CHIRAL METHODOLOGY Asymmetric Reactions – Part One
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What is asymmetric hydrogenation and why is it industrially important?
Adding H₂ across C=C, C=O, or C=N using chiral metal catalysts. Important due to high efficiency (TON/TOF), high ee, and industrial scalability
What variables must be optimized in asymmetric hydrogenation?
Hydrogen source, pressure, temperature, solvent, metal (Rh, Ru, Ir), and chiral ligand.
How can you make a chiral reducing agent from LiAlH₄?
Add a chiral diol and a simple alcohol (ROH) to form a chiral aluminum hydride complex for enantioselective carbonyl reduction.
What is atropisomerism and how does it create chirality?
Chirality from restricted rotation around a single bond (e.g., in biphenyls with bulky ortho substituents). Results in non-superimposable mirror images
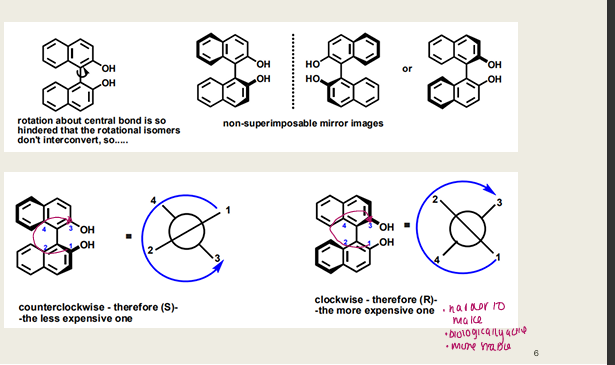
in the example shown, which atropisomer is more expensive and why?
he (R)-enantiomer (clockwise twist) is more expensive — likely due to being the biologically active form or harder to synthesize.
What is BINAL-H and how does it achieve high enantioselectivity?
Chiral reducing agent from BINOL + AlH₃. Works via a chair-like 6-membered transition state that controls hydride delivery to one face of the carbonyl.
What causes the high selectivity in BINAL-H reductions?
n-π repulsion between the ketone’s alkyl group and BINOL’s aromatic system disfavors one transition state, favoring the other.
Name four chiral catalysts/reagents and their uses.
CBS reagent – ketone reduction
Alpine-Borane – alkyne reduction
Ru-BINAP-diamine – asymmetric hydrogenation (Noyori)
DIP-Chloride – stereoselective reduction (Brown)
How does Alpine-Borane achieve stereoselective alkyne reduction?
The bulky α-pinene group blocks one face of the alkyne, directing hydride delivery to the less hindered side
What are two methods for asymmetric imine reduction?
Iridium-catalyzed H₂ hydrogenation (high pressure, >99% ee)
Transfer hydrogenation with HCOOH/NEt₃ (no high pressure, 97% ee)
If a reaction gives 32% ee in favor of S, what is the % of R?
34% R (S = 66%, R = 50 – 16 = 34%)
Why does replacing isopropyl with phenyl increase ee?
Phenyl is larger, rigid, and engages in extra steric/electronic interactions with the catalyst, improving facial discrimination.
How can you separate enantiomers after a reaction?
Chiral column chromatography
diastereomeric salt formation,
kinetic resolution.
What is the stereochemical outcome of SN2 vs SN1 reactions?
SN2 = Inversion (backside attack). SN1 = Racemic mixture (carbocation intermediate).
What does the Mitsunobu reaction guarantee?
SN2 substitution with complete inversion of configuration at alcohols.
What two reagents are essential for the classic Mitsunobu reaction?
PPh₃ (triphenylphosphine)
DEAD (diethyl azodicarboxylate)
What are the byproducts of the Mitsunobu reaction and why do they matter?
O=PPh₃ (stable) and reduced DEAD. The strong P=O bond formation drives the reaction forward.
What type of nucleophile is required for Mitsunobu and why?
Acidic nucleophile (pKa < 15) so it can be deprotonated to become a good attacking Nu⁻
Give three examples of Mitsunobu nucleophiles.
Carboxylic acids (pKa ~4-5), phenols (pKa ~10), phthalimide (pKa ~8-9)
Why is the 2019 Mitsunobu advancement important for drug discovery?
Greener, safer, higher atom economy, no toxic byproducts, easier scale-up for pharmaceutical synthesis
How does chiral catalysis relate to drug safety?
One enantiomer may be therapeutic; the other may be toxic or inactive. Asymmetric synthesis ensures high ee of the active form.