, imaging, and treatment of Rickets.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What is rickets?
A disease in children where bones soften and deform due to defective mineralization.
What age group does rickets primarily affect?
Infants and young children.
What are the two main classifications of rickets?
Metabolic and genetic.
What is the most common cause of rickets?
Vitamin D deficiency (nutritional rickets).
What are other causes of rickets besides deficiency?
Malabsorption disorders like Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, and ulcerative colitis.
What populations are at higher risk for rickets?
Premature infants, children with darker skin, and those in northern latitudes.
Why does exclusive breastfeeding pose a risk for rickets?
Breast milk lacks sufficient vitamin D.
What is the most common symptom of rickets?
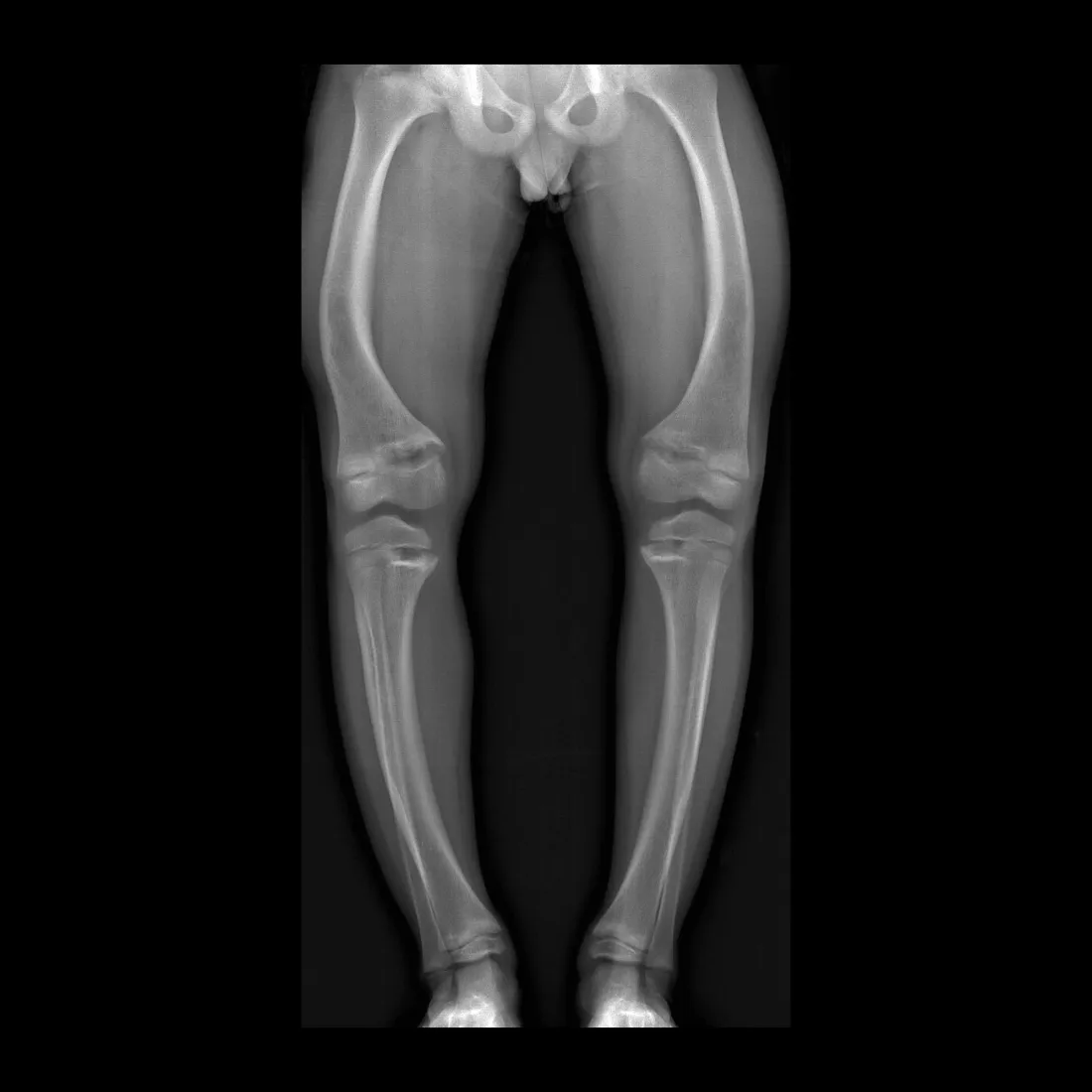
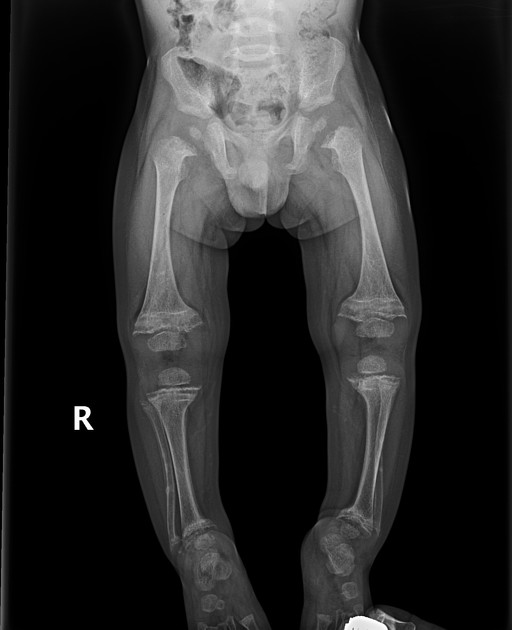
Bowed legs.
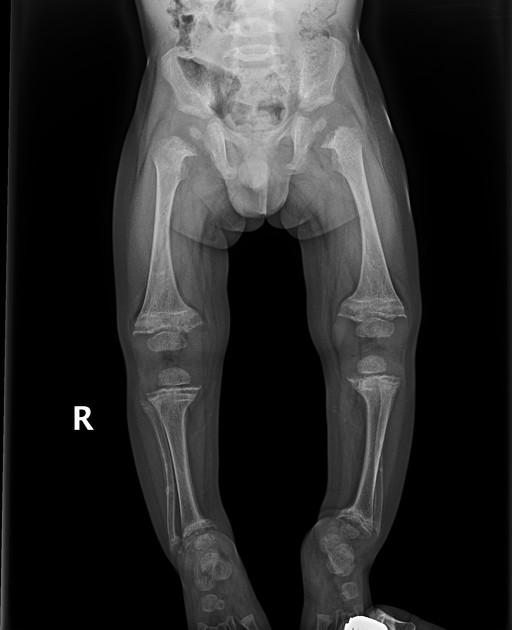
What other physical signs are associated with rickets?
Growth delay, skull deformities, thickened wrists, and ankle swelling.
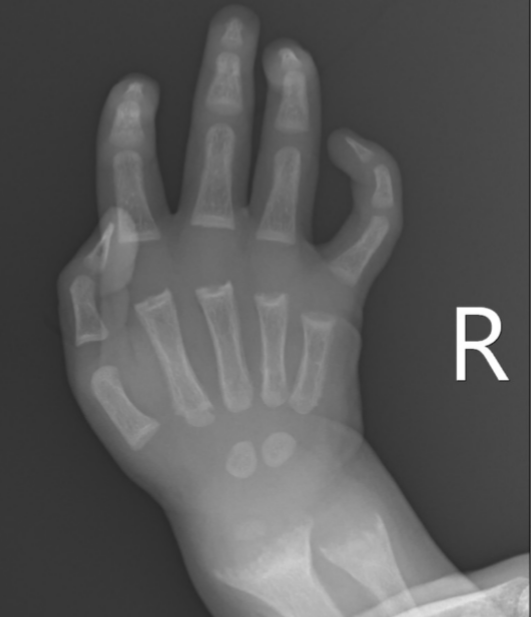
What is the most common form of rickets pathologically?
Calcipenic rickets caused by vitamin D deficiency.
What biochemical chain reaction occurs in vitamin D deficiency?
↓ Vitamin D → ↓ Ca absorption → Hypocalcemia → ↑ PTH → ↑ phosphate excretion → Hypophosphatemia.
How does hypophosphatemia affect bone growth?
It impairs chondrocyte apoptosis, leaving growth plates unmineralized.
What is the best imaging modality to diagnose rickets?
Plain X-rays.
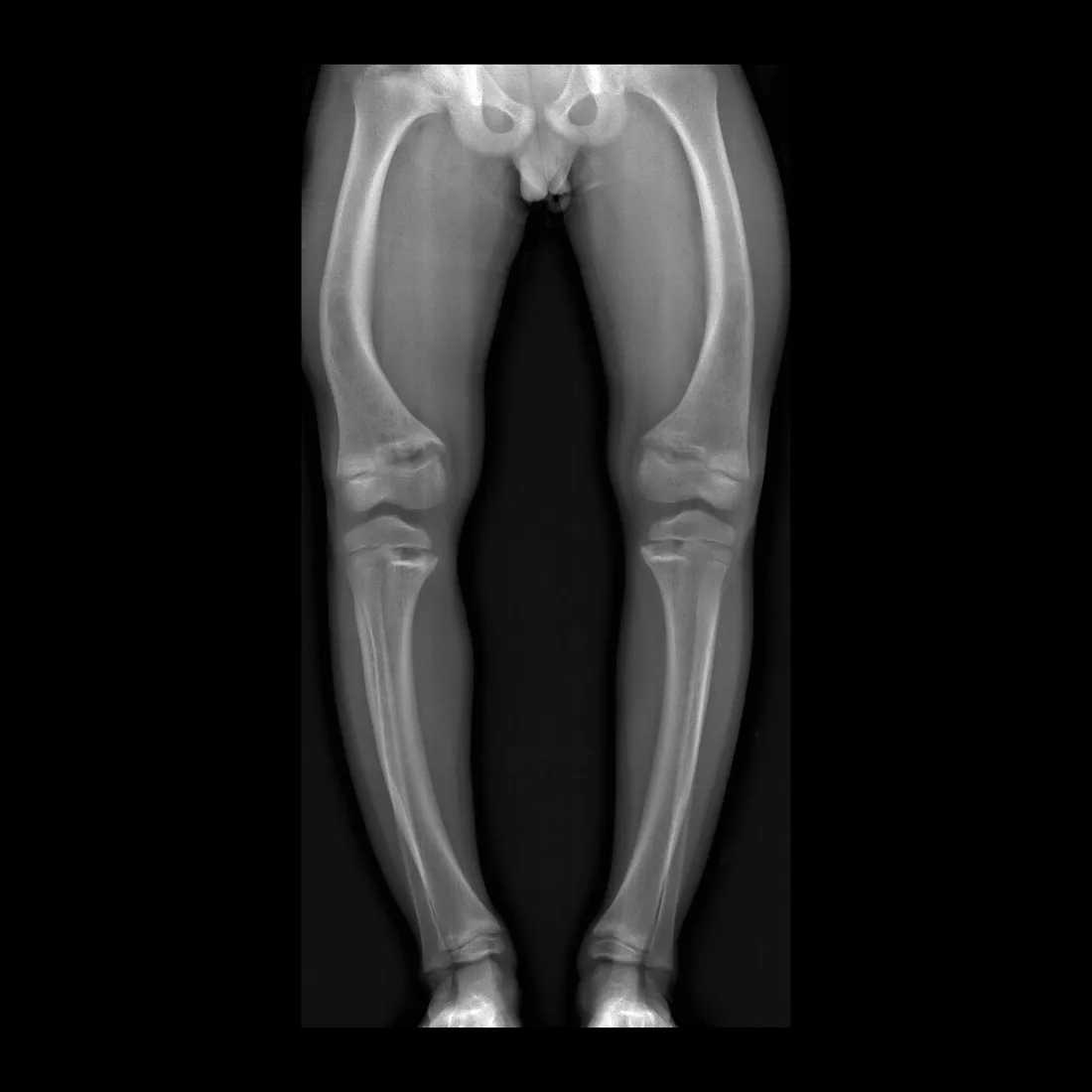
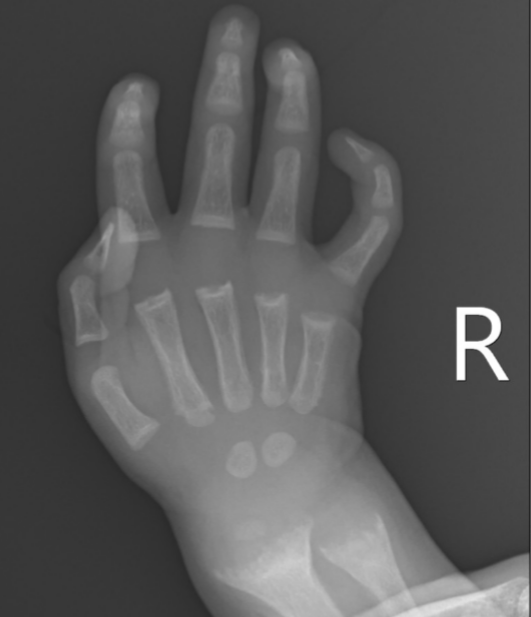
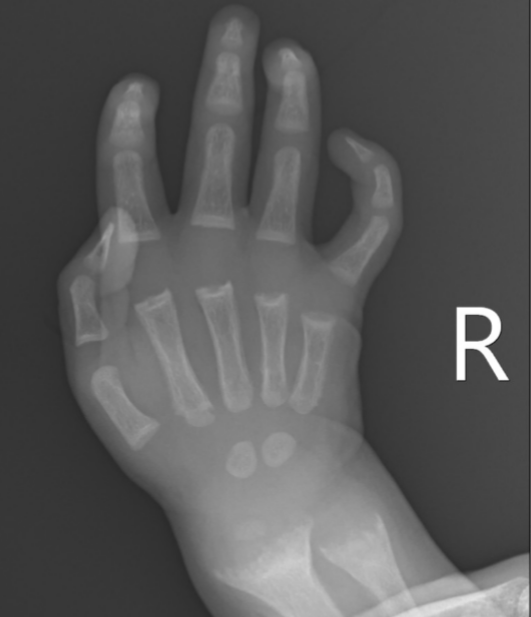
What is seen on X-rays of a rickets patient?
Bowed legs and widened wrists due to metaphyseal cupping.
What causes the widening at the metaphysis in rickets?
Accumulation of non-mineralized bone tissue.
What mineral supplements are used in rickets treatment?
Vitamin D and calcium.
Why is outdoor activity recommended for rickets patients?
Sunlight exposure boosts vitamin D production.
What orthopedic device can be used in rickets?
Braces to correct bone alignment.
What surgical option treats severe rickets deformities?
Hemiepiphysiodesis, which uses metal plates to guide bone growth.
Why must metabolic control be achieved before surgery?
Without correcting rickets first, bones won’t heal or grow properly post-surgery.