Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What are the 5 subdivision of the spinal cord?
Cervical (C1 - C8)
Thoracic (T1 - T12)
Lumbar (L1 - L5)
Sacral (S1 - S5)
Coccygeal (C1)
What are the 7 spinal cord features?
Cervical Enlargement
Lumbar Enlargement
Conus Medullaris
Fillum Terminale
Posterior Median Sulcus
Anterior Median Fissure
Cervical Enlargement
lots of axons on spinal cord, innervate UPPER LIMBS
Enlargement: attachment of large nerves
Lumbar Enlargement
lots of axons on spinal cord, innervate LOWER LIMBS
Enlargment: attachment of large nerves
Conus Medullaris
Tapered lower end of spinal cord (where nerve starts to thin out)
Cauda Equina
group of axons on spinal cord, project INFERIORLY from spinal cord
Fillum Terminale
thin strands of pia mater on spinal cord, anchors CONUS MEDULLARIS to coccyx
Posterior Median Sulcus
narrow groove on posterior surface of spinal cord
DIMINISHES in lower spinal cord
Anterior Median Fissure
wider groove on anterior surface of spinal cord
INCREASES in lower spinal cord
Gray Matter in the spinal cord
Anterior Gray Horn
Lateral Gray Horn (only found in T1 - L2)
Posterior Gray Horn
Gray Commisure
Draw and Label a spinal cord regarding gray matter
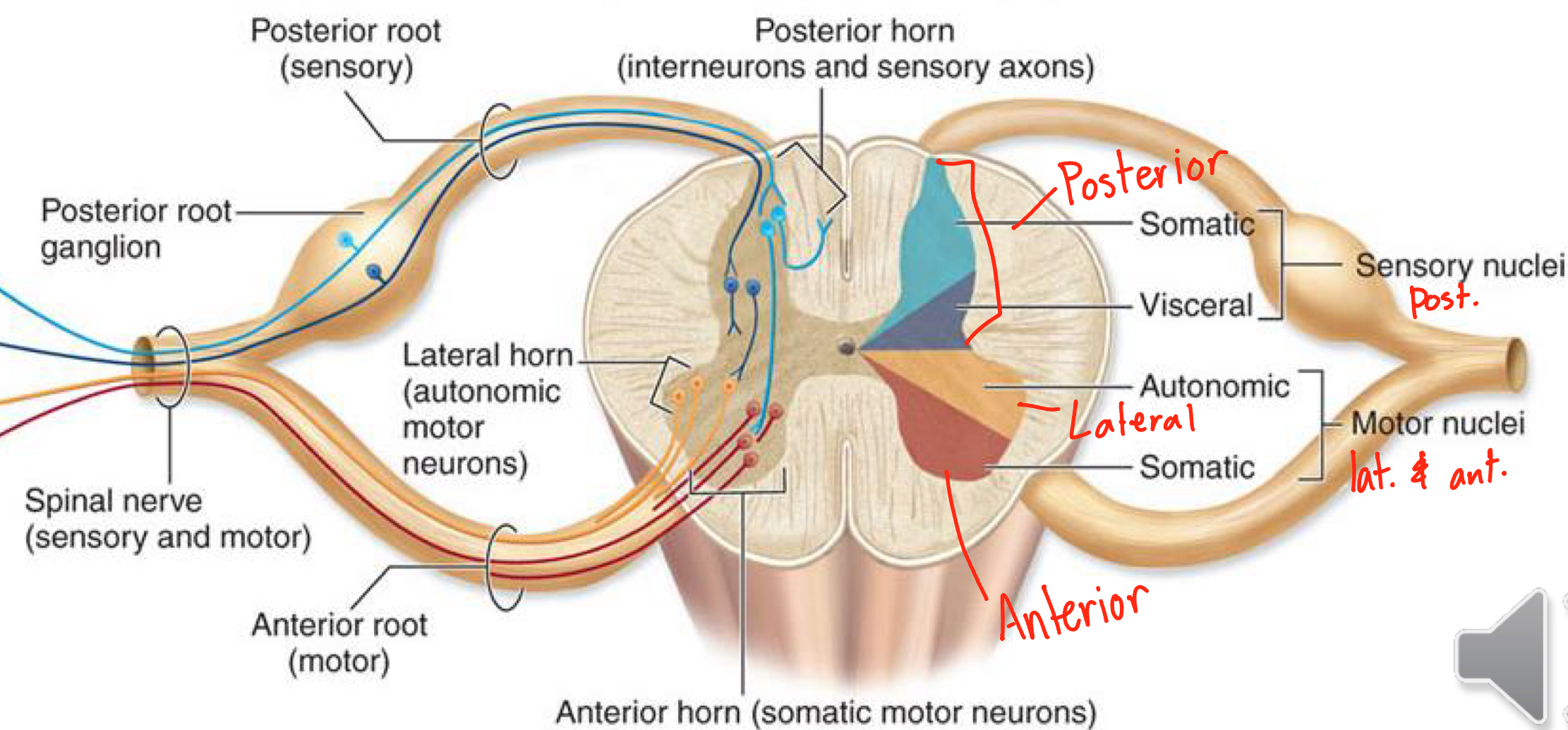
What Nuclei is in Anterior Gray Horn?
Somatic Motor Nuclei - innervate (send signals to) skeletal muscles (voluntary)
What nuclei is found in lateral gray horn?
Autonomic Motor Nuclei - innervate (send signals to) smooth muscle (involuntary)
What nuclei is found in Posterior Gray Horn?
Somatic Sensory Nuclei - RECIEVE signals from sensory receptors of skin
Visceral Sensory Nuclei - RECIEVE signals from viscera and smooth muscles
Anterior Gray Horn
In spinal cord, contain somatic motor cell bodies (VOLUNTARY MOTOR)
Lateral Gray Horn
in spinal cord (ONLY T1-L2), contain autonomic motor cell bodies (INVOLUNTARY MOTOR)
Posterior Gray Horn
contains:
axons of SENSORY NEURONS
cell bodies of INTERNEURONS
Gray Commisure
in spinal cord, unmyelinated axons, communicates between left and right horns
What is a Funiculi?
White part of spinal cord
Poster, Lateral, Anterior (connected by white commisure)
Order of Spinal Cord Meninges
Order of Spinal Cord Meninges (superficial → deep)
Vertebra
Epidural Spcae (mainly fat, NOT IN CRANIAL)
Dura Mater (single meningeal layer)
Subdural Space
Arachnoid Mater
Subarachnoid Space (contians in CSF)
Pia Mater
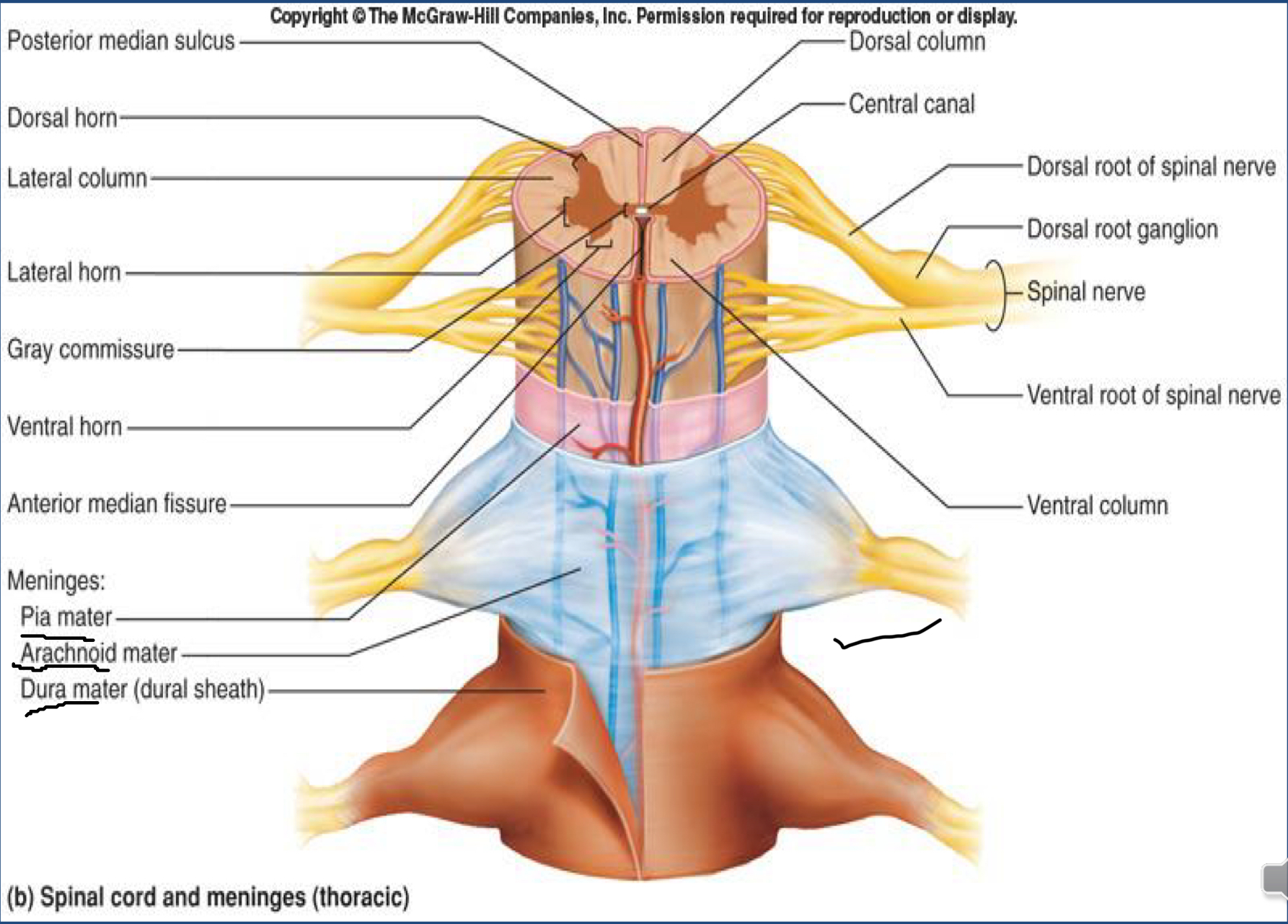
What are two of the differences between Cranial Meninges and Spinal Cord Meninges
Epidural space does NOT exist in cranial meninges
Dura Mater in SPINAL CORD MENINGES is SINGLE LAYER
Draw and Label Spinal Nerve
Anterior Rootlets
Anterior Root
Posterior Rootlets
Posterior Root
Dorsal Root Ganglion
Spinal Nerve (splits into Posterior Ramus, Anterior Ramus, Rami Communicates)
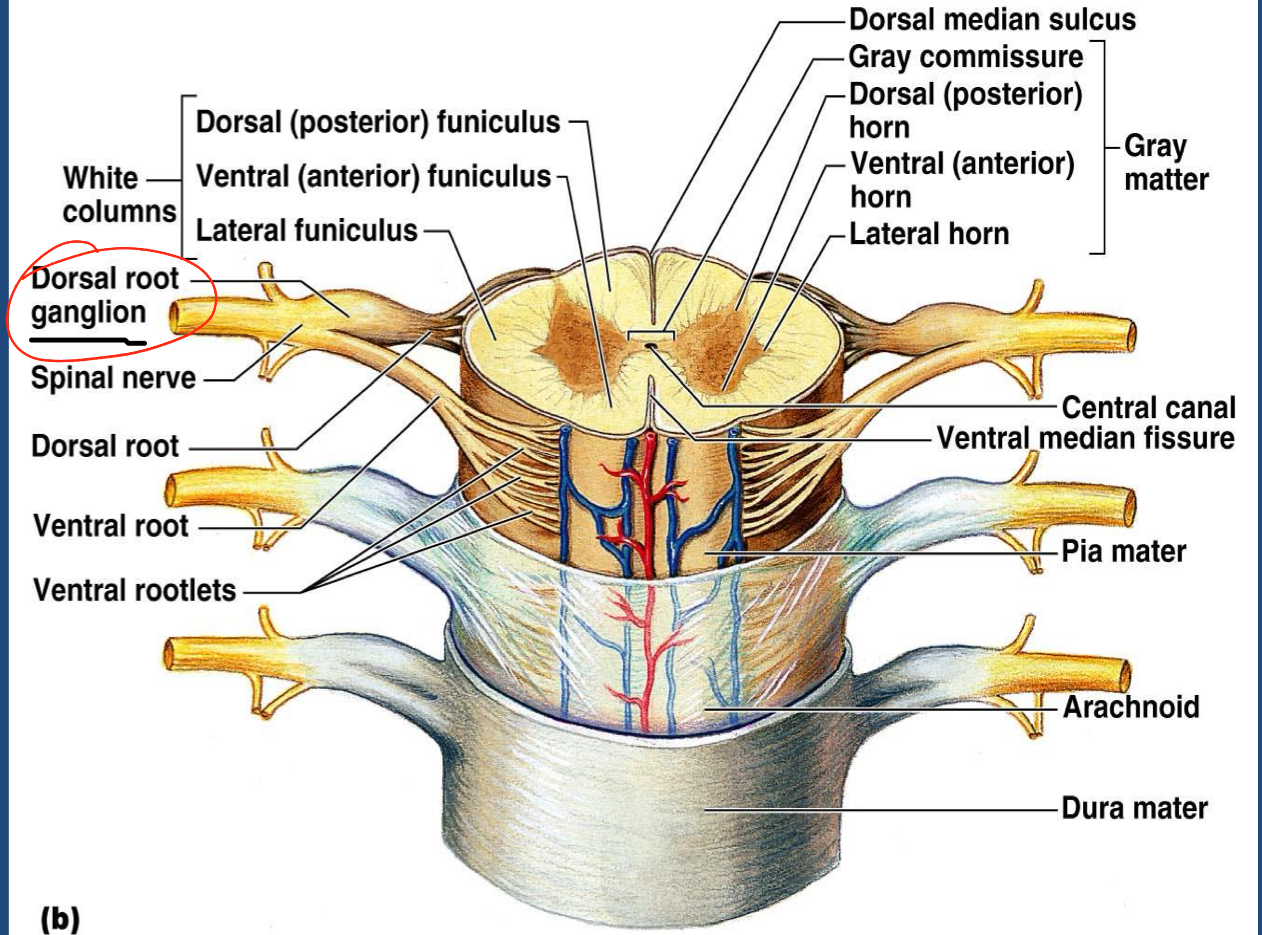
What type of ganglion is a Dorsal Root Ganglion
Unipolar Ganglion! ONLY sensory cell bodies
What neurons are in Posterior Root? Anterior Root?
Posterior Root: Afferent (Sensory)
Anterior Root: Efferent (Motor)
What does the spinal nerve split into?
Posterior Ramus
Anterior Ramus
Rami Communicates
Posterior Ramus
smaller/thinner; innervates DEEP back muscles, helpswith posture
Anterior Ramus
larger, anterior AND lateral trunk/lower limbs/upper limbs, splits further to form nerve plexuses
Rami Communicates
Axons associated w/ autonomic nervous system, goes to AUTONOMIC ganglion trunk (sending signals to involuntary muscles)
Autonomic Nervous System Pathway
Preganglionic Neuron: BEFORE autonomic ganglion, in CNS → goes to outside spinal cord (anterior root) to ganglia
Postganglion Neuron: after autonomic ganglion, unmyelinated axons in parasympathetic N.S,
Effector: organ affected
Parasympathetic Nervous System Pathway
Preganglionic Neuron (LONGER)
Autonomic Ganglia (near effector)
Postganglionic Neuron (SHORTER)
Effector Organ
Sympathetic Nervous System Pathway (2)
Preganglionic Neuron (SHORTER)
Autonomic Ganglion (near spinal cord)
Postganglionic Neuron (LONGER)
Effector Organ
OR
Preganglionic Neuron
Adrenal Medulla
Cholinergic Fibers
release Acytelcholine
in all ganglionic BESIDES sympathetic postganglionic axons NOT in sweat glands
Adrenergic Fibers
release Norepinephrine
in ALL sympathetic postganglionic BESIDES sweat glands
What ganglion have cholinergic fibers?
Parasympathetic Preganglionic Neurons
Parasympathetic Postganglionic Neurons
Sympathetic Preganglionic Neurons
Sympathetic Postganglionic Neurons IN SWEAT GLANDS
What ganglion have Adrenergic Fibers?
Sympathetic Postganglionic NOT in sweat glands
Adrenal Medulla
contain Chromaffin cells
Release Norepinephrine and Epinephrine (adrenaline, only in stress situations)
stimulated by sympathetic preganglionic neuron
What is a Dermatone?
a segment of skin SPECIFIC spinal nerve is responsible for
What is an example of Referred Pain?
Having a heart attack and feeling pain in left arm because they have the same innervations
Getting kicked in the balls and feeling pain in your abdomen
What are the four Nerve Plexuses
Cervical Plexus (C1 - C4)
Brachial (C5 - C8)
Lumbar (L1 - L4)
Sacral (L4 - S4)
What spinal cord region has no Nerve Plexuses
THORACIC REGION
What main nerve is in the Cervical Plexus
Phrenic Nerve: innervates DIAPHRAGM
What main nerves are part of Brachial Plexus
POSTERIOR CORD: Axillary Nerve, Radial Nerve
LATERAL CORD: Muscutaneous Nerve
LATERL+ MEDIAL CORD: Median Nerve
MEDIAL CORD: Ulnar Nerve
Axillary Nerve innervation
Deltoid and Teres Major
Radial Nerve innervation
most of posterior side of the arm (EXTENSORS!)
Triceps Brachii
Brachioradialis
Extensors!
Musculotaneous Nerve innervations
flexors in ARM (FLEXION)
Brachialis
Biceps Brachii
Coracobrachialis
Median Nerve innervations
flexors in FOREARM (FLEXION!)
besides Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
Ulnar Nerve innervation
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
What nerves are in the Lumbar Plexus
Femoral Nerve: anterior! more lateral → ABDUCTOR!
Obturator Nerve: medial! more medial → ADDUCTOR! (comes out of obturator)
What are the nerves in the Sacral Plexus?
Sciatic Nerve: BIGGEST NERVE, all leg BESIDES anterior thigh (femoral nerve) and medial thigh (obturator nerve); splits into tibial nerve and common fibular nerve
Tibial Nerve: Posterior - (opposite) FLEXORS
Common Fibular Nerve: Anterior - (opposite) EXTENSORS