CMS II: GI - EXAM #1 (quizlet)
1/195
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
196 Terms
Dyspepsia is defined as
epigastric pain or burning, early satiety, postprandial fullness
also described as Nausea or vomiting
distinguish from heart burn!! Heartburn= retrosternal burning and GERD present
most common cause of chronic dyspepsia
functional dyspepsia--> no obvious organic cause exists
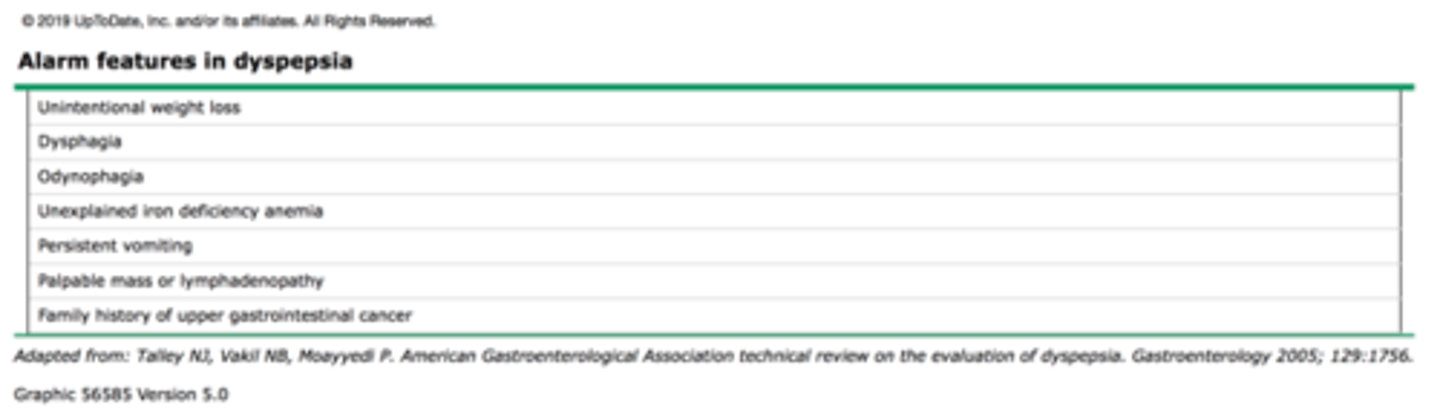
GI alarm symptoms
-constant or severe pain that wakes the patient in the middle of the night
-unintentional weight loss (think cancer)
-persistent vomiting
-Dysphagia
-Odynophagia
-Hematemesis
-Melena
-Hematochezia
-palpable mass or LAD
-unexplained iron deficiency anemia
-Fam Hx of GI cancer
any of these warrant an endoscopy/colonoscopy
a 65 year old male patient presents to your clinic complaining of abdominal pain. He admits to a 30 pack year hx of smoking. He says that his pain is changed when he eats. What type of dyspepsia is this?
peptic ulcer dyspepsia
-these are usually older patients (>55) with a hx of smoking and the pain changes with food or meds
-non-ulcer dypepsia think younger pt with variety of GI symptoms and associated with ic anxiety, depression, or stress
study of choice for dyspepsia
upper endoscopy (EGD)
-done in primarily ALL pts >60 years old or <60 years old with alarm symptoms
NOTE: for patients born in areas like Asia with increased incidence of gastric cancer refer for endoscopy for those >45 yrs old!!!
Best initial tx option for dyspepia
lifestyle modifications
-reduce or D/C alcohol, caffeine, fatty food intake
-D/C smoking
-don't lay down right after big meals/prop yourself up
-no food 3 hours before bedtime
if this doesn't help go to H2RA blockers or PPIs
important side effects of PPIs
-increased risk for C. Diff infections
so not the best for older people who are on other concurrent abxs long term
-Bone Fxs (won't be absorbing ca as well)
-hypomagnesium, hypocalcemia, low B12 and iron
important complications of vomiting
-dehydration
-hypokalemia
-metabolic alkalosis
-pulmonary aspiration
-Boerhaave's syndrome
-Mallory-Weiss tear
best tx for chemotherapy induced nausea
steroids (dexamethasone)
singultus
hiccups
medical definition of constipation
-<3 bowel movements in a week
-excessive straining with defecation
-puborectalis muscle and external sphincter fails to relax in response to rectal pressure
spasm of anal sphincter associated with cramping & ineffective straining at stool
Tenesmus
if pain is relieved by defecation think
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
M/C symptom in _______________ change in bowel patterns***
Genetics + Environment
IBD
Abdominal radiation
>50 years old
African Americans
M>F
Uncontrolled acromegaly
Obesity
Diabetes
Red and processed meat; charred meat
Smoking/ Alcohol
Colonoscopy is the BEST test when suspected
colon cancer
most common cause of constipation
inadequate fiber or fluids
If a 20 yr old patient comes in complaining of constipation but they have no alarm symptoms, what's the next best step?
give a bulking agent (fiber supplement)
like metamucil
if they have any alarm symptoms must refer for colonoscopy!!!
which type of laxative must be avoided in people >55 years of age w/ known kidney disease or if they are on meds that affect kidney function (NSAIDS/ACE I/ ARBS/ DIURETICS)
SODIUM PHOSPHATE (osmoprep, fleets phosphorsoda)
study for a fecal impaction that is diagnostic and therapeutic
DRE
main different between non-inflammatory and inflammatory acute diarrhea
non-inflammatory=NON-BLOODY
inflammatory= BLOODY
-will also have fever
-complication includes Hemolytic uremic syndrome from E coli H157
alarm symptoms for acute diarrhea
-bloody diarrhea
-fever
-abdominal pain
all together
best abx tx for acute infectious diarrhea
-ciprofloxacin
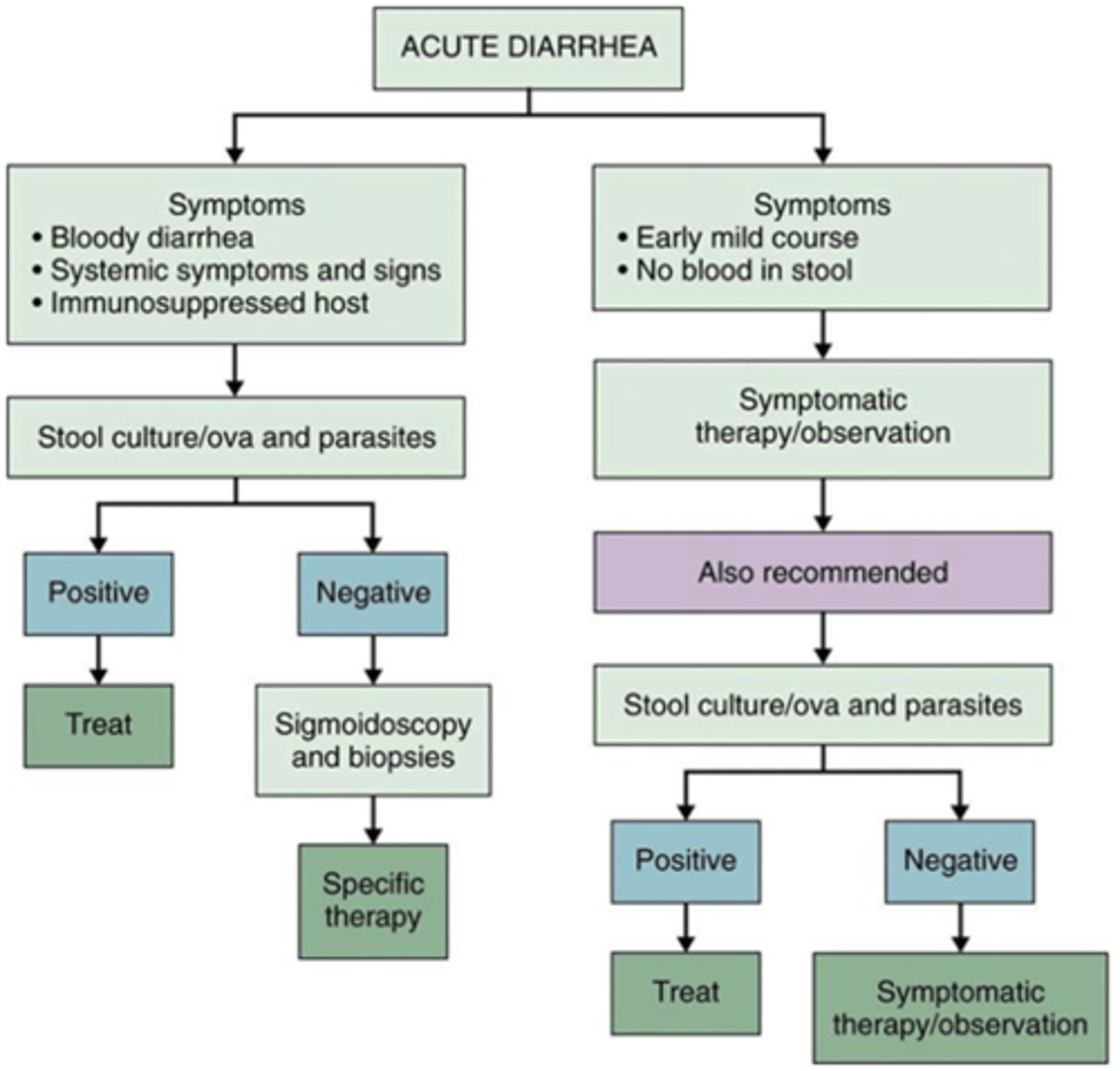
what should always be avoided in acute inflammatory diarrhea
AVOID ANTI-DIARRHEAL AGENTS IN THESE PTS
chronic diarrhea is defined as
occurring for > 4 weeks
always r/o cancer as a cause of chronic diarrhea!!
-mass only would allow liquid through
a 28 yr old female comes in to the ER complaining of large amounts of watery diarrhea (>1 L/day) and vomiting that has been going on non-stop for the past 3 days. The patient has hardly eaten anything yet the symptoms have continued. What type of diarrhea are they most likely suffering from?
secretory diarrhea
-patient had no change with fasting
diarrhea that gets better with fasting
osmotic diarrhea
radiation enteritis is a cause of _____
inflammatory diarrhea
-cancer patient undergoing radiation and chemo may experience diarrhea due to inflammation of the colon
test of choice for malabsorption
fecal fat!!
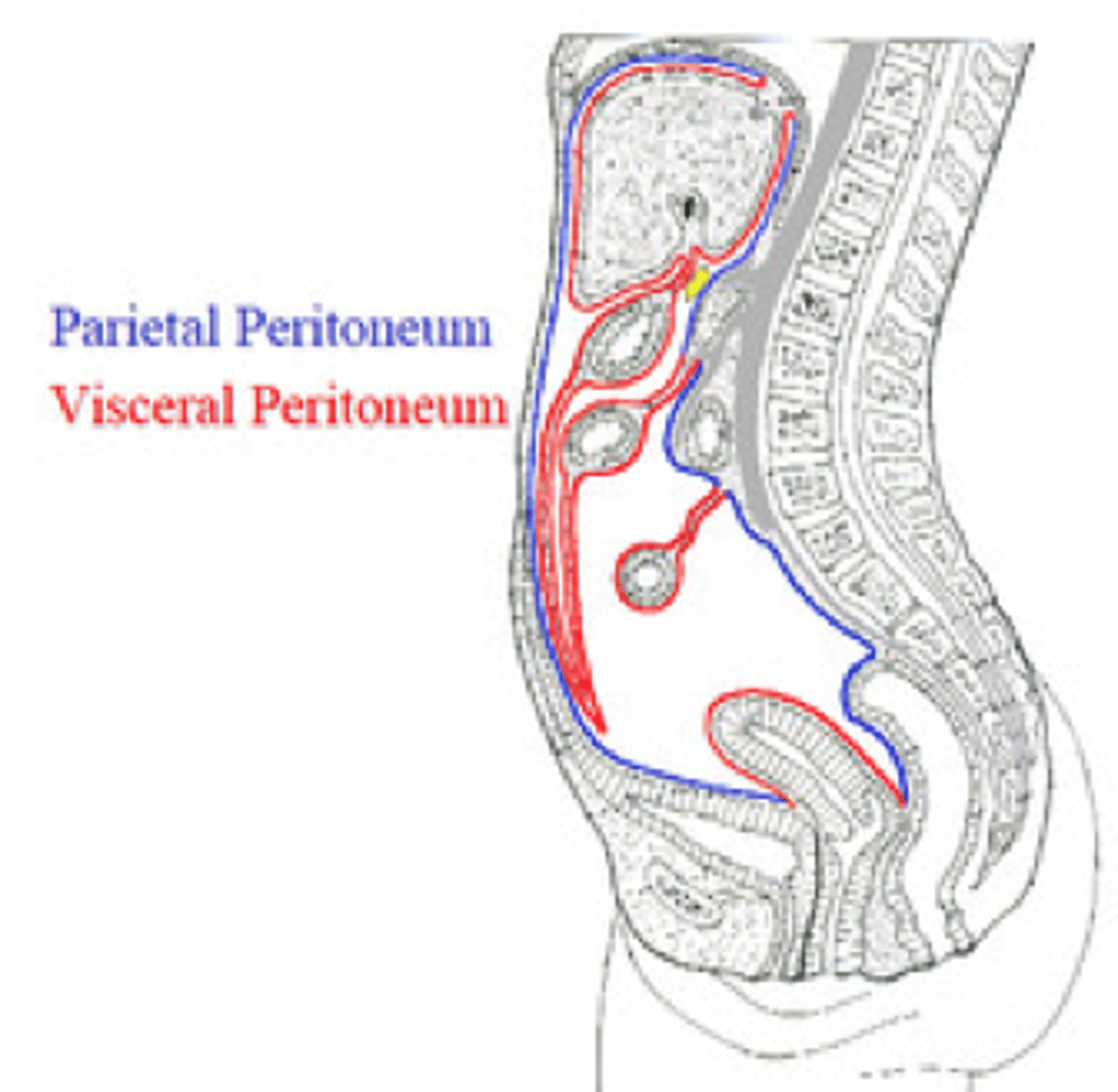
1. visceral peritoneum is innervated by ____
2. Parietal peritoneum is innervated by ____
1. ANS
-often poorly localized, dull achy pain
2. spinal somatic nerves
-often localized very sharp pain
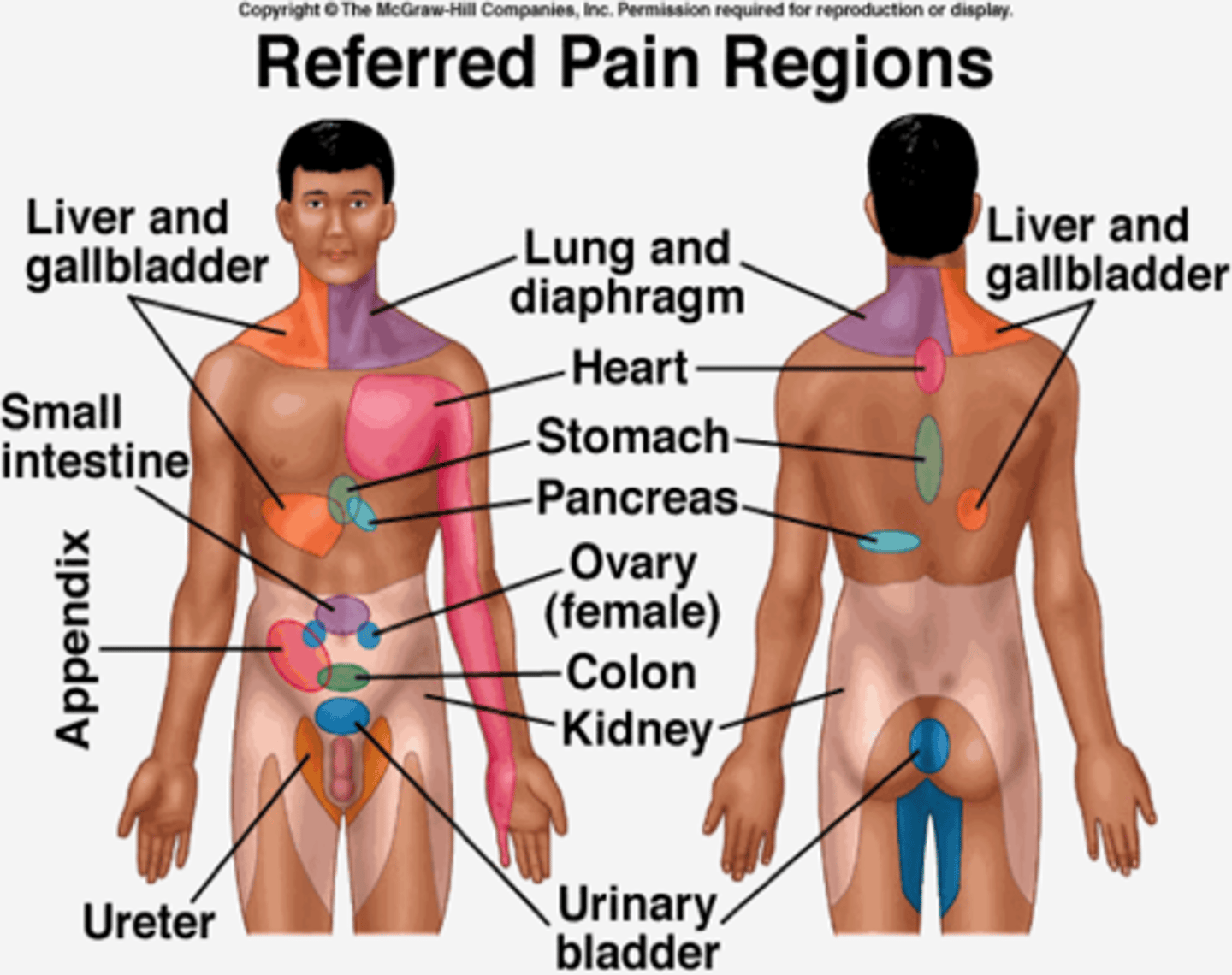
1. common referred pain region for the pancreas
2. common referred pain region for the liver and gallbladder
1. back
2. shoulder and back
what exams must always be included for acute abdominal pain besides GI physical exam?
rectal and gynecologic!!!
UPPER 1/3 of the esophagus is composed of ____ muscle and controlled by _____
striated muscle; CN IX & X
LOWER 2/3 of the esophagus is composed of ____ muscle and controlled by _____
2. smooth muscle; CN X and esophageal myenteric nerve plexus-->remains tonically constricted
Odynophagia or painful swallowing always think ________________.
severe erosive or infectious esophagitis
HALLMARK FOR INFECTIOUS ESOPHAGITIS
What is the term for sensation of a constant "lump in the throat"?
Globus Pharyngeus (globus hystericus)
-caused when Cricopharyngeal muscle becomes too tight
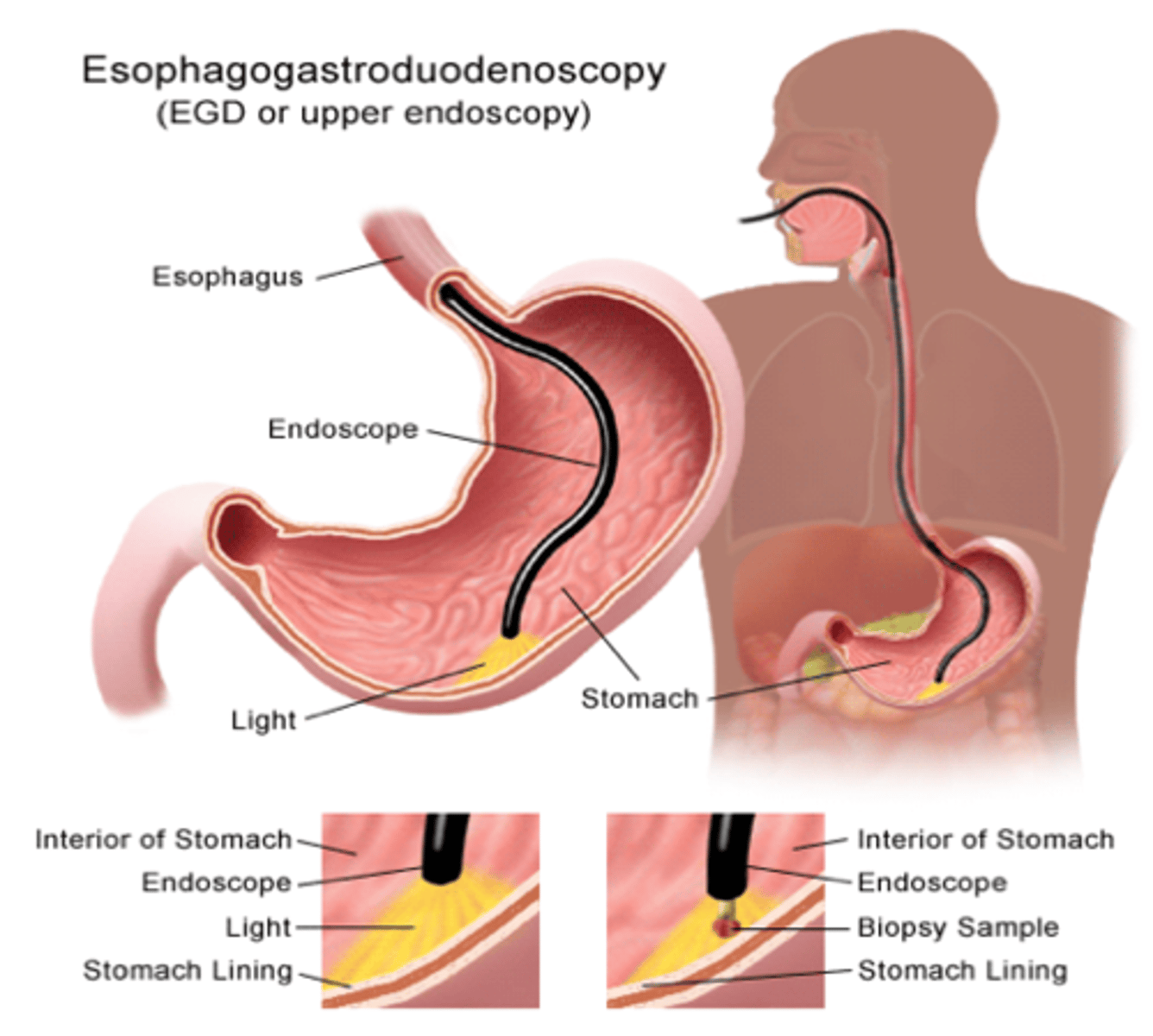
Study of choice for **persistent heartburn, odynophagia, abnormalities** noted on barium studies.
EGD (EsophagoGastroDuodenoscopy)
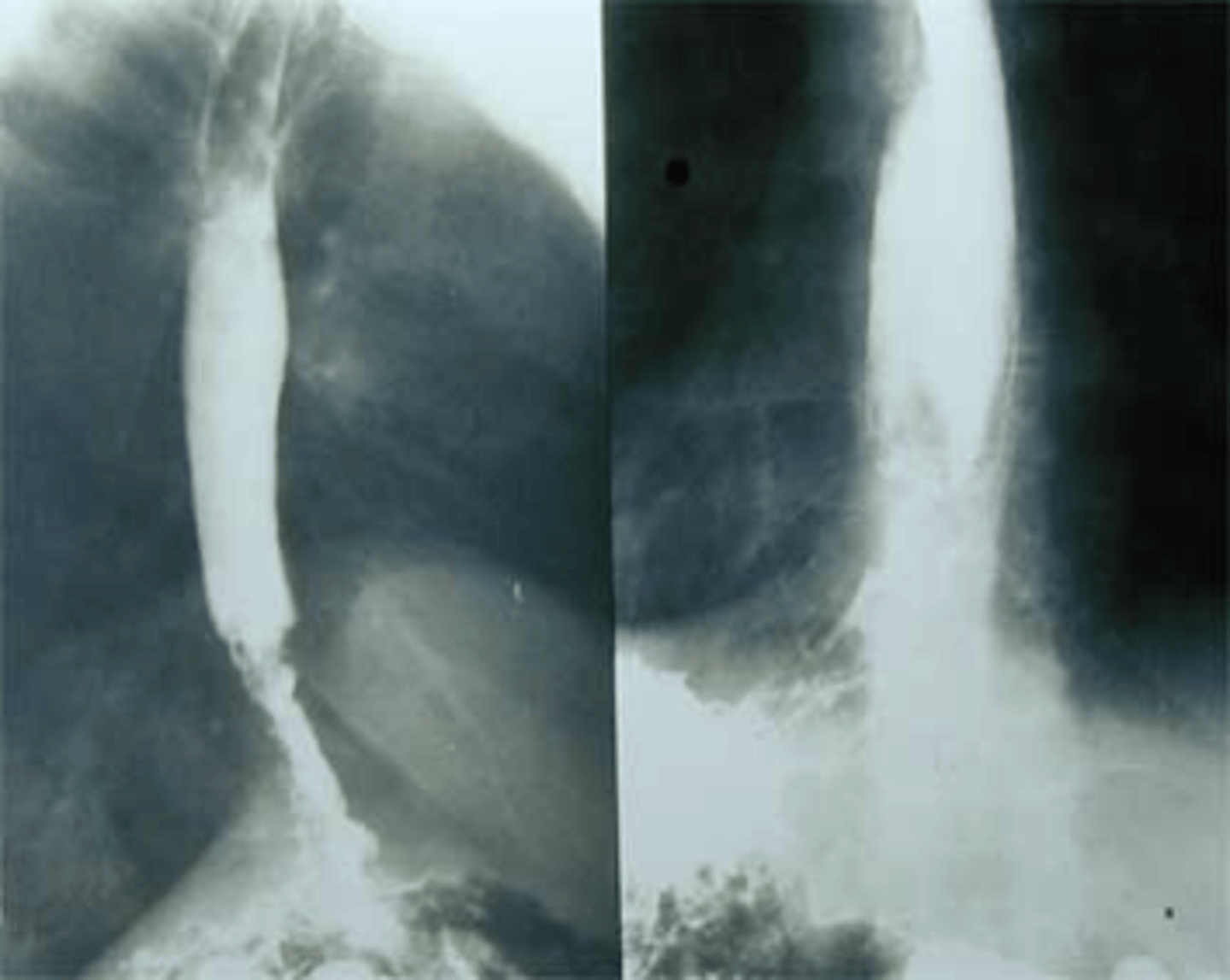
Study that differentiates between mechanical and motility disorders
- evaluates strictures/structural abnormalities
- if barium swallow comes back normal then it is likely a motility disorder
- NOT USED TO Dx GERD
Barium Esophagography/Barium swallow (BA swallow, UGI series)
Gold standard for assessing motility disorders.
***NOT INITIAL TESTING. (Used after taking Hx, barium radiology, or endoscopy).
esophageal manometry
-barium swallow comes back normal so there's no stricture or mass so now do this since it is a likely a motility disorder
Study to evaluate typical symptoms of GERD (heartburn and regurgitation) that do not respond to treatment with medications.
- To evaluate atypical symptoms of GERD (chest pain, coughing, wheezing, hoarseness, and sore throat).
Esophageal pH Monitoring
____________________________ is used for pre-operative evaluation
- The wireless capsule is used most often
Ambulatory esophageal pH monitoring
Substernal burning sensation that originates in the epigastrium and may radiate upward into the chest and what foods exacerbate this condition?
GERD
exacerbated by:
-chocolate
-onions
-peppermint
-spicy foods
-caffeine
-high fat foods
________________:
-includes a peritoneal layer that forms a true hernia sac; pushes on esophagus
- Requires Surgical Repair when reflux symptoms won't resolve or emergent conditions
(both can cause heartburn)
Paraesophageal Hiatal Hernia
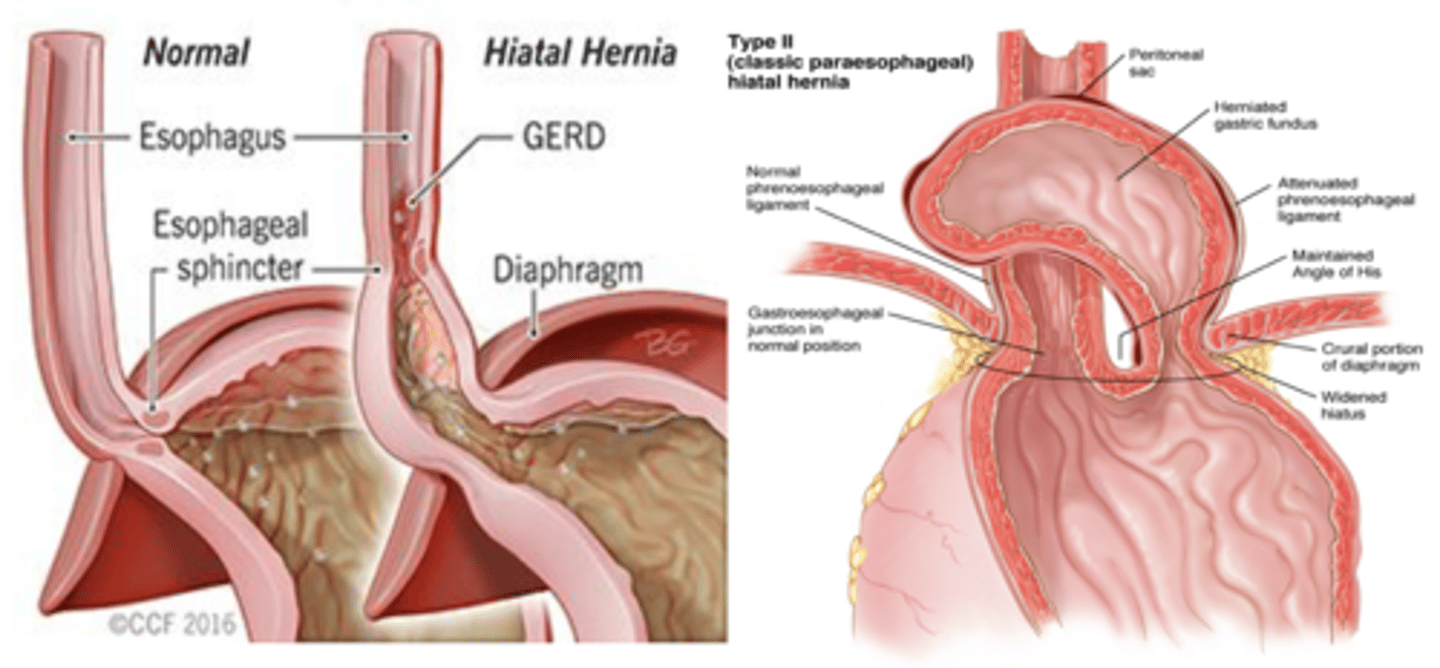
__________________:
- caused by weakened muscle tissue surrounding the hiatus
- usually asymptomatic and discovered incidentally
Sliding Hiatal Hernia
if a patient is diagnosed with GERD and also has asthma, chronic cough, laryngitis, or chest pain
refer these patients to cardio and pulm for further eval!!!
What test is indicated for pt's with GERD and alarm symptoms?
EGD (EsophagoGastroDuodenoscopy)
T/F: H. Pylori screening is recommended in GERD patients
FALSE!
-only screen for this if they have epigastric pain and you are concerned for gastritis or PUD
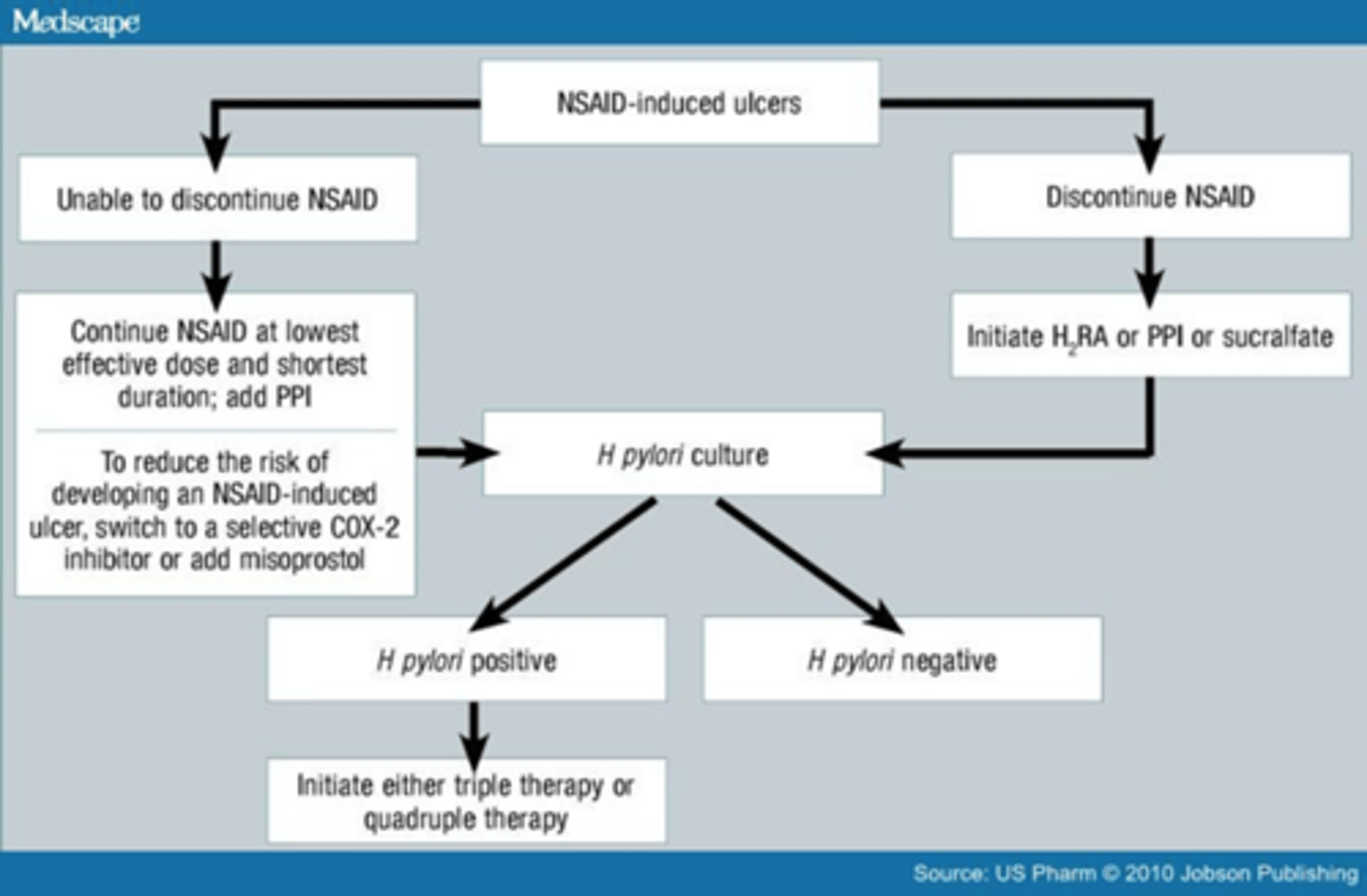
FIRST step for GERD tx
lifestyle modifications!
-weight loss
-avoid laying down after eating
-avoid meals 2-3 hours before bedtime
-elevate head 6"
-D/C alcohol and smoking
if this alone does not help:
-PPI (omeprazole) for GERD + erosive disease
-H2RA (Ranitidine) if w/o erosive disease
_______ are first-line Rx for the tx of
-mod-severe GERD
-erosive esophagitis
-NSAID-induced ulcers
-eradication of H. Pylori associated ulcers
PPIs
1ST-LINE DOC for GERD. Should be given once/ day, BEFORE the first meal of the day.
PPIs
___________________:
-squamous epithelium in the distal esophagus is replaced by metaplastic columnar epithelium
-presence of dysplasia-->inc risk of adenocarcinoma
-10% of pts with chronic GERD
-Diagnose with EGD; recommended in pts with > 1 yr of GERD
-tx: long-term PPI (***only agents that heal ulcers and erosions)
Barrett's esophagus
pts most commonly affected by infectious esophagitis = _____________________
immune compromised
Best Tx option for types of infectious esophagitis:
1. Candida
2. HSV
3. CMV
1. Fluconazole
2. Acyclovir
3. ganciclovir
Mainly in immunocompromised pts
Pathogens:
Candida albicans*
- In those with uncontrolled DM, or on systemic corticosteroids or immunosuppresion
HSV*
CMV (especially with AIDS)
- Rate has declined with use of anti-retrovirals
↑ in pts with solid organ transplants
Sx:
- Odynophagia
- Dysphagia
Infectious Esophagitis
A 16 yr old male pt presents to your clinic complaining of difficulty swallowing and retrosternal burning after eating big meals then laying down. The only pertinent medical hx is that he has asthma and eczema that is under control. Suspecting GERD, you put them on a PPI and have them f/u in two weeks. 2 weeks later your pt says they have no improvement with the PPIs. What is your suspected Dx? What should your next step be?
Eosinophilic Esophagitis
-will not respond to PPI therapy
-associated with food and environmental allergies
next step: do EGD and look for linear lines and concentric circles
pathophysiology of ________________:
allergic inflammation and remodeling
eosinophilic esophagitis
endoscopy findings for ___________________:
- multiple concentric rings resembling the trachea
- linear furrows
- white patches
eosinophilic esophagitis
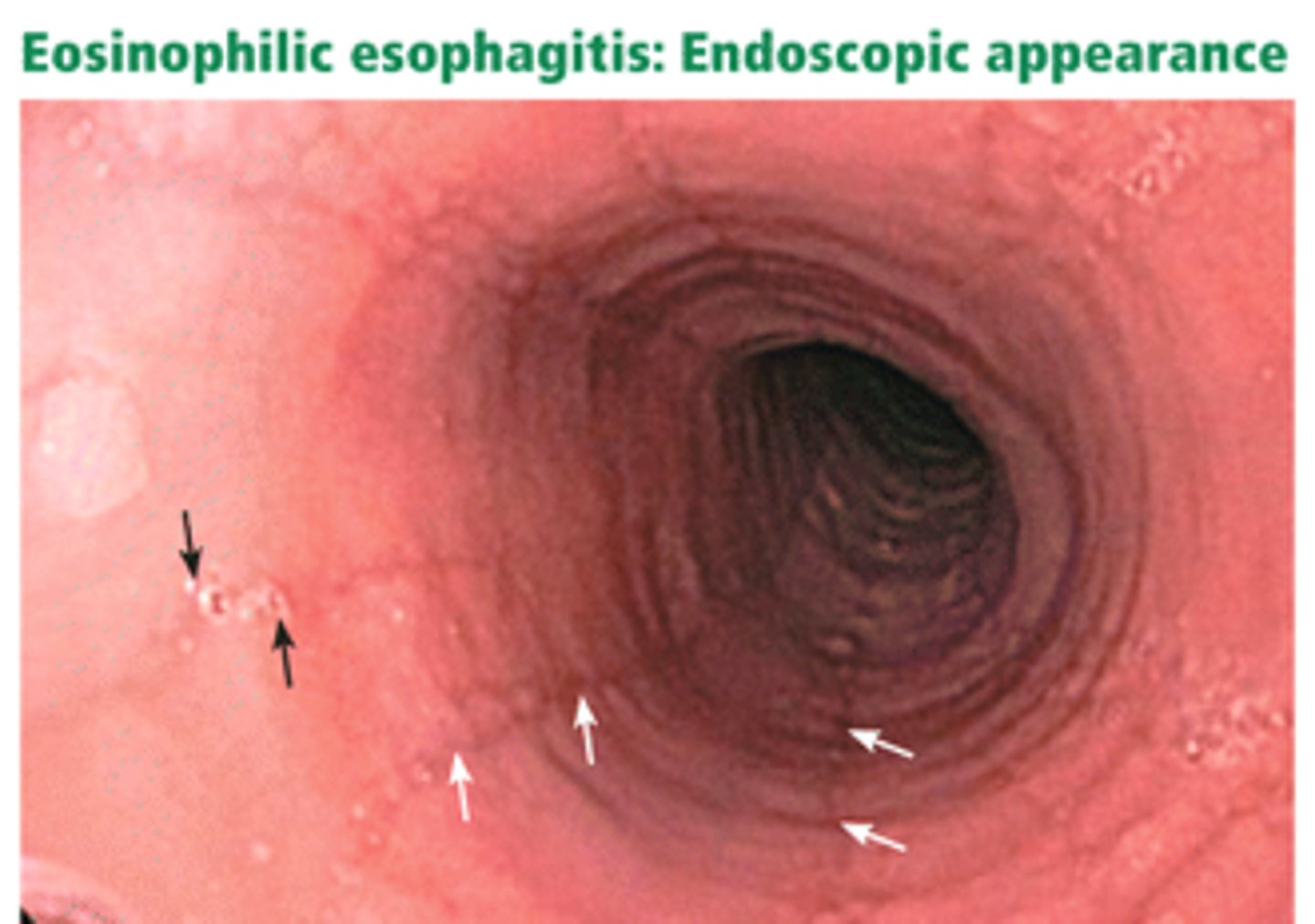
common causes of ____________________
NSAIDs
KCL
BISPHOSPHONATES
-occurs higher in the esophagus than reflux esophagitis
NEVER PRESCRIBE THESE AGENTS TO PATIENTS WITH ESOPHAGEAL DYSMOTILITY OR STRICTURES
educate pts to swallow meds w/ full glass of water, remain upright for 30 min after taking meds
pill-induced esophagitis
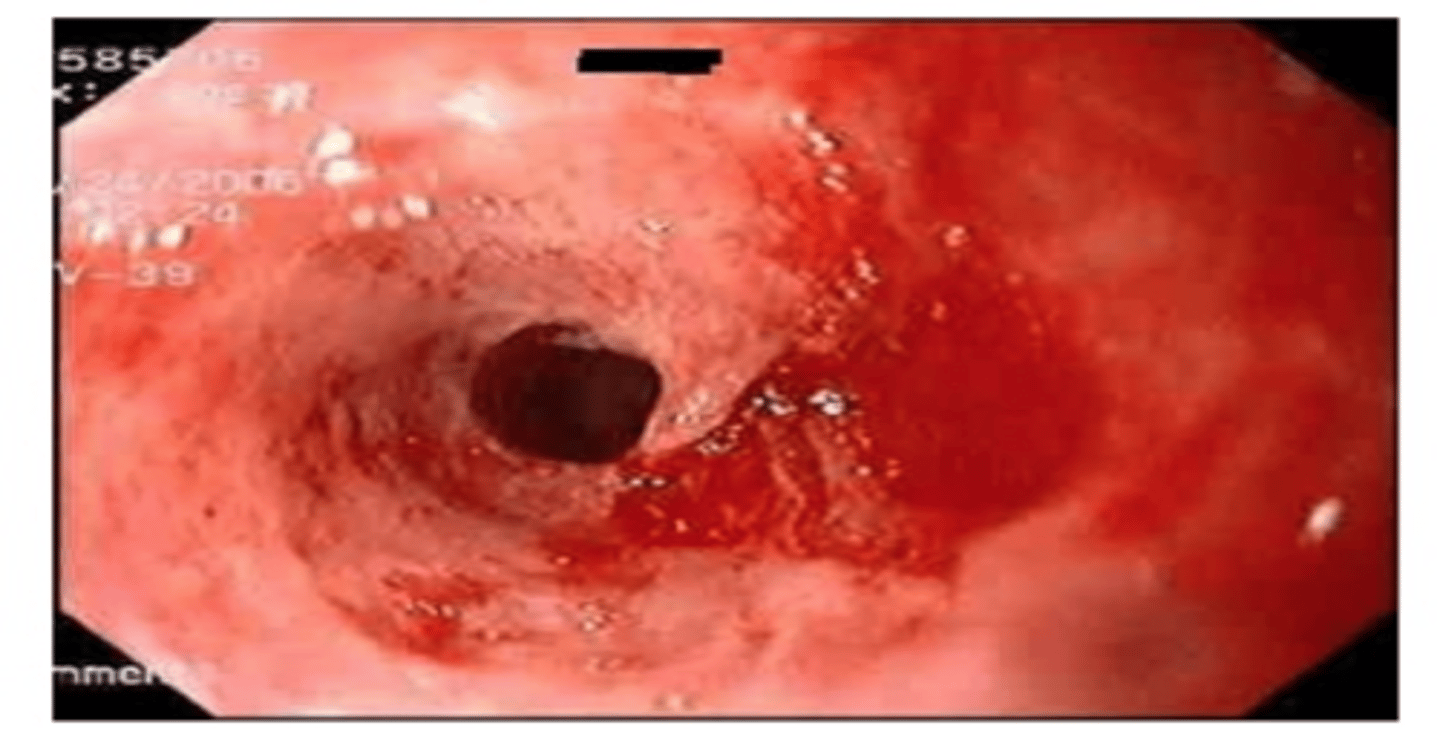
_____________: Full-thickness (Transmural) tear in esophagus; usually from overindulgence in food and alcohol --> forceful vomiting
Typically, a left posterior distal rupture
- Chemical, then infectious mediastinitis
- Severe chest pain, sepsis, shock
- Pneumomediastinum (Hamman's sign)
- Pyopneumothorax
Boerhaave's syndrome
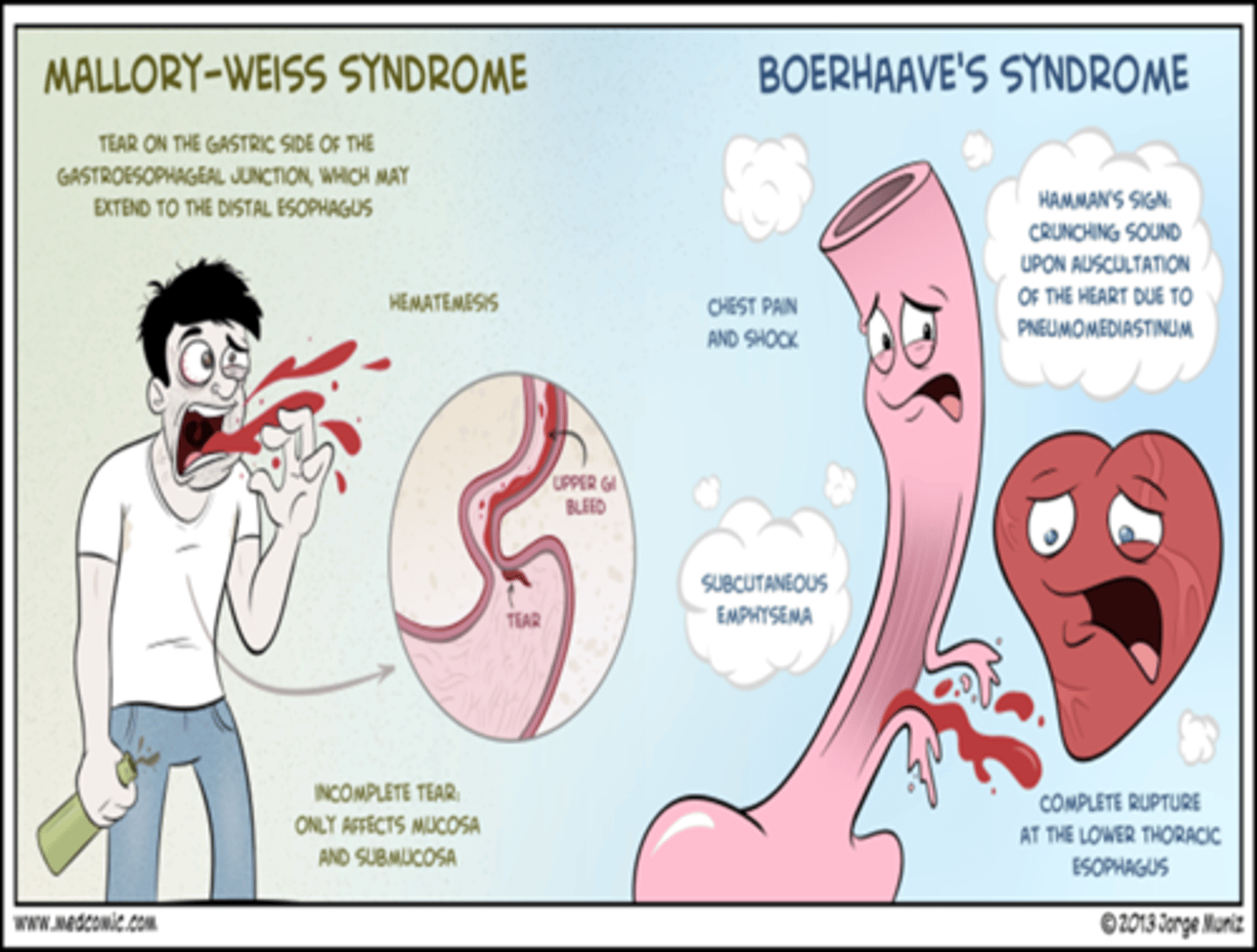
_______________ - incomplete mucosal tear at GE junction that is usually caused by prolonged vomiting/retching; most heal on their own in 24-48 hrs
Mallory Weiss tear
Concomitant Portal HTN, increases the risk of massive bleeding from a __________________.
Mallory Weiss tear
Pt with **forceful vomiting then **severe chest pain, sepsis, shock, pneumomediastinum (Hamman's sign) think ______________________.
Boerhaave syndrome (Effort rupture)
-PERFORM UGI SERIES W/ GASTROGRAFIN
(not safe to use barium w/ risk of full thickness perforation)
________________: in middle-aged women with iron deficiency anemia
-seen with **Esophageal Webs** (thin fibrous protrusions of squamous epithelium)
FAV BOARD QUESTION
Plummer-Vinson syndrome
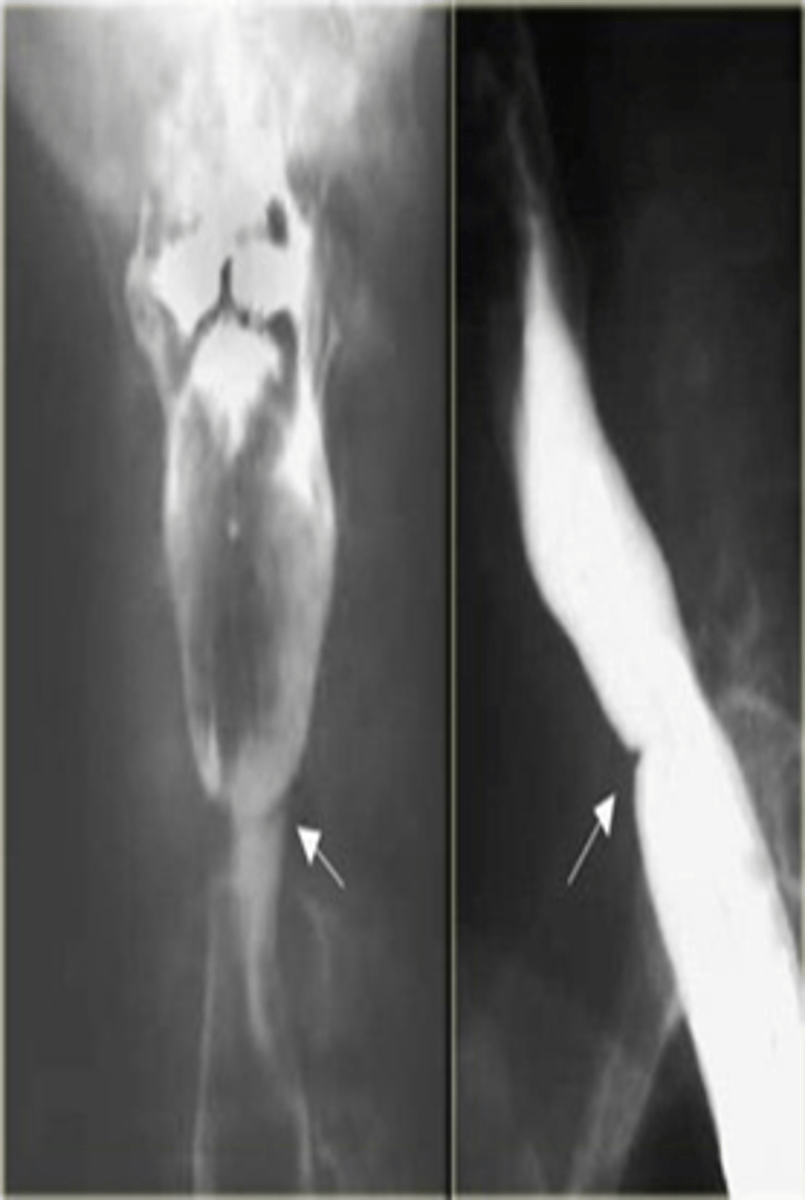
_________________ are associated with:
Plummer-Vinson syndrome
▪ In middle-aged women with iron deficiency anemia
▪ Increased incidence of SCC
Bullous diseases
▪ Pemphigus
▪ Bullous pemphigoid
Graft vs. Host disease
Celiac disease
Esophageal Webs
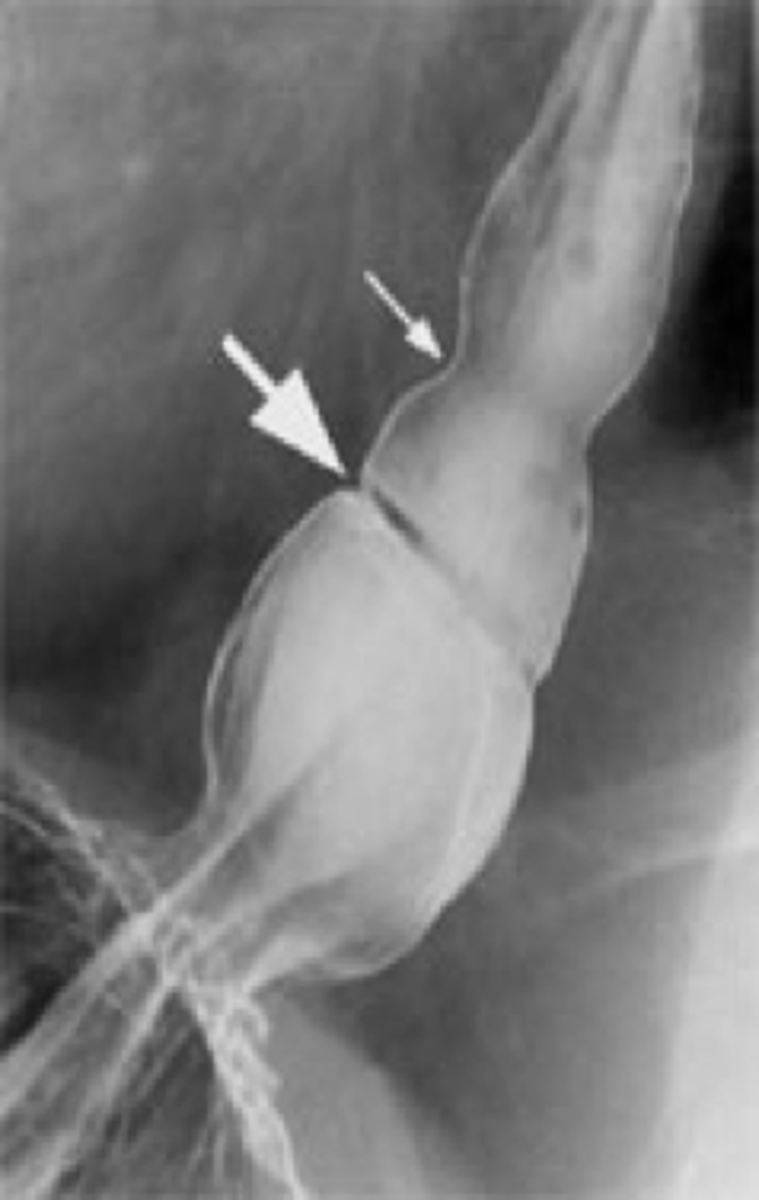
_____________: thin weblike constriction at or near border of LES (**DISTAL esophagus) that causes intermittent solid food dysphagia
-fix with dilation
Schatzki's ring (esophageal rings)
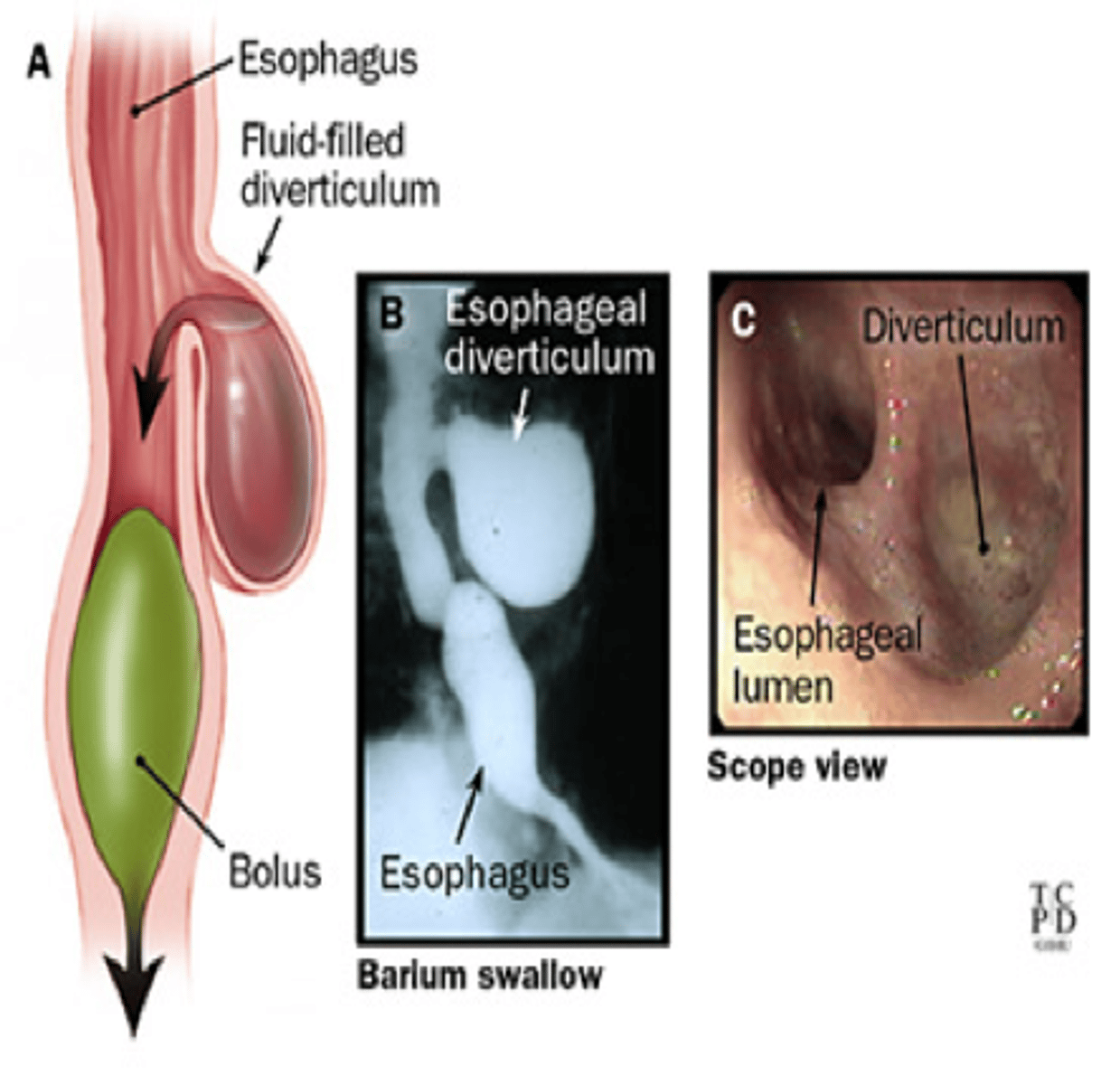
____________: outpouchings in esophageal wall that are Secondary to motility disorders or strictures.
- food will get stuck in these and cause people to regurgitate; may have dysphagia also
esophageal diverticula
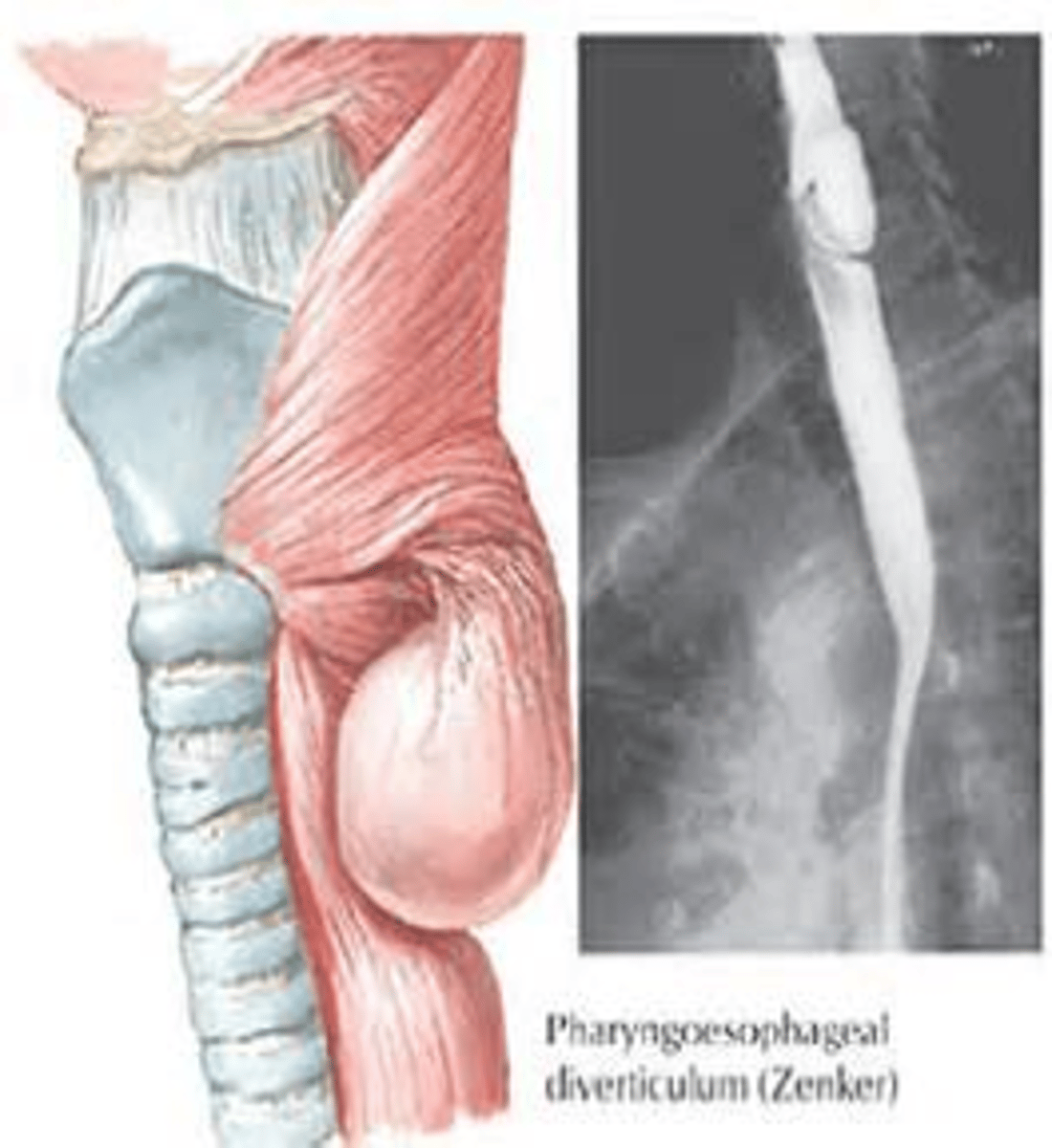
________________: pharyngeal mucosa protrusion at the hypopharyngeal wall
- appears as a natural zone of weakness in posterior hypopharyngeal wall --> Killian's triangle
- regurgitation of food that gets stuck
- severe halitosis
- choking, gurgling
Zenker's Diverticulum
______________: Enlarged venous collateral channels that dilate as a result of portal HTN**
- Present in 50% of patients with cirrhosis
- 1/3 of these will bleed within 2 yrs of Dx
- Highest mortality & morbidity of any upper GI bleed (up to 38% mortality at 5 years)
Esophageal Varices
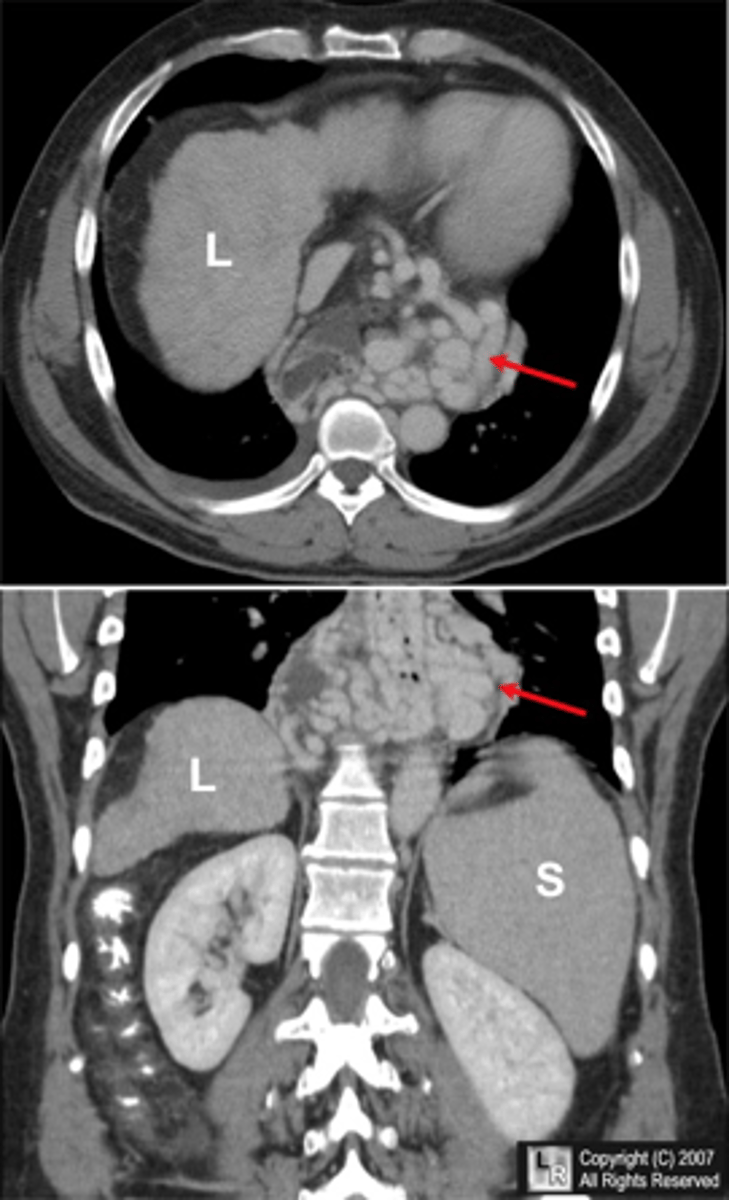
Pathogenesis:
Collateral venous pathways dilate from ↑ portal pressure in an attempt to transport blood from the splanchnic bed surrounding the cirrhotic liver→ heart
This complex venous network lies just beneath the mucosa at the proximal stomach & esophagus
- ↑ portal pressures→ massive rupture
- Exsanguination occurs 10-15% of the time even in the hospital setting
Esophageal Varices
hypotensive, tachycardic, and vomiting blood think _________________.
Esophageal Varices
S&S:
Acute GI bleed (hypovolemia)
- Hematemesis, melena, hematochezia
Rx:
- Fluid resuscitation
- FFP/ platelets
- Spontaneous resolution in 50%
-- ½ of these will re-bleed within 6-8 wks
- Emergent endoscopy (within 2-12 hours)
-- Banding
-- Sclerotherapy
Esophageal Varices
Rx to start first with ______________:
***IV Octreotide
(somatostatin analog that decreases splanchnic blood flow)
- IV Vasopressin and NTG
- Vitamin K (abnormal PT)
Chronic BP management:
- Nonselective ß-blockers (propranolol, nadolol)
-- To ↓ resting HR by 25%
- Long-acting nitrates (isosorbide mononitrate)
-- Synergist action with BB to ↓ portal pressure
Esophageal Varices
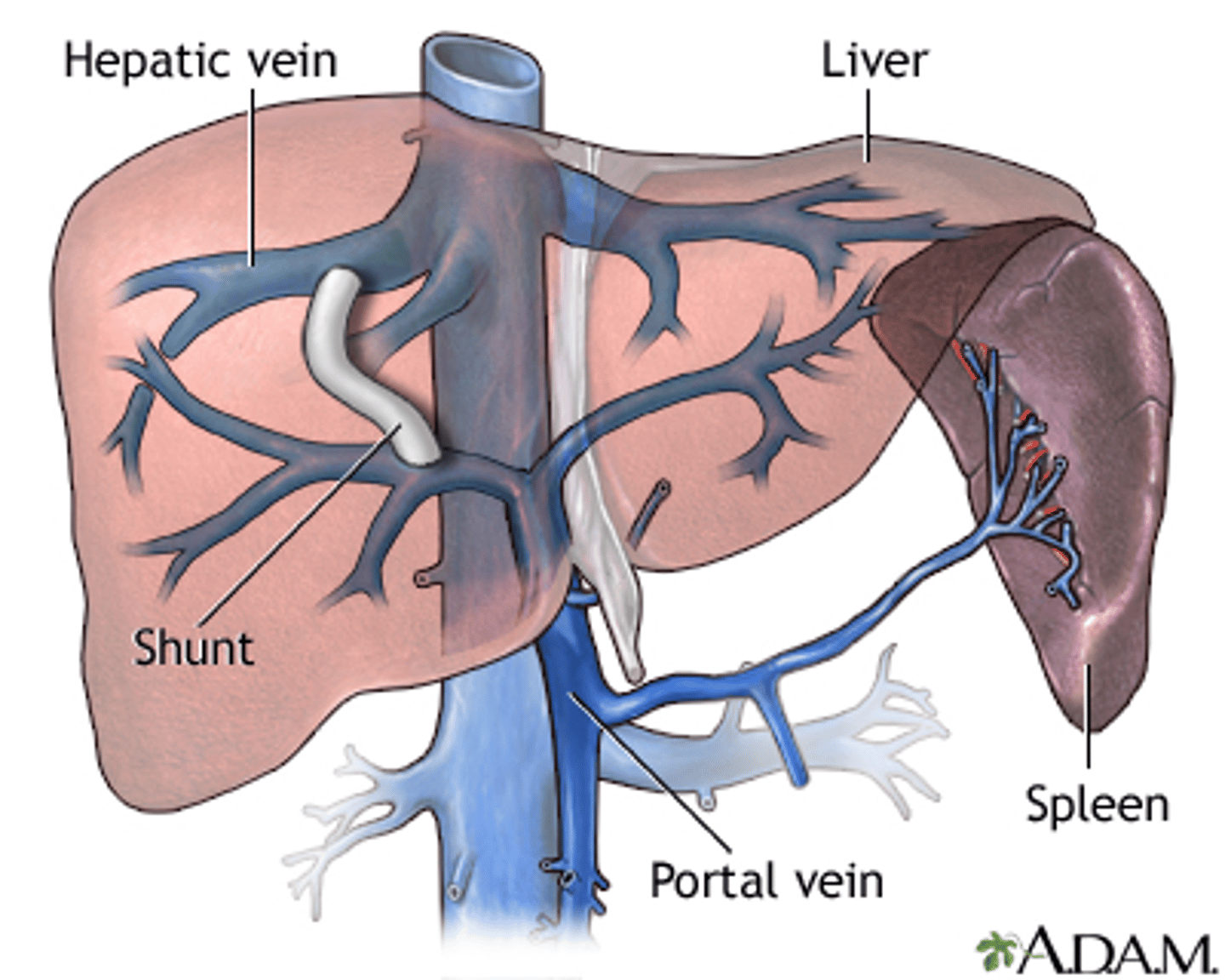
_____________________ is used for a more last resort method for esophageal varices
- usually for stabilizing pts waiting for liver transplants OR reserved for recurrent bleeds
- shunts blood from portal vein to hepatic vein
- risk for encephalopathy and CHF
TIPS (Transvenous Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt)
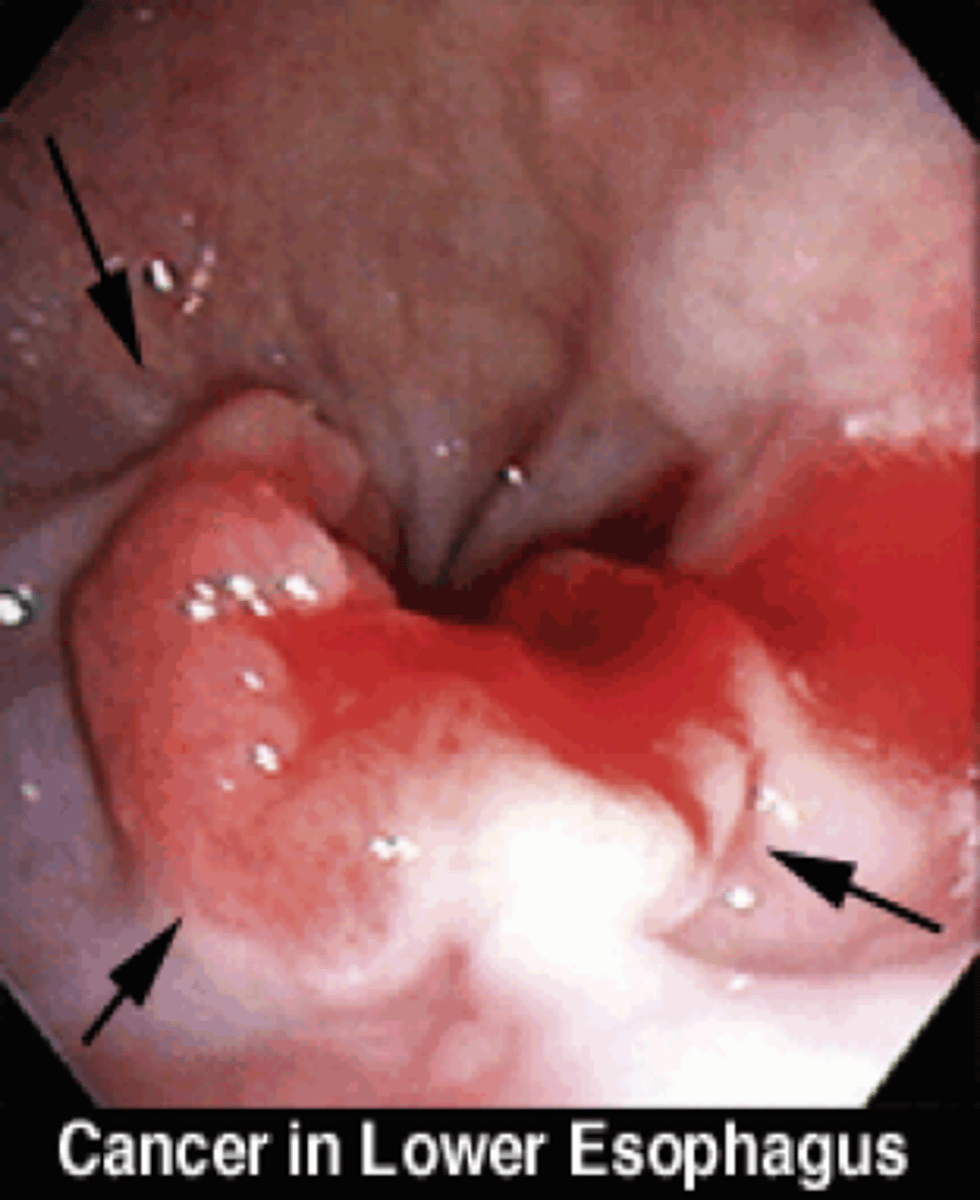
M/C esophageal cancer: _________________
S&S:
- Anorexia/weight loss
- Supraclavicular LAD (Virchow's node) and cervical LAD
DX with UPPER endoscopy w/ Bx
60% of these pts will not be candidates for surgery --> Palliative therapy
Adenocarcinoma
most important predictor of survival in a pt with esophageal cancer?
spread to lymph node
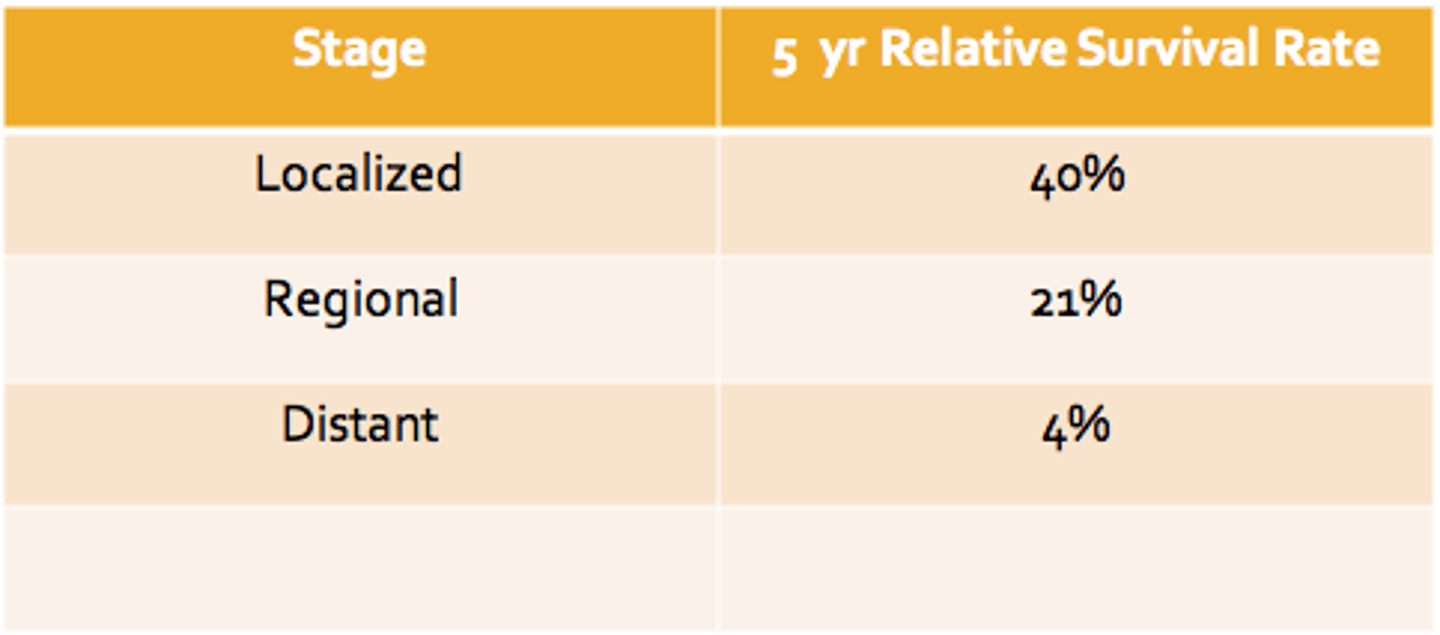
____________: Aperistalsis in distal 2/3 of esophagus
- Failure/incomplete relaxation of the LES
-occurs form loss of inhibitory vagal innervation in the esophagus
Primary disease = degeneration of Auerbach's Plexus**)
Achalasia
Your patient is complaining of progressive solid food dysphagia and regurgitation of undigested food. You tell them to swallow in front of you. When they attempt to swallow they lift their neck, throw their shoulders back, and Valsalva. What is the likely cause of their dysphagia?
Achalasia
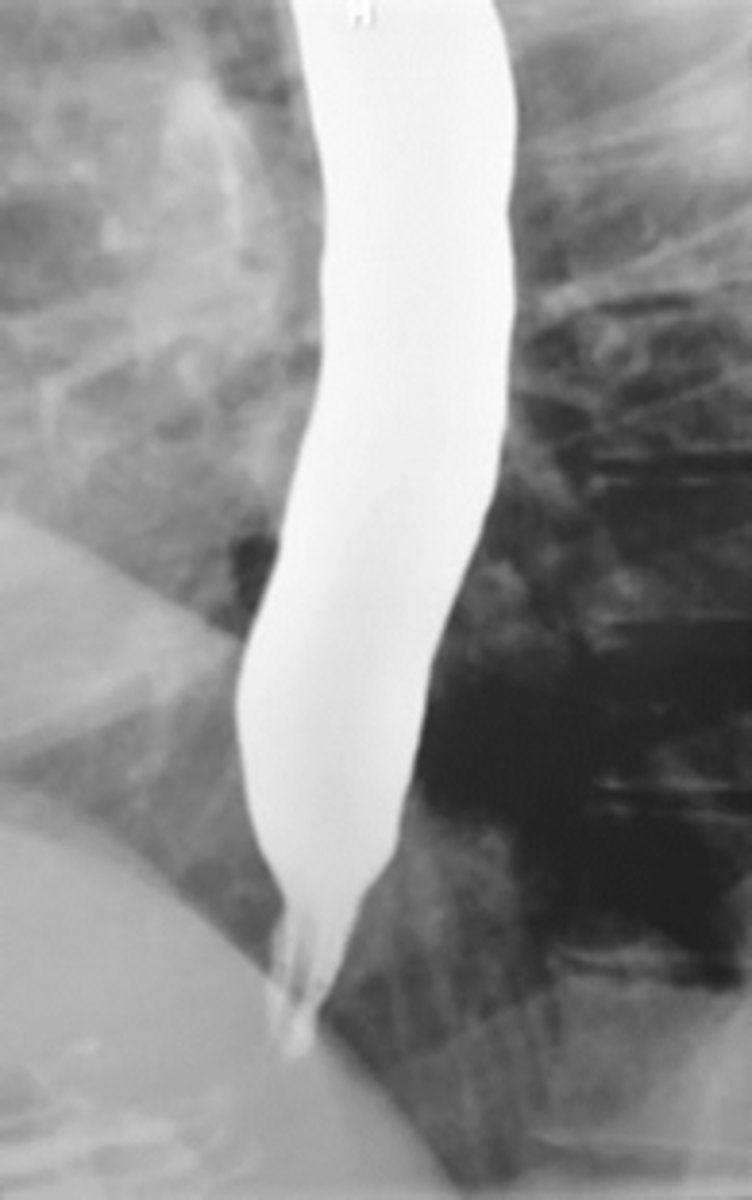
Barium esophogram showing ***"Bird's beak" tapering of the esophagus think _____________.
- Confirm by manometry since this is a motility disorder!
- Endoscopy to r/o neoplasm
tx: pneumatic dilation of LES, surgery, CCB like Nifedipine or Botox to relax smooth muscle
Achalasia
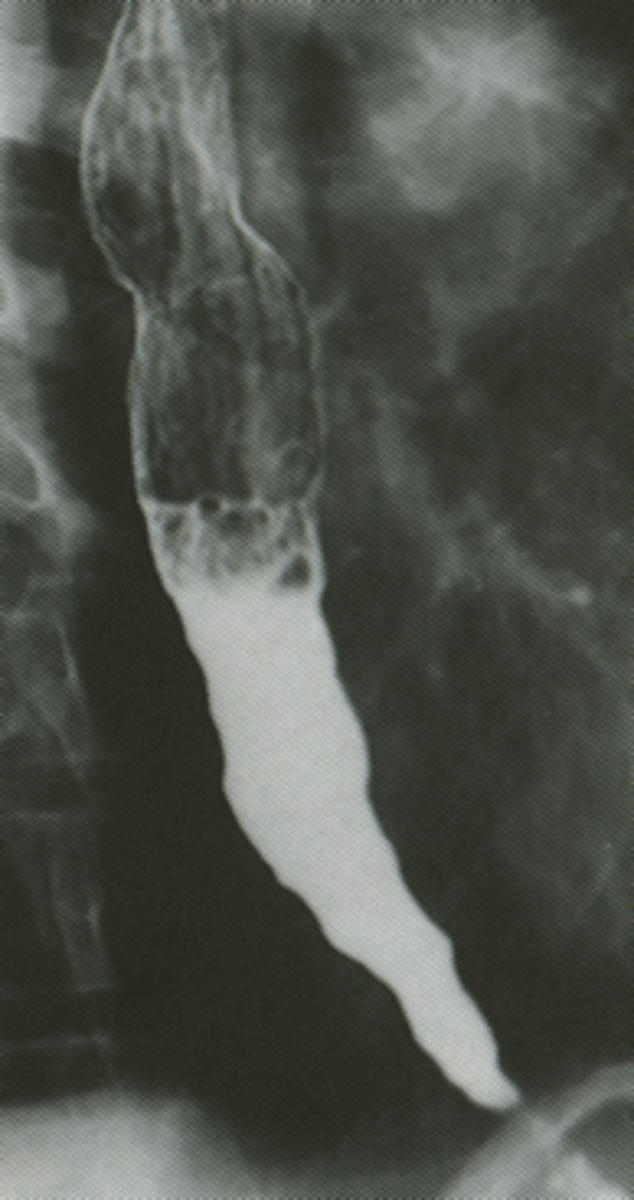
_______________: M/C **motility disorder**
- esophageal contractions are coordinated but amplitude is excessive
- pt will report more chest pain than dysphagia
Nutcracker esophagus
______________: Characterized by simultaneous uncoordinated, non propulsive contractions of segments of the esophagus
- Prevents normal movement of the food bolus
Etiology: unknown
Seen in ~3-5% of pts with unexplained CP
nutcracker is coordinated whereas DES is UNCOORDINATED, nonpropulsive contractions of segments of the esophagus
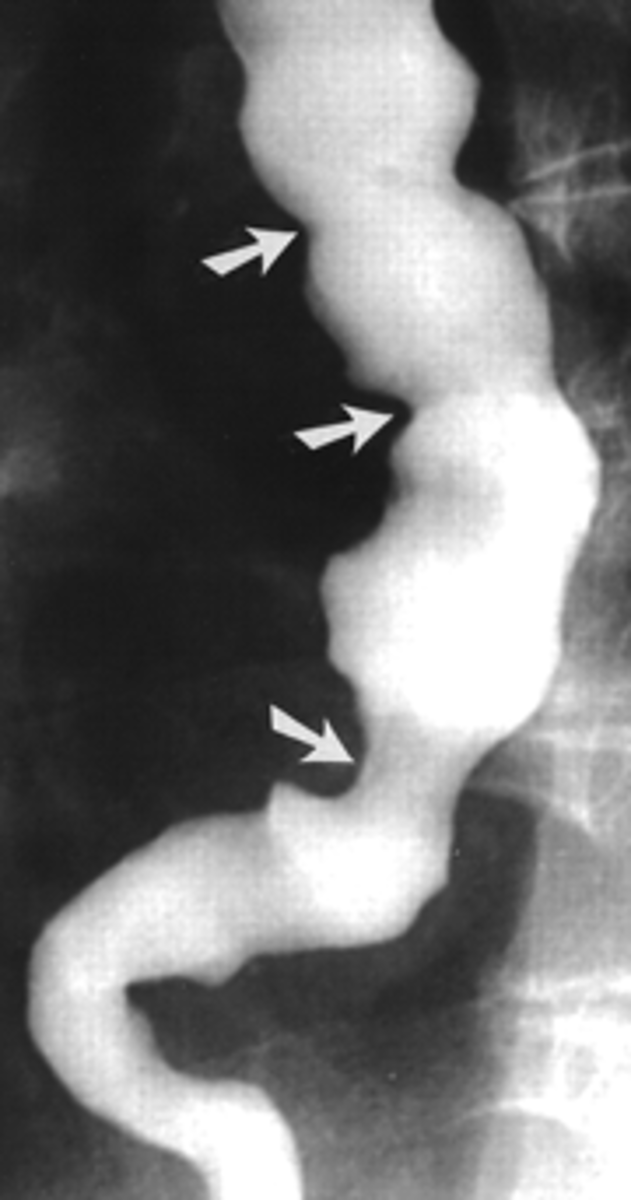
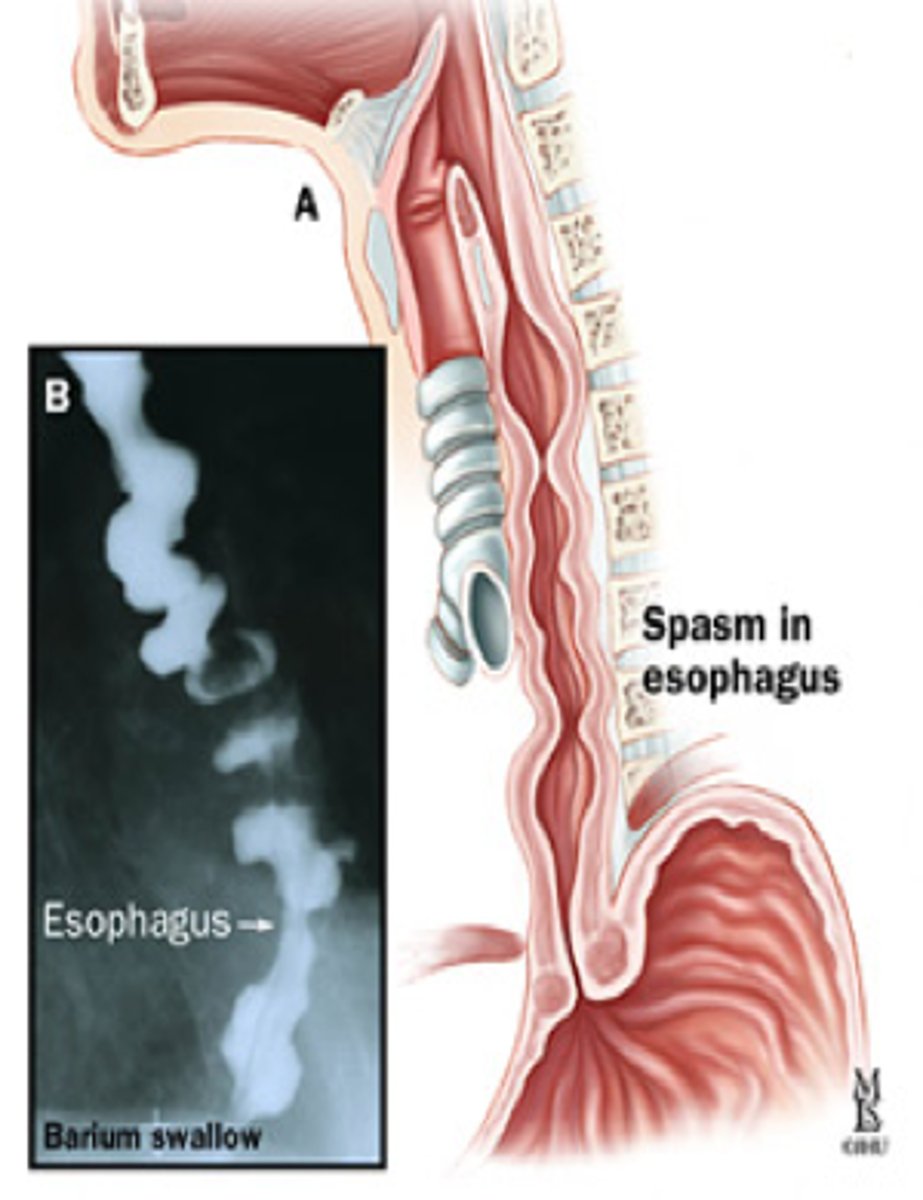
A 48 yr old female comes into the ER complaining of chest pain. She says it is a 10/10 pain and feels it behind her sternum. She also notes some difficulty swallowing. She says she has been super stressed with work lately. EKG comes back normal. Next, you decide to get a barium esophagram to see what is going on and notice a "Corkscrew" appearance of the DES. What's the most likely Dx? Tx?
Diffuse Esophageal Spasm
-tx: PPIs for acid suppresion or surgery if refractory
often confused w/ angina pectoris because CP is relieved with NTG!!!
What hormone works opposite as CCK (cholecystokinin)
Ghrelin
-increases your appetite and produces weight gain
-CCK is what makes you feel full
___________:
"coffee ground" emesis & possibly melena
-on upper endoscopy: subepithelial hemorrhages, petechiae, erosions
erosive/hemorrhagic gastritis
Why is it important to start Prophylactic H2RA or PPI therapy upon admission to the ICU in Stress Gastritis patients
mucosal erosions & subepithelial hemorrhages can develop within 72 hours in majority of critically ill pts
-6% will bleed; bleeding is associated with high mortality in these patients
-factors that increase bleeding risk: platelets <50,000 and INR > 1.5
pharmacologic prophylaxis has decreased the incidence of clinically significant bleeds by 50%
only agents to heal ulcers
PPIs
-empiric 2-4 week trial of PPI is recommended for pts with NSAID related dyspepsia!
Best tx option for prevention of NSAID-induced gastric ulcers in someone who needs to take NSAIDS on a regular basis for their arthritis? What patients cannot receive this medication and why?
Misoprostol (Cytotec)
DO NOT PRESCRIBE TO WOMEN OF CHILDBEARING AGE DUE TO POSSIBILITY OF TERMINATION OF PREGNANCY!!!
(this medication is used for elective abortions)
What type of Gastritis is listed below?
-H pylori infection
-associated w/ pernicious anemia & eosinophilic gastritis
(since parietal cells are no longer secreting intrinsic factor)
nonerosive/nonspecific gastritis
One of the only kinds of bacteria that can survive in the stomach and that's a group 1 carcinogen
H pylori
-spiral gram negative urease secreting bacterium (urease converts urea to ammonium which is what neutralizes the stomach acidity so it can survive)
How is H. pylori transmitted?
the mode is unknown
What population is affected most by this infection?
immigrants from developing countries (correlates inversely with lower socioeconomic status)
When it comes to an H. Pylori infection, which gastritis phenotype puts one at a greater risk for gastric ulcers and gastric cancer?
inflammation mainly in the gastric body

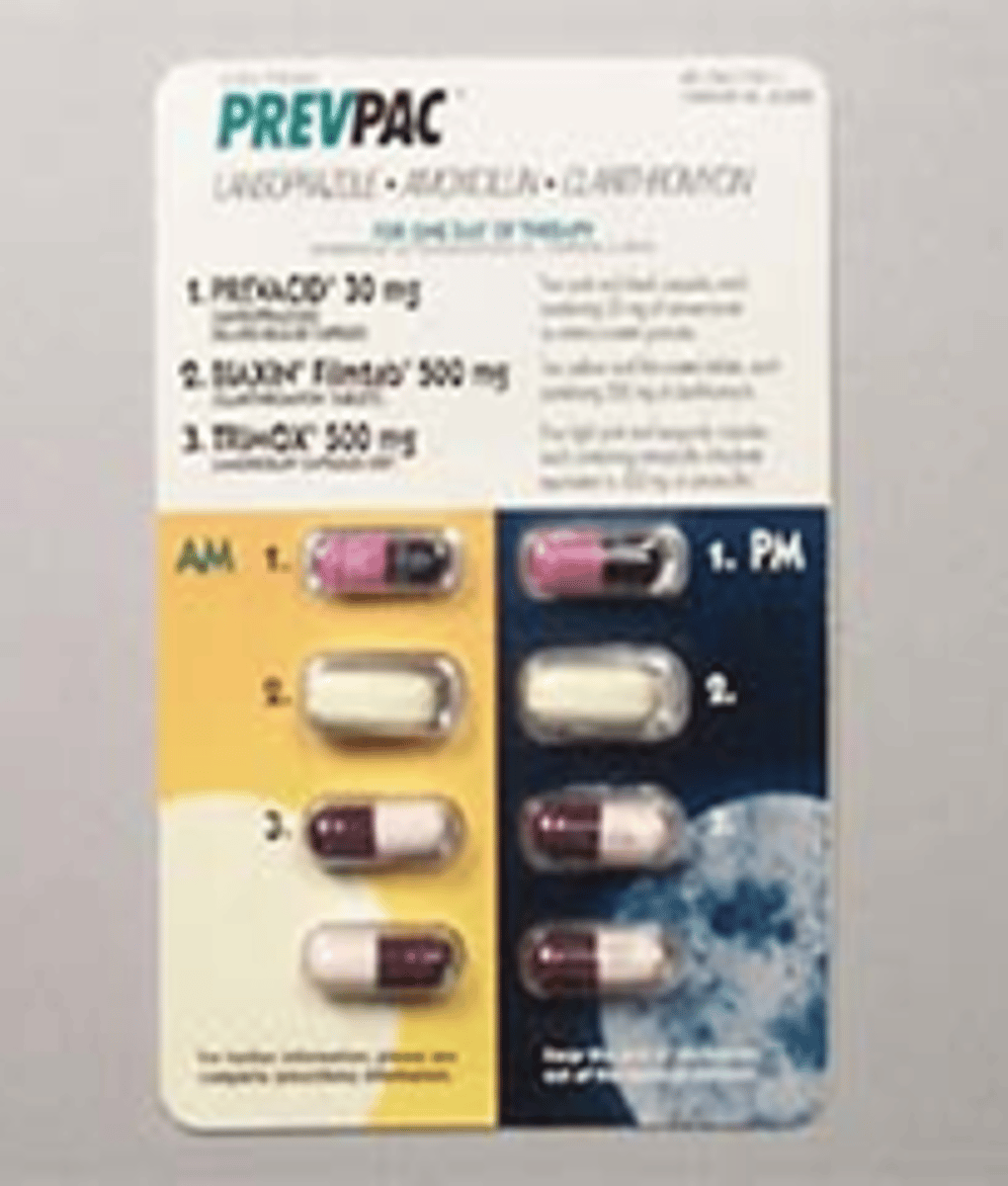
first line therapy for H. Pylori infection ("CAP")
triple therapy:
1. Clarithromycin
2. Amoxicillin
3. PPI
example= PrevPac: lansoprazole + amoxicillin + clarithromycin
H Pylori testing is recommended in what individuals
-pts <60 yrs old with uncomplicated dyspepsia--> test and treat empirically
-pts with functional dyspepsia
-immigrants from regions with high prevalence of H. Pylori and gastric cancer (Japan, Korea, China)
H. Pylori Noninvasive Testing: (> 95% accuracy)
- Urea breath test
- Fecal antigen immunoassay
_________________ must be D/C prior to testing!!
PPIs and antibiotics
T/F: The best and most accurate test for H. Pylori is serologic testing
FALSE
-urea breath test or fecal antigen immunoassay are the most accurate!!
PPIs must be D/C ____ days prior to performing a urea breath test or fecal antigen immunoassay
7-14 days
Antibiotics must be D/C at least ____ days prior to performing a urea breath test or fecal antigen immunoassay
28 days
___________________: anti-intrinsic factor antibodies (autoimmune disorder)
-loss of acid inhibition of G cells---> achlorhydria & hypergastrinemia
-hypergastrinemia can lead to development of carcinoid tumors
pernicious anemia gastritis
why is an EGD with a Bx indicated with any new Dx of pernicious anemia
their risk of gastric cancer is increased threefold
(Hypergastrinemia may lead to devlopment of carcinoid tumors; These cells are morphing in order to fit their new environemnt)
M/C risk factors for _______________
-H. Pylori
-NSAID/ASA use
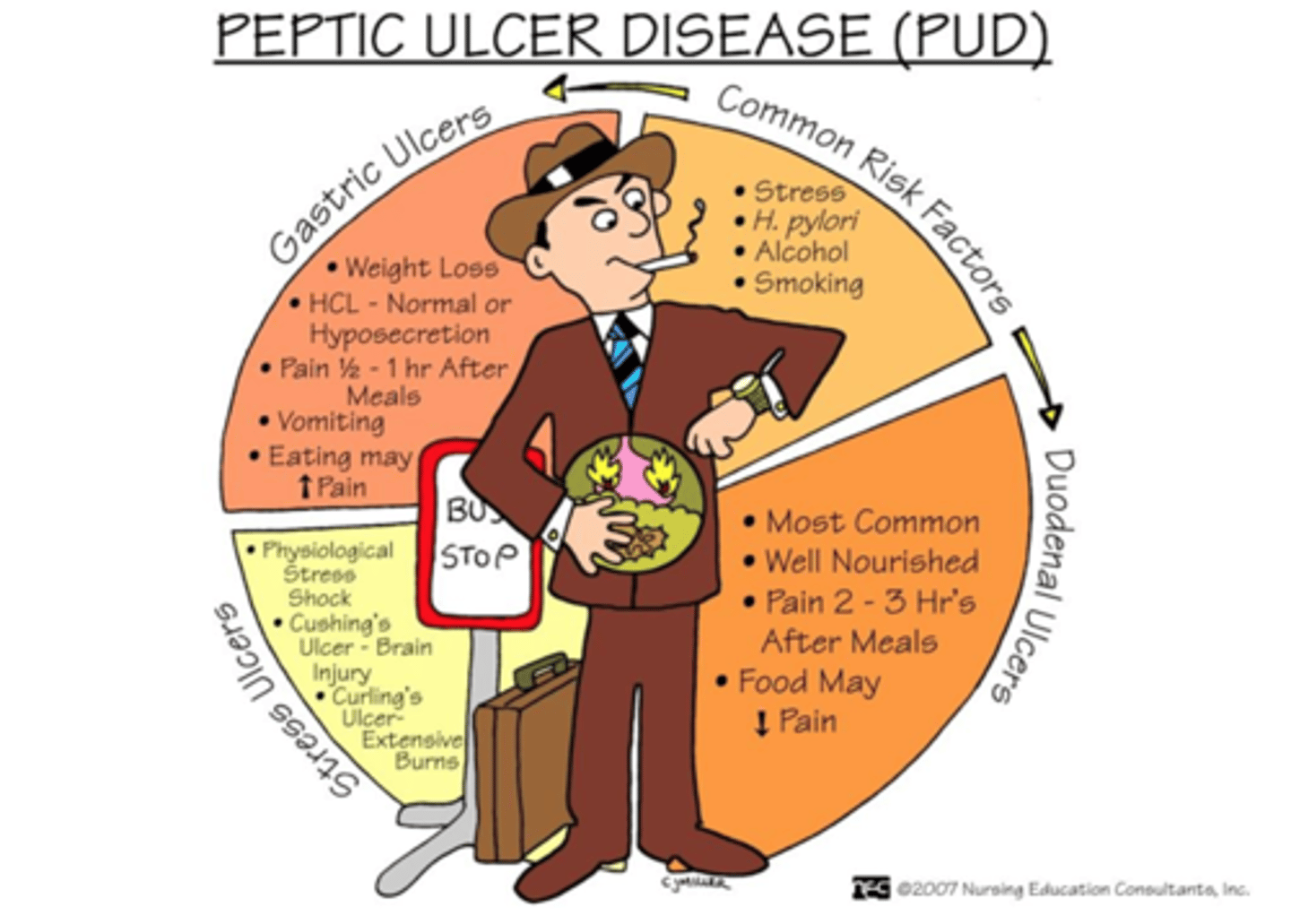
Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD)
PUD PPP 188
Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD)
Epigastric pain that is described as dull, gnawing, aching, "empty", "hunger like" sensation think _________________.
Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD)