Cells-Smallest unit of life
1/320
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
321 Terms
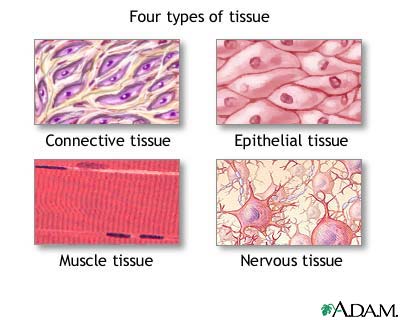
What is a Tissue?
A collection of the same type of cell
What are the four types of tissue?
The four types of tissue are epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous
What is a organ?
A collection of different tissues that work together to perform a specific function or set of functions in a organism
What is an organ system?
A group of multiple organs that work together to perform a major function or set of related functions in the body.
What if an organ system is one level above an organ, then what is one level above an organ system?
The organism itself
What are the four levels of organization for a body system?
Cells, Tissues, Organs, then the organ system.
What do all cells have?
All cells have three main parts: a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and DNA. The cell membrane separates the inside of the cell from the outside environment. The cytoplasm is a jelly-like substance where cell parts float, and DNA holds the genetic instructions for life.
What are the two main categories of cells?
The two main categories are eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Prokaryotic cells lack these structures and are usually single-celled organisms like bacteria.
What makes eukaryotic cells different from prokaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus that contains DNA and many specialized organelles. They are more complex and include plant and animal cells. Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus, and their genetic material floats freely in the cytoplasm.THey include bacteria
Eukaryotic cells are found in ________ and ________.
plants and animals.
What does the term “organelle” mean?
What does the term “organelle” mean?
The word organelle means “little organ.” Organelles are specialized structures inside cells that each have a unique job. They help the cell carry out important processes like making energy, proteins, and waste removal.
What is the function of the nucleus?
The nucleus is the control center of the cell. It stores the DNA, which tells the cell what to do and how to function. It also contains the nucleolus, where ribosomes are made.
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
The Golgi apparatus receives proteins and materials from the endoplasmic reticulum. It modifies, sorts, and packages them into forms the cell can use. This often involves folding proteins or adding molecules like lipids or carbohydrates.
What is the function of the nucleolus?
The nucleolus is found inside the nucleus. It is where ribosomes are made. These ribosomes will later make proteins for the cell.
What do ribosomes do?
Ribosomes are responsible for making proteins. They can float freely in the cytoplasm or attach to the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Proteins made by ribosomes are essential for most of the cell’s activities and structure.
What is the difference between rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (ER)?
The rough ER has ribosomes attached to its surface, making it look rough. It helps transport and modify proteins made by the ribosomes. The smooth ER has no ribosomes and helps make lipids and remove toxins.
What is the job of the mitochondria?
The mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of the cell. They use a process called cellular respiration to make ATP, the main energy source for the cell. Cells that need more energy have more mitochondria.
The process that occurs in mitochondria to make energy is called ________.
cellular respiration.
What do vacuoles do in a cell?
Vacuoles are storage sacs inside cells. They hold materials such as water, food, or waste. In plant cells, the central vacuole is especially large and stores water to help maintain the plant’s structure.
What are lysosomes and what do they do?
Lysosomes act like the garbage collectors of the cell. They contain enzymes that break down worn-out parts and other debris. This cleanup process helps keep the cell healthy and efficient.
What is the function of the cytoskeleton?
The cytoskeleton gives the cell its shape and internal organization. It is made up of microfilaments and microtubules, which are both forms of protein fibers. These structures also help with movement inside the cell.
What organelle allows plants to perform photosynthesis?
The chloroplast allows plants to perform photosynthesis. It captures sunlight and turns it into chemical energy. The green pigment chlorophyll inside chloroplasts helps absorb sunlight.
What structures do plant cells have that animal cells do not?
Plant cells have a cell wall and chloroplasts, which animal cells lack. The cell wall gives structure, support, and protection. The chloroplast allows plants to make their own food from sunlight.
What structures do only some specialized cells have?
Some cells have cilia or flagella. Cilia are small, hair-like projections that move in waves to trap or move particles. Flagella are tail-like structures that help certain cells, like sperm, move around.
What do cilia do in the human body?
Cilia line the respiratory tract and move in waves. They help trap particles like dust or germs from the air we breathe. These trapped particles are then expelled when we cough or sneeze.
What is the purpose of a flagellum?
A flagellum helps a cell move or swim. It acts like a tiny tail that propels the cell forward. In humans, the sperm cell is the only cell that has a flagellum.
The only human cell with a flagellum is the ________.
sperm cell.
What are prokaryotic cells always classified as?
Prokaryotic cells are always unicellular, meaning they consist of just one cell. They are simple organisms like bacteria. Despite their simplicity, they perform all functions needed for life.
What are chromosomes and when do they form?
Chromosomes are condensed forms of DNA. They appear when a cell is about to divide. This packaging helps ensure that genetic material is accurately passed to new cells.
What is the cytoplasm and what does it do?
Cytoplasm is the jelly-like fluid inside the cell. It holds all organelles in place and allows materials to move around. It also helps cushion and protect the cell’s internal structures.
What is cell structure and organelles? How do these parts work together?
Cell structure refers to the organized system of organelles that each perform specific jobs to keep the cell alive. These organelles interact constantly — for example, the nucleus provides DNA instructions, ribosomes make proteins, and the ER and Golgi prepare them for use. Together, they maintain the cell’s structure, function, and survival.
How do membranous and non-membranous organelles differ, and why is this difference important?
Membranous organelles have lipid membranes that form compartments for specific chemical reactions, such as in the nucleus or mitochondria. Non-membranous organelles, like ribosomes and the cytoskeleton, lack these boundaries and work directly in the cytoplasm. This division helps the cell stay organized while carrying out both structural and chemical tasks efficiently.
How do the nucleus, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and vesicles work together to make and transport proteins?
The nucleus holds DNA that provides instructions for building proteins. Ribosomes follow those instructions to make the proteins, which are then folded and moved through the endoplasmic reticulum. The Golgi apparatus modifies and packages them into vesicles that deliver the proteins to their final destinations inside or outside the cell.
Why do plant cells need both chloroplasts and mitochondria, and how does this differ from animal cells?
Chloroplasts capture sunlight and make sugars through photosynthesis, while mitochondria turn those sugars into ATP energy. Both are needed for plants to create and use energy efficiently. Animal cells lack chloroplasts but use mitochondria to make ATP from food they consume.
Why are specialized cell structures important for multicellular organisms?
Specialized structures allow cells to perform unique tasks that benefit the entire organism. For example, cilia move debris, mitochondria provide energy, and the cytoskeleton supports shape and movement. This division of labor lets complex organisms operate efficiently and respond to different needs.
What is a ribosome?
Ribosomes are tiny structures that make proteins for the cell. They can be free-floating in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum. They use instructions from DNA to link amino acids together into proteins.
The control center of the cell that holds genetic material is the ________.
nucleus.
What does the nucleus do?
The nucleus stores the cell’s DNA and controls all cellular activities. It sends out instructions for making proteins and other molecules. It is surrounded by a nuclear membrane that protects its contents.
What is the function of the nucleolus?
The nucleolus is a small, dense structure inside the nucleus. It makes ribosomes, which later help produce proteins. This makes it an essential part of the cell’s protein synthesis process.
The structure that controls what enters and leaves the cell is the ________.
cell membrane.
What is the cell membrane?
The cell membrane is a thin, flexible layer that surrounds the cell. It regulates what enters and leaves the cell, maintaining balance or homeostasis. It’s made mostly of lipids and proteins.
What is a lysosome and what does it do?
Lysosomes are small, enzyme-filled organelles that digest waste materials and worn-out cell parts. They act like the cell’s recycling system. By breaking down old components, they help keep the cell clean and efficient.
What is the cell wall and where is it found?
The cell wall is a rigid outer layer found only in plant cells (and some bacteria). It provides strength, shape, and protection. It is located outside the cell membrane and made mostly of cellulose.
What is the function of mitochondria?
Mitochondria are known as the “powerhouse” of the cell. They use a process called cellular respiration to make ATP, the cell’s energy source. Cells that need more energy, like muscle cells, contain many mitochondria.
What is cytoplasm?
Cytoplasm is a jelly-like fluid that fills the cell. It holds all the organelles in place and allows materials to move throughout the cell. It also helps cushion and protect internal structures.
What is the centrosome?
The centrosome is an organelle that helps organize microtubules and coordinate cell division. It contains centrioles that help pull chromosomes apart during mitosis. It’s essential for forming the spindle fibers used in cell division.
What does the cytoskeleton do?
The cytoskeleton gives the cell shape, strength, and the ability to move. It is made of protein filaments called microfilaments and microtubules. It also helps transport materials inside the cell.
What is the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (smooth ER)?
The smooth ER has no ribosomes on its surface. It makes lipids, processes toxins, and helps regulate calcium levels in some cells. It plays a major role in detoxifying harmful substances.
What is the rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER)?
The rough ER has ribosomes attached to its surface, making it look “rough.” It helps produce and transport proteins. These proteins are often sent to the Golgi apparatus for further processing.
The thin, hollow tubes that make up part of the cytoskeleton are called ________.
microtubules.
What are microtubules?
Microtubules are hollow tubes made of protein that form part of the cytoskeleton. They help maintain the cell’s shape and serve as tracks for moving organelles. They are also involved in cell division.
What is the function of cilia?
Cilia are short, hair-like projections found on the surface of some cells. They move in wave-like motions to move substances or the cell itself. In humans, they help clear particles from the respiratory tract.
What is the Golgi apparatus and what does it do?
The Golgi apparatus receives proteins and lipids from the ER, modifies them, and packages them for delivery. It folds proteins or attaches carbohydrates and lipids to them. It acts as the cell’s “post office,” preparing materials for transport.
The double-layered barrier surrounding the nucleus is called the ________.
nuclear membrane.
What is the nuclear membrane?
The nuclear membrane (or nuclear envelope) surrounds and protects the nucleus. It controls what enters and leaves the nucleus through nuclear pores. This ensures that DNA stays safe while still allowing important materials to pass through.
What is a peroxisome and what is its function?
Peroxisomes are small organelles that break down fatty acids and detoxify harmful chemicals. They contain enzymes that convert toxins into safer substances. They also help prevent damage from reactive oxygen molecules in the cell.
What are the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Similarities:
Both are cells, the basic unit of life.
Both contain DNA as their genetic material.
Both have a cell membrane and cytoplasm.
Both carry out essential life processes like growth, energy use, and reproduction.
Differences:
Prokaryotic cells:
Have no nucleus; DNA is free in the cytoplasm.
Are usually smaller and simpler in structure.
Are always unicellular (single-celled), like bacteria.
Were the first cells to evolve and remain the most common.
Eukaryotic cells:
Have a nucleus that encloses the DNA.
Contain membrane-bound organelles (e.g., mitochondria, ER, Golgi apparatus).
Are usually larger and more complex.
What does the term “prokaryote” mean, and what are its main characteristics?
The word “prokaryote” comes from “pro,” meaning before, and “karyon,” meaning nucleus. Prokaryotic cells lack a true nucleus — their DNA floats freely in the cytoplasm in an area called the nucleoid. Examples include traditional bacteria like E. coli and archaebacteria.
What does the term “eukaryote” mean, and what are its main characteristics?
“Eukaryote” means “true nucleus” (“eu” = true, “karyon” = nucleus). Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and evolved from prokaryotic cells. They reproduce by mitosis and cytokinesis, are larger (5–100 µm), and include fungi, plants, animals, and protists.
What is the structure and function of the nucleus and nucleolus?
The nucleus has a double membrane with pores that allow materials to pass in and out for communication with the rest of the cell. It contains genetic information in the form of chromosomes. Inside, the nucleolus makes ribosomes, which are essential for protein production.
What are mitochondria and what do they do?
Mitochondria are double-membraned organelles that have their own DNA. The inner folds, called cristae, increase the surface area for chemical reactions. They produce ATP (energy) through aerobic respiration, powering most of the cell’s activities.
What do ribosomes do and where are they found?
Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis. They can be found floating freely in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum. They link amino acids together based on genetic instructions from the nucleus.
What is the structure and function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (rER)?
The rER is made of flattened membrane disks called cisternae and is located near the nucleus. It has ribosomes attached to its surface. Its main function is to transport proteins to the Golgi apparatus for further processing.
What is the structure and role of the Golgi apparatus (Golgi body)?
The Golgi apparatus is made of stacked membrane sacs called cisternae and is found near the cell membrane. It modifies, sorts, and repackages proteins received from the rER. The modified proteins are then sent out in vesicles to their destinations.
What are lysosomes and what do they do?
Lysosomes are small sacs formed from the Golgi apparatus and contain powerful digestive enzymes. They break down ingested food, damaged organelles, and sometimes the entire cell when it dies. Under a microscope, they appear dark because of their dense enzyme content.
What are the similarities and differences between plant and animal cells?
Similarities:
Both are eukaryotic cells with a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
Both have mitochondria, a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and ribosomes.
Both perform cellular respiration to produce ATP energy.
Both contain a cytoskeleton to help maintain shape and structure.
Differences:
Plant Cells:
Have a cell wall made of cellulose for extra support and structure.
Contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis.
Have a large central vacuole that stores water and helps maintain pressure.
Typically have a more rigid, box-like shape.
Animal Cells:
Do not have a cell wall or chloroplasts.
Have smaller vacuoles or sometimes none at all.
Contain centrioles and lysosomes more commonly.
Usually rounder and more flexible in shape.
What organelle is labeled box #1?
Cell membrane — it surrounds and protects the cell.

Which organelle is located at box #2 and functions as the powerhouse of the cell?
Mitochondria.
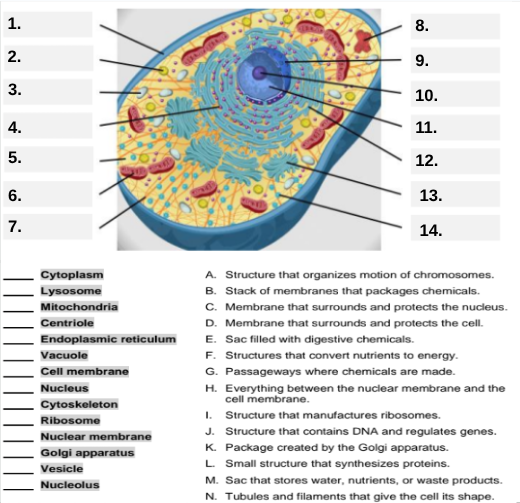
What organelle goes into box #3 and is responsible for digesting old parts and waste?
Lysosome.
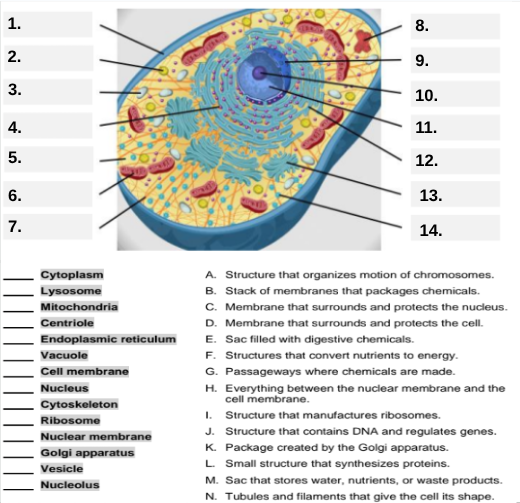
Which organelle is shown at box #4 and provides the cell’s internal shape and support?
Cytoskeleton.

What organelle is located at box #5 and serves as the jelly-like fluid that fills the cell?
Cytoplasm.
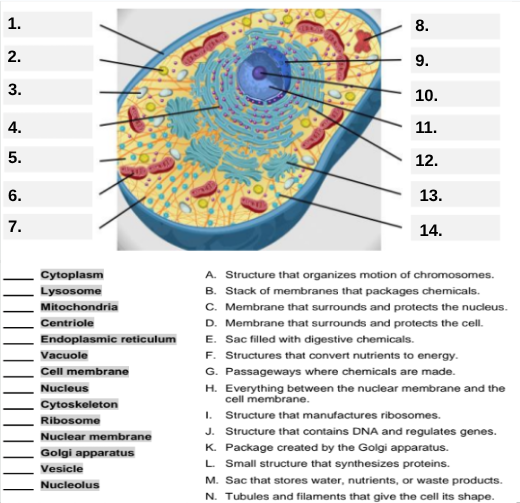
Box #6 points to the structure that surrounds the nucleus. What is it?
Nuclear membrane.
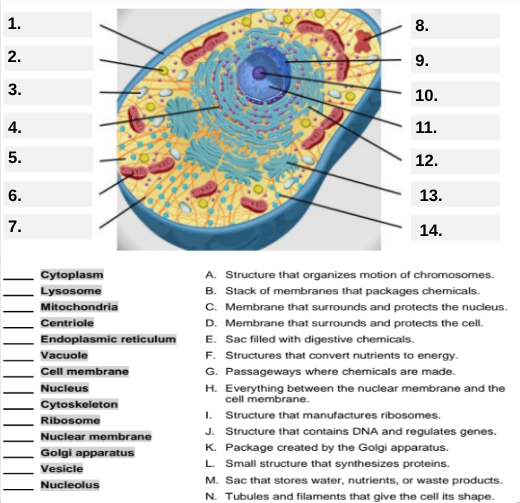
What organelle is indicated by box #7 and produces proteins?
Ribosome.
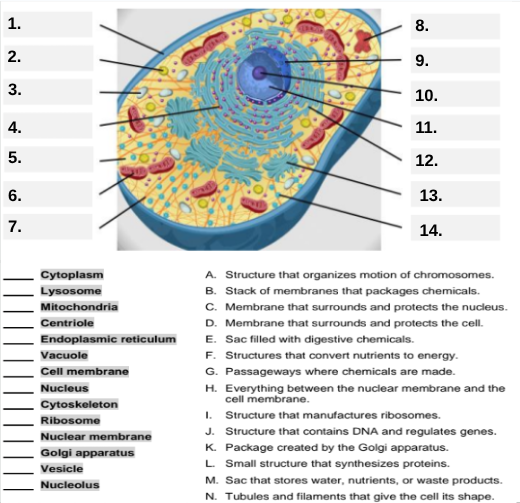
Which organelle is represented by box #8 and is covered with ribosomes?
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (rER).
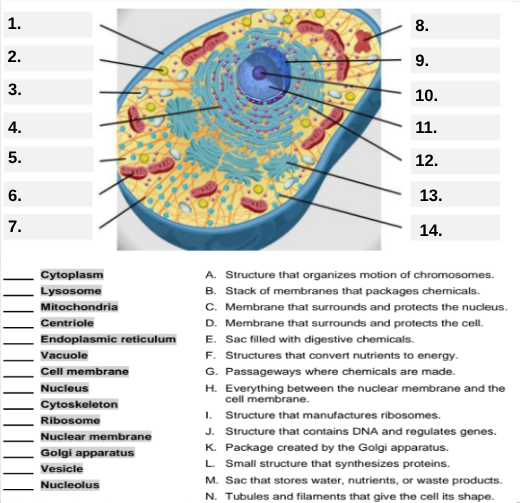
Box #9 shows the organelle that modifies and packages proteins — which one is it?
Golgi apparatus (Golgi body).
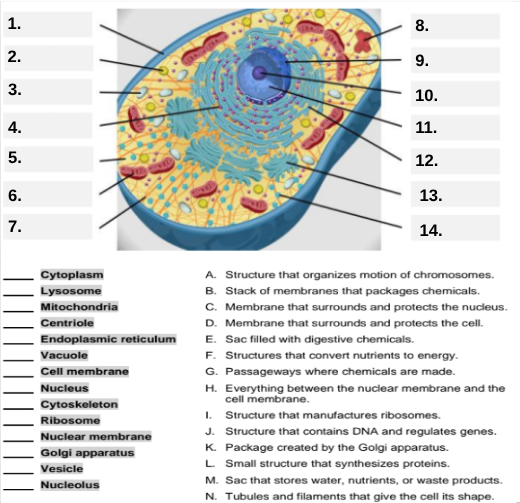
What organelle is labeled box #10 and produces ribosomes?
Nucleolus.
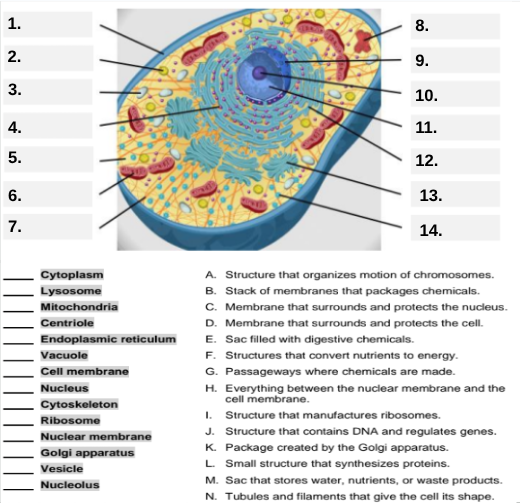
Box #11 marks the organelle that contains DNA — what is it called?
Nucleus.
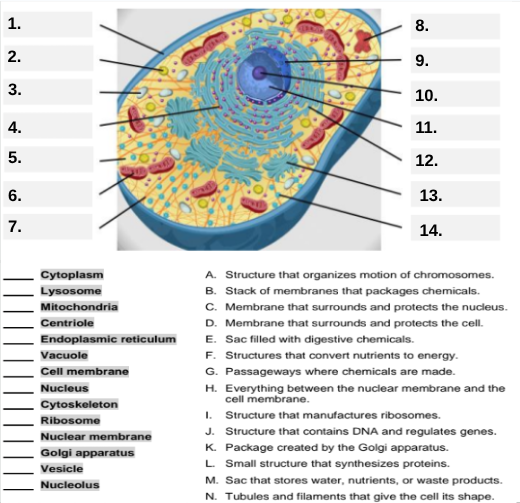
Which organelle is shown at box #12 and functions as a storage sac for water and nutrients?
Vacuole.
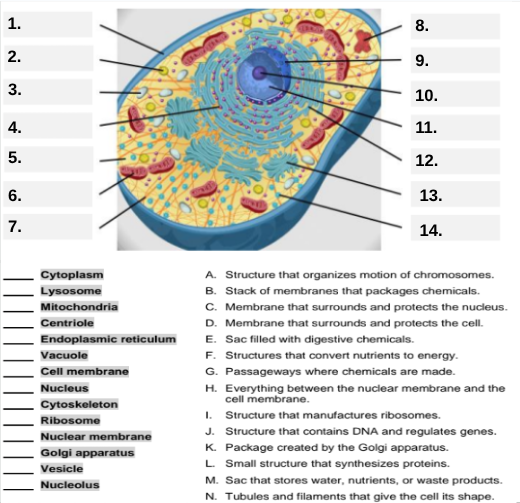
Box #13 points to the tiny sacs that carry materials from one part of the cell to another — name this structure.
Vesicle.
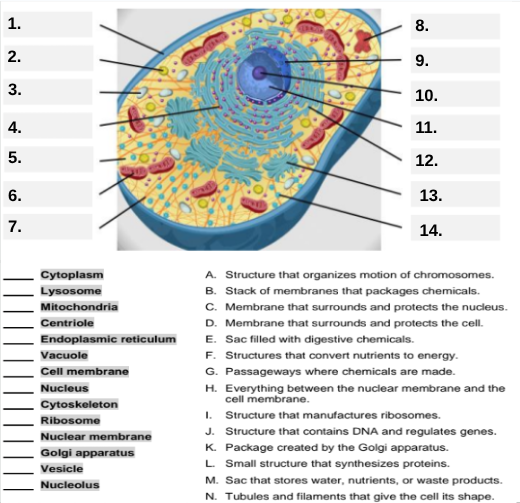
What organelle goes into box #14 and serves as the smooth network for making lipids?
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER).
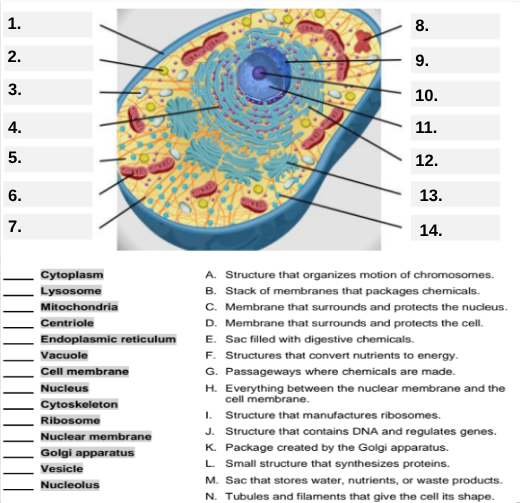
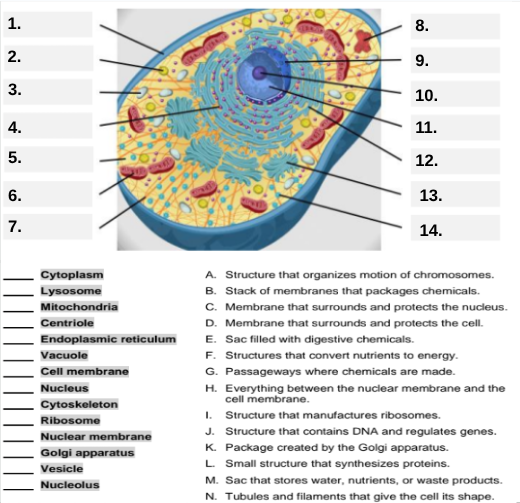
Which letter matches the definition “Structure that organizes the motion of chromosomes”?
A — Centriole.
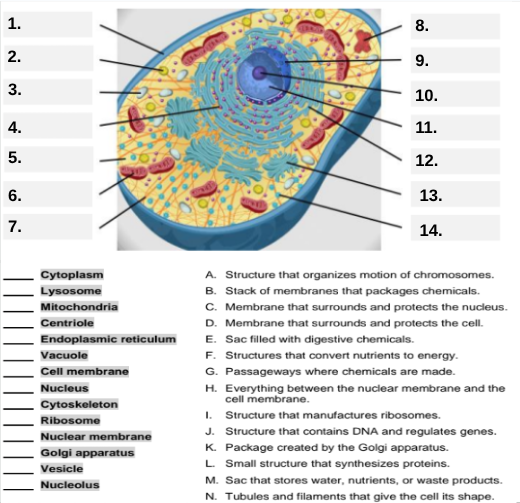
What organelle corresponds to letter B, the “stack of membranes that packages chemicals”?
Golgi apparatus.
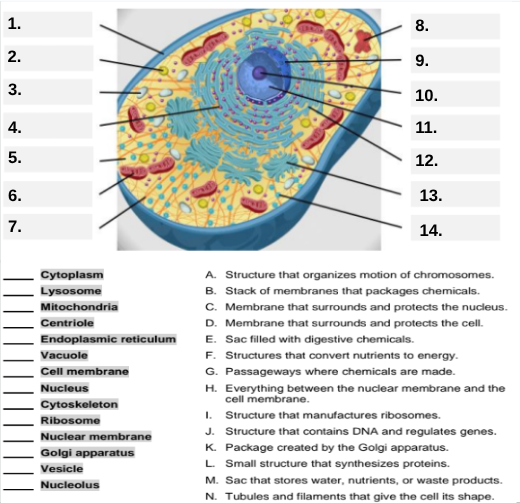
What letter represents the “membrane that surrounds and protects the nucleus”?
C — Nuclear membrane.
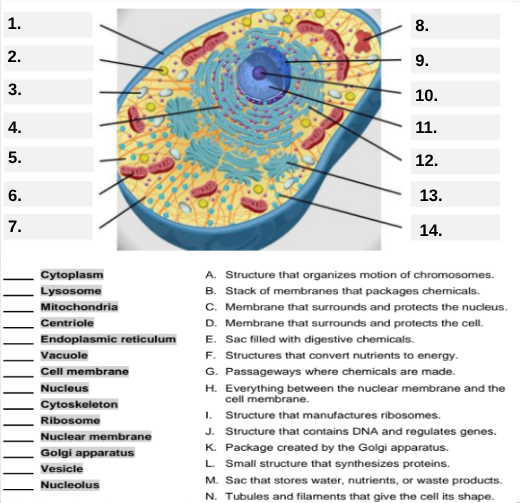
Which organelle is described by letter D, “membrane that surrounds and protects the cell”?
Cell membrane.
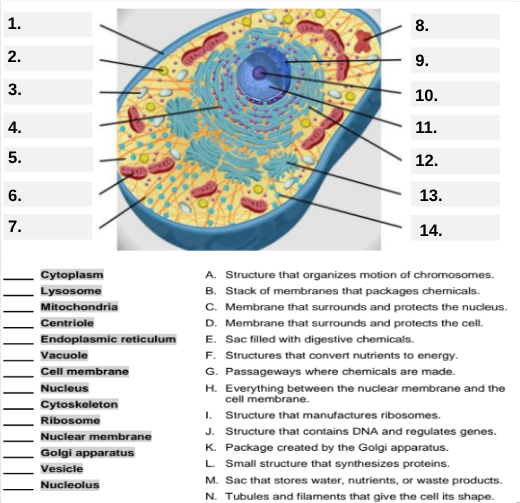
Letter E defines an “enzyme-filled sac that digests materials.” Which organelle is this?
Lysosome.
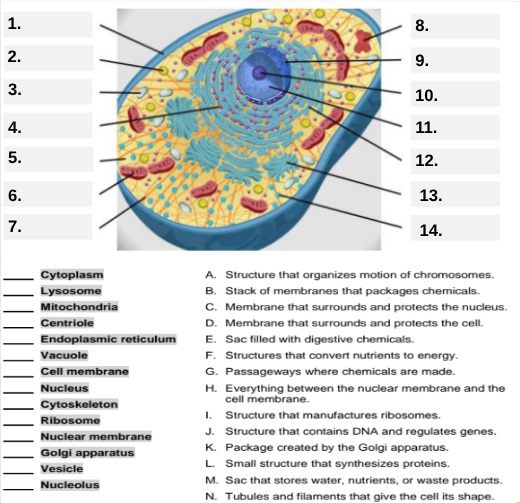
Which organelle matches letter F, “structures that convert nutrients to energy”?
Mitochondria.

What organelle goes with letter G, “passageways where chemicals are made”?
Endoplasmic reticulum.
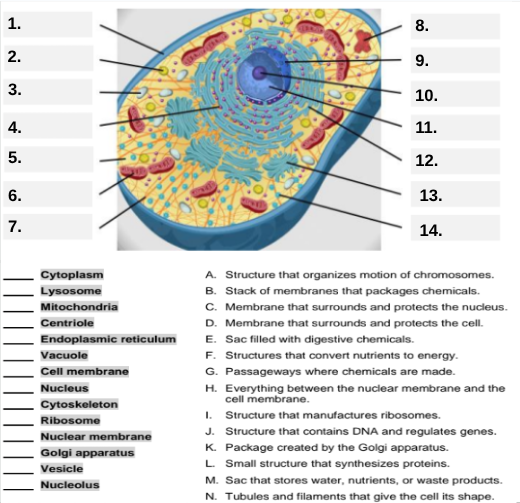
Which word matches “everything between the nuclear membrane and the cell membrane”?
H — Cytoplasm.
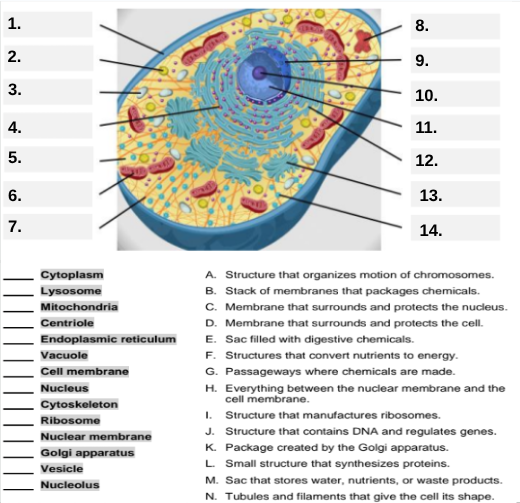
What organelle corresponds to letter I, “structure that manufactures ribosomes”?
Nucleolus.
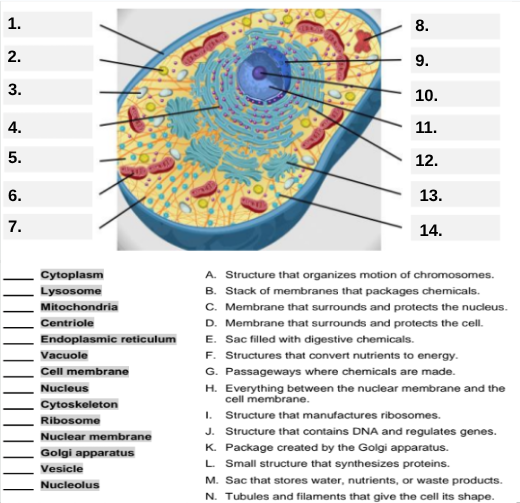
Which letter matches “structure that contains DNA and regulates genes”?
J — Nucleus.
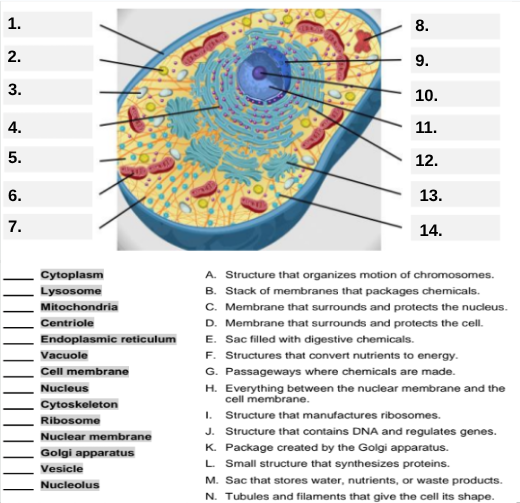
Letter K describes a “package created by the Golgi apparatus.” What is that structure?
Vesicle.
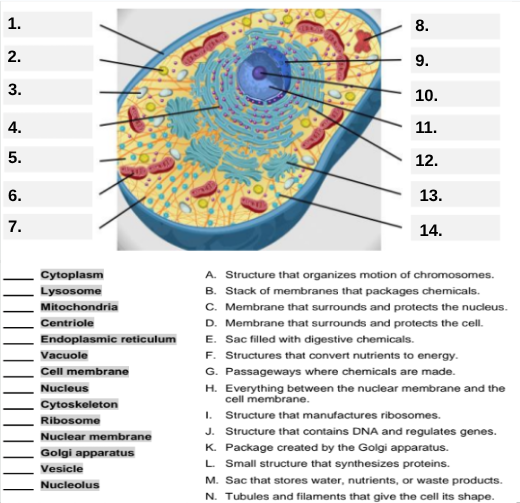
The small structure that synthesizes proteins is labeled by which letter?
L — Ribosome.
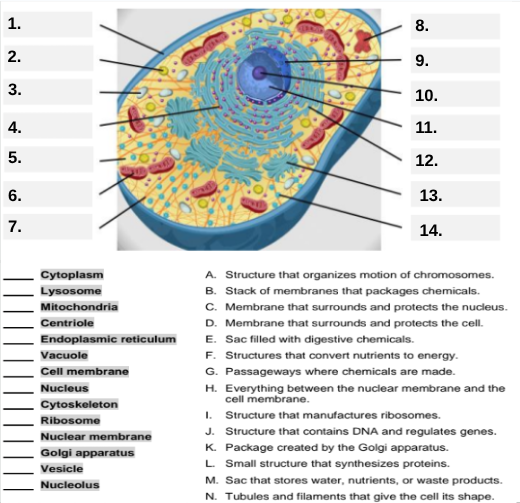
What organelle is represented by letter M, “a sac that stores water, nutrients, or waste products”?
Vacuole.
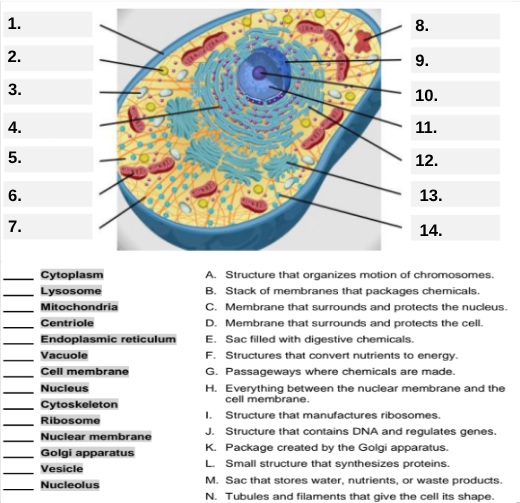
Letter N defines “tubules and filaments that give the cell its shape.” Which organelle is that?
Cytoskeleton.
I am a thin layer that forms the outside boundary of the cell opening. I control what enters and exits the cell. I am found in both plant and animal cells. What am I?
Cell membrane
I am found in plant cells and prokaryotic cells. I help protect and support the cell, giving the plant cell its shape. What am I?
Cell wall
I am a large structure that controls all activities of the cell. I contain the DNA. What am I?
Nucleus
I am the gel-like fluid filling the area between the cell membrane and the nuclear membrane. I protect organelles and provide cell shape. Many chemical reactions happen here. What am I?
Cytoplasm