Spatial Composition Final
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Benefits of using regulating lines
Gives visual representation of relationships (clarity), organizes elements, guards against capriciousness, gives hierarchy, clarity of design, relates most important elements. Don’t express axis. Don’t run all the way through unless defining at ends.
Elevation vs. facade
Elevation is lifting something up from plan, doesn’t show everything. Facade is the artful design of the face of a building, its shows all details and components. Elevation is the plan reflected, the facade doesn’t necessarily reflect the plan, doesn’t show interior composed as exterior surface.
Arnhiem’s diagram
Highlights the importance of corners in a square
Anti-space vs. space according to Petterson and Littenberg and in the urban fabric
Anti-space is the left over space between a grid and a landmark. It is space with no boundaries, it is left over, but not necessarily a void. If there is a grid, and a landmark is placed non directly on the grid, the anti-space is the area between the grid and the landmark. Space is more purposefully designed. Space is defined by us, using planes, edges, corners, etc. Anti space is undefined, the inverse, for example a building in a park that is not defining anything around it, not aligned with edges, just floating.
Characteristics used to group building typologies
Formal relationships (ovals, circles, rectangles), Functional relationships (hospitals, schools, etc), and Organizational relationships (by program, form, entrance, gallery)
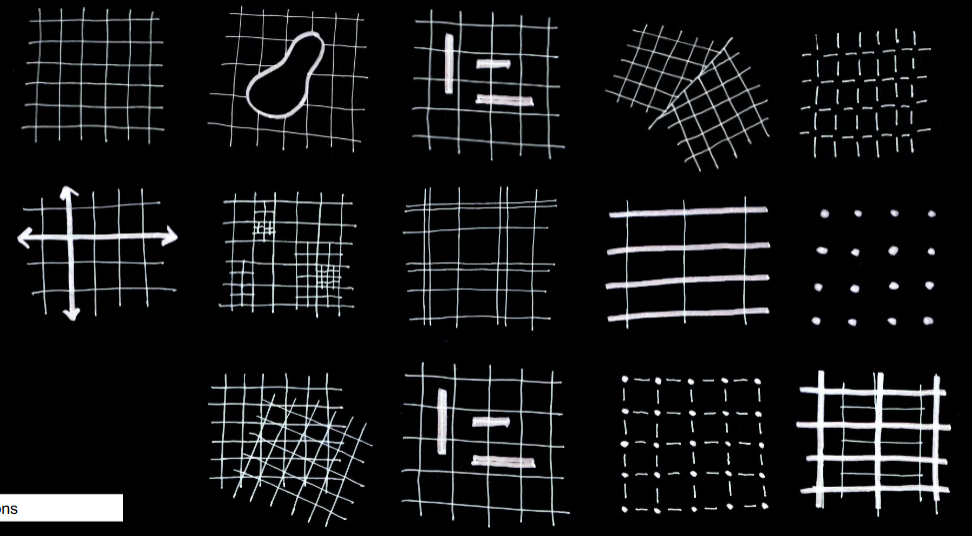
Orthogonal
Intersecting or lying at right angles. Common, uses standard materials and tools, wayfinding, repeatable, modular, grid might be limitation
Non-orthogonal
Inherent complexity dynamic, responds to site forces, makes a statement, responds to program. Lose repetitive nature, lose reusability. Some of earliest structures were non orthogonal. Reasons to use: we are not orthogonal, landscape is not orthogonal, acoustics are better. Not as defined, more free. Form can carry meaning.
Articulation
individual elements are expressed, how it contributes. Action or manner of jointing or interrelating, of giving utterance and acceptance. Small elements, parti fi s a piece, articulation is the detail. It highlights
Tectonics
expression of structure, construction, materiality (exposed beam, column). Tectonics are the poetry of construction. Clarity (shows how thing is put together, structure expressed). Internal dialog (old + new). Context (very different than something surrounding but still responding to context)
Transformation
To change (composition, structure, shape, form character). Not open ended. Stretches will look the same
Types of cities
Organic city, (added to overtime, small scale organization decisions, displays series of moments. Grided city (strictly planned, block by block pattern. Grand manner (organized by important buildings, DC, Rome. You know where you are based on those buildings. All cities organized by paths, edges, districts, nodes, landmarks.
Parti
Simple and repetitive. Space within a space, our inherent sense of order
Reasons for the grid
Orthogonal furniture, fits into buildings way easier, grids make it clear what is important, easier to understand, relate spaces where ever they sit, produces hierarchy (of streets and blocks), easier to measure area and fit things, produces housing for lots of people and is less expensive, easy to create, repeat, expandable and entirely the same, can be reduced.
Parti
Course of action, strategy of choice, decision, outline, thesis. Prendre part: to make up one’s mind, to take part.
Analysis
Detailed exam of elements or structure of something, a basis for discussion or interpretation. Contrasted w/Synthesis
Composition vs. compose
Composition into artistic form, compose is to orderly form.
Typology
The method of studying or grouping phenomena that are similar to one another. As a analytical tool, organizes thoughts, explores all possibilities. Organizational relationship, and problem solving tool.
Proportions
The comparative, proper, or harmonious relation of one part to another or to the whole.
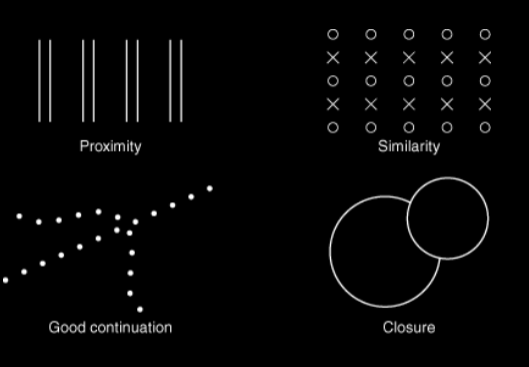
Gestalt Psychology - Principles of how people organize into patterns
Proximity, similarity, good continuation, closure
Frank Lloyd Wright
The complete architect is a master of the elements:
earth, air, fire, light, and water.
Typology vs. Taxonomy
Typology is The study of, or analysis or classification based on types or categories. Taxonomy is the study of general principles of scientific classification. Ordering and naming of groups.
Parti extra definitions bc its hella confusing
Parti’ encapsulates the essential minimum of
the design, without which the scheme would
not exist, but from which the architecture can
be generated.
Parti: Course of action, strategy, choice,
decision
Diagram that defines the basic spatial organization of a project. Not the same as a concept or a program, it is the geometry/structure.
Types of Grids
Non-orthogonal examples

City scale
When all gridded cities are compared at the same scale, they show the differences in block and street sizes
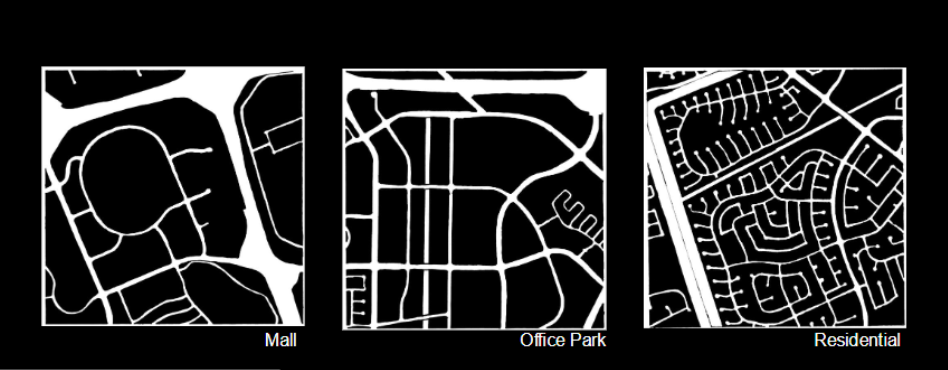
City Organizations
Organized around malls, around houses, around offices. ETC
Urban Fabric Diagram
Plat
a small piece of ground with actual or proposed features
Articulation
the action or manner of jointing or interrelating, the act of giving utterance or expression
Transformation
to change entirely or essentially in
composition or structure;
can mean a change in outward
shape or form or in character,
nature, or function
On Growth and Form reading
Stretch a fish, and it looks like another one.
Differences between the form of related species
are represented geometrically
Chronophotography
Photographic documentation
of movements or processes
Animation
A series of images visually
linked together to give the
illusion of motion; drawings or
cartoons that achieve this end
typically require a consistent
frame as a reference
Transparency
Simultaneous awareness of various spatial locations
Literal Transparency
Glass, transparent surfaces, see-through, clear, low-opacity materials
Phenomenal Transparency
apparent space between objects, openings, visual connections
Transparency of meaning
apparent space between solid objects, light, air, view, colors and geometries can create transparency
In-between
Where two spaces overlap, a threshold
Plat
grain of difference, plot of land