Understanding Emotion, Prejudice, and Relationships
1/217
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
218 Terms
Thoughts
Cognitive processes like perception, memory, reasoning.
Feelings
Emotional responses influencing motivation and attitudes.
Behavior
Actions and decisions influenced by emotions.
Survival
Avoiding negatives and approaching positives.
Emotion
Temporary state motivating adaptive behavior changes.
Moods
Long-lasting emotional states not linked to events.
Affect
Broad evaluation of experiences as good or bad.
Cognitive change
Focuses resources on relevant situations.
Physiological change
Prepares body for action via hormonal responses.
Action tendency
Increases likelihood of goal-oriented behavior.
Communicative signal
Displays conveying intentions through facial and vocal cues.
Feeling
Subjective experience guiding goal-oriented actions.
Happiness
Enhances cognitive breadth and creative thinking.
Negative emotions
Signal issues, narrowing focus on problems.
Position emotions
Broaden attention and associations for better outcomes.
Threat construal
Perceiving inability to achieve a difficult goal.
Challenge construal
Believing in ability to achieve a difficult goal.
Flow state
Optimal experience during challenging tasks.
Action intensity
Depends on emotion severity and available options.
Valence
Positive or negative evaluation of emotional experiences.
Arousal
Physiological activation level accompanying emotions.
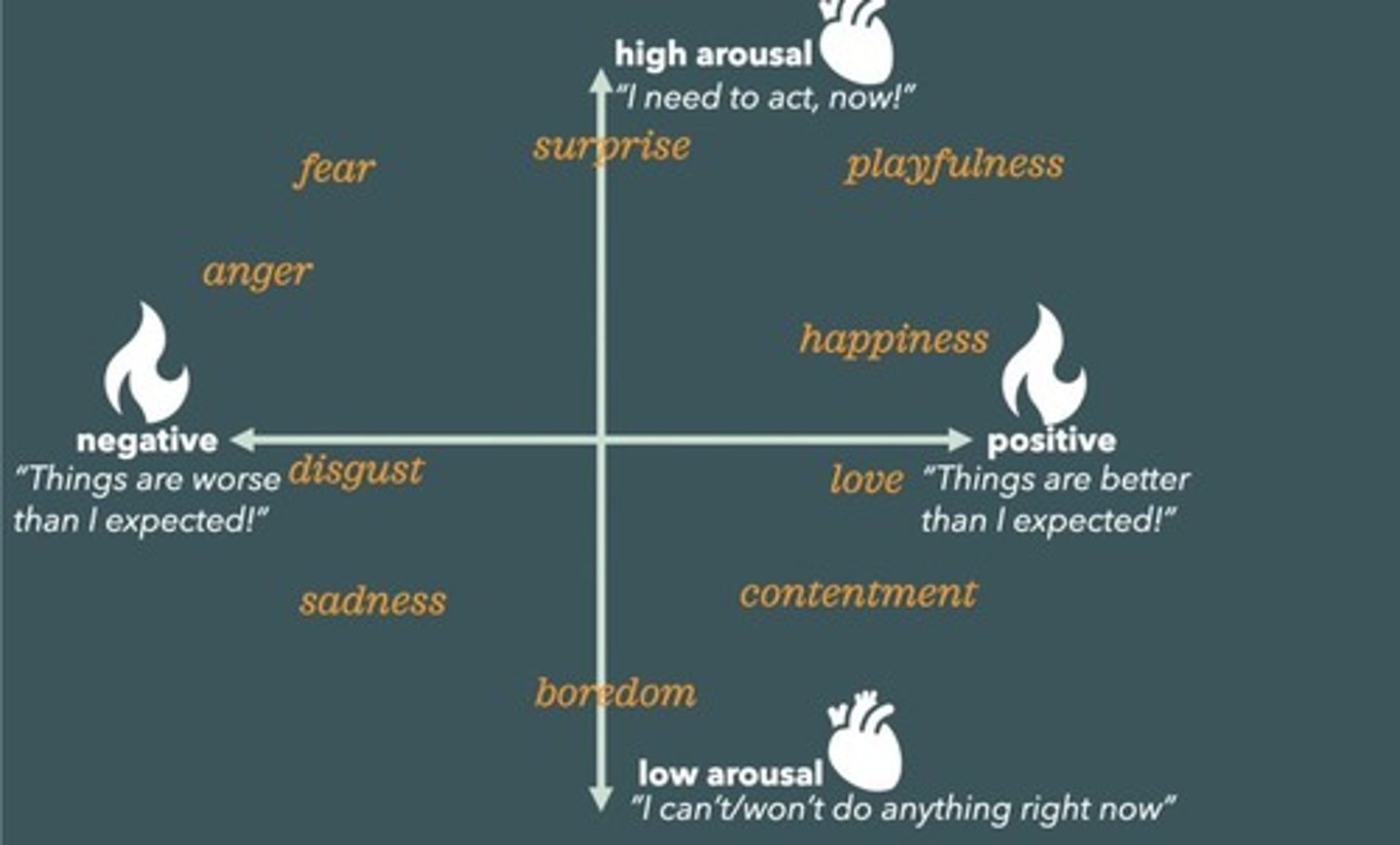
Construal
Appraisal process determining emotional state.
Intensity of emotion
Determined by relevance to personal goals.
Cognitive resources
Mental capacity allocated to process emotional situations.
Construal Tree
Framework indicating how construals shape emotions.
Emotional Regulation
Managing emotional states for desired outcomes.
Reappraisal
Changing perception of a situation to alter emotions.
Suppression
Inhibiting emotional expression or experience.
Emotion
Temporary state driving behavior and physiological changes.
Attitudes
Stable evaluations of people, objects, or ideas.
Origins of Attitudes
Formed by past emotions, beliefs, and experiences.
Affective Component
Emotional aspect of attitudes influencing evaluations.
Play
Engaging in fun activities, often exploratory.
Phylogenetic Play
Play behavior observed in mammals and non-mammals.
Building Blocks of Play
Cognitive, physiological, and communicative changes during play.
Cognitive Change
Broadening associations and forming novel connections.
Physiological Change
Alterations in bodily responses during play.
Action Tendency
Unpredictable and awkward movements during play.
Communicative Signal
Signals like laughter indicating playful behavior.
Costs of Play
Energy expenditure and potential for injury.
Functions of Mammalian Play
Developing skills and practicing adult behaviors.
Stereotypes
Schemas about categories of people influencing behavior.
Intergroup Bias
Cognitive, emotional, and behavioral components of prejudice.
Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
Beliefs leading to behaviors that confirm those beliefs.
Prejudice
Emotionally charged attitude towards a group.
Discrimination
Behavioral manifestation of prejudiced attitudes.
Warmth and Competence
Core dimensions in stereotype evaluations.
Stereotype Content
Determines attitudes based on warmth and competence.
Group Evaluation
Assess group attributes related to personal goals.
Perceived Threat
Different threats lead to varied discrimination forms.
Contamination Threat
Leads to feelings of disgust.
Imminent Threat
Causes feelings of fear.
Intentional Blocking
Results in feelings of anger.
Distal-Level Factors
Situational factors like environment and migration.
Proximal-Level Factors
Cultural products and social interactions influence behavior.
Psychological Factors
Includes thinking, feeling, and personality traits.
Implicit Bias
Unconscious attitudes affecting behavior and judgment.
Explicit Bias
Conscious attitudes and beliefs about groups.
Social Influence
Impact of group dynamics on individual behavior.
Discrimination Effects
Harms safety, health, resources, and social capital.
Chronic Stress
Long-term stress due to discrimination experiences.
Internalized Prejudice
Acceptance of negative stereotypes about oneself.
Stereotype Threat
Fear of confirming negative stereotypes affecting performance.
Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
Expectation leads to behavior that confirms it.
Cognitive Load
Increased mental effort due to stereotype management.
Meta-Analysis
Study of 328 studies on discrimination's psychological impact.
Disadvantaged Groups
More affected by perceived discrimination's psychological effects.
Prejudice Reduction Strategies
Methods to combat prejudice through changing mindsets.
Contact Hypothesis
Promotes cooperation among groups to reduce prejudice.
Implicit Bias Training
Tools to recognize and combat personal biases.
Injunctive Norms
Statements of what behaviors are considered acceptable.
Descriptive Norms
Describes what behaviors are commonly practiced.
Active Integration
Removing barriers to promote equality and inclusion.
Stereotype Replacement
Recognizing and replacing stereotypical thoughts.
Counter-Stereotypic Imaging
Imagining individuals who defy stereotypes.
Perspective Taking
Adopting the viewpoint of stigmatized individuals.
Contact
Increased exposure to stigmatized groups reduces prejudice.
Confrontation
Directly addressing prejudice to promote change.
Hypothetical Confrontation
Preferred method for Black participants in studies.
Direct Confrontation
Addressing prejudice without avoidance or ambiguity.
Targeting Action
Focusing on specific prejudiced behaviors.
Labeling Prejudice
Identifying actions as prejudiced to raise awareness.
Systemic Racism
Linking individual prejudice to broader societal issues.
Calm Approach
Typical advice to remain composed during confrontation.
Internal Attribution
Believing behavior stems from personal traits.
Stable Attribution
Viewing behavior as consistent over time.
Global Attribution
Generalizing behavior across different situations.
External Attribution
Attributing behavior to situational factors.
Temporary Attribution
Seeing behavior as changeable and context-dependent.
Specific Attribution
Focusing on particular instances of behavior.
Behavior-focused Confrontation
More effective in changing perpetrator's actions.
Person-focused Confrontation
Feels like rejection, hindering relationship repair.
Prejudice
Cognitive and affective processes applied to social categories.
Stereotype
Cognitive belief about a group of people.
Discrimination
Behavioral manifestation of prejudice against individuals.
Aggression
Behavior intended to harm or intimidate others.
Hostile Aggression
Emotional response aimed at removing a threat.
Instrumental Aggression
Planned attack for personal gain or reward.
Frustration-Aggression Hypothesis
Frustration can lead to aggressive behavior.
Relational Aggression
Harming others through social manipulation or exclusion.