GCSE AQA Geography Section B: The Changing Economic World
5.0(1)Studied by 6 people
Card Sorting
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:26 PM on 9/24/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
1
New cards
What is development?
It is the progress in economic growth, use of technology and improving welfare that a country has made.
2
New cards
What is the global development gap?
The difference in development between more and less developed countries
3
New cards
Define Gross National Income (GNI)
The value of the output of goods and services produced in a country in a year, including money that leaves and enters the country.
4
New cards
Define GNI per head
The GNI divided by the population of country, aka as GNI per capita.
5
New cards
Define Birth rate
The number of babies born per 1000 people per year.
6
New cards
Define Death rate
The number of deaths per 1000 people per year.
7
New cards
Define infant mortality rate
The number of deaths of infants under age 1 per 1000 live births in a given year.
8
New cards
Define people per doctor
The average number of people for each doctor.
9
New cards
Define literacy rate
The percentage of a country's people who can read and write.
10
New cards
Define access to safe water
The percentage of people who can get clean drinking water.
11
New cards
Define life expectancy
The average period that a person may expect to live.
12
New cards
Define HDI (Human Development Index)
The combination of measures means that a country's HDI value tells you about both the country's level of economic development and the quality of life for people who live there, between 0 and 1.
13
New cards
Explain a limitation of an economic measure
It's an average as variations within the country do not show up
14
New cards
Explain a limitation of a social measure
As a country develops some aspects develop before others making it seem more developed than it actually is
15
New cards
What is a HIC? + examples
HIC's are the wealthiest countries in the world, where the GNI per head is high
e.g. UK, USA
e.g. UK, USA
16
New cards
What is a LIC? + examples
LIC's are the poorest countries in the world, where the GNI per head is very low
e.g. Somalia, Uganda
e.g. Somalia, Uganda
17
New cards
What is a NEE? + examples
NEE's are rapidly getting richer as their economy moves from being based on primary industry to secondary industry
e.g. BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa) + MINT (Mexico, Indonesia, Nigeria and Turkey)
e.g. BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa) + MINT (Mexico, Indonesia, Nigeria and Turkey)
18
New cards
What is the Demographic Transition Model?
It's a model that indicates what will happen to a society or country's population. It's based on birth rate, death rate, and the total population.
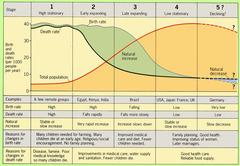
19
New cards
What does natural increase mean when used in the DTM?
when birth rate is higher than dead rate, so population grows
20
New cards
What does natural decrease mean when used in the DTM?
when the death rate is higher than the birth rate
21
New cards
Explain stage 1 of the DTM
- least developed
- high birth rate which is fluctuating as there's no contraception
- lots of children as infant mortality rate is high
- high death rate which is fluctuating due to poor healthcare/famine and life expectancy is low
- e.g. tribes in Brazil
- high birth rate which is fluctuating as there's no contraception
- lots of children as infant mortality rate is high
- high death rate which is fluctuating due to poor healthcare/famine and life expectancy is low
- e.g. tribes in Brazil
22
New cards
Explain stage 2 of the DTM
- not very developed, LIC zone
- high birth rate as economy is based on agriculture so people have children to work on farms
- lower death rate as better healthcare increases
- e.g. Gambia
- high birth rate as economy is based on agriculture so people have children to work on farms
- lower death rate as better healthcare increases
- e.g. Gambia
23
New cards
Explain stage 3 of the DTM
- more developed, NEE zone
- birth rate falls rapidly as the use of contraception increases + more women work instead of having children/ economy changes from farming to manufacturing so fewer children are needed for manual labour
- improved healthcare means that the death rate falls and life expectancy increases
- e.g. India
- birth rate falls rapidly as the use of contraception increases + more women work instead of having children/ economy changes from farming to manufacturing so fewer children are needed for manual labour
- improved healthcare means that the death rate falls and life expectancy increases
- e.g. India
24
New cards
Explain stages 4/5 of the DTM
- most developed, HIC zone
- low birth rates as people expect a high standard of living and may have dependent elderly relatives so there is not enough money available for children
- healthcare is good so death rate is low and life expectancy is high
- e.g. UK and Japan
- low birth rates as people expect a high standard of living and may have dependent elderly relatives so there is not enough money available for children
- healthcare is good so death rate is low and life expectancy is high
- e.g. UK and Japan
25
New cards
Describe the physical causes of uneven development
1. A Poor Climate
- varied climates where not much will grow meaning less food, undernourishment have a low quality of life
2. Poor Farming Land
- steep or infertile land, limited crop production leading to malnourishment
3. Few Raw Materials
- limited raw materials, less exports, no development money
- some countries have resources, no money to exploit them
4. Lots of Natural Disasters
- money spent on rebuilding, low quality of life
- varied climates where not much will grow meaning less food, undernourishment have a low quality of life
2. Poor Farming Land
- steep or infertile land, limited crop production leading to malnourishment
3. Few Raw Materials
- limited raw materials, less exports, no development money
- some countries have resources, no money to exploit them
4. Lots of Natural Disasters
- money spent on rebuilding, low quality of life
26
New cards
What are the economic factors that can cause uneven development?
1. Poor Trade Links
- poor trade links = limited money made, less to spend on development
2. Lots of Debt
- money has to be repaid with interest, less money for development
3. An Economy Based on Primary Products
- countries that export primary products tend to be less developed because they're sold for less profit than manufactured goods
- poor trade links = limited money made, less to spend on development
2. Lots of Debt
- money has to be repaid with interest, less money for development
3. An Economy Based on Primary Products
- countries that export primary products tend to be less developed because they're sold for less profit than manufactured goods
27
New cards
What are the historical causes of uneven development?
Colonisation
- European countries colonised many countries in Asia, Africa, Australasia and America between the 16th and 20th centuries removing raw materials and sold back manufactured goods meaning profits went to colonisers not the colonised countries, increasing inequality
- prevented countries from developing their own industries
Conflict
- war/civil wars slow development, money spent on war
- war contributes to decreased healthcare, higher infant mortality rates and a decline in literacy rates
- European countries colonised many countries in Asia, Africa, Australasia and America between the 16th and 20th centuries removing raw materials and sold back manufactured goods meaning profits went to colonisers not the colonised countries, increasing inequality
- prevented countries from developing their own industries
Conflict
- war/civil wars slow development, money spent on war
- war contributes to decreased healthcare, higher infant mortality rates and a decline in literacy rates
28
New cards
Explain the consequences of uneven development (Wealth)
Wealth
- people in more developed countries = obtain higher incomes = varied standard of living
- in 2017, the richest 10% of Kenya's population earned, on average, 23x more than the poorest 10%
- people in more developed countries = obtain higher incomes = varied standard of living
- in 2017, the richest 10% of Kenya's population earned, on average, 23x more than the poorest 10%
29
New cards
Explain the consequences of uneven development (Health)
Health
- HIC's live longer, e.g. the UK's life expectancy is 81, but Chad is on 53
- in 2016, diarrhoea is estimated to have killed over 1.4 million people in South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa
- HIC's live longer, e.g. the UK's life expectancy is 81, but Chad is on 53
- in 2016, diarrhoea is estimated to have killed over 1.4 million people in South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa
30
New cards
Explain the consequences of uneven development (International Migration)
International Migration
- people from LIC's/NEE's move to HIC's to escape conflict or to improve their quality of life
- e.g. 130000+ people move from mexico (NEE) the the USA (HIC) legally each year in search of better jobs + quality of life
- migrant workers contribute to the economies of HIC's they move to instead of the LIC's they leave further widening the development gap
- people from LIC's/NEE's move to HIC's to escape conflict or to improve their quality of life
- e.g. 130000+ people move from mexico (NEE) the the USA (HIC) legally each year in search of better jobs + quality of life
- migrant workers contribute to the economies of HIC's they move to instead of the LIC's they leave further widening the development gap
31
New cards
What are the strategies to help reduce the global development gap?
Investment, Aid, Fair trade, Using Intermediate Technology, Micro-finance Loans, Industrial Development, Debt Relief
32
New cards
How is investment reducing the global development gap?
- FDI (foregin-direct investment)is where people buy property in another country or invest
- increases access to finance, technology + expertise,
- improves the services
- e.g. between 1987 and 2018, Vietnam received FDI worth more than US $182 billion , developed motorbike manufacturing and telecommunications
- increases access to finance, technology + expertise,
- improves the services
- e.g. between 1987 and 2018, Vietnam received FDI worth more than US $182 billion , developed motorbike manufacturing and telecommunications
33
New cards
How is Aid helping to reduce the global development gap?
- 2018-19, UK provided £180+ million to South Sudan funding 17 projects, improving access to water, healthcare and education
- can be wasted by corrupt governments/ runs out
- can be wasted by corrupt governments/ runs out
34
New cards
How is Fair Trade helping to reduce the global development gap?
- have to pay producers a fair price + premium extra
- 2016, fair trade tea farmers in Malawi used some of their premium to expand their local hospital, build a new school and install a pipeline for clean water
- tiny proportion of the extra money reaches the producers, rest boosts retailers' profits
- 2016, fair trade tea farmers in Malawi used some of their premium to expand their local hospital, build a new school and install a pipeline for clean water
- tiny proportion of the extra money reaches the producers, rest boosts retailers' profits
35
New cards
How is Intermediate Technology helping to reduce the global development gap?
- affordable and simple tools, machines and systems that improve quality of life
- e.g. solar-powered LED light bulbs used in parts of Nepal compared to polluting kerosene lamps
- e.g. solar-powered LED light bulbs used in parts of Nepal compared to polluting kerosene lamps
36
New cards
How is Microfinance loans helping to reduce the global development gap?
- small loans are given to LIC's to start their own businesses becoming financially independent
- Amhara region of Ethiopia, benefited from higher incomes, invested in more livestock
- can cause problems by encouraging people to get into debt but it's not clear that it can reduce poverty on a large scale
- Amhara region of Ethiopia, benefited from higher incomes, invested in more livestock
- can cause problems by encouraging people to get into debt but it's not clear that it can reduce poverty on a large scale
37
New cards
How is Industrial Development helping to reduce the global development gap?
- agriculture makes up a large portion of the economy developing industry boosting GNI and development, as productivity, skills and infrastructure are improved
38
New cards
How is Debt Relief helping to reduce the global development gap?
- some/all of country's debt is cancelled, interest rates lowered, country has more money for development
- Zambia had $4 billion of debt cancelled in 2005, in 2006, the country had enough money to start a free healthcare scheme for millions of people in rural areas
- Zambia had $4 billion of debt cancelled in 2005, in 2006, the country had enough money to start a free healthcare scheme for millions of people in rural areas
39
New cards
Describe the causes of economic change in the UK (de-industrialisation)
De-industrialisation
- UK's industrial base declined as increased automation (machines) led to job losses in secondary sector
- became more expensive in UK to manufacture from cheaper labour abroad, UK factories closed
- UK's industrial base declined as increased automation (machines) led to job losses in secondary sector
- became more expensive in UK to manufacture from cheaper labour abroad, UK factories closed
40
New cards
Describe the causes of economic change in the UK (globalisation)
- manufacturing moved overseas, labour costs are cheaper e.g. M&S manufactures clothes in India and China
- TNC's have moved some of their tertiary/quaternary operations to the UK e.g. Apple employed nearly 6500 people in the UK
- trade is an increasing part of the UK GDP; proportion of UK GDP that comes from foreign trade increased from 38% in 1965 to 62% in 2017
- TNC's have moved some of their tertiary/quaternary operations to the UK e.g. Apple employed nearly 6500 people in the UK
- trade is an increasing part of the UK GDP; proportion of UK GDP that comes from foreign trade increased from 38% in 1965 to 62% in 2017
41
New cards
Describe the causes of economic change in the UK (government policies)
- 1980's, key manufacturing industries had been owned/run by government were privatised e.g. steel and ship-building leading to job losses but increased efficiency
- since 1980's, government carried out lots of deregulation - removing restrictions and taxes on businesses to encourage entrepreneurs and investors to move to the UK attracting tertiary + quaternary industries e.g financial institutions
- since 1980's, government carried out lots of deregulation - removing restrictions and taxes on businesses to encourage entrepreneurs and investors to move to the UK attracting tertiary + quaternary industries e.g financial institutions
42
New cards
How does industry impact the physical environment in the UK? + example
- factories may release pollution of greenhouse gases + running them + lots of energy + water
- extracting raw materials damages the environment by destroying habitats and releases toxic chemicals into water courses
e.g. Unicorn Group produces various products (bins/floor tiles) in Lisburn, Northern Ireland. Installed solar panels and biomass boilers in its factory, 100% renewable sources, recycling left over steel and plastic
- extracting raw materials damages the environment by destroying habitats and releases toxic chemicals into water courses
e.g. Unicorn Group produces various products (bins/floor tiles) in Lisburn, Northern Ireland. Installed solar panels and biomass boilers in its factory, 100% renewable sources, recycling left over steel and plastic
43
New cards
How is UK transport networks improving?
roads: 'smart motorways' with extra lanes e.g. building a new dual carriageway to link the A5 to the M1 near Luton
railways: the proposed HS2 line linking London, Birmingham, Leeds and Manchester increases capacity and allows faster journeys between major English cities
airports: one proposal for a third runway at Heathrow airport allowing an extra 700 planes a day but this would increase air + noise pollution in the area increasing emissions
ports: London Gateway, opened at the mouth of the River Thames in 2013, handles world's largest container ships, hoped it will become a hub for global trade.
railways: the proposed HS2 line linking London, Birmingham, Leeds and Manchester increases capacity and allows faster journeys between major English cities
airports: one proposal for a third runway at Heathrow airport allowing an extra 700 planes a day but this would increase air + noise pollution in the area increasing emissions
ports: London Gateway, opened at the mouth of the River Thames in 2013, handles world's largest container ships, hoped it will become a hub for global trade.
44
New cards
Describe the strong links the UK has with other countries (trade/culture/transport/electronic communications)
Trade: overseas exports are worth over £160 billion per year; links to USA, Europe and Asia are significant
Culture: creative industries means UK culture is exported worldwide e.g. the Shaun the Sheep TV series made by Aardman Animations in Bristol is shown in 170 countries
Transport: Channel Tunnel links UK to France, providing a route to mainland Europe, Heathrow acts as an international hub
Electronic Communications: telephones + internet makes communication easier so strengthening the UK's overseas links
Culture: creative industries means UK culture is exported worldwide e.g. the Shaun the Sheep TV series made by Aardman Animations in Bristol is shown in 170 countries
Transport: Channel Tunnel links UK to France, providing a route to mainland Europe, Heathrow acts as an international hub
Electronic Communications: telephones + internet makes communication easier so strengthening the UK's overseas links
45
New cards
How has the UK formed economic and political links with other countries?
European Union: EU is an economic and political partnership of 27 countries, Goods and people can move freely between EU countries, strengthening links between members but the UK left the EU in 2020.
The Commonwealth: association of 53 states, including the UK and many former colonies promoting cooperation between member countries e.g. through trade/aid
The Commonwealth: association of 53 states, including the UK and many former colonies promoting cooperation between member countries e.g. through trade/aid
46
New cards
describe the social + economic changes in the rural landscape in an area of population growth
North Somerset
- rural area in south-west England
- population increased 7.8% between 2005-15; many people moved to towns/villages near Bristol
- houses prices rose by 6.7% in 2017-18, pricing out locals but employment/wages are above national average
- congestion with commuters to Bristol and services are oversubscribed + elderly move to this area pressuring healthcare.
- rural area in south-west England
- population increased 7.8% between 2005-15; many people moved to towns/villages near Bristol
- houses prices rose by 6.7% in 2017-18, pricing out locals but employment/wages are above national average
- congestion with commuters to Bristol and services are oversubscribed + elderly move to this area pressuring healthcare.
47
New cards
describe the social + economic changes in the rural landscape in an area of population decline
South Lakeland, Cumbria
- rural county in north west England including the Lake District National Park
- population decreased by 0.8% from 2005-15 due to a decline in jobs [mainly agriculture]
- In Barrow, shops like Gamestation has closed,
- younger people left, higher proportion of older people, strained medical services and social care; continued decline = schools may close.
- rural county in north west England including the Lake District National Park
- population decreased by 0.8% from 2005-15 due to a decline in jobs [mainly agriculture]
- In Barrow, shops like Gamestation has closed,
- younger people left, higher proportion of older people, strained medical services and social care; continued decline = schools may close.
48
New cards
Explain evidence for the north-south divide
- lower wages in north e.g. 2014 avg weekly wage in Huddersfield was 40% lower than in London
- Health is worse in the north e.g. life expectancy for male babies born in Glasgow in 2012 was 72.6 years but in East Dorset it was 82.9 years
- GCSE results are better in the South of England than in the Midlands/North
- However, the north has wealthy areas like parts of Cheshire and the South has high areas of deprivation like Cornwall.
- Health is worse in the north e.g. life expectancy for male babies born in Glasgow in 2012 was 72.6 years but in East Dorset it was 82.9 years
- GCSE results are better in the South of England than in the Midlands/North
- However, the north has wealthy areas like parts of Cheshire and the South has high areas of deprivation like Cornwall.
49
New cards
How is the government attempting to resolve regional differences? {Developing More Powers}
Developing More Powers:
- Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland have their own devolved governments and some powers are being devolved to local councils in England too
- money on schemes to benefit community e.g. developing public transport
- Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland have their own devolved governments and some powers are being devolved to local councils in England too
- money on schemes to benefit community e.g. developing public transport
50
New cards
How is the government attempting to resolve regional differences? {Creating Enterprise Zones}
- around 50 enterprise zones have been created across England, Scotland and Wales; enterprise zones help:
reduced taxes- business rates are reduced up to 100%
financial benefits: businesses who invest in buildings/equipment reduce future tax bills
improved infrastructure: superfast broadband
e.g. Sheffield City Region Enterprise Zone
reduced taxes- business rates are reduced up to 100%
financial benefits: businesses who invest in buildings/equipment reduce future tax bills
improved infrastructure: superfast broadband
e.g. Sheffield City Region Enterprise Zone
51
New cards
Explain the Sheffield City Region Enterprise Zone in reducing the north-south regional differences
2011, UK government approved the creation of the zone; projects that have been set up include:
McLaren Composites Technology Centre: partnered with researchers from University of Sheffield to build facilities for developing cutting edge materials, could bring £100m to local economy
Great Yorkshire Way: a major new road is being built connecting Sheffield City Region with Doncaster Sheffield Airport making it easier to travel
by 2017, created 16 000 jobs, £318 million of investment from private companies
McLaren Composites Technology Centre: partnered with researchers from University of Sheffield to build facilities for developing cutting edge materials, could bring £100m to local economy
Great Yorkshire Way: a major new road is being built connecting Sheffield City Region with Doncaster Sheffield Airport making it easier to travel
by 2017, created 16 000 jobs, £318 million of investment from private companies
52
New cards
How is the government attempting to resolve regional differences? {The Northern Powerhouse)
- attracts investment into north, improving transport links between northern cities; plan includes extending the coverage of super fast broadband and spending £70 million on improving schooling
- however, more focused on Manchester than smaller towns and cities in the north, limited development as a whole
- however, more focused on Manchester than smaller towns and cities in the north, limited development as a whole