TOPIC 2- Microbial Cell Structure and Function
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
cytoplasmic membrane

inner leaflet
side of the phospholipid bilayer closer to the inside of the cell
outer leaflet
the side of a phospholipid bilayer closer to the outside of the cell
integral membrane proteins
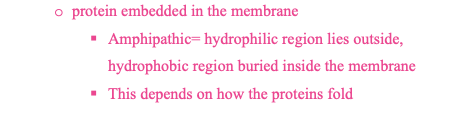
peripheral membrane proteins

ether linked
the bond type for the phospholipids present in Archaea cell membranes
ester linkage
the bond type for the phospholipids present the Bacteria and Eukarya cell membranes
isoprene
makes up the hydrocarbon chains on the phospholipids on Archaeal cell membrane; makes the membrane less fluid bcuz they fit together well. this leads to better membrane fluidity at higher temperatures
phytanyl
some archaeal membranes are made of glycerol diether phospholipids w long branched tails called ________
diglycerol tetraether phospholipid
other archaeal membranes are made from _____ _______ _____, which forms a monolayer
facilitated diffusion

active transport

saturation effect
happens in active transport
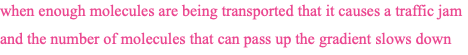
simple transporter
type of active transport
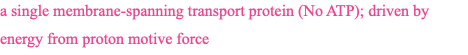
symport
a type of simple transport

antiport
a type of simple transport
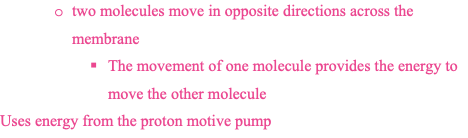
group translocation
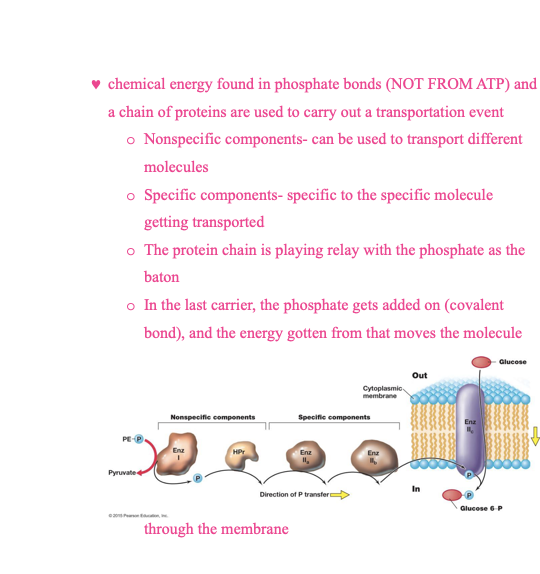
ATP binding cassette transportation system

periplasmic binding protein
ABC Transportations system

ATP binding protein
ABC transportation system

monoderm
gram-positive cell wall; 1 thick layer of peptidoglycan
diderm
gram-negative cell wall; a thin layer of peptidoglycan and an outer membrane
lysozyme
penicillin

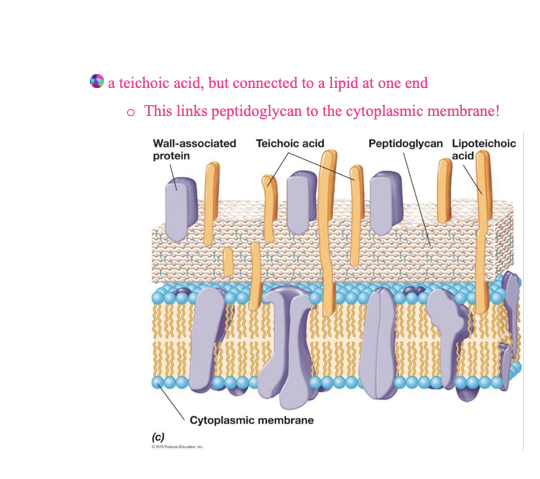
teichoic acids
lipoteichoic acid
outer membrane
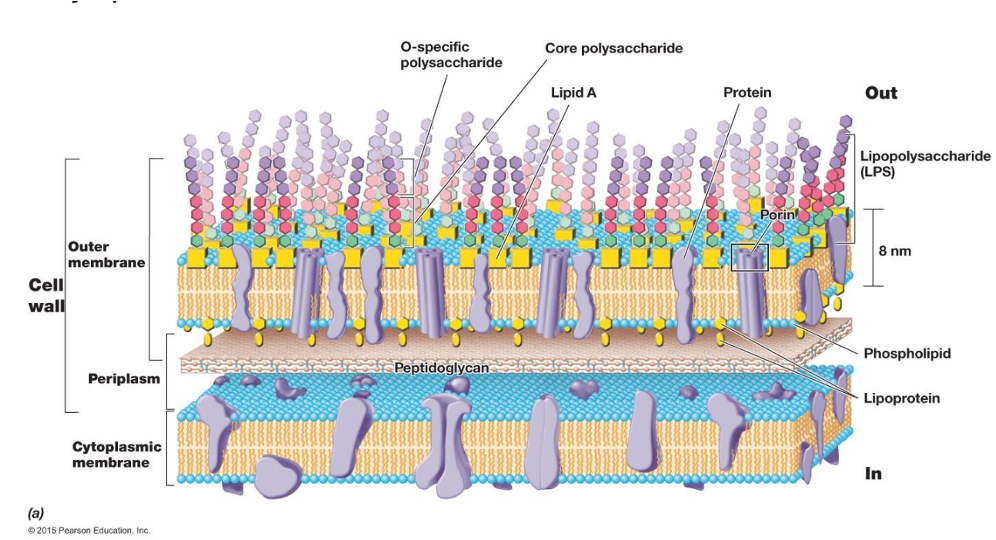
additional phospholipid membrane on gram-negative bacterial cells with LPS units attached
periplasmic space

lipid a
porins

periplasm
substrate binding protein
binds substrates and moves them to the cytoplasmic membrane for transport into the cell in the periplasm
hydrolytic enzyme
degrades foreign substances in the periplasm
penicillin binding proteins

s-layer

pseudomurein

lipoglycan
tetraether lipid monolayer cytoplasmic membrane
cytoplasm
the material bounded by the cytoplasmic membrane
nucleoid

plasmids

ribosomes
site of protein function for all cell functions
cytoplasmic ribosomes
makes cytoplasmic proteins so the ribosomes floats freely in the cytoplasm
membrane associated ribosomes

capsules and slime layers

fimbriae

pili

carbon storage polymers

polyphosphate granules

sulphur granules
magnetotaxis
magnetosomes
gas vesicles

vegetative cell
a normal, metabolically active cell capable of normal growth
endospore

septum
line that separated the forespore and the mother cell
core wall

cortex

flagella
filament

flagellin
identical protein subunits
hook
special part of the flagella that connects the filament and the basal body
basal body

random walk

biased random walk

twitching motility

gliding motility

eukaryotes
organisms with a true nucleus
histones
DNA that has been wound around a lot to organize it; so it doesn’t tangle