Simulation: Skills Modules 3.0Module: Wound Specimen collection & Wound Care
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
What are the general steps to collect a wound specimen?
Perform___ ____, wear clean _____, and if the wound is bandaged, remove the _____ and ____ the wound with _____ water or ___% ____ ____ solution. Then, collect the specimen from the ____ of the wound using a sterile swab or syringe.
Perform hand hygiene, wear clean gloves, and if the wound is bandaged, remove the dressing and clean the wound with sterile water or 0.9% sodium chloride solution. Then, collect the specimen from the center of the wound using a sterile swab or syringe.
** ITS IMPORTANT TO ALWAYS CLEAN THE WOUND BEFORE COLLECTING A SPECIMEN.
________ ____ : Indicates dead or infected tissue that may require debridement to promote healing.
Nonviable Tissue
Nonviable Drainage Types
________ _______
Appearance: Thick, yellow, green, or brown pus.
Indicates: Infection, dead tissue, and bacteria.
Treatment: Wound cleaning, debridement, antibiotics.
______ ______ Drainage
Appearance: Strong, offensive odor.
Indicates: Infection and possible nonviable tissue.
Treatment: Wound cleaning, debridement, antibiotics.
_____ or _______ Drainage
Appearance: Green or brown in color.
Indicates: Bacterial infection (e.g., Pseudomonas); nonviable tissue.
Treatment: Debridement, antibiotics, wound care.
Purulent Drainage
Foul smelling Drainage
Green or Brown Drainage
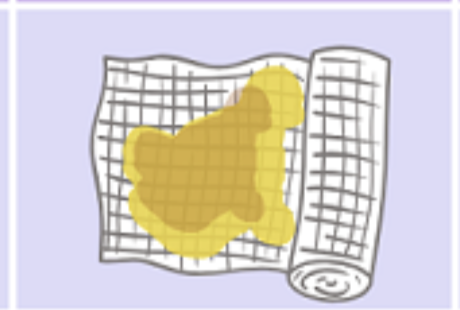
_________ ______
Appearance: Pinkish due to a mix of clear fluid and blood.
Indicates: Normal early healing; excessive drainage may signal improper healing.
Treatment: Monitor; ensure proper healing.
Serosanguineous Drainage
Sanguineous drainage and serosanguineous drainage are both viable types of fluid, indicating a healthy, healing wound.
Excessive or ongoing sanguineous drainage could indicate complications (e.g., bleeding issues), but both are not a sign of nonviable tissue
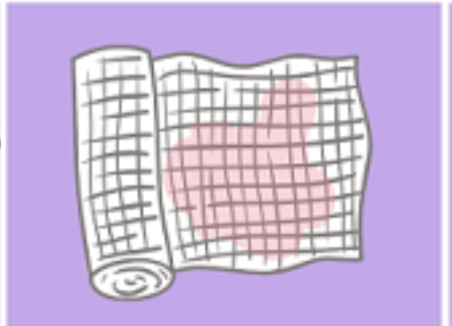
__________ _______
Appearance: Bright red, blood-tinged fluid.
Indicates: Bleeding or possible clotting issue; may signal wound complication.
Treatment: Control bleeding; check for clotting problems.
Sanguineous Drainage
Sanguineous drainage and serosanguineous drainage are both viable types of fluid, indicating a healthy, healing wound.
Excessive or ongoing sanguineous drainage could indicate complications (e.g., bleeding issues), but both are not a sign of nonviable tissue
Why should you avoid collecting a wound specimen from the edges of the wound?
The ____ of the wound may be contaminated with outside skin ___, which can lead to _____ results. Always collect specimens from the ____ of the wound.
The edges of the wound may be contaminated with outside skin flora, which can lead to inaccurate results. Always collect specimens from the center of the wound.
Where should you avoid collecting wound drainage from?
Never collect drainage from ___ or ____ exudates as they may not represent the true _____ site.
Never collect drainage from pus or pooled exudates as they may not represent the true infection site.
How do you collect a wound specimen using a sterile swab?
Use a sterile swab to obtain the sample from the ____ of the wound. Place the swab into a sterile test ____, ensuring it does not touch the _____ of the test tube. Break the _____, place the sample in the test tube medium, and secure the lid.
Use a sterile swab to obtain the sample from the center of the wound. Place the swab into a sterile test tube, ensuring it does not touch the edges of the test tube. Break the ampule, place the sample in the test tube medium, and secure the lid.
How should you handle and transport the wound specimen?
After securing the lid on the test tube, ____ the sample and prepare it for transport to the laboratory. Check with the laboratory for proper _____, ____, and transport ____.
After securing the lid on the test tube, label the sample and prepare it for transport to the laboratory. Check with the laboratory for proper collection, storage, and transport time.
What should you document when collecting a wound specimen?
Document the ______, ____ signs, date, time, ____, and the client's ______ of the procedure in the client's medical record.
Document the assessments, vital signs, date, time, location, and the client's tolerance of the procedure in the client's medical record.
Why is accurate labeling important when collecting a wound specimen?
Inaccurate collection or mislabeling can lead to repeated ______ and ______, which can _____ appropriate treatment.
Inaccurate collection or mislabeling can lead to repeated collections and misdiagnosis, which can delay appropriate treatment.
What should accompany the wound specimen when transported to the laboratory?
A completed _______ form with the necessary details should be sent to the laboratory with the specimen.
A completed requisition form with the necessary details should be sent to the laboratory with the specimen.
What is the primary purpose of processing wound specimens in the laboratory?
The primary purpose is for _____ and ______ testing, which helps identify the bacteria present and determine the most effective antibiotic therapy.
The primary purpose is for culture and sensitivity testing, which helps identify the bacteria present and determine the most effective antibiotic therapy.
What is the two-step testing process for wound specimens?
The two-step process involves determining the type of _______ in the wound and testing the wound's sensitivity to various ______ to guide appropriate therapy.
The two-step process involves determining the type of bacteria in the wound and testing the wound's sensitivity to various antibiotics to guide appropriate therapy.
What is a common issue when processing wound cultures, and how is it addressed?
Wound cultures can be contaminated with ___ from the surrounding skin. If this occurs, a ____ culture is often recommended to ensure accurate results.
Wound cultures can be contaminated with flora from the surrounding skin. If this occurs, a repeat culture is often recommended to ensure accurate results.
Why is it recommended to obtain a wound culture prior to initiating broad-spectrum antibiotics?
To avoid ______ test results due to the presence of _____, which may affect bacterial growth or sensitivity, making it difficult to identify the right treatment.
To avoid altering test results due to the presence of antibiotics, which may affect bacterial growth or sensitivity, making it difficult to identify the right treatment.
Why should you indicate if a client is already receiving antibiotics on the laboratory requisition form?
Indicating current antibiotic use helps the laboratory interpret the results ______, as _____ can alter the outcome of the culture and sensitivity test.
Indicating current antibiotic use helps the laboratory interpret the results accurately, as antibiotics can alter the outcome of the culture and sensitivity test.
Why do many providers wait for wound culture results before prescribing antibiotics?
With increasing concerns about medication _____, waiting for the results allows for more _____ and appropriate antibiotic therapy.
With increasing concerns about medication resistance, waiting for the results allows for more targeted and appropriate antibiotic therapy.
A _____ _____ is a quick test that can be requested to analyze drainage from the wound. It helps identify ______ sooner, allowing healthcare providers to prescribe appropriate treatment more quickly.
A Gram stain is a quick test that can be requested to analyze drainage from the wound. It helps identify bacteria sooner, allowing healthcare providers to prescribe appropriate treatment more quickly.
What key aspects should you inquire about when taking a wound history?
Ask about the _____ of the wound, any _____ injury or known cause, associated manifestations (pain, itching), changes over time, and major health problems that may affect wound development or healing.
Ask about the onset of the wound, any acute injury or known cause, associated manifestations (pain, itching), changes over time, and major health problems that may affect wound development or healing.
How often should wounds be assessed?
Wounds should be assessed at each ______ change to monitor for progress or deterioration, but the frequency of assessment may vary based on the wound's acuity and facility guidelines.
Wounds should be assessed at each dressing change to monitor for progress or deterioration, but the frequency of assessment may vary based on the wound's acuity and facility guidelines.
What should be assessed visually when examining a wound?
Visually assess location, shape, size, color, exudate, bleeding, and the presence of necrosis, erythematous tissue, or infected tissue. Also look for tunneling, undermining, edema, and healthy tissue like granulating tissue or clean wound edges.
What temperature and textural changes might be noted during a wound assessment?
Temperature changes range from warm (indicating ______ ) to cold (indicating ______ compromise). Textural changes could include roughened or raised skin, or deep wounds that disrupt the skin's natural contour.
Temperature changes range from warm (indicating infection) to cold (indicating vascular compromise). Textural changes could include roughened or raised skin, or deep wounds that disrupt the skin's natural contour.
____ can indicate specific infectious organisms or help identify the cause of the wound, making it a key factor in assessing the wound's condition.
Odor can indicate specific infectious organisms or help identify the cause of the wound, making it a key factor in assessing the wound's condition.
What should you assess in the periwound area during a wound assessment?
The condition of the skin surrounding the wound (periwound skin) should be examined for signs of ______,________, or_______.
The condition of the skin surrounding the wound (periwound skin) should be examined for signs of irritation, breakdown, or infection.
Why is assessing the psychosocial impact of a wound important?
It's important to evaluate the client’s response to the wound, considering stress, body image, self-concept, and sexuality, as well as the resources available to help them adapt.
What are wound assessment scales used for?
They are used to assess risk for ______ injuries and to monitor the _______ process of existing wounds.
They are used to assess risk for pressure injuries and to monitor the healing process of existing wounds.
How should wounds be measured during an assessment?
Wounds should be measured in ____, ____, and ____ using rulers or other measuring tools. _____ and areas of ________ should be measured separately.
Wounds should be measured in length, width, and depth using rulers or other measuring tools. Tunnels and areas of undermining should be measured separately.
How are pressure injuries classified?
_____ stages
Pressure injuries are classified using six stages, but these stages are specifically for pressure injuries only.
A ______ injury is an area of compromised skin integrity over a bony prominence resulting from prolonged pressure. Common sites include the _____ bone,____, heel, trochanter, and malleolus.
A pressure injury is an area of compromised skin integrity over a bony prominence resulting from prolonged pressure. Common sites include the occipital bone, sacrum, heel, trochanter, and malleolus.
What are the most common sites for pressure injuries?
The most common sites are the occipital bone, spinous process, sacrum, ischium, heel, trochanter, and lateral and medial malleolus.
What factors increase the risk for pressure injury development?
Factors include friction, shear, moisture, altered sensory perception, consciousness, and inadequate nutrition.
______ occurs when skin rubs against a surface, irritating the epithelial tissue. _____ happens when the skin stays in place, but the subcutaneous tissues shift, stretching blood vessels and causing soft-tissue ischemia.
Friction occurs when skin rubs against a surface, irritating the epithelial tissue. Shear happens when the skin stays in place, but the subcutaneous tissues shift, stretching blood vessels and causing soft-tissue ischemia.
What is an example of shear in pressure injuries?
An example is when a client slides downward in bed, causing the sacrum to move faster than the skin over it, resulting in stretching and blood vessel breakage.
How can the risk of shear be reduced?
The risk of shear can be reduced by keeping the head of the bed no higher than ___ degrees.
The risk of shear can be reduced by keeping the head of the bed no higher than 30 degrees.
How does moisture affect pressure injury development?
Moisture reduces skin's resistance to _____ and ____, increasing the risk of breakdown. Body fluids like _____, ____, _____ drainage, and ______ can contribute to moisture-related damage.
Moisture reduces skin's resistance to friction and shear, increasing the risk of breakdown. Body fluids like urine, feces, wound drainage, and perspiration can contribute to moisture-related damage.
How does altered sensory perception impact pressure injury risk?
Clients with altered sensory perception or consciousness may not be able to _____, ______, or _____ to pressure, increasing their risk for pressure injuries.
Clients with altered sensory perception or consciousness may not be able to detect, communicate, or respond to pressure, increasing their risk for pressure injuries.
________ nutrition can weaken the skin and reduce its ability to repair itself, increasing the risk for pressure injury development. Consultation with a dietitian may be necessary.
Inadequate nutrition can weaken the skin and reduce its ability to repair itself, increasing the risk for pressure injury development. Consultation with a dietitian may be necessary.
_________ is essential for preventing pressure injuries in clients with limited or complete immobility. This should be done regularly, both when the client is sitting and in bed. **reposition every __ hours.
Repositioning is essential for preventing pressure injuries in clients with limited or complete immobility. This should be done regularly, both when the client is sitting and in bed.**reposition every 2 hours, every 1 for high risk.
Pressure injuries
Stage ___: Nonblanchable redness over a bony prominence,
Stage 1
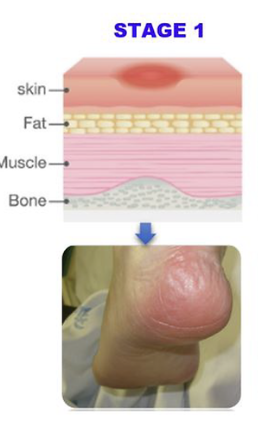
Pressure injuries
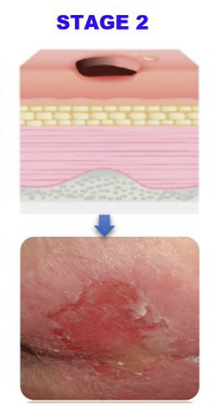
Stage ___: Partial-thickness skin loss with visible injury or fluid-filled blister.
Stage 2
Pressure injuries
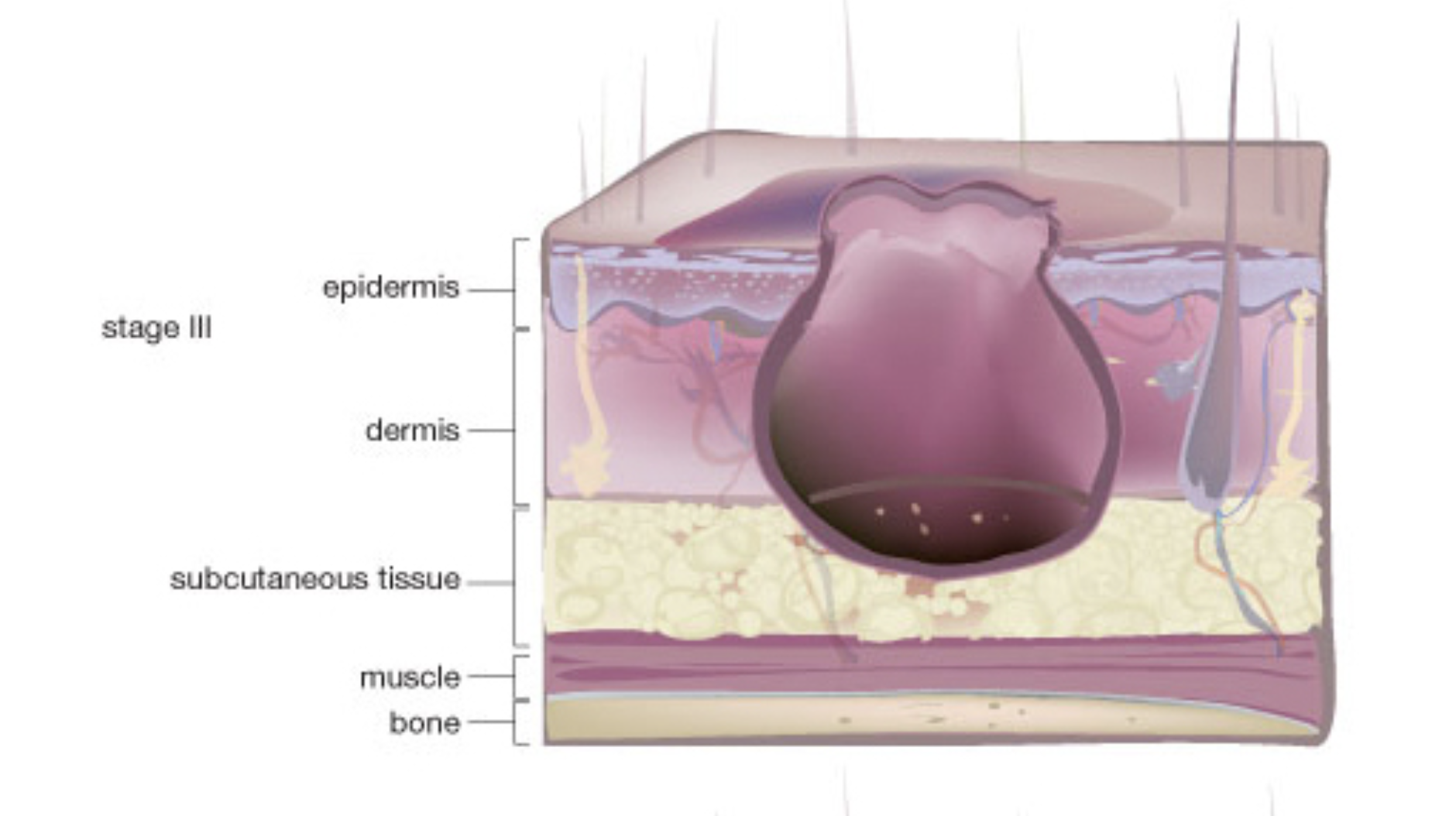
Stage __: Full-thickness tissue loss without exposed muscle or bone,
Stage 3
Pressure injuries
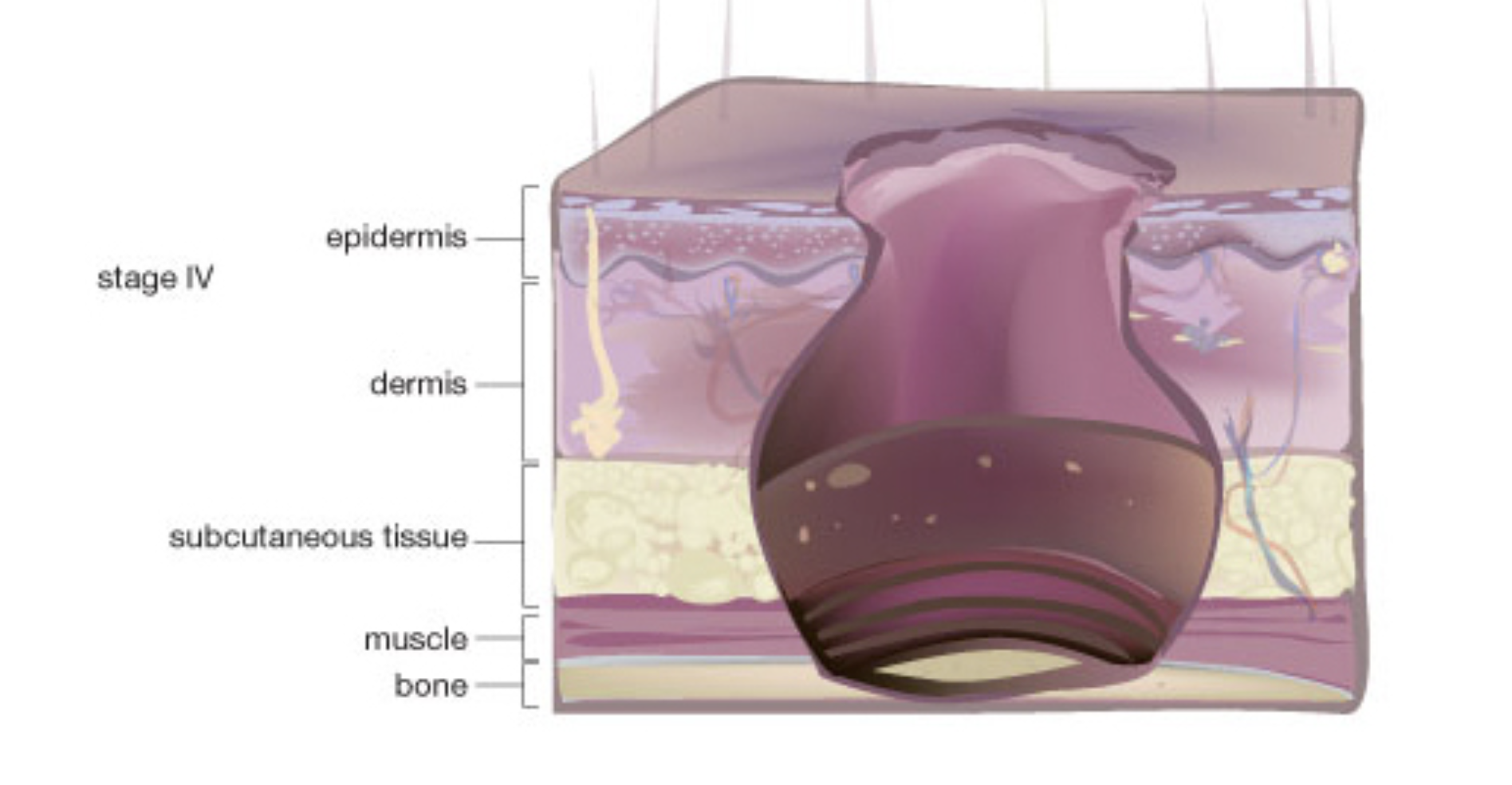
Stage ___: Full-thickness tissue loss with exposed muscle or bone
Stage 4
________: Wound stage cannot be determined due to eschar or slough obscuring the wound.
unstageable
A suspected ____ ____ injury is an area of discolored intact skin caused by damage to underlying tissue, but it is not considered a stage in the NPIAP system.
A suspected deep tissue injury is an area of discolored intact skin caused by damage to underlying tissue, but it is not considered a stage in the NPIAP system.
Stage __ is defined by nonblanchable redness typically over a bony prominence, indicating pressure-induced damage to the skin.
Stage 1
Stage ___ involves partial-thickness skin loss, which includes visible injury or the formation of a fluid-filled blister.
Stage 2
Stage ___ involves full-thickness tissue loss without exposure of muscle or bone. It may also include undermining or tunneling.
Stage 3
Stage __ involves full-thickness tissue loss with exposed bone or muscle, with the possibility of undermining or tunneling, and the presence of eschar or slough.
stage 4
An _______ injury occurs when eschar or slough obscures the wound, making it impossible to determine its stage.
unstageable injury
The Braden Scale is used to assess the risk of pressure injury formation based on six subscales: sensory _______,_____,_____, _____, _____, and ______/shear.
The Braden Scale is used to assess the risk of pressure injury formation based on six subscales: sensory perception, moisture, activity, mobility, nutrition, and friction/shear.
What is the scoring range for the Braden Scale, and what is the cutoff for most adults?
The Braden Scale scores range from 6 to 23. A score of __ or lower generally indicates a higher risk for pressure injury formation in most adults.
The Braden Scale scores range from 6 to 23. A score of 18 or lower generally indicates a higher risk for pressure injury formation in most adults.
A _____ score on the Braden Scale indicates a higher risk for developing pressure injuries.
lower
What are the three main phases of wound healing?
The three main phases are: Inflammatory Phase, Proliferative Phase, Maturation Phase.
The _________ phase begins after injury and lasts about 24 hours for partial-thickness wounds. Key characteristics include skin color changes, heat, swelling, pain, and loss of function, with white blood cells aiding in infection control and healing.
The inflammatory phase
The ________ phase restores skin integrity by filling the wound with new tissue, including angiogenesis, granulation tissue formation, epithelialization, and collagen deposition.
The proliferative phase
The ________ phase is the final phase, which can take over a year, involving collagen remodeling to increase strength and changes in skin appearance.
The maturation phase
What are some intrinsic factors that can affect wound healing?
Key intrinsic factors include ___, _____ illness, and reduced ______
Key intrinsic factors include age, chronic illness, and reduced sensation.
What are some extrinsic factors that can affect wound healing?
Key extrinsic factors include _____, ____ treatments, inadequate ______, _____, and repeated ____ or _____.
Key extrinsic factors include medications, cancer treatments, inadequate nutrition, stress, and repeated trauma or infection.
How do chronic wounds heal differently from acute wounds?
Chronic wounds heal via ______ intention, characterized by granulation tissue formation and inefficient keratinocyte migration.
Chronic wounds heal via secondary intention, characterized by granulation tissue formation and inefficient keratinocyte migration.
______ _____: Wound edges are approximated and heal quickly.
Primary intention
________ _______: Wound edges do not approximate and heal through granulation tissue.
Secondary intention
In chronic wounds, the _______ phase is inefficient, characterized by irregular wound edges, high fluid concentrations, and slower healing.
proliferative phase
In chronic wounds, ______ can be delayed due to uneven collagen deposition and slow scar remodeling.
maturation
_____ dressings are typically made from gauze pads and are used for wounds with small amounts of exudate. They can stick to heavily exudative wounds.
Dry
What are the issues with wet-to-dry dressings?
Wet-to-dry dressings are _______, painful to _____, _____-consuming, can cause _____, and pose cross-______ risks.
Wet-to-dry dressings are nonselective, painful to remove, time-consuming, can cause maceration, and pose cross-contamination risks.
______-_______ dressings contain agents to enhance healing, used only for wounds that will respond to the specific agent.
Chemical-impregnated
_____ dressings are absorbent, create a moist healing environment, and protect the wound, providing extra protection for bony prominences.
Foam
_______ dressings are ideal for wounds with heavy exudate, promoting a moist environment for healing.
Alginate
________ dressings help maintain a moist healing environment and are used for wounds with necrosis and infection.
Hydrogel
_______ ______ provide a moist environment beneath dressings and help with debridement, beneficial for deep wounds with exudate.
Wound fillers
______ ____ dressings create a barrier to the environment and allow oxygen exchange, best for superficial skin tears.
Transparent film
_______ dressings maintain a moist healing environment and are used for autolytic debridement.
Hydrocolloid
Wound ______ materials include sutures, staples, tissue adhesives, and adhesive skin closures.
Wound closure materials include sutures, staples, tissue adhesives, and adhesive skin closures.
____ secures dressings to wounds, available in different varieties, and should be removed carefully to avoid skin damage.
Tape
_______ provide support to body areas and are often used after surgery but should be monitored for irritation.
Binders provide support to body areas and are often used after surgery but should be monitored for irritation.
______ _____ include antiseptic agents, antibiotic ointments, antifungal agents, chemical debridement gels, and barrier creams.
Topical agents
______ ______ is used to remove necrotic tissue, purulent drainage, and debris from the wound area to promote healing.
Wound cleansing is used to remove necrotic tissue, purulent drainage, and debris from the wound area to promote healing.
What are the different methods of wound cleansing?
Methods include passive irrigation, mechanical cleansing, and pressurized irrigation.
______ Irrigation
Description: Involves the use of gravity to facilitate the flow of irrigation solution over the wound.
How it works: The solution is allowed to flow over the wound without any added pressure or force. This method is typically used when there’s no significant wound debris or infection to clear.
Example: Pouring sterile saline over a wound and letting it drain away naturally.
passive irrigation
_________ Irrigation
Description: Involves the use of mechanical force or pressure to help cleanse the wound.
How it works: The solution is delivered to the wound using some form of mechanical equipment, such as a syringe, squeeze bottle, or irrigation device. This helps to remove debris and bacteria from the wound more effectively.
Example: Using a syringe with a catheter to irrigate a wound with saline or antiseptic solution, applying moderate pressure.
Mechanical Irrigation
________ Irrigation
Description: Involves the use of high-pressure fluid delivery to irrigate and clean the wound.
How it works: The irrigation solution is forced into the wound at a higher pressure, often using a pressure irrigation system or specialized equipment. This helps remove stubborn debris, necrotic tissue, or bacteria from the wound more thoroughly.
Example: A pressurized irrigation device that uses controlled force to flush the wound with saline or another irrigating solution.
Pressurized Irrigation
______ is related to mechanical therapy because it uses a vacuum pump and dressing system to provide suction pressure to the wound, which is a mechanical force.
NPWT (negative pressure wound therapy
_______ ____ are used for wound cleansing but are less practical due to access and infection control issues.
Whirlpool tubs
What should be considered when cleansing a wound?
Consider client comfort, safety, and ensuring a clean environment during wound cleansing.
_______ Debridement: Physical removal of necrotic tissue (e.g., wet-to-dry dressings).
Mechanical
_______ Debridement: Natural breakdown of tissue using the body’s enzymes (e.g., moisture-retentive dressings).
Autolytic
_______ Debridement: Use of chemicals or enzymatic agents to dissolve dead tissue (e.g., collagenase ointment).
chemical
_______ Debridement: Removal of dead tissue through surgical means (e.g., scalpel or scissors).
Surgical
Why are wet-to-dry dressings no longer commonly used for debridement?
They are nonselective, may remove healthy tissue, cause pain, and are outdated due to these disadvantages.
________ irrigation uses a solution delivered at high pressure through a syringe to effectively cleanse the wound.
Pressurized
What is the primary purpose of Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT)?
NPWT assists in wound ______, promotes ______, and removes _____ from the wound
NPWT assists in wound contraction, promotes debridement, and removes exudate from the wound.
______ _____ ___ ____ applies suction to the wound area using a porous foam or gauze dressing sealed with transparent adhesive tape.
Negative pressure wound therapy
What are the benefits of using NPWT?
NPWT helps ____ limbs, speeds up wound _____, and is ____-effective.
NPWT helps salvage limbs, speeds up wound healing, and is cost-effective.
When should Negative Pressure Wound Therapy NOT be used?
NPWT should not be used in areas with skin _____, clients on _____, or _____ with exposed vessels.
NPWT should not be used in areas with skin cancer, clients on anticoagulants, or wounds with exposed vessels.
Who can apply NPWT and how is it applied?
A trained ____ care specialist can apply NPWT using a ____ foam dressing sealed with adhesive tape and a _____ unit.
A trained wound care specialist can apply NPWT using a porous foam dressing sealed with adhesive tape and a vacuum unit.
What safety considerations should be taken when using NPWT?
Caution is advised for clients with decreased ______, _______ therapy, or _____ with tracts.
Caution is advised for clients with decreased sensation, anticoagulant therapy, or wounds with tracts.
The______ unit creates negative pressure cycling through on and off states to manage drainage.
The NPWT unit creates negative pressure cycling through on and off states to manage drainage.
How should an NPWT device be monitored and troubleshooted?
The NPWT device should be regularly assessed to ensure correct pressure settings and consult appropriate resources for troubleshooting.
What are the main purposes of drains in wound care?
Drains are used to collect _____, _____ drainage, _____ surrounding skin, and contain ________.
Drains are used to collect exudate, measure drainage, protect surrounding skin, and contain microorganisms.