Digestive and Immune Systems Overview
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Calories
Calories are a measure of energy.
Small calories (cal)
Estimate the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1g of water by 1 °C.
Big calories (kilocalories (Cal))
Refer to the calories in food.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are obtained from cereals, grains, and breads.
Calories per gram of carbohydrates
On average, carbohydrates contain 4.1 Calories per gram.
Dietary fats
Dietary fats are obtained from oils, margarine, and butter and are abundant in fried foods, meats, and processed snack foods.
Calories per gram of fats
Fats contain 9.3 Calories per gram.
Proteins
Proteins can be obtained from many foods, including poultry, fish, meat, and grains.
Calories per gram of proteins
Proteins have 4.1 Calories per gram.
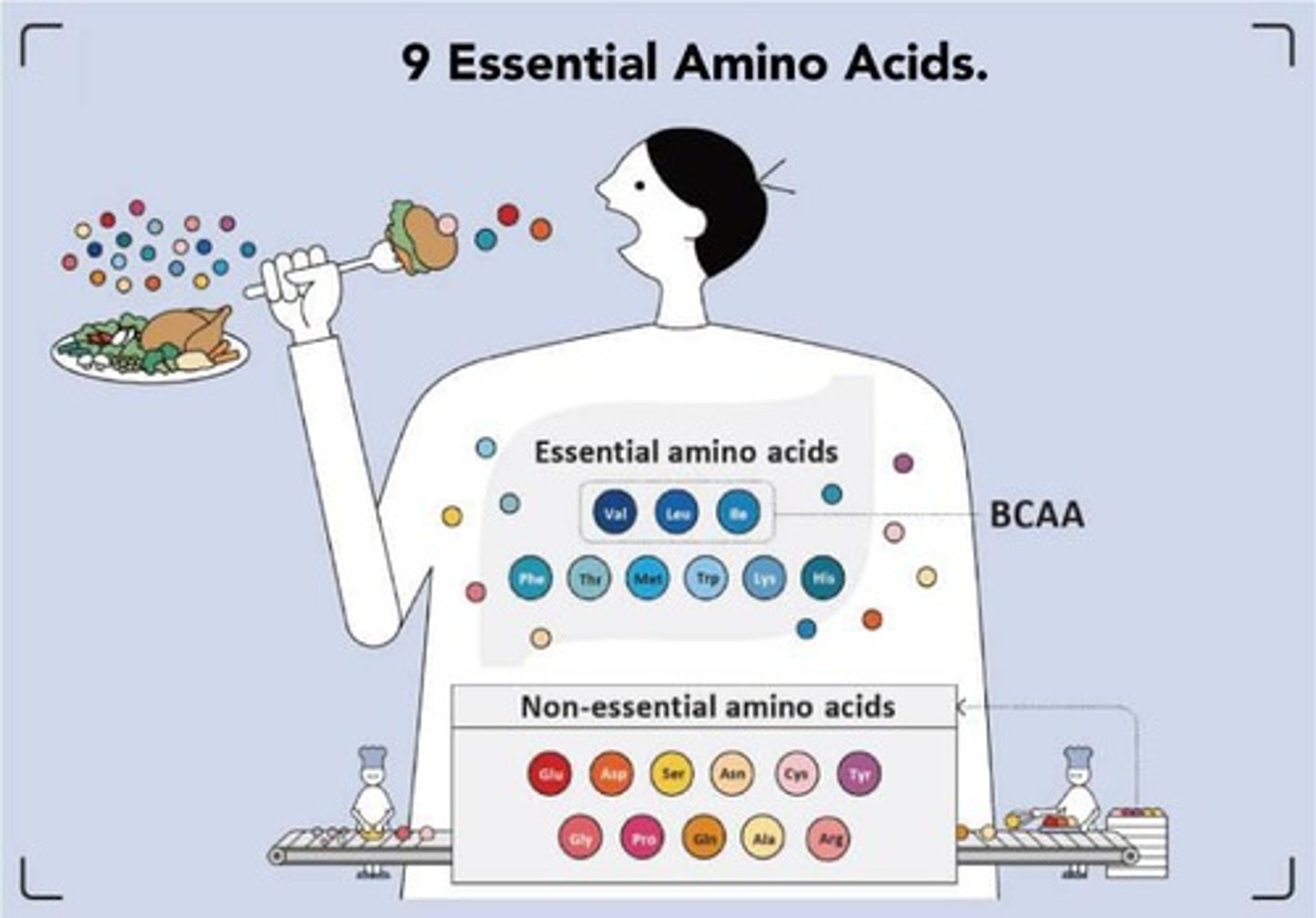
Essential Amino Acids
Humans are unable to synthesize eight amino acids, which must be obtained from proteins in food.
Fiber
Fiber is the part of plant food that cannot be digested by humans.

Low fiber diet
Diets that are low in fiber result in a slower passage of food through the colon.
Trace Elements
Some minerals are required in very small amounts and are called trace elements.
Vitamins
Essential organic substances that are used in trace amounts are called vitamins.
Heterotrophs
Heterotrophs are divided into three groups based on their food sources.
Herbivores
Herbivores eat plants exclusively.
Carnivores
Carnivores are meat eaters.
Omnivores
Omnivores eat both plants and animals.
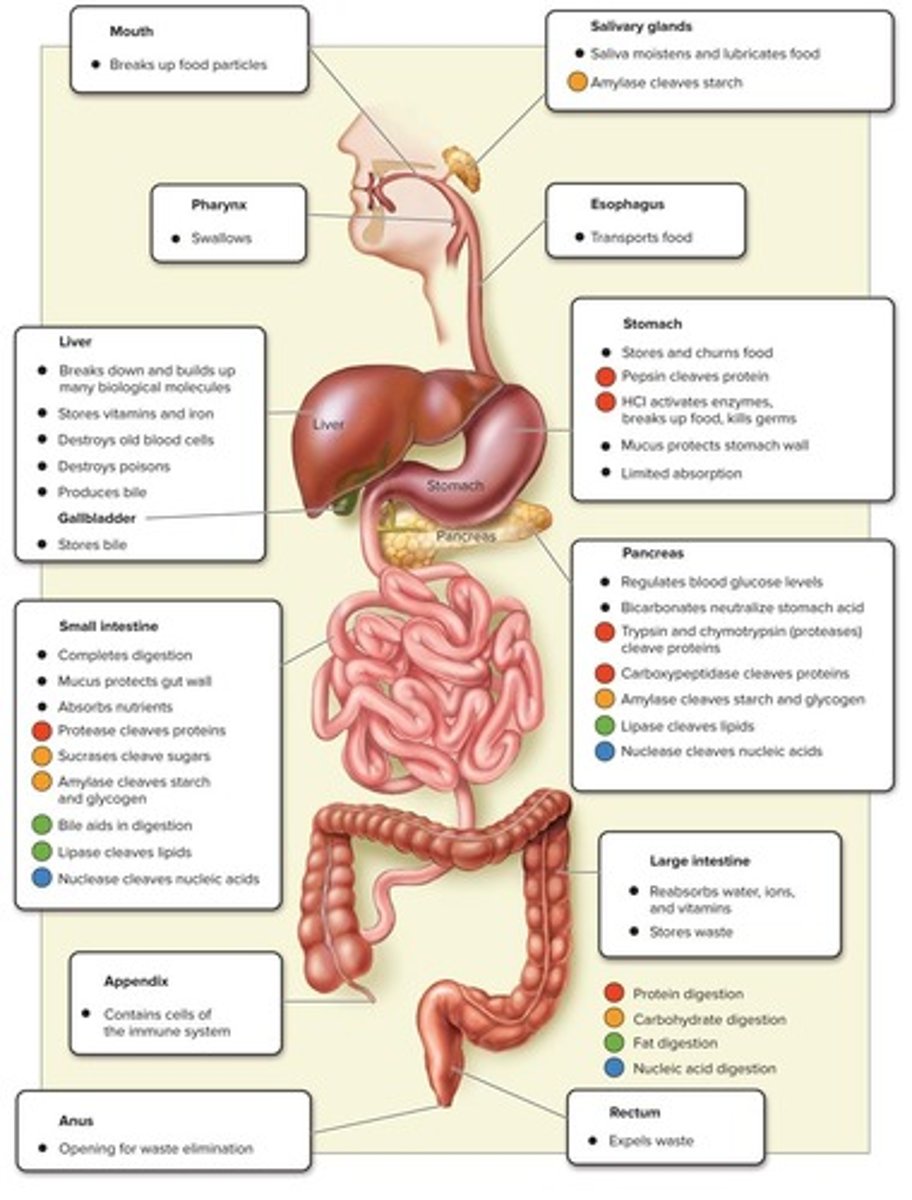
Alimentary Canal
The alimentary canal is a digestive tract with a separate mouth and anus.
Chemical digestion
Chemical digestion breaks down the food into individual subunits.
Physical forces in digestion
Physical forces break the ingested food into smaller fragments.
Vertebrate Digestive Systems
The digestive system consists of a tubular gastrointestinal tract and accessory organs.
Carnivores
Organisms that have shorter intestines than herbivores.
Herbivores
Organisms that have long, convoluted small intestines due to ingesting a large amount of plant cellulose.
Chewing
The process that breaks up food into small particles and mixes it with fluid secretions.
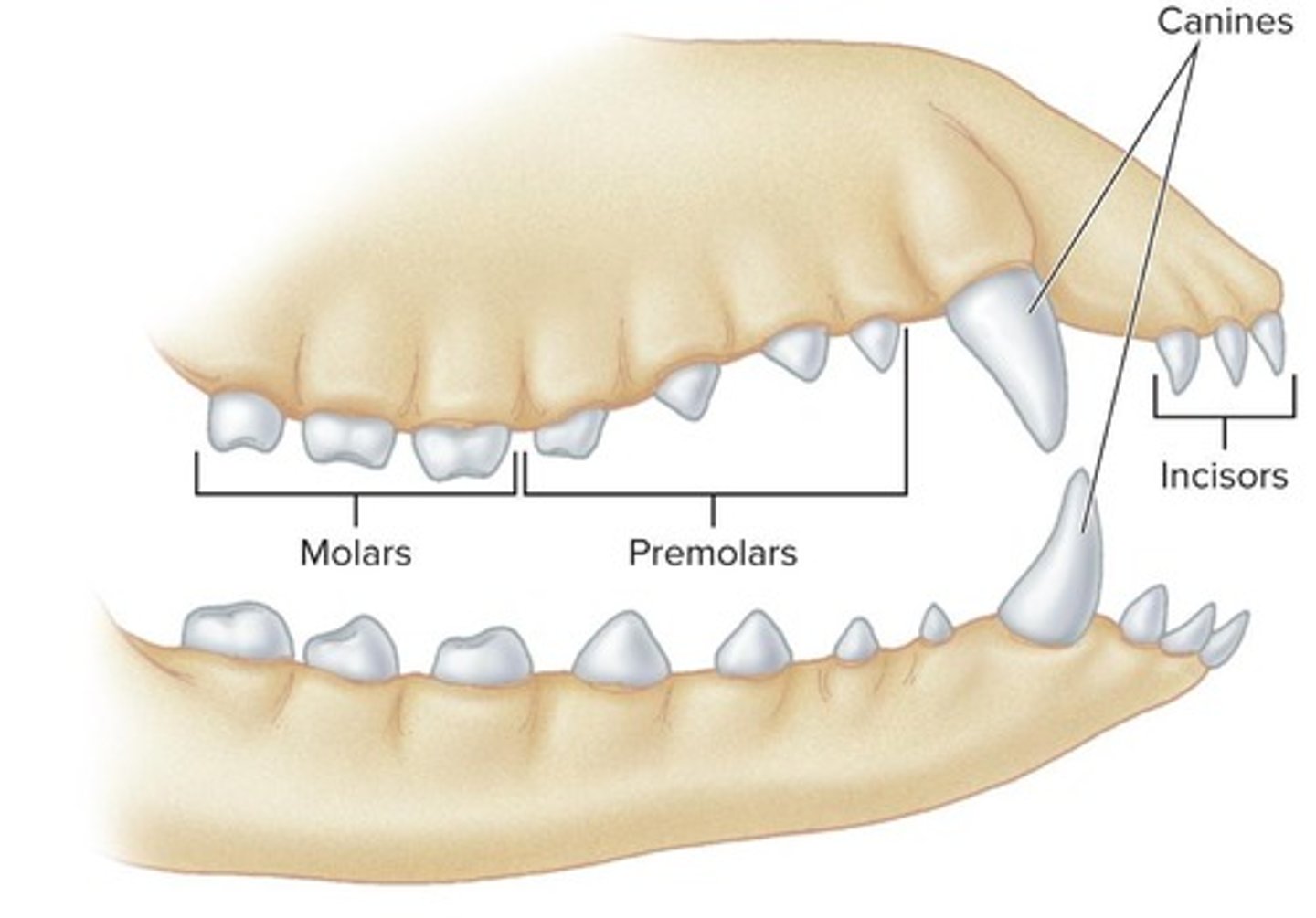
Heterodont Teeth
Teeth of different specialized types found in mammals, depending on their diets.
Carnivores' Teeth
Teeth that have prominent canines and other teeth that are more bladelike and sharp.
Herbivores' Teeth
Teeth that have well-developed incisors for snipping, reduced or absent canines, and large, flat molars with complex ridges for grinding.
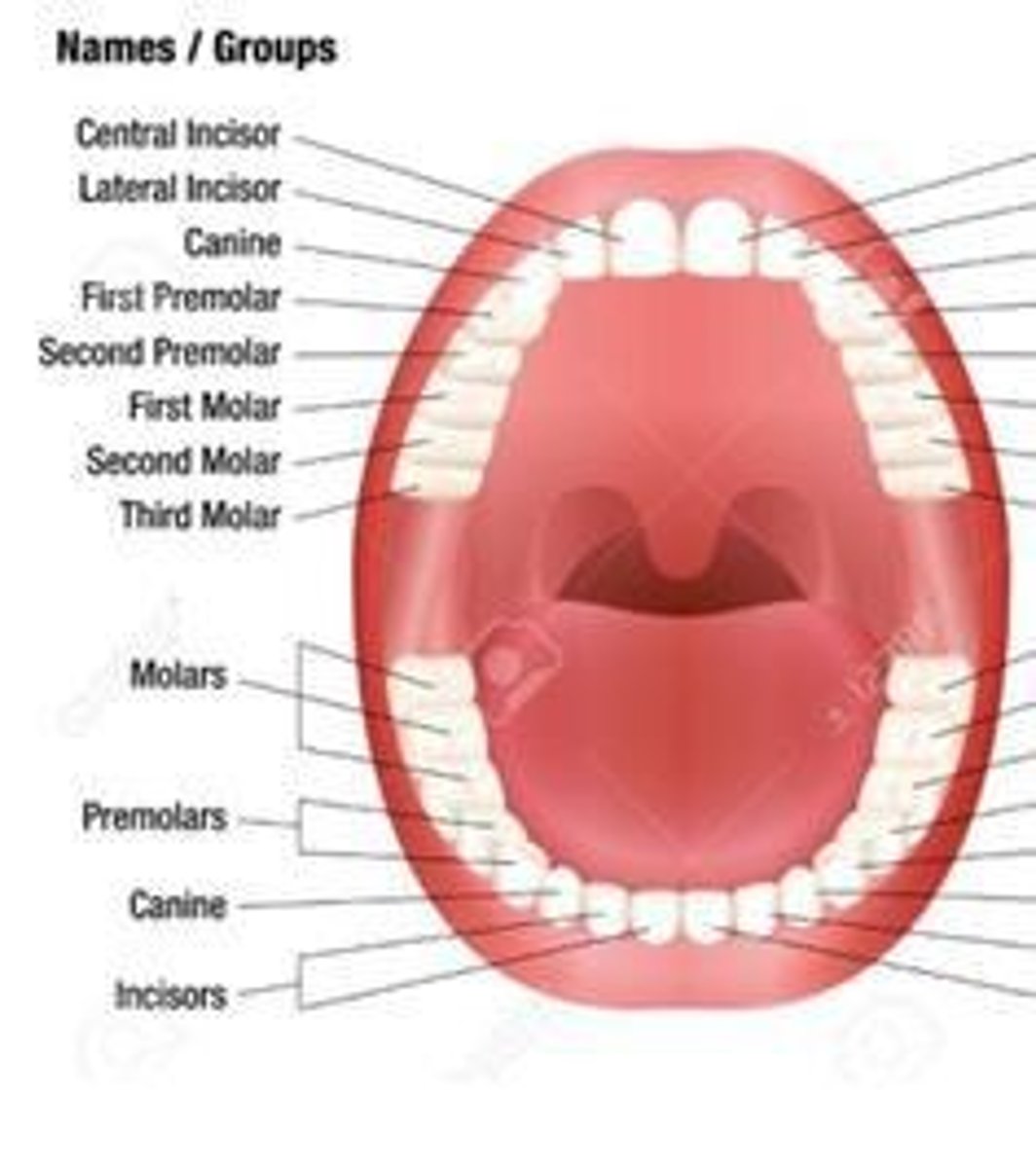
Humans as Omnivores
Humans have teeth specialized for eating both plant and animal material, with carnivorous teeth in the front and herbivorous teeth in the back.
Saliva
A solution that moistens and lubricates food, making it easier to swallow, and contains the enzyme amylase, which initiates the breakdown of starch.
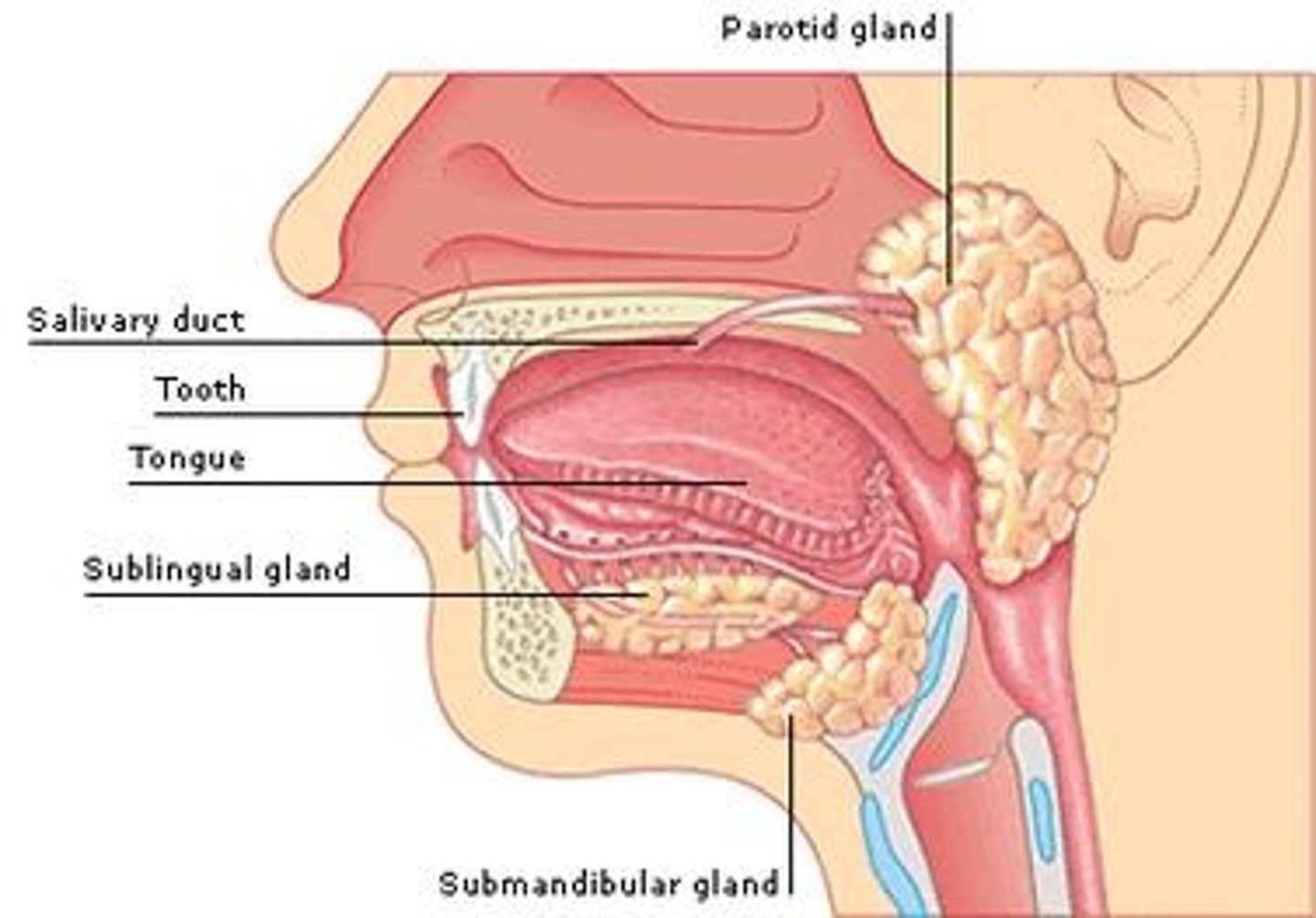
Esophagus
A muscular tube that connects the pharynx to the stomach, with the upper third having skeletal muscle for voluntary control and the lower two-thirds having involuntary smooth muscle.

Peristalsis
The progression of coordinated contraction of involuntary circular muscles that propels a ball of food along the digestive tract.
Sphincter
A ring of smooth muscle that controls the movement of food from the esophagus into the stomach and prevents food from moving back into the esophagus.
Acid Reflux
A condition that occurs when relaxing of the sphincter leads to stomach acid moving into the esophagus.
Stomach
A saclike portion of the digestive tract that contains an extra layer of smooth muscle for churning food.
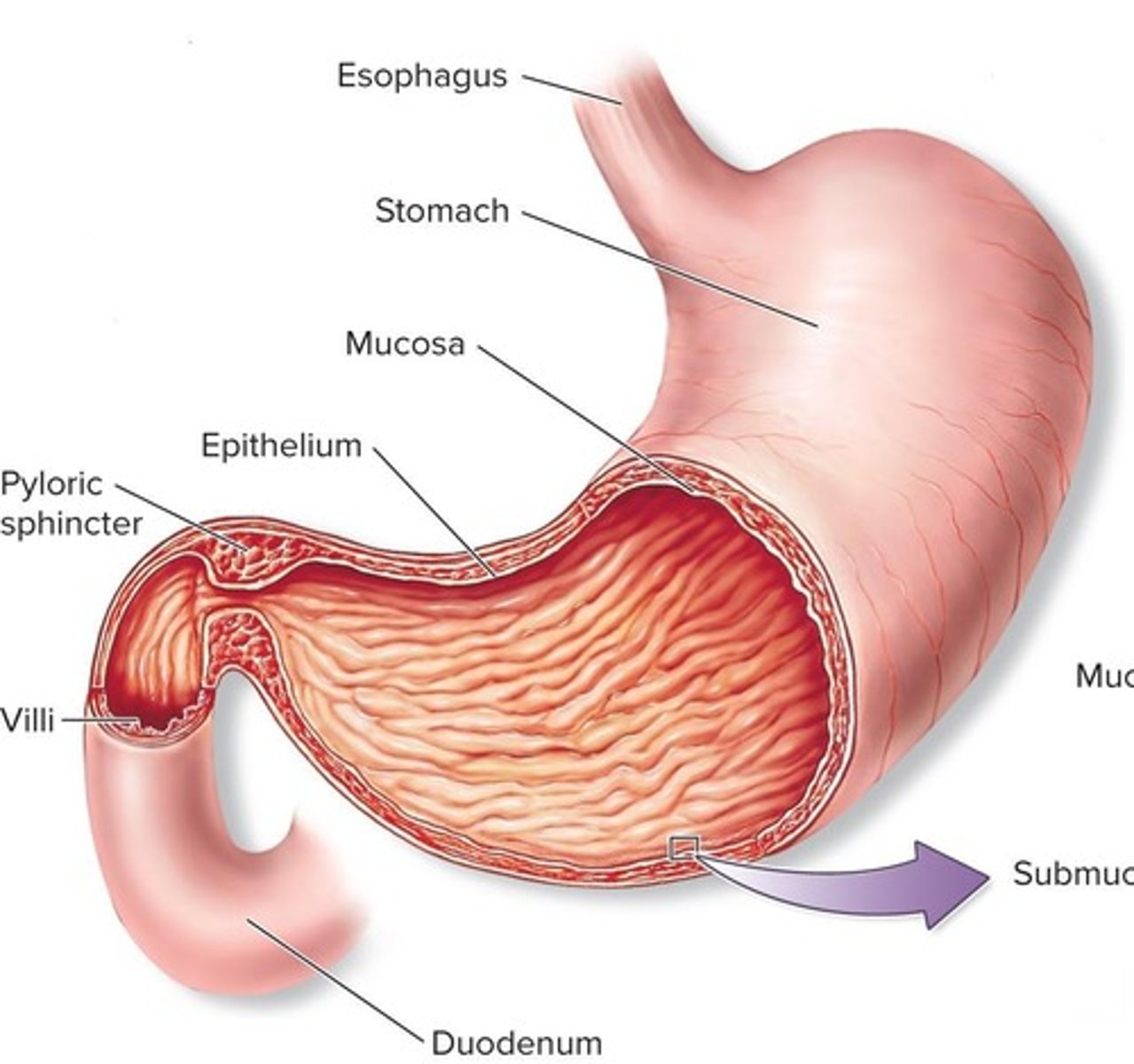
Gastric Juice
A digestive fluid with a pH of 2 that helps to denature protein and kill most bacteria, containing pepsin which hydrolyzes food proteins into smaller pieces.
Chyme
The mixture of partially digested food and gastric juice.
Gastric Ulcers
Holes that can form in the wall of the stomach due to overproduction of gastric acid, increased by an infection of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
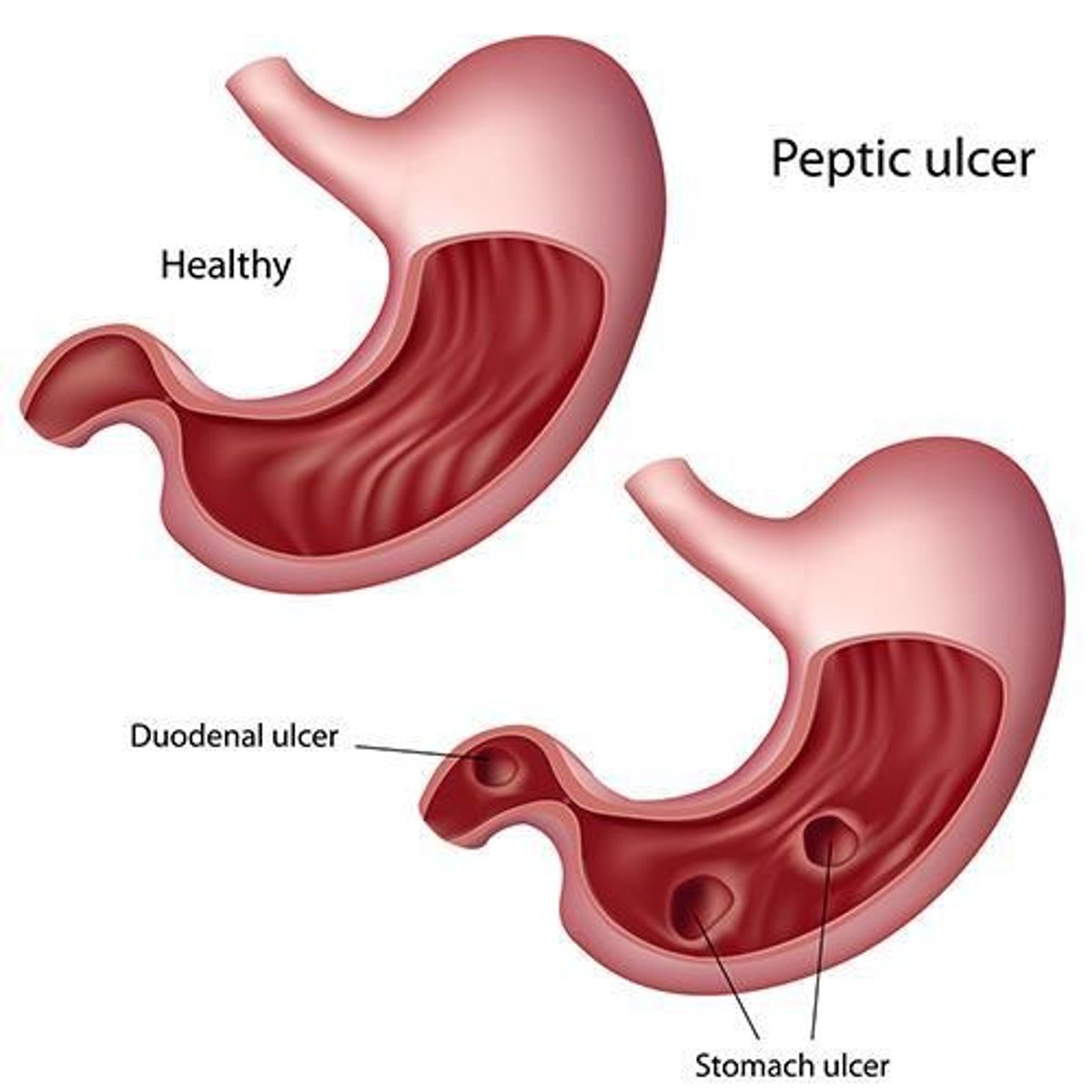
H. pylori Discovery
The discovery by Barry Marshall and Robin Warren that H. pylori could lead to stomach ulcers, previously thought to be due to stress or lifestyle factors.
Marshall's Experiment
Barry Marshall cultured H. pylori from a patient with gastritis and drank the organisms in a 'cloudy broth', leading to severe illness.
Endoscopy
A procedure that confirmed the presence of bacteria and gastritis after 10 days.
Small Intestine
Where most of the digestion occurs, with small portions of chyme introduced at one time.
Chyme
Partially digested food that is introduced into the small intestine.
Large Intestine
Has a wider diameter than the small intestine and compacts and stores undigested material as feces.
Fluid Absorption in Large Intestine
Only about 6% to 7% of fluid absorption occurs here.
Pancreas
Produces most enzymes necessary for digestion and secretes fluid into the small intestine.
Trypsin and Chymotrypsin
Enzymes produced by the pancreas that digest proteins.
Pancreatic Amylase
An enzyme produced by the pancreas that digests starch.
Lipase
An enzyme that digests fats, produced by the pancreas.
Bicarbonate
Secreted by the pancreas to neutralize HCl from the stomach.
Islets of Langerhans
Regions in the pancreas that produce hormones regulating blood sugar.
Insulin
A pancreatic hormone that lowers blood sugar levels.
Glucagon
A pancreatic hormone that raises blood sugar levels.
Liver
The largest internal organ that produces bile salts and stores them in the gallbladder.
Bile Salts
Produced by the liver and involved in fat digestion.
Ruminants
Animals with large divided stomachs that can digest cellulose due to symbiotic prokaryotes.
Cud
A portion of food that returns from the stomach to the mouth to be chewed again.
Cecum
A part of the digestive system in some herbivores that harbors microorganisms capable of digesting cellulose.
Colon Cancer Symptoms
May include blood in the stool, a change in bowel movements, weight loss, and fatigue.
Risk Factors for Colon Cancer
Include diet, obesity, smoking, and lack of physical activity, with red meat and alcohol increasing risk.
Preventive Measures for Colon Cancer
Drinking at least 5 glasses of water a day and eating a high-fiber diet may decrease risk.
Digestive System Function
Allows us to break down food to use the energy inside of it.
Alimentary Canal
A unidirectional digestive system found in humans and other mammals.
Three lines of defense
The vertebrate body is defended from infection by three lines of defense: Skin and mucous membranes, Cellular counterattack, Specific immune response.
Skin
The first defense against invasion by microbes, consisting of an outer epidermis and a lower dermis.
Epidermis
The outer layer of skin that is 10 to 30 cells thick, continuously shedding and being replaced.
Stratum corneum
The outer layer of the epidermis where cells are continuously shed and replaced.
Basal layer
The layer of the epidermis that lies below the stratum corneum, containing actively dividing cells.
Dermis
The layer of skin that is 15 to 40 times thicker than the epidermis and provides structural support.
Subcutaneous layer
The layer beneath the dermis, comprised of fat-rich cells that act as shock absorbers and provide insulation.
Chemical defense of skin
The skin provides chemical defense through acidic oil glands and sweat containing lysozyme.
Tears
Contain lysozyme to fight bacterial infections.
Stomach acid
Provides protection in the digestive tract against microbes.
Cellular counterattack
The second line of defense involving cellular and chemical defenses that kill invading microbes.
Lymphatic system
The central location for the storage and distribution of substances involved in the second line of defense.
Macrophages
Cells that kill bacteria by ingesting them and are a type of white blood cell.
Neutrophils
White blood cells that ingest bacteria and secrete chemicals to neutralize everything living in the infected area.
Natural Killer Cell
A type of white blood cell that attacks infected body cells by puncturing their membranes.
Complement System
A system of ~20 proteins that circulate in the plasma in an inactive state until they encounter a fungal or bacterial cell wall.
Complement proteins
Proteins that aggregate to form a membrane attack complex that creates a pore in the foreign cell's membrane, causing water to burst the cell.
Interferons
Act as messengers to prevent a virus from spreading to new cells, allowing the infected cells to remain unable to make new viruses.
Inflammatory Response
The response where infected/injured cells release chemical alarm signals, increasing blood flow and attracting phagocytes to attack invaders.
Fever
A response where macrophages send a signal to the brain to raise body temperature above normal, curbing microbial growth but potentially inactivating critical cellular enzymes.
Lymphocytes
White blood cells that are critical to the specific immune response.
T cell lymphocytes
Lymphocytes that originate in the bone marrow and migrate to the thymus gland for maturation, recognizing microorganisms and viruses by their antigens.
B cell lymphocytes
Lymphocytes that complete maturation in the bone marrow and produce antibodies that coat antigens for destruction.
Memory Cells
Cells produced by B and T cells that recall previous exposures to antigens and mount a rapid attack against them.
Major histocompatibility proteins (MHC)
Special marker proteins on the surface of every cell in the body that help in the immune response.
Antigens
Small pieces of foreign particles that remain after digestion and are moved to the surface of the cell to attract T cells.
Cytotoxic T Cells
T cells that directly kill infected cells.
B Cells: The Humoral Response
B cells respond to helper T cells, marking pathogens for destruction without attacking infected cells directly.
Antibodies
Markers produced by B cells that bind to antigens, marking them for destruction.
Secondary Immune Response
A more effective immune response due to the presence of a large group of lymphocytes that recognize a pathogen from a previous infection.
Overactive Immune System
Many diseases reflect an overactive immune system.
Autoimmune disease
The body attacks its own tissues.
Examples of Autoimmune Diseases
Multiple sclerosis, type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and Graves' disease.
Allergy
The body mounts a major defense against harmless antigens.
Asthma
A condition where the body has an exaggerated immune response to allergens.
Vaccination
The introduction of a dead or disabled pathogen into a body.
Purpose of Vaccination
Vaccination triggers an immune response against the pathogen, without an infection occurring.