Special Sensory Systems Poll Everywhere
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
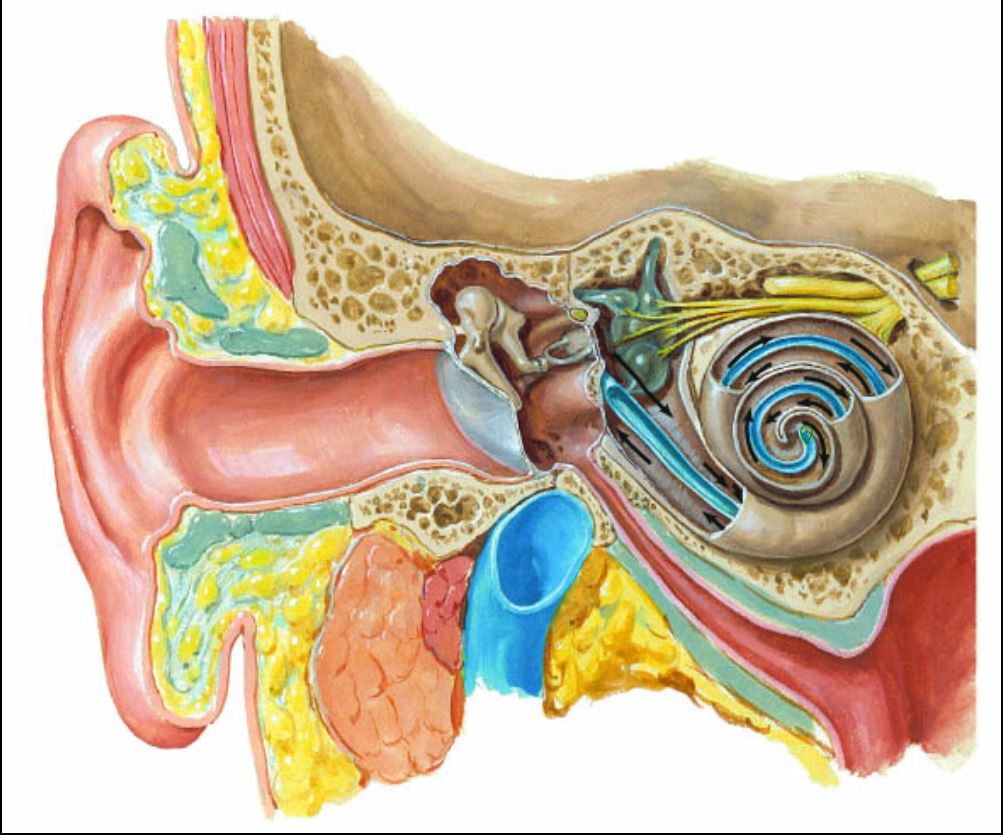
What is marked?
Cochlea
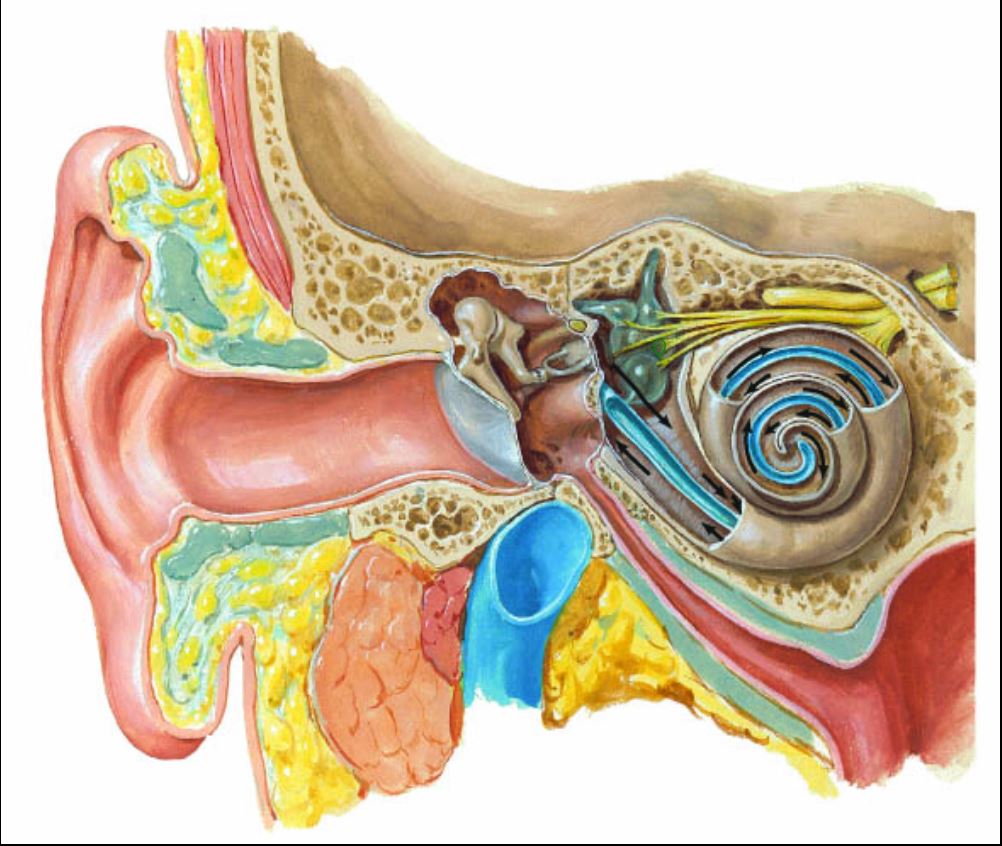
What is marked?
Semicircular Canals
Which cranial nerve is attached to the hair cells in the cochlea and semicircular canals?
CN VII
CN VIII
CN IX
CN X
CN XI
CN VIII
The endolymph fluid contains a high concentration of K+ in the vestibular and auditory systems (True/False)
True
Hair cells are located:
At the base of each semicircular canal
Utricle
saccule
Cochlear duct (scala media)
All of the above
All of the above
When hair cells stereocilia bend from short to the tall kinocilium, K+ enters the cell and the cell is depolarized (True/False)
True
The utricle and saccule hair cells detect linear acceleration (True/False)
True
The semicircular canals hair cells detect head rotation (True/False)
True
Which tract activates the antigravity muscles?
Medial vestibulospinal tracts
v
None of the above
Lateral vestibulospinal tracts
In the vestibular-ocular reflex (VOR), the fast eye movement in the direction of the head turn is called nystagmus (True/False)
True
In the caloric vestibular test, cold water poured into the right ear will cause nystagmus to:
the right side
the left side
both sides
neither side
the left side
A head turn to the left, causes nystagmus to the left (True/False)
True
In the vestibular rotatory test, a spin to the right will result in nystagmus to the
left side
right side
neither side
left side
Vestibular signs and symptoms include:
Spontaneous nystagmus
Decreased antigravity muscle reflexes
Motion sickness
Vertigo
All of the above
All of the above
High frequency sound waves are received at the base of the cochlea whereas low frequency sound waves are received at the apex of the cochlea (True/False)
True
Ventral cochlear nuclei
Timing of sounds
Dorsal cochlear nuclei
Vertical sound location
Superior Olivary nuclei
First place to compare input from both ears, analyzes to help locate the sound source
Inferior colliculi
Integrates function from all brainstem nuclei
Vestibular schwannoma is an example of a sensorineural lesion (True/False)
True
Rinne's test will determine if your patient has a conductive hearing loss (True/False)
True
The 1st neuron in the visual pathway is the:
Rod
Cone
Bipolar cell
Ganglion cell
None of the above
Bipolar cell
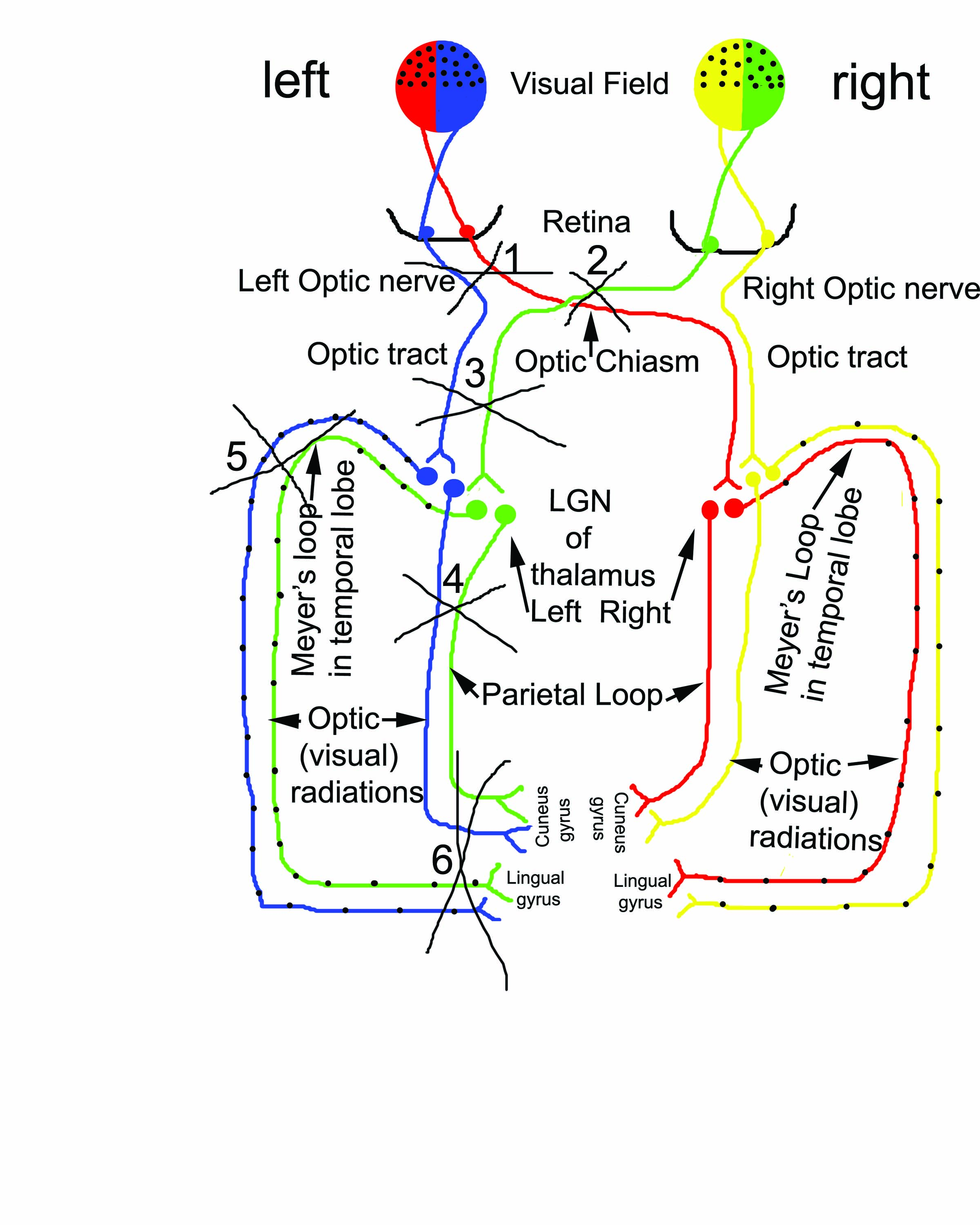
What area (1-6) when lesioned will cause bitemporal hemianopsia (tunnel vision)
Lesion #2, Optic Chiasm (medial portion)
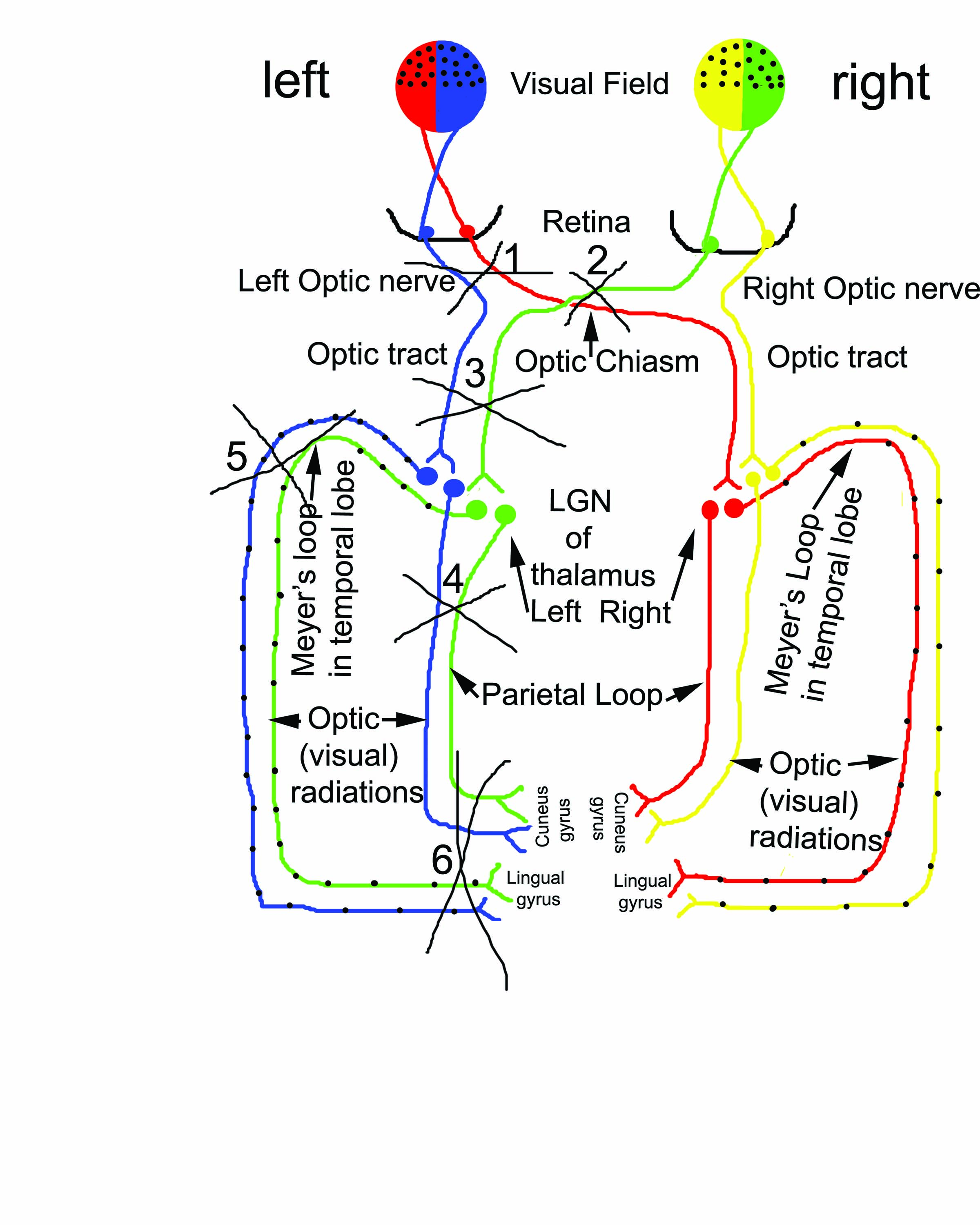
What area (1-6) when lesioned will cause contralateral homonymous superior quadrantopsia
Lesion #5, Meyer’s Loop in temporal lobe
Which 2 cranial nerves are part of the pupillary light reflex?
II & III
III & IV
III & VI
II & IV
II & V
II & III
Which cell is the glial-like supporting cell for the olfactory system?
Basal cell
Sustentactular cell
Olfactory nerve
None of the above
Sustentactular cell
A lesion to the olfactory nerve or the olfactory bulb and tract will result in:
Ipsilateral ageusia
Ipsilateral hemiballism
Contralateral homonymous hemianopsia
Ipsilateral ansomia
None of the above
Ipsilateral ansomia
Which 2 cranial nerves relay the sense of taste?
VI & VII
II & VI
VII & IX
VII & VIII
VIII & IX
VII & IX
Taste buds regenerate every 10 - 14 days (True/False)
True
List the 5 basic types of tase
-Salty
-Sour
-Sweet
-Bitter
-Umami
Which of the following are clinical terms describing taste lesions?
Ageusia
Hypogeusia
Dysgeusia
All of the above
None of the above
All of the above