Ch. 40 Physical Principles of Gas Exchange
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards about Physical Principles of Gas Exchange
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What supplies the energy for diffusion?
The kinetic motion of molecules
What causes the pressure of gases?
What relationship does pressure have to the concentration of gas molecules?
Impacts of moving particles against a surface.
Directly proportional
What two factors are partial pressure determined by?
Concentration and solubility coefficient
What is Henry's Law?
Partial pressure is equal to the concentration over soluability of the gas in a liquid.
It states that at a constant temperature, the amount of gas that dissolves in a liquid is directly proportional to its partial pressure.
What determines net diffusion between the lungs and blood?
The difference between the 2 partial pressures
Upon inspiration, what happens to the air we inhale?
T/F: temperature of water determines the water vapor pressure
becomes humidified
true
What factors determine the net rate of diffusion?
Pressure gradient difference
solubility of gas in fluid
cross-sectional area of fluid
distance of diffusion
molecular weight of gas
temperature of the fluid
*all have a proportional relationship with net rate of diffusion EXCEPT distance of diffusion
What ultimately dilutes all the other gases?
Humidification of air
Composition of air
What is the atmospheric value of air in regards to oxygen?
What happens once the oxygen is breathed in and humidified? What happens as it reaches the alveoli?
How does this compare to CO2?
159 mmHg
Decreases and decreases further to 104 mmHg in the alveoli because the oxygen is now mixing with the lower PO2 already sitting in the lungs
At atmospheric pressure, CO2 is 0.3 mmHg and stays the same as we breathe in air but increases to 40 mmHg in the alveoli
What are the 3 gases we find in the atmosphere from most to least abundant?
T/F: Concentration of gases only change in pressure in different locations
Nitrogen, Oxygen, Carbon dioxide
false - the concentration of gases DO NOT change but the pressure does in different locations (atmospheric air vs air in alveoli)
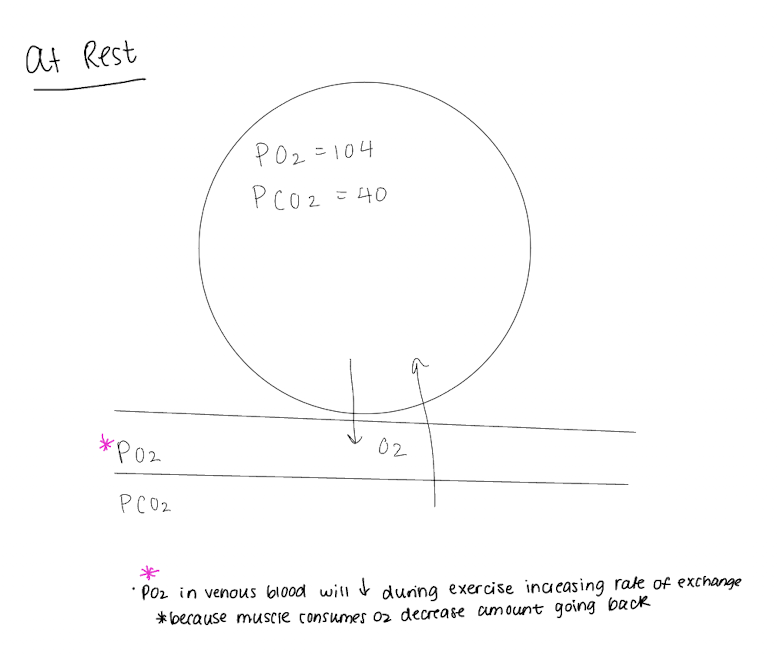
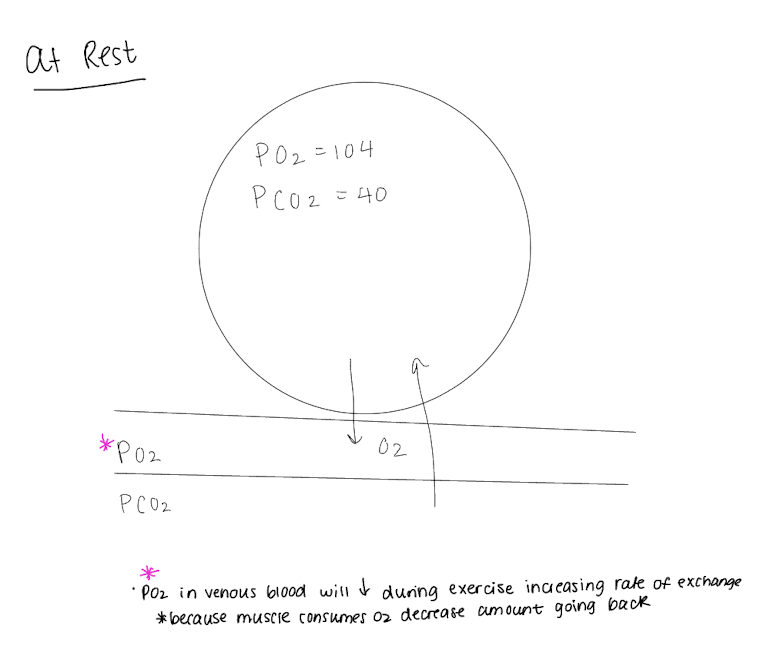
What controls the oxygen concentration and partial pressure in the alveoli?
Rate of absorption of oxygen into blood
rate of entry of new oxygen into lungs by breathing
as new oxygen enters, fresh air has a higher partial pressure of O2 vs CO2, flushing out old air and increasing partial pressure concentration
As alveolar ventilation increases, alveolar partial pressure increases
How does alveolar Pco2 relate to the rate of carbon dioxide excretion?
How does alveolar PCO2 relate to alveolar ventilation?
Increase in PCO2 occurs increasing release of carbon dioxide
*Inverse relationship because we take more oxygen in than CO2
What diffusion factors affect the rate through the respiratory membrane?
Thickness of membrane
surface area of membrane
diffusion coefficient of gas in the membrane
partial pressure difference across the membrane
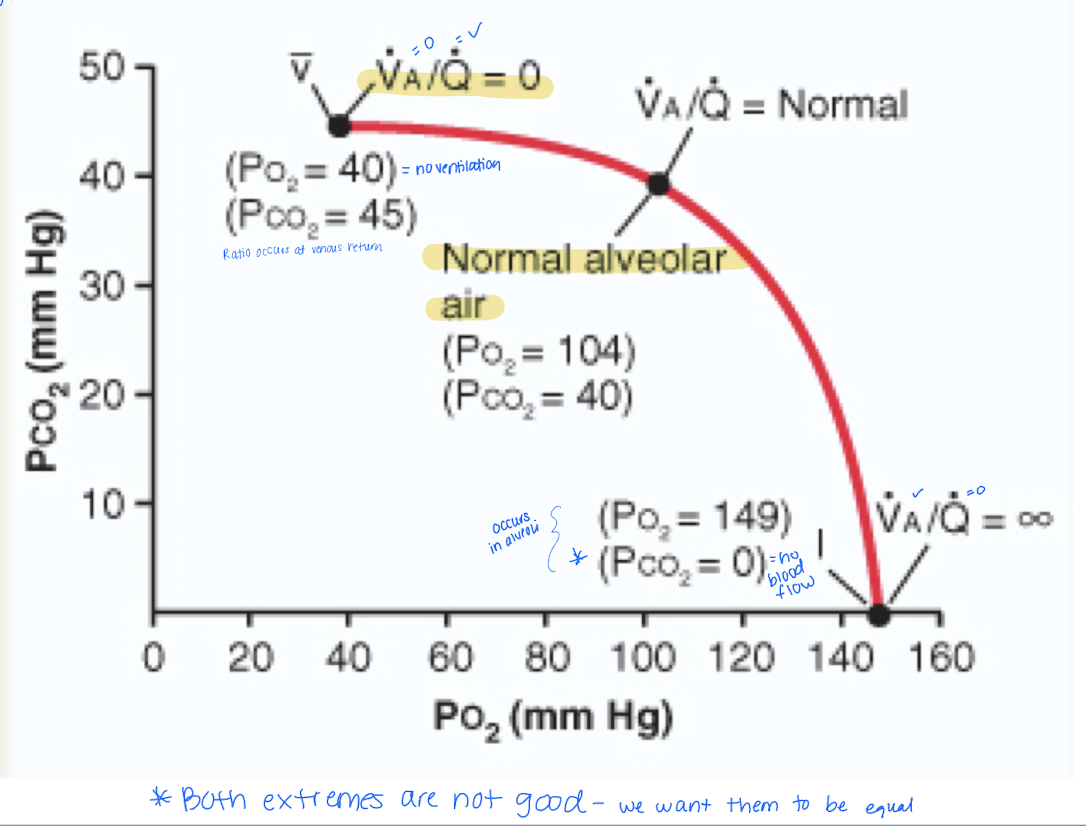
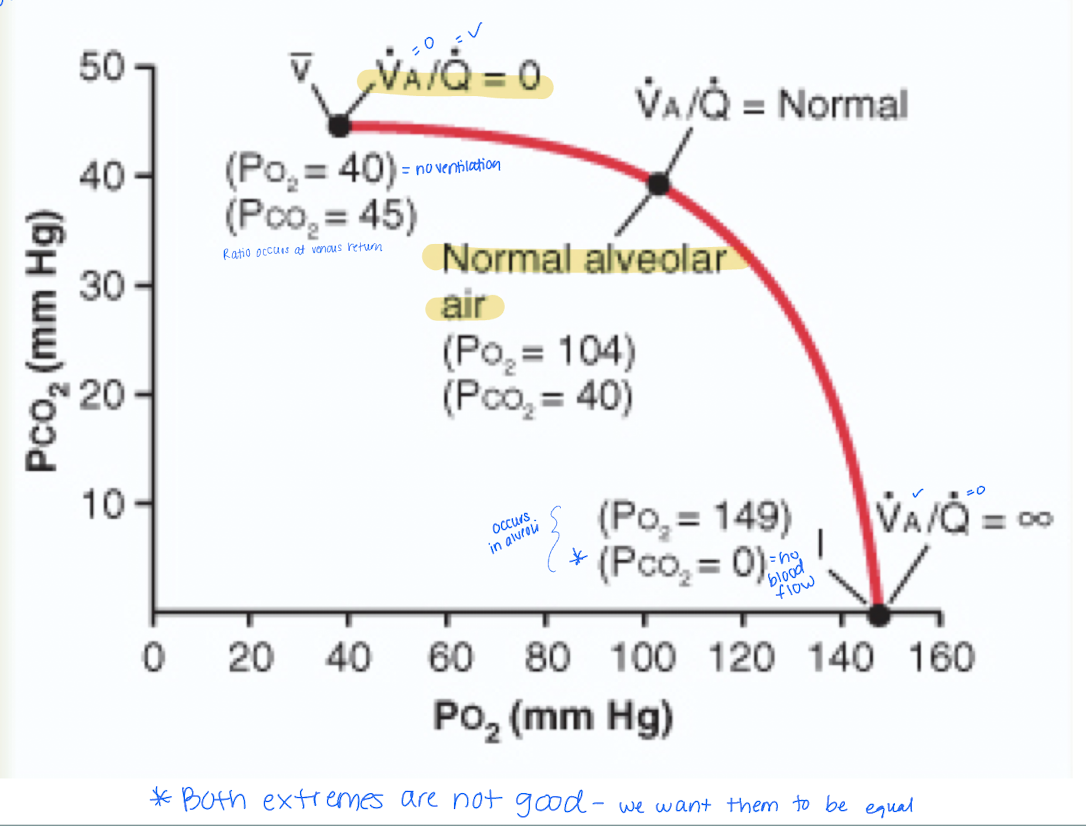
Some areas of lungs are well ventilated but little to no blood flow. Others have no ventilation but normal blood flow. Either way gas exchange is impaired so we look at ventilation-perfusion ratio. Describe it.
Represents the balance between alveolar ventilation (V, the amount of air reaching the alveoli) and pulmonary perfusion (Q, the amount of blood flowing through the capillaries surrounding the alveoli)
Ventilation-Perfusion Ratio (VA/Q)
how would the formula present when there is no ventilation?
VA = 0 and Q is infinite (0/infinite) = zero indicates no gas exchange occurs.
*PO2 = 40 mmHg
Ventilation-Perfusion Ratio (VA/Q)
how would the formula present when there is no perfusion?
VA = infinite and Q =0 (inifinte/0) = ventilation is present
*perfusion is zero when PO2 = 149 mmHg
What is shunted blood?
When ventilation does not adequately oxygenate blood as it passes through the lungs
What is physiologic dead space?
When ventilation is good but there is not enough blood flow meaning ventilation in alveoli is wasted because air is not going anywhere
is a problem with diseased individuals but not for young and healthy
How is optimal relationship between ventilation and perfusion reached?
should equal each other but they are not equal across the lung
The top of the lung is poorly perfused (but good ventilation)
Bottom of the lung has more perfusion (creating physiologic shunt)
What is total atmospheric pressure at sea level?
760 mmHg
Why do individuals feel short of breath when exercising at high altitudes?
a. The air is too thin to breathe
b. There is less oxygen in the air
c. Higher CO2 levels present
d. Lower partial pressure reduces diffusion rate
d. Lower partial pressure reduces diffusion rate
Lower atmospheric pressure results in lower partial pressure because of the reduction in the pressure gradient for oxygen diffusion from alveoli to blood = gas exchange is less efficient